Two New Species of Large Predatory Dinosaur With Crocodile-Like Skulls Discovered on Isle of Wight (original) (raw)
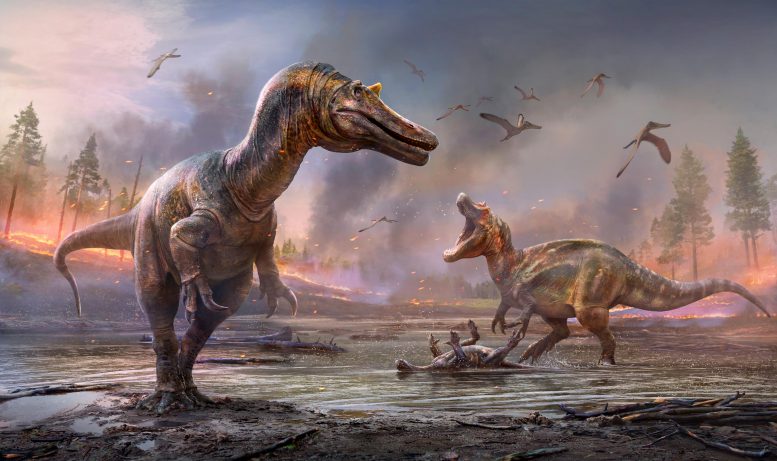
Artist’s impressions of the Spinosaurids. Ceratosuchops inferodios in the foreground, Riparovenator milnerae in the background. Credit: Anthony Hutchings
A new study led by paleontologists at the University of Southampton suggests that bones found on the Isle of Wight belong to two new species of spinosaurid, a group of predatory theropod dinosaurs closely related to the giant Spinosaurus. Their unusual, crocodile-like skulls helped the group expand their diets, allowing them to hunt prey on both land and in the water.
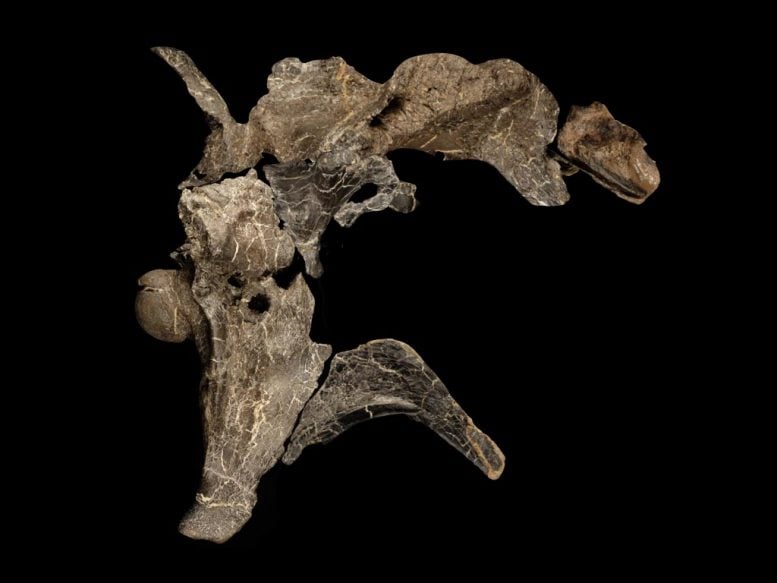
The haul of bones was discovered on the beach near Brighstone over a period of several years. Keen-eyed fossil collectors initially found parts of two skulls, and a crew from Dinosaur Isle Museum recovered a large portion of a tail. In all, over 50 bones from the site have been uncovered from rocks that form part of the Wessex Formation, laid down over 125 million years ago during the Early Cretaceous.
The only spinosaurid skeleton previously unearthed in the UK belonged to Baryonyx, which was initially discovered in 1983 in a quarry in Surrey. Most other finds since have been restricted to isolated teeth and single bones.
Analysis of the bones carried out at the University of Southampton and published in Scientific Reports suggested they belonged to species of dinosaurs previously unknown to science.
Chris Barker, a PhD student at the University of Southampton and lead author of the study, said: “We found the skulls to differ not only from Baryonyx, but also one another, suggesting the UK housed a greater diversity of spinosaurids than previously thought.”
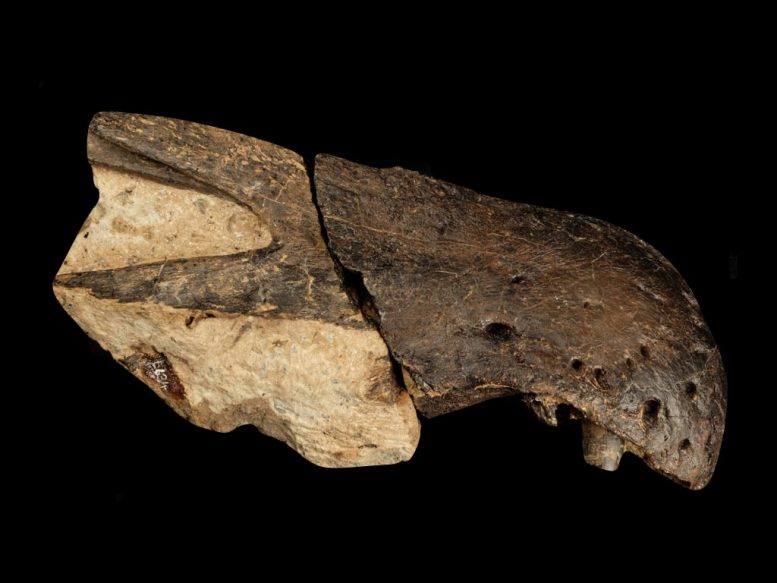
Snout from Ceratosuchops inferodios. Credit: Chris Barker
The discovery of spinosaurid dinosaurs on the Isle of Wight was a long time coming. “We’ve known for a couple of decades now that _Baryonyx_-like dinosaurs awaited discovered on the Isle of Wight, but finding the remains of two such animals in close succession was a huge surprise,” remarked co-author Darren Naish, an expert in British theropod dinosaurs.
The first specimen has been named Ceratosuchops inferodios, which translates as the “horned crocodile-faced hell heron.” With a series of low horns and bumps ornamenting the brow region the name also refers to the predator’s likely hunting style, which would be similar to that of a (terrifying) heron. Herons famously catch aquatic prey around the margins of waterways but their diet is far more flexible than is generally appreciated, and can include terrestrial prey too.
Braincase from Riparovenator milnerae. Credit: Chris Barker
The second was named Riparovenator milnerae. This translates as “Milner’s riverbank hunter,” in honor of esteemed British paleontologist Angela Milner, who recently passed away. Dr. Milner had previously studied and named Baryonyx – a major palaeontological event whose discovery substantially improved our understanding of these distinctive predators.
Dr. David Hone, co-author from Queen Mary University of London: “It might sound odd to have two similar and closely related carnivores in an ecosystem, but this is actually very common for both dinosaurs and numerous living ecosystems.”
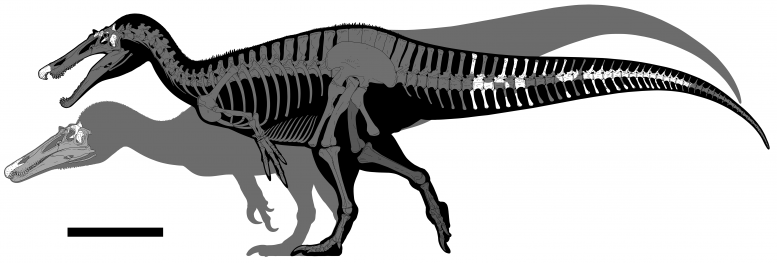
Although the skeletons are incomplete, the researchers estimate that both Ceratosuchops and Riparovenator measured around nine meters in length, snapping up prey with their meter-long skulls. The study also suggested how spinosaurids might have first evolved in Europe, before dispersing into Asia, Africa, and South America.
Dr. Neil J. Gostling of the University of Southampton, who supervised the project, said: “This work has brought together universities, Dinosaur Isle museum, and the public to reveal these amazing dinosaurs and the incredibly diverse ecology of the south coast of England 125 million years ago.”
The Early Cretaceous rocks on the Isle of Wight describe an ancient floodplain environment bathed in a Mediterranean-like climate. Whilst generally balmy, forest fires occasionally ravaged the landscape, and the remains of burnt wood can be seen throughout the cliffs today. With a large river and other bodies of water attracting dinosaurs and housing various fish, sharks, and crocodiles, the habitat provided the newly discovered spinosaurids with plenty of hunting opportunities.
Silhouettes showing the bones discovered. Ceratosuchops inferodios in the foreground, Riparovenator milnerae in the background. Credit: Barker et al 2021 and Dan Folkes
Fossil collector Brian Foster from Yorkshire, who made an important contribution to the finds and publication, said: “This is the rarest and most exciting find I’ve made in over 30 years of fossil collecting.” Fellow collector Jeremy Lockwood, who lives on the Isle of Wight and discovered several bones added, “we realized after the two snouts were found that this would be something rare and unusual. Then it just got more and more amazing as several collectors found and donated other parts of this enormous jigsaw to the museum.”
Dr. Martin Munt, Curator of Dinosaur Isle Museum, noted how these new finds cement the Isle of Wight’s status as one of the top locations for dinosaur remains in Europe. The project also solidified how collectors, museums, and universities can work together to bring fossil specimens to light.
Dr. Munt added: “On behalf of the museum I wish to express our gratitude to the collectors, including colleagues at the museum, who have made these amazing finds, and made them available for scientific research. We also congratulate the team who have worked on these exciting finds and brought them to publication.”
The new fossils will go on display at Dinosaur Isle Museum at Sandown.
Reference: “New spinosaurids from the Wessex Formation (Early Cretaceous, UK) and the European origins of Spinosauridae” by Chris T. Barker, David W. E. Hone, Darren Naish, Andrea Cau, Jeremy A. F. Lockwood, Brian Foster, Claire E. Clarkin, Philipp Schneider and Neil J. Gostling, 29 September 2021, Scientific Reports.
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-97870-8