C Programming Interview Questions (2025) (original) (raw)
**At Bell Labs, **Dennis Ritchie developed the C programming language between 1971 and 1973. C is a mid-level structured-oriented programming and general-purpose programming. It is one of the oldest and most popular programming languages. There are many applications in which C programming language is used, including languagecompilers, operating systems, assemblers, network drivers, text editors, print spoolers, modern applications, language interpreters, databases, and utilities.
In this article, you will get the frequently and most asked C programming interview questions and answers at the **fresher and **experienced levels.
Table of Content
- C Programming Interview Questions - For Freshers
- C Programming Interview Questions - Intermediate Level
- C Programming Interview Questions – For Experienced
Preparing for a C programming interview requires a solid understanding of core concepts.
So, let us start with Questions for freshers.
C Programming Interview Questions - For Freshers
1. Why is C called a mid-level programming language?
Due to its ability to support both low-level and high-level features, C is considered a middle-level language. It supports both an assembly-level language, i.e. a low-level language, and a higher-level language. Using asm or __asm__ function, can write low-level program and also, we can write high-level program using the C syntax. Hence, C is called as mid-level programming language.
**2. What are the features of the C programming language?
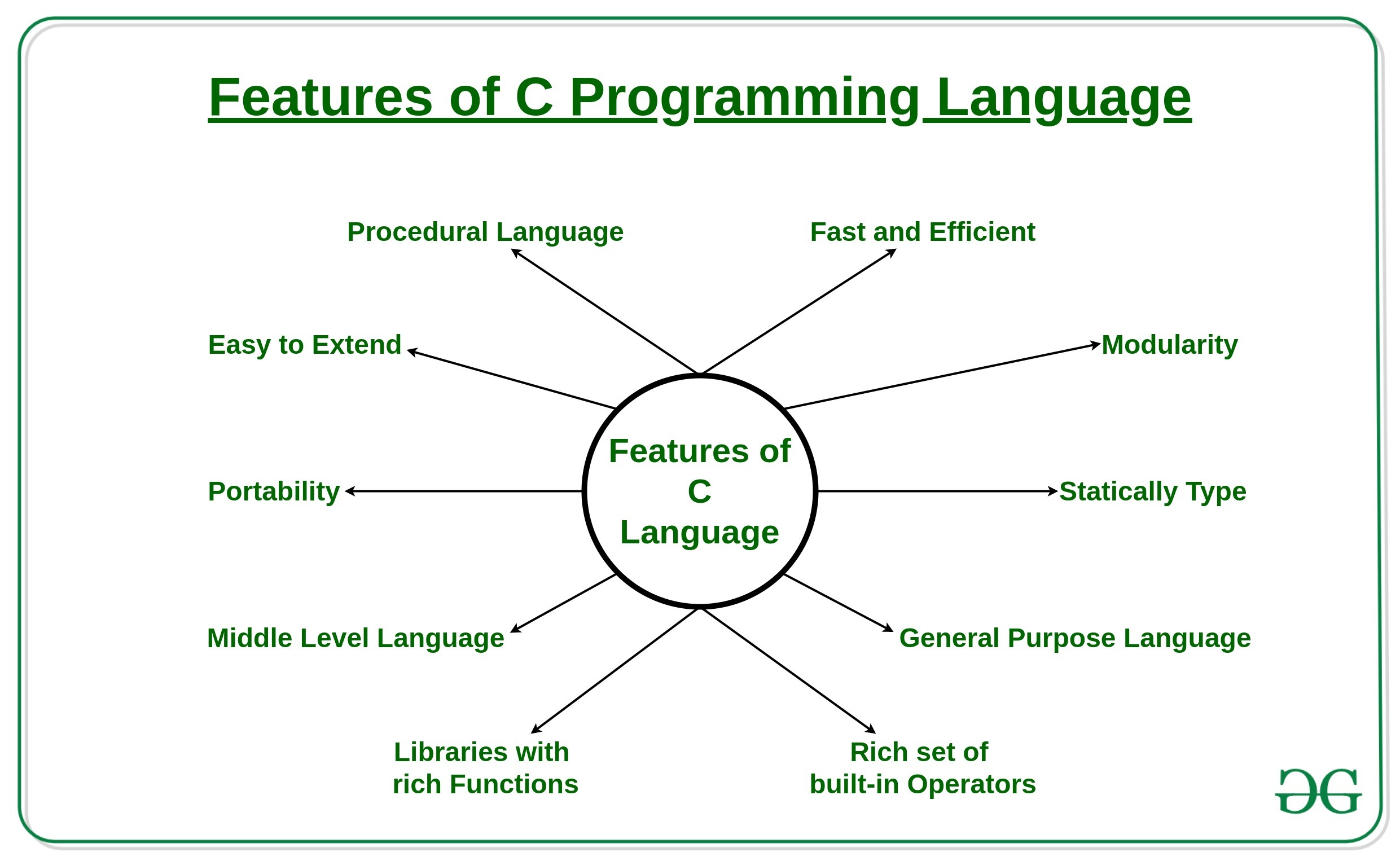
Features of C Programming language
For more information, refer to the article -_Features of C programming language_.
3. What are basic data types supported in the C Programming Language?
In the C programming language, the basic data types are the fundamental building blocks used to declare variables and allocate memory. These data types define the type and size of data that can be stored in a variable. Here are the basic data types supported in C:
- **int
- **char
- **float
- **double
- **void
For more information, refer to the article -_Data Types in C
4. What are tokens in C?
Tokens are identifiers or the smallest single unit in a program that is meaningful to the compiler. In C we have the following tokens:
- **Keywords: Predefined or reserved words in the C programming language. Every keyword is meant to perform a specific task in a program. C Programming language supports 32 keywords.
- **Identifiers: Identifiers are user-defined names that consist of an arbitrarily long sequence of digits or letters with either a letter or the underscore (_) as a first Character. Identifier names can’t be equal to any reserved keywords in the C programming language. There are a set of rules which a programmer must follow in order to name an identifier in C.
- **Constants: Constants are normal variables that cannot be modified in the program once they are defined. Constants refer to a fixed value. They are also referred to as literals.
- **Strings: Strings in C are an array of characters that end with a null character (‘\0). Null character indicates the end of the string;
- **Special Symbols: Some special symbols in C have some special meaning and thus, they cannot be used for any other purpose in the program. # = {} () , * ; [] are the special symbols in C programming language.
- **Operators: Symbols that trigger an action when they are applied to any variable or any other object. Unary, Binary, and ternary operators are used in the C Programming language.
For more information, refer to the article -_Tokens in C
5. What do you mean by the scope of the variable?
Scope in a programming language is the block or a region where a defined variable will have its existence and beyond that region, the variable is automatically destroyed. Every variable has its defined scope. In simple terms, the scope of a variable is equal to its life in the program. The variable can be declared in three places These are:
- **Local Variables: Inside a given function or a block
- **Global Variables: Out of all functions globally inside the program.
- **Formal Parameters: In-function parameters only.
For more information, refer to the article -_Scope in C
6. What are preprocessor directives in C?
In C preprocessor directives are considered the built-in predefined functions or macros that act as a directive to the compiler and are executed before the program execution. There are multiple steps involved in writing and executing a program in C. Main types of Preprocessor Directives are Macros, File Inclusion, Conditional Compilation, and Other directives like #undef, #pragma, etc.
-768.png)
Processor in C
For more information, refer to the article - Preprocessor Directives in C
7. What is the use of static variables in C?
Static variables in the C programming language are used to preserve the data values between function calls even after they are out of their scope. Static variables preserve their values in their scope and they can be used again in the program without initializing again. Static variables have an initial value assigned to 0 without initialization.
C `
// C program to print initial // value of static variable #include <stdio.h> int main() { static int var; int x; printf("Initial value of static variable %d\n", var); printf("Initial value of variable without static %d", x); return 0; }
`
Output
Initial value of static variable 0 Initial value of variable without static 0
For more information, refer to the article - _Static Variables in C
8. What is the difference between malloc() and calloc() in the C programming language?
calloc() and malloc() library functions are used to allocate dynamic memory. Dynamic memory is the memory that is allocated during the runtime of the program from the heap segment. “stdlib.h” is the header file that is used to facilitate dynamic memory allocation in the C Programming language.
| Parameter | Malloc() | Calloc() |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | It is a function that creates one block of memory of a fixed size. | It is a function that assigns more than one block of memory to a single variable. |
| Number of arguments | It only takes one argument. | It takes two arguments. |
| Speed | malloc() function is faster than calloc(). | calloc() is slower than malloc(). |
| Efficiency | It has high time efficiency. | It has low time efficiency. |
| Usage | It is used to indicate memory allocation. | It is used to indicate contiguous memory allocation. |
For more information, refer to the article - _Dynamic Memory Allocation in C using malloc(), calloc(), free(), and realloc()
9. What do you mean by dangling pointers and how are dangling pointers different from memory leaks in C programming?
Pointers pointing to deallocated memory blocks in C Programming are known as dangling pointers i.e, whenever a pointer is pointing to a memory location and In case the variable is deleted and the pointer still points to that same memory location then it is known as a dangling pointer variable.
In C programming memory leak occurs when we allocate memory with the help of the malloc() or calloc() library function, but we forget to free the allocated memory with the help of the free() library function. Memory leak causes the program to use an undefined amount of memory from the RAM which makes it unavailable for other running programs this causes our program to crash.
10. Write a program to convert a number to a string with the help of sprintf() function in the C library.
C `
// C program to convert number to // string using sprintf() #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h>
// Driver code int main() { char res[20]; float a = 32.23; sprintf(res, "%f", a); printf("\nThe string for the num is %s", res); return 0; }
`
Output
The string for the num is 32.230000
For more information, refer to the article - _sprintf() in C
11. What is recursion in C?
Recursion is the process of making the function call itself directly or indirectly. A recursive function solves a particular problem by calling a copy of itself and solving smaller subproblems that sum up the original problems. Recursion helps to reduce the length of code and make it more understandable. The recursive function uses a LIFO ( Last In First Out ) structure like a stack. Every recursive call in the program requires extra space in the stack memory.
For more information, refer to the article - _Recursion
12. What is the difference between the local and global variables in C?
Local variables are declared inside a block or function but global variables are declared outside the block or function to be accessed globally.
| Local Variables | Global Variables |
|---|---|
| Declared inside a block or a function. | Variables that are declared outside the block or a function. |
| By default, variables store a garbage value. | By default value of the global value is zero. |
| The life of the local variables is destroyed after the block or a function. | The life of the global variable exists until the program is executed. |
| Variables are stored inside the stack unless they are specified by the programmer. | The storage location of the global variable is decided by the compiler. |
| To access the local variables in other functions parameter passing is required. | No parameter passing is required. They are globally visible throughout the program. |
13. What are pointers and their uses?
Pointers are used to store the address of the variable or a memory location. Pointer can also be used to refer to another pointer function. The main purpose of the pointer is to save memory space and increase execution time. Uses of pointers are:
- To pass arguments by reference
- For accessing array elements
- To return multiple values
- Dynamic memory allocation
- To implement data structures
- To do system-level programming where memory addresses are useful
-768.png)
Working of Pointer
For more information, refer to the article - _Pointer Uses in C.
14. What is typedef in C?
In C programming, typedef is a keyword that defines an alias for an existing type. Whether it is an integer variable, function parameter, or structure declaration, typedef will shorten the name.
**Syntax:
typedef
Here,
- **existing type is already given a name.
- **alias name is the new name for the existing variable.
**Example:
typedef long long ll
15. What are loops and how can we create an infinite loop in C?
Loops are used to execute a block of statements repeatedly. The statement which is to be repeated will be executed n times inside the loop until the given condition is reached. There are two types of loops Entry controlled and Exit-controlled loops in the C programming language. An Infinite loop is a piece of code that lacks a functional exit. So, it repeats indefinitely. There can be only two things when there is an infinite loop in the program. One it was designed to loop endlessly until the condition is met within the loop. Another can be wrong or unsatisfied break conditions in the program.
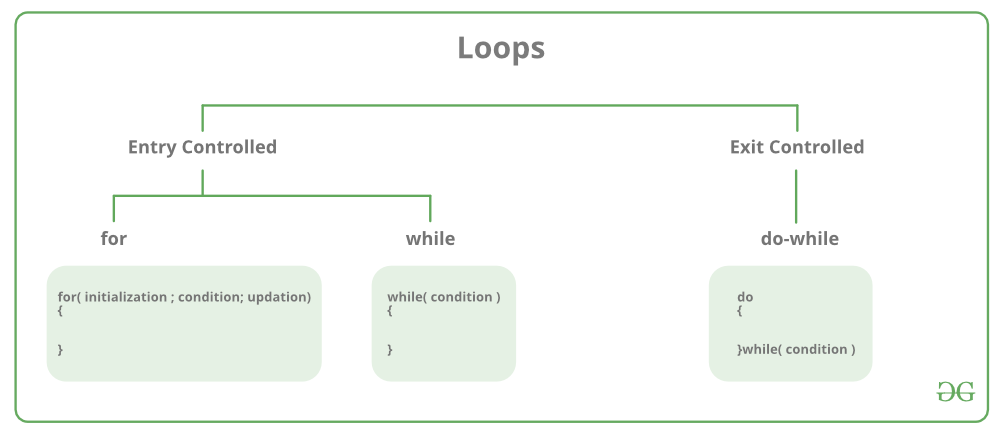
Types of Loops
Below is the program for infinite loop in C:
C `
// C program for infinite loop // using for, while, do-while #include <stdio.h>
// Driver code int main() { for (;;) { printf("Infinite-loop\n"); }
while (1) {
printf("Infinite-loop\n");
}
do {
printf("Infinite-loop\n");
} while (1);
return 0;}
`
For more information, refer to the article - _Loops in C
16. What is the difference between type casting and type conversion?
| Type Casting | Type Conversion |
|---|---|
| The data type is converted to another data type by a programmer with the help of a casting operator. | The data type is converted to another data by a compiler. |
| It can be applied to both compatible data types as well as incompatible data types. | Type conversion can only be applied to only compatible data types. |
| In Type casting in order to cast the data type into another data type, a caste operator is needed | In type conversion, there is no need for a casting operator. |
| Type casting is more efficient and reliable. | Type conversion is less efficient and less reliable than type casting. |
| Type casting takes place during the program design by the programmer. | Type conversion is done at compile time. |
| **Syntax: destination_data_type = (target_data_type) variable_to_be_converted; | **Syntax: int a = 20; float b; b = a; // a = 20.0000 |
For more information, refer to the article - _Type Casting and Type Conversion
17. What are header files and their uses?
C language has numerous libraries which contain predefined functions to make programming easier. Header files contain predefined standard library functions. All header files must have a ‘.h’ extension. Header files contain function definitions, data type definitions, and macros which can be imported with the help of the preprocessor directive ‘#include’. Preprocessor directives instruct the compiler that these files are needed to be processed before the compilation.
_There are two types of header files i.e, User-defined header files and Pre-existing header files. For example, if our code needs to take input from the user and print desired output to the screen then ‘stdio.h’ header file must be included in the program as #include<stdio.h>. This header file contains functions like scanf() and printf() which are used to take input from the user and print the content.
For more information, refer to the article - _Header Files in C
18. What are the functions and their types?
The function is a block of code that is used to perform a task multiple times rather than writing it out multiple times in our program. Functions avoid repetition of code and increase the readability of the program. Modifying a program becomes easier with the help of function and hence reduces the chances of error. _There are two types of functions:
- **User-defined Functions: Functions that are defined by the user to reduce the complexity of big programs. They are built only to satisfy the condition in which the user is facing issues and are commonly known as “tailor-made functions”.
- **Built-in Functions: Library functions are provided by the compiler package and consist of special functions with special and different meanings. These functions give programmers an edge as we can directly use them without defining them.
For more information, refer to the article - _Functions in C
19. What is the difference between macro and functions?
A macro is a name that is given to a block of C statements as a pre-processor directive. Macro is defined with the pre-processor directive. Macros are pre-processed which means that all the macros would be preprocessed before the compilation of our program. However, functions are not preprocessed but compiled.
| Macro | Function |
|---|---|
| Macros are preprocessed. | Functions are compiled. |
| Code length is increased using macro. | Code length remains unaffected using function. |
| Execution speed using a macro is faster. | Execution speed using function is slower. |
| The macro name is replaced by the macro value before compilation. | Transfer of control takes place during the function call. |
| Macro doesn't check any Compile-Time Errors. | Function check Compile-time errors. |
For more information, refer to the article - _Macro vs Functions

20. How to convert a string to numbers in C?
In C we have 2 main methods to convert strings to numbers i.e, Using string stream, Using stoi() library Function or using atoi() library function.
- **sscanf(): It reads input from a string rather than standard input.
- **stoi() or atoi(): These functions takes a string literal or a character array as an argument and an integer value is returned.
For more information, refer to the article -_String to Numbers in C
21. What are reserved keywords?
Every keyword is meant to perform a specific task in a program. Their meaning is already defined and cannot be used for purposes other than what they are originally intended for. C Programming language supports 32 keywords. Some examples of reserved keywords are auto, else, if, long, int, switch, typedef, etc.
For more information, refer to the article - _Variables and Keywords in C
22. What is a structure?
The structure is a keyword that is used to create user-defined data types. The structure allows storing multiple types of data in a single unit. The structure members can only be accessed through the structure variable.
**Example:
struct student
{
char name[20];
int roll_no;
char address[20];
char branch[20];
};
Below is the C program to implement structure:
C `
// C Program to show the // use of structure #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h>
// Structure student declared struct student { char name[20]; int roll_no; char address[50]; char branch[50]; };
// Driver code int main() { struct student obj;
strcpy(obj.name, "Kamlesh_Joshi");
obj.roll_no = 27;
strcpy(obj.address, "Haldwani");
strcpy(obj.branch, "Computer Science And Engineering");
// Accessing members of student obj
printf("Name: %s\n", obj.name);
printf("Roll_No: %d \n", obj.roll_no);
printf("Address: %s\n", obj.address);
printf("Branch: %s", obj.branch);
return 0;}
`
Output
Name: Kamlesh_Joshi Roll_No: 27 Address: Haldwani Branch: Computer Science And Engineering
For more information, refer to the article - _Structure in C
23. What is union?
A union is a user-defined data type that allows users to store multiple types of data in a single unit. However, a union does not occupy the sum of the memory of all members. It holds the memory of the largest member only. Since the union allocates one common space for all the members we can access only a single variable at a time. The union can be useful in many situations where we want to use the same memory for two or more members.
**Syntax:
union name_of_union
{
data_type name;
data_type name;
};
For more information, refer to the article - _Union in C
24. What is an r-value and value?
An "l-value" refers to an object with an identifiable location in memory (i.e. having an address). An "l-value" will appear either on the right or left side of the assignment operator(=). An "r-value" is a data value stored in memory at a given address. An "r-value" refers to an object without an identifiable location in memory (i.e. without an address). An "r-value" is an expression that cannot be assigned a value, therefore it can only exist on the right side of an assignment operator (=).
**Example:
int val = 20;
Here, val is the 'l-value', and 20 is the 'r-value'.
For more information, refer to the article - _r-value and l-value in C
25. What is the difference between call by value and call by reference?
| Call by value | Call by Reference |
|---|---|
| Values of the variable are passed while function calls. | The address of a variable(location of variable) is passed while the function call. |
| Dummy variables copy the value of each variable in the function call. | Dummy variables copy the address of actual variables. |
| Changes made to dummy variables in the called function have no effect on actual variables in the calling function. | We can manipulate the actual variables using addresses. |
| A simple technique is used to pass the values of variables. | The address values of variables must be stored in pointer variables. |
For more information, refer to the article - _Call by Value and Call by Reference
26. What is the sleep() function?
sleep() function in C allows the users to wait for a current thread for a given amount of time. sleep() function will sleep the present executable for the given amount of time by the thread but other operations of the CPU will function properly. sleep() function returns 0 if the requested time has elapsed.
For more information, refer to the article - _sleep() Function in C
27. What are enumerations?
In C, enumerations (or enums) are user-defined data types. Enumerations allow integral constants to be named, which makes a program easier to read and maintain. For example, the days of the week can be defined as an enumeration and can be used anywhere in the program.
enum enumeration_name{constant1, constant2, ... };
C `
// An example program to demonstrate working // of enum in C #include <stdio.h>
enum week { Mon, Tue, Wed, Thur, Fri, Sat, Sun };
int main() { enum week day; day = Wed; printf("%d", day); return 0; }
`
In the above example, we declared “day” as the variable, and the value of “Wed” is allocated to day, which is 2. So as a result, 2 is printed.
For more information, refer to the article - Enumeration (or enum) in C
28: What is a volatile keyword?
Volatile keyword is used to prevent the compiler from optimization because their values can’t be changed by code that is outside the scope of current code at any time. The System always reads the current value of a volatile object from the memory location rather than keeping its value in a temporary register at the point it is requested, even if previous instruction is asked for the value from the same object.
29. Write a C program to print the Fibonacci series using recursion and without using recursion.
-768.png)
Fibonacci Numbers
C `
// C program to print Fibonacci Series // with recursion and without recursion #include <stdio.h>
// Recursive Function to print // Fibonacci Series void Fibonacci(int num, int first, int second, int third) { if (num > 0) { third = first + second; first = second; second = third;
printf("%d ", third);
// Recursive call for it's
// n-1 value
Fibonacci(num - 1, first, second, third)
}}
// Driver code int main() { int num;
printf("Please Enter number of Elements: ");
scanf("%d", &num);
printf(
"Fibonacci Series with the help of Recursion:\n");
printf("%d %d ", 0, 1);
// we are passing n-2 because we have
// already printed 2 numbers i.e, 0 and 1
Fibonacci(num - 2, 0, 1, 0);
printf("\nFibonacci Series without Using Recursion:\n");
int first = 0, second = 1, third = 0;
printf("%d %d ", 0, 1);
// Loop will start from 2 because we have
// already printed 0 and 1
for (int i = 2; i < num; i++) {
third = first + second;
printf("%d ", third);
first = second;
second = third;
}
return 0;}
`
**Output: Please Enter number of Elements: 5 Fibonacci Series with the help of Recursion: 0 1 1 2 3 Fibonacci Series without Using Recursion: 0 1 1 2 3
For more information, refer to the article - _Fibonacci Numbers
30. Write a C program to check whether a number is prime or not.

Number Prime or not
C `
// C program to check if a // number is prime #include <math.h> #include <stdio.h>
// Driver code int main() { int num; int check = 1;
printf("Enter a number: \n");
scanf("%d", &num);
// Iterating from 2 to sqrt(num)
for (int i = 2; i <= sqrt(num); i++) {
// If the given number is divisible by
// any number between 2 and n/2 then
// the given number is not a prime number
if (num % i == 0) {
check = 0;
break;
}
}
if (num <= 1) {
check = 0;
}
if (check == 1) {
printf("%d is a prime number", num);
}
else {
printf("%d is not a prime number", num);
}
return 0;}
`
For more information, refer to the article - _Prime or Not
31. How is source code different from object code?
| Source Code | Object Code |
|---|---|
| Source code is generated by the programmer. | object code is generated by a compiler or another translator. |
| High-level code which is human-understandable. | Low-level code is not human-understandable. |
| Source code can be easily modified and contains less number of statements than object code. | Object code cannot be modified and contains more statements than source code. |
| Source code can be changed over time and is not system specific. | Object code can be modified and is system specific. |
| Source code is less close to the machine and is input to the compiler or any other translator. | Object code is more close to the machine and is the output of the compiler or any other translator. |
| Language translators like compilers, assemblers, and interpreters are used to translate source code to object code. | Object code is machine code so it does not require any translation. |
For more information, refer to the article - _Source vs Object Code
32. What is static memory allocation and dynamic memory allocation?
- **Static memory allocation: Memory allocation which is done at compile time is known as static memory allocation. Static memory allocation saves running time. It is faster than dynamic memory allocation as memory allocation is done from the stack. This memory allocation method is less efficient as compared to dynamic memory allocation. It is mostly preferred in the array.
- **Dynamic memory allocation: Memory allocation done at execution or run time is known as dynamic memory allocation. Dynamic memory allocation is slower than static memory allocation as memory allocation is done from the heap. This memory allocation method is more efficient as compared to static memory allocation. It is mostly preferred in the linked list.
For more information, refer to the article - _Static and Dynamic Memory Allocation in C
**33. What is pass-by-reference in functions?
Pass by reference allows a function to modify a variable without making a copy of the variable. The Memory location of the passed variable and parameter is the same, so any changes done to the parameter will be reflected by the variables as well.
C `
// C program to change a variable // using pass by reference #include <stdio.h>
// * used to dereference the variable void change(int* num) { // value of num changed to 30 *num = 30; }
// Driver code int main() { int num = 20; printf("Value of num before passing is: %d\n", num);
// Calling change function by passing address
change(&num);
printf("Value of num after changing with the help of "
"function is: %d",
num);
return 0;}
`
For more information, refer to the article - _Pass By Reference
34. What is a memory leak and how to avoid it?
Whenever a variable is defined some amount of memory is created in the heap. If the programmer forgets to delete the memory. This undeleted memory in the heap is called a memory leak. The Performance of the program is reduced since the amount of available memory was reduced. To avoid memory leaks, memory allocated on the heap should always be cleared when it is no longer needed.
For more information, refer to the article - _Memory Leak
35. What are command line arguments?
Arguments that are passed to the main() function of the program in the command-line shell of the operating system are known as command-line arguments.
**Syntax:
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){/*code which is to be executed*/}
For more information, refer to the article - _Command Line Arguments in C
36. What is an auto keyword?
Every local variable of a function is known as an automatic variable in the C language. Auto is the default storage class for all the variables which are declared inside a function or a block. Auto variables can only be accessed within the block/function they have been declared. We can use them outside their scope with the help of pointers. By default auto keywords consist of a garbage value.
For more information, refer to the article - _Storage Classes in C
37. Write a program to print "Hello-World" without using a semicolon.
C `
// C program to print hello-world // without using semicolon #include <stdio.h>
// Driver code int main() { // This will print the hello-world // on the screen without giving any error if (printf(“Hello - World”)) { } return 0; }
`
For more information, refer to the article - _Hello World in C
38. Write a C program to swap two numbers without using a third variable.
-768.png)
Swap Two Number
C `
// C program to swap two variables // without using a third variable #include <stdio.h>
int main() { // Variable declaration int var1 = 50; int var2 = 60;
printf(
"Values before swap are var1 = %d and var2 = %d\n",
var1, var2);
// var1 = 110 ( 50 + 60)
var1 = var1 + var2;
// var2 = 50 (110 - 50)
var2 = var1 - var2;
// var1 = 60 (110 - 50)
var1 = var1 - var2;
printf("Values after swap are var1 = %d and var2 = %d",
var1, var2);
return 0;}
`
Output
Values before swap are var1 = 50 and var2 = 60 Values after swap are var1 = 60 and var2 = 50
39. Write a program to check whether a string is a palindrome or not.
C `
// C program to check whether a // string is palindrome or not. #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h>
// Palindrome function to check // whether a string is palindrome // or not void Palindrome(char s[]) { // Start will start from 0th index // and end will start from length-1 int start = 0; int end = strlen(s) - 1;
// Comparing characters until they
// are same
while (end > start) {
if (s[start++] != s[end--]) {
printf("%s is not a Palindrome \n", s);
return;
}
}
printf("%s is a Palindrome \n", s);}
// Driver code int main() { Palindrome("abba"); return 0; }
`
Output
abba is a Palindrome
40. Explain modifiers.
Modifiers are keywords that are used to change the meaning of basic data types in C language. They specify the amount of memory that is to be allocated to the variable. There are five data type modifiers in the C programming language:
- long
- short
- signed
- unsigned
- long long
C Programming Interview Questions – For Experienced
41. Write a program to print the factorial of a given number with the help of recursion.

Factorial of a Number
C `
// C program to find factorial // of a given number #include <stdio.h>
// Function to find factorial of // a given number unsigned int factorial(unsigned int n) { if (n == 0) return 1; return n * factorial(n - 1); }
// Driver code int main() { int num = 5; printf("Factorial of %d is %d", num, factorial(num)); return 0; }
`
Output
Factorial of 5 is 120
42. Write a program to check an Armstrong number.
C `
#include <stdio.h> #include <math.h>
// Function to calculate the number of digits int countDigits(int n) { int count = 0; while (n != 0) { count++; n /= 10; } return count; }
int main() { int n; printf("Enter Number: \n"); scanf("%d", &n);
int var = n;
int sum = 0;
// Get number of digits
int D = countDigits(n);
// Calculate the sum of digits raised
// to the power D
while (n > 0) {
int rem = n % 10;
sum += pow(rem, D);
n = n / 10;
}
// If the sum equals the original number,
// it's an Armstrong number
if (var == sum) {
printf("%d is an Armstrong number \n", var);
} else {
printf("%d is not an Armstrong number \n", var);
}
return 0;}
`
**Output
Enter number: 8208 8208 is an Armstrong number
43. Write a program to reverse a given number.
C `
// C program to reverse digits // of a number #include <stdio.h>
// Driver code int main() { int n, rev = 0;
printf("Enter Number to be reversed : ");
scanf("%d", &n);
// r will store the remainder while we
// reverse the digit and store it in rev
int r = 0;
while (n != 0)
{
r = n % 10;
rev = rev * 10 + r;
n /= 10;
}
printf("Number After reversing digits is: %d", rev);
return 0;}
`
**Output:
Enter Number to be reversed : Number After reversing digits is: 321
44. What is the use of an extern storage specifier?
The extern keyword in C extends the visibility of variables and functions across multiple files. It's particularly useful when a variable defined in one file needs to be accessed from another file. By using extern, a variable or function can be declared in one file and defined in another. This allows multiple files to share the same variable or function. By default, functions are visible throughout the program, so there is no need to declare or define extern functions unless they are being used across different files.
45. What is the use of printf() and scanf() functions in C Programming language? Also, explain format specifiers.
**printf() function is used to print the value which is passed as the parameter to it on the console screen.
**Syntax:
print("%X",variable_of_X_type);
**scanf() method, reads the values from the console as per the data type specified.
**Syntax:
scanf("%X",&variable_of_X_type);
In C format specifiers are used to tell the compiler what type of data will be present in the variable during input using scanf() or output using print().
- %c: Character format specifier used to display and scan character.
- %d, %i: Signed Integer format specifier used to print or scan an integer value.
- %f, %e, or %E: Floating-point format specifiers are used for printing or scanning float values.
- %s: This format specifier is used for String printing.
- %p: This format specifier is used for Address Printing.
For more information, refer to the article - _Format Specifier in C
46. What is near, far, and huge pointers in C?
- **Near Pointers: Near pointers are used to store 16-bit addresses only. Using the near pointer, we can not store the address with a size greater than 16 bits.
- **Far Pointers: A far pointer is a pointer of 32 bits size. However, information outside the computer's memory from the current segment can also be accessed.
- **Huge Pointers: Huge pointer is typically considered a pointer of 32 bits size. But bits located outside or stored outside the segments can also be accessed.
47. Mention file operations in C.
In C programming Basic File Handling Techniques provide the basic functionalities that programmers can perform against the system.
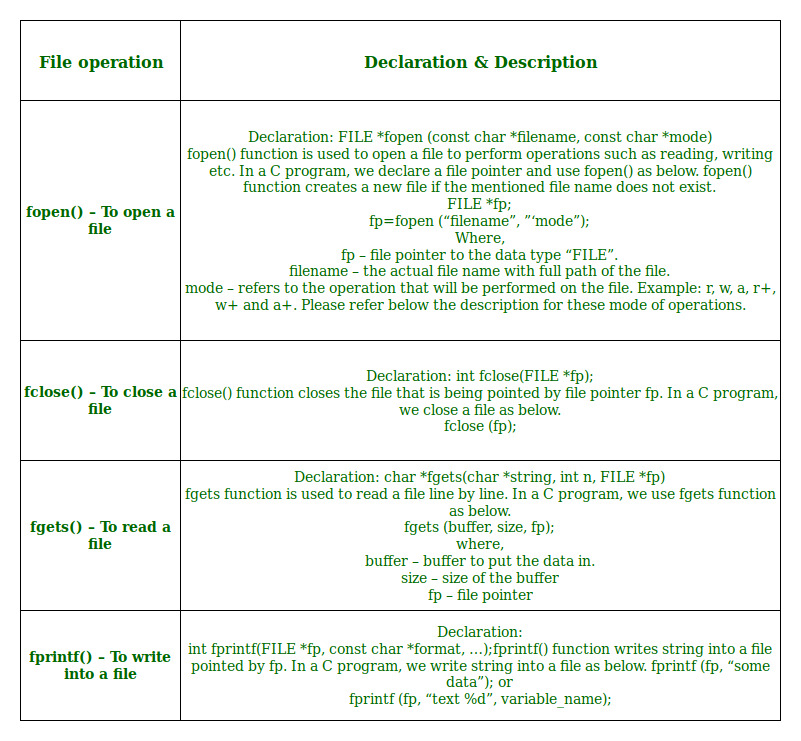
File Operations in C
48. Write a Program to check whether a linked list is circular or not.
C `
// C program to check if the linked list is circular #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> struct Node { int data; struct Node* next; }; int isCircular(struct Node* head) {
// If given linked list is null then it is circular
if (head == NULL) {
return 1;
}
struct Node* ptr;
ptr = head->next;
// Traversing linked list till last node
while (ptr != NULL && ptr != head) {
ptr = ptr->next;
}
// will return 1 if Linked list is circular else 0
return (ptr == head);}
struct Node* newnode(int data) { struct Node* first; first = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); first->data = data; first->next = NULL; return first; }
int main() {
struct Node* head = newnode(10);
head->next = newnode(12);
head->next->next = newnode(14);
head->next->next->next = newnode(16);
head->next->next->next->next = head;
// if it will be 1 then it means linked list is
// circular
if (isCircular(head)) {
printf("Linked List is Circular\n");
}
else {
printf("Linked List is Not Circular\n");
}
return 0;}
`
For more information, refer to the article - _Circular Linked List
49. Write a program to Merge two sorted linked lists.
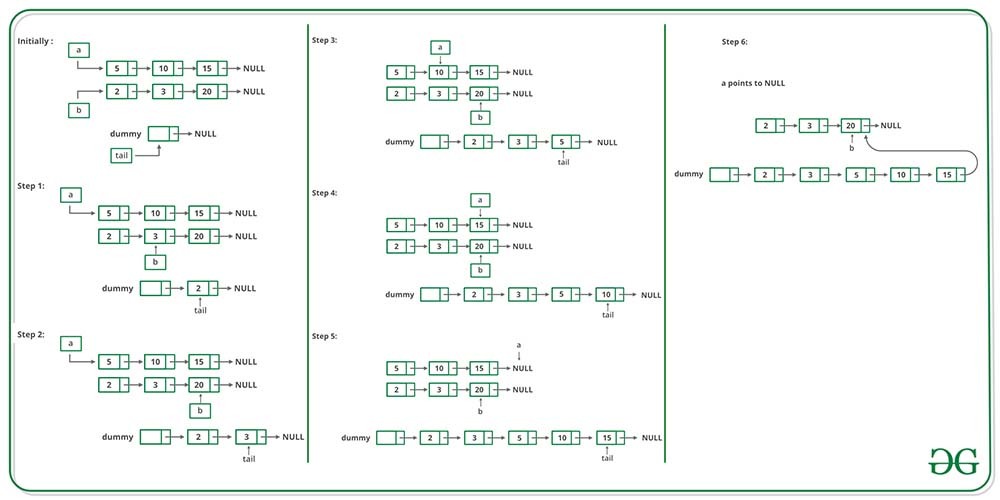
Merge two sorted linked lists
C `
// C program to merge two sorted // linked lists #include <assert.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>
// Linked List Node struct Node { int data; struct Node* next; };
/* Pull off the front node of the source and put it in dest / void MoveNode(struct Node* destRef, struct Node** sourceRef);
/* Takes two lists sorted in increasing order, and splices their nodes together to make one big sorted list which is returned. / struct Node SortedMerge(struct Node* a, struct Node* b) { /* A dummy first node to hang the result on */ struct Node dummy;
/* tail points to the last result node */
struct Node* tail = &dummy;
/* so tail->next is the place to add new
nodes to the result. */
dummy.next = NULL;
while (1) {
if (a == NULL) {
/* if either list runs out, use the
other list */
tail->next = b;
break;
}
else if (b == NULL) {
tail->next = a;
break;
}
if (a->data <= b->data)
MoveNode(&(tail->next), &a);
else
MoveNode(&(tail->next), &b);
tail = tail->next;
}
return (dummy.next);}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS / / MoveNode() function takes the node from the front of the source, and move it to the front of the dest. It is an error to call this with the source list empty.
Before calling MoveNode(): source == {1, 2, 3} dest == {1, 2, 3}
After calling MoveNode(): source == {2, 3} dest == {1, 1, 2, 3} / void MoveNode(struct Node* destRef, struct Node** sourceRef) { /* The front source node / struct Node newNode = *sourceRef; assert(newNode != NULL);
/* Advance the source pointer */
*sourceRef = newNode->next;
/* Link the old dest off the new node */
newNode->next = *destRef;
/* Move dest to point to the new node */
*destRef = newNode;}
/* Function to insert a node at the beginning of the linked list / void push(struct Node* head_ref, int new_data) { /* allocate node / struct Node new_node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;}
/* Function to print nodes in a given linked list / void printList(struct Node node) { while (node != NULL) { printf("%d ", node->data); node = node->next; } }
/* Driver program to test above functions*/ int main() { /* Start with the empty list / struct Node res = NULL; struct Node* a = NULL; struct Node* b = NULL;
/* Let us create two sorted linked lists to test
the functions
Created lists, a: 5->10->15, b: 2->3->20 */
push(&a, 15);
push(&a, 10);
push(&a, 5);
push(&b, 20);
push(&b, 3);
push(&b, 2);
/* Remove duplicates from linked list */
res = SortedMerge(a, b);
printf("Merged Linked List is: \n");
printList(res);
return 0;}
`
Output
Merged Linked List is: 2 3 5 10 15 20
For more information, refer to the article - _Merge Two Sorted Linked List
50. What is the difference between getc(), getchar(), getch() and getche().
- **getc(): The function reads a single character from an input stream and returns an integer value (typically the ASCII value of the character) if it succeeds. On failure, it returns the EOF.
- **getchar(): Unlike getc(), gechar() can read from standard input; it is equivalent to getc(stdin).
- **getch(): It is a nonstandard function and is present in 'conio.h' header file which is mostly used by MS-DOS compilers like Turbo C.
- **getche(): It reads a single character from the keyboard and displays it immediately on the output screen without waiting for enter key.
For more information, refer to the article - _Difference between getc(), getchar(), getch(), getche()
Conclusion
C programming is an important language for both beginners and experienced developers because of its flexibility and usefulness. Whether you’re working on system programming or building applications, knowing the basics and advanced topics of C is crucial. This article has shared key interview questions, covering everything from simple syntax to more advanced topics like memory management and recursion. Reviewing these questions will help you feel more confident and prepared for your C programming interviews.