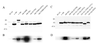The akt kinase: molecular determinants of oncogenicity - PubMed (original) (raw)
The akt kinase: molecular determinants of oncogenicity
M Aoki et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998.
Abstract
The serine-threonine kinase Akt is a downstream target of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase); it is activated by the phosphoinositide 3-phosphate-dependent kinases PDK1 and PDK2. Certain mutated forms of Akt induce oncogenic transformation in chicken embryo fibroblast cultures and hemangiosarcomas in young chickens. This ability to transform cells depends on localization of Akt at the plasma membrane and on the kinase activity of Akt. A transdominant negative form of Akt interferes with oncogenic transformation induced by the p3k oncogene, which codes for an activated form of PI 3-kinase. Akt is therefore an essential mediator of p3k-induced oncogenicity.
Figures
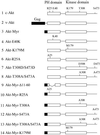
Figure 1
Schematic structures of Akt constructs. Group-specific antigen (Gag) sequence in v-Akt or myristylation signals are highlighted as black boxes. Functionally important amino acid residues in the PH and kinase domains are noted. The HA epitope tag is on the amino terminus of constructs 1 and 4–8; on all others, it is on the carboxyl terminus.
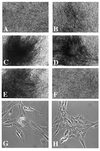
Figure 2
Morphology of CEF transfected with Akt constructs. (A) RCAS vector control. (B) c-Akt. (C) v-Akt. (D) Akt-E40K. (E) Akt-Myr. (F) Akt-K179M. (G and H) Phase-contrast micrographs of CEFs transfected with Akt-Myr (G) or RCAS vector (H).
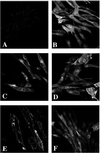
Figure 3
Subcellular localization of the HA-tagged Akt proteins in CEF. (A) RCAS vector control. (B) c-Akt. (C) v-Akt. (D) Akt-E40K. (E) Akt-Myr. (F) Akt-K179M.
Figure 4
Expression and in vitro kinase activity of Akt proteins. (A and C) Lysates of CEF stably transfected with HA-tagged Akt were probed with anti-HA antibody in Western blots. (B and D) In vitro immune complex kinase assay of the HA-tagged Akt constructs with histone H2B as substrate.
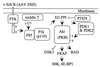
Figure 5
Akt and cellular signaling. See text for details.
Similar articles
- Transformation of chicken cells by the gene encoding the catalytic subunit of PI 3-kinase.
Chang HW, Aoki M, Fruman D, Auger KR, Bellacosa A, Tsichlis PN, Cantley LC, Roberts TM, Vogt PK. Chang HW, et al. Science. 1997 Jun 20;276(5320):1848-50. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5320.1848. Science. 1997. PMID: 9188528 - A role of the kinase mTOR in cellular transformation induced by the oncoproteins P3k and Akt.
Aoki M, Blazek E, Vogt PK. Aoki M, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Jan 2;98(1):136-41. doi: 10.1073/pnas.98.1.136. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11134523 Free PMC article. - Inhibition of protein synthesis by Y box-binding protein 1 blocks oncogenic cell transformation.
Bader AG, Vogt PK. Bader AG, et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Mar;25(6):2095-106. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.6.2095-2106.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15743808 Free PMC article. - Molecular targeting: PI3 kinase pathway.
Dancey JE. Dancey JE. Ann Oncol. 2004;15 Suppl 4:iv233-9. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdh932. Ann Oncol. 2004. PMID: 15477314 Review. No abstract available. - Kinase phosphorylation: Keeping it all in the family.
Peterson RT, Schreiber SL. Peterson RT, et al. Curr Biol. 1999 Jul 15;9(14):R521-4. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(99)80326-1. Curr Biol. 1999. PMID: 10421571 Review.
Cited by
- AKT1/PKBalpha kinase is frequently elevated in human cancers and its constitutive activation is required for oncogenic transformation in NIH3T3 cells.
Sun M, Wang G, Paciga JE, Feldman RI, Yuan ZQ, Ma XL, Shelley SA, Jove R, Tsichlis PN, Nicosia SV, Cheng JQ. Sun M, et al. Am J Pathol. 2001 Aug;159(2):431-7. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)61714-2. Am J Pathol. 2001. PMID: 11485901 Free PMC article. - v-Crk activates the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathway in transformation.
Akagi T, Shishido T, Murata K, Hanafusa H. Akagi T, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Jun 20;97(13):7290-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.140210297. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10852971 Free PMC article. - Protein Phosphatase 1 Regulatory Subunit SDS22 Inhibits Breast Cancer Cell Tumorigenesis by Functioning as a Negative Regulator of the AKT Signaling Pathway.
Paul D, Bargale AB, Rapole S, Shetty PK, Santra MK. Paul D, et al. Neoplasia. 2019 Jan;21(1):30-40. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2018.10.009. Epub 2018 Nov 27. Neoplasia. 2019. PMID: 30500680 Free PMC article. - Inhibitor of MYC identified in a Kröhnke pyridine library.
Hart JR, Garner AL, Yu J, Ito Y, Sun M, Ueno L, Rhee JK, Baksh MM, Stefan E, Hartl M, Bister K, Vogt PK, Janda KD. Hart JR, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Aug 26;111(34):12556-61. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1319488111. Epub 2014 Aug 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25114221 Free PMC article. - ets-2 is a target for an akt (Protein kinase B)/jun N-terminal kinase signaling pathway in macrophages of motheaten-viable mutant mice.
Smith JL, Schaffner AE, Hofmeister JK, Hartman M, Wei G, Forsthoefel D, Hume DA, Ostrowski MC. Smith JL, et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Nov;20(21):8026-34. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.21.8026-8034.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11027273 Free PMC article.
References
- Chang H W, Aoki M, Fruman D, Auger K R, Bellacosa A, Tsichlis P N, Cantley L C, Roberts T M, Vogt P K. Science. 1997;276:1848–1850. - PubMed
- Toker A, Cantley L C. Nature (London) 1997;387:673–676. - PubMed
- Rodriguez-Viciana P, Warne P H, Dhand R, Vanhaesebroeck B, Gout I, Fry M J, Waterfield M D, Downward J. Nature (London) 1994;370:527–532. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous