Neuroprotective effects of berry fruits on neurodegenerative diseases (original) (raw)
Abstract
Recent clinical research has demonstrated that berry fruits can prevent age-related neurodegenerative diseases and improve motor and cognitive functions. The berry fruits are also capable of modulating signaling pathways involved in inflammation, cell survival, neurotransmission and enhancing neuroplasticity. The neuroprotective effects of berry fruits on neurodegenerative diseases are related to phytochemicals such as anthocyanin, caffeic acid, catechin, quercetin, kaempferol and tannin. In this review, we made an attempt to clearly describe the beneficial effects of various types of berries as promising neuroprotective agents.
Keywords: nerve regeneration, berry fruit, neurodegenerative disease, neuroprotection, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, review, neural regeneration
Introduction
Many epidemiological studies have shown that regular flavonoid rich fruit intake is associated with delayed Parkinson's disease (PD), Alzheimer's disease (AD), ischemic diseases and aging effects (Ono et al., 2003; Savaskan et al., 2003; Marambaud et al., 2005; Alzheimer's Association, 2008; Pandey and Rizvi, 2009). Data from in vitro and animal studies suggest that among the sources of antioxidants, phytochemicals in berry fruits (e.g., anthocyanin and caffeic acid) have a beneficial role in brain aging and neurodegenerative disorders because of their anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, anti-viral and anti-proliferative properties (Youdim et al., 2001). Since oxidative stress and inflammation appear to be involved in brain aging and in neurodegenerative diseases (Casadesus et al., 2002), it is theorized that increased consumption of antioxidants may be effective in preventing or ameliorating these changes. The neuroprotective effects of strawberry, bilberry, black currant, blackberry, blueberry and mulberry, were demonstrated by many scholars (Basu et al., 2010; Rendeiro et al., 2012). Neuroinflammatory processes in the brain are believed to play a crucial role in the development of neurodegenerative diseases, especially due to increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) (Zheng et al., 2003; Shaffer et al., 2006). Because of low activity of antioxidant defense systems, the brain is susceptible to oxidative stress more than other organs (Rahman, 2007; Uttara et al., 2009). Moreover, many neurotransmitters are autoxidized to generate ROS (Lau et al., 2003). In agreement with these observations, there is evidence that increased oxidative stress plays an important role in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases such as AD, PD, ischemic diseases and aging (Esposito et al., 2012). The neuroprotective effects of many polyphenols rely on their ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and directly scavenge pathological concentrations of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species and chelate transition metal ions (Aquilano et al., 2008). Different polyphenolic compounds were shown to have scavenging activity and the ability to activate key antioxidant enzymes in the brain, thus breaking the vicious cycle of oxidative stress and tissue damage (Lau et al., 2003; Esposito et al., 2012). There is a growing interest in the potential of natural polyphenols in berries (Chen et al., 2013; Rios de Souza et al., 2014) to improve memory, learning and general cognitive abilities. Preclinical evidence has indicated that flavonoids may exert powerful actions on mammalian cognitive function and may reverse age-related declines in memory and learning. These beneficial effects are mainly in demand in preventing against brain damage, such as ischemic and neurodegenerative diseases, reducing neuronal apoptosis, and improving memory, learning and cognitive functions (Kovasova et al., 2010; Angeloni et al., 2012). In this review, we made an attempt to clearly describe the beneficial effects of various types of berries as promising neuroprotective agents.
Strawberry
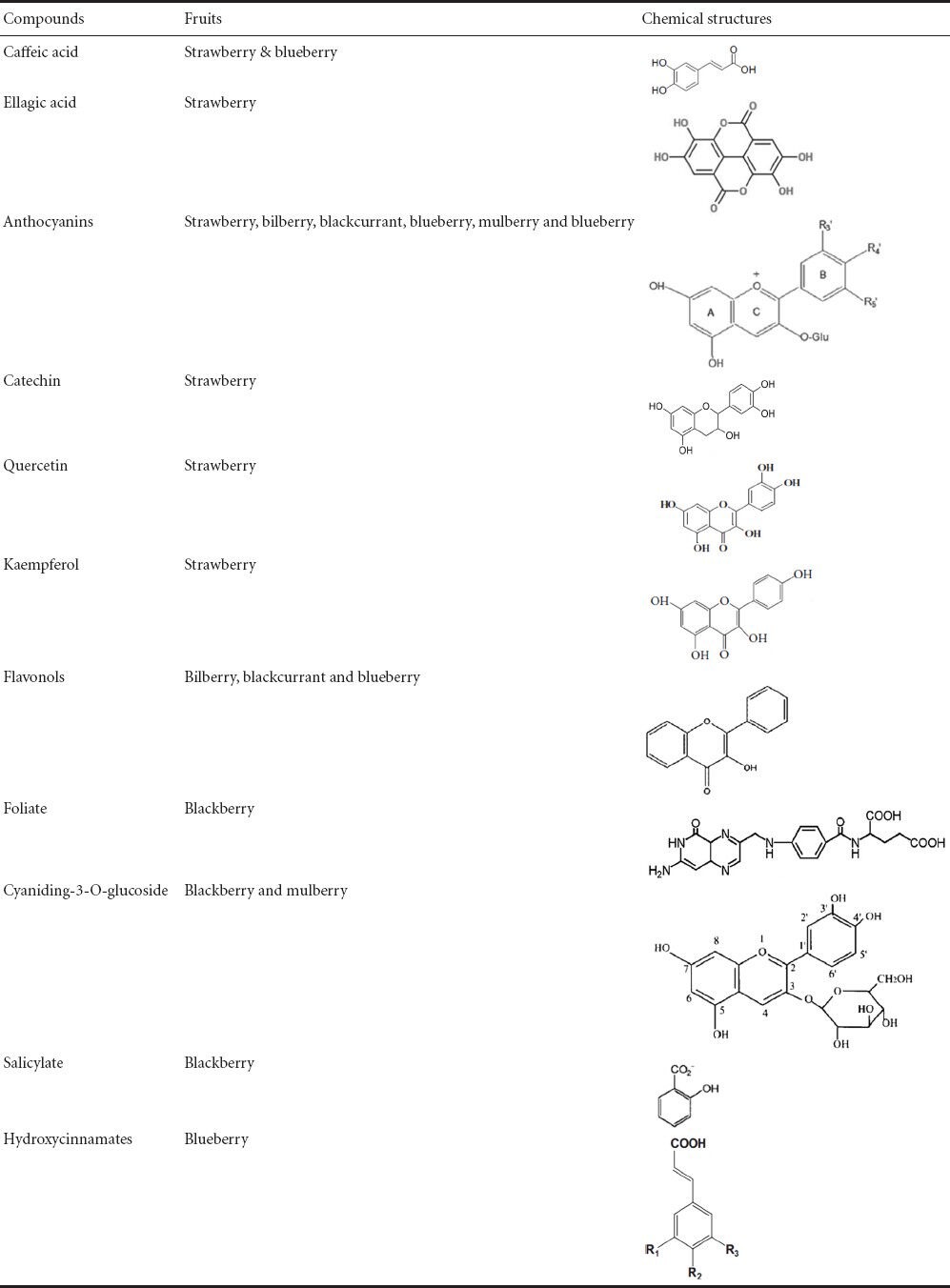
Strawberry tree (Arbutus unedo L.; Ericaceae family) is an evergreen shrub, a native Mediterranean species that are also cultivated in other regions of Eastern Europe. The wide range of antioxidants (Tulipani et al., 2009) in strawberry fruit makes strawberry as a “health promoting food”. The most abundant antioxidants are caffeic acid, ellagic acid, and certain flavonoids including anthocyanins, tannins, catechin, quercetin, kaempferol, gallic acid derivatives, vitamins C, E and carotenoids (Table 1; Hakkinen et al., 2009; Simirgiotis et al., 2010; Karlund et al., 2014)
Table 1.
Structures of important active compounds of the berry fruits
Seeram et al. (2001) studied the inhibitory effects of strawberries on cyclooxygenase (COX) in vitro, which is a key enzyme that plays an important role in the conversion of arachidonic acid to various eicosanoids involved in inflammation. There are two isoforms of COX, namely COX-1 and COX-2. Extracts from strawberries are moderately effective in inhibiting COX-1, and are more potent inhibitors of COX-2 as well. COX-2 is the main promoter of inflammatory prostaglandins, while COX-1 is known to produce some gastroprotective prostaglandins. Selective inhibition of COX-2 could be important because the inflammatory process is involved in the etiology of a wide range of neurodegenerative diseases, including AD and PD (Ferencik et al., 2001).
Previous studies have shown that strawberry extracts offer protection to age-induced deficits by enhancing GTPase activity, calcium content, oxotremorine-enhanced K+-evoked striatal dopamine (DA) release, and alterations in membrane rigidity and are effective in preventing the loss of sensitivity in Purkinje cells (Joseph et al., 1998; Balk et al., 2006). In addition, strawberry extracts can improve cognitive function as shown by Morris water maze performance. Another study has demonstrated that strawberry extracts can improve motor behavioral performance on the rod walking (Joseph et al., 1998). These findings suggest that phytochemicals present in strawberry benefit age-related deficits in addition to the known beneficial effects on cancer and other cardiovascular diseases.
Young rats exposed to 56Fe particle radiation showed neurochemical and behavioral changes which are similar to those seen in aged organisms (Joseph et al., 2000). Some scholars (Joseph et al., 1998, 1999; Bickord et al., 2000; Youdim et al., 2001) have reported that maintaining rats for 2 months in antioxidant diets containing strawberry extracts can prevent the occurrence of neurochemical and behavioral changes that are characteristic of ageing. Precisely, maintaining rats for 2 months in diets containing strawberry extracts increased oxotremorine-enhanced dopamine release from striatal slices when compared to control diet-fed animals. In addition to the improvement in dopaminergic function, there were improvements in motor behavior, spatial learning and memory (Joseph et al., 1998, 1999; Bickord et al., 2000; Youdim et al., 2001). A study done by Rabin et al. (2002) showed that diet (2% strawberry extracts) reduced the effects of oxidative stress following exposure to 56Fe particles. These results suggest that antioxidant-rich diet may serve as effective countermeasures to prevent neurochemical and behavioral changes following exposure to heavy particles. Strawberry and vitamin E are shown to have equal protective effects on age-related deficits (Joseph et al., 1998).
Bilberry
Bilberries provide significant health benefits because of their high levels of anthocyanins, flavonols, vitamins C, E, and manganese and contain carotenoid, lutein, and zeaxanthin (Murray et al., 2009; Nile et al., 2014). The biological function (including benefits for eyes, mouth, gum health), powerful anti-inflammatory (Luo et al., 2014), anti-hyperglycemic (Stefanut et al., 2013) and antioxidative effects (Davarmanesh et al., 2013; Baum et al., 2014; Calo and Marabini, 2014) can protect blood vessels and improve blood circulation (Pantelidis et al., 2007; Szajdek et al., 2008).
A number of studies have shown that aging and particularly brain aging are associated with free radicals action (Grady and Craik, 2000; Liu et al., 2003). Glutathione and its related enzymes participate in the maintenance of oxidant homeostasis and in the aging process and are associated with a gradual pro-oxidizing shift in the glutathione redox state. There is a close link between glutathione metabolism and oxidant homeostasis that can be manifested as learning and synaptic plasticity deficits under the condition of low glutathione content (Sayre et al., 2008; Johnson, 2012). There are few suitable animal models to study the supplemental antioxidant functions in age-related deficits in learning and memory. OXYS rats with inherited features of accelerated aging and high sensitivity to oxidative stress are potential genetic murine models. These rats have significantly shortened lifespan (28% shorter than Wistar rats). Therefore, OXYS rats have become a murine animal model to elucidate the basic mechanisms of age-related changes in brain functions, such as learning and cognitive deficiencies in age-related diseases (Obukhova et al., 2009). Kolosova et al. (2006) reported that the level of glutathione in the brain of young OXYS rats is 1.3 times lower as compared to Wistar rats. At the same time, superoxide dismutase activity was higher in 3-month-old OXYS rats than in age-matched Wistar rats. It is known that in many cells the expression of genes whose products exhibit antioxidant activity might be induced by reactive oxygen species generation. Therefore, a simultaneous increase in superoxide dismutase activity and a decrease in glutathione level might indicate the increased level of ROS generation in the brain of young OXYS rats.
The above data support the theory that the reduction of cellular expression and activity of antioxidant proteins is a fundamental cause of the aging process and neurodegenerative diseases. Memory loss is accompanied but not necessarily caused by accumulation of oxidative damage to lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, all of which can disrupt neuronal function. They also demonstrated that the bilberry extract is effective in decreasing lipid peroxides and increasing superoxide dismutase activity in the brain. Furthermore, long term supplementation of bilberry extract prevents learning and memory deficits in OXYS rats. It is known that high efficiency of bilberry extract might be provided by its flavonoids, which have high free radical scavenging activity and disease-fighting properties (Rahman, 2007; Uttara et al., 2009).
Blackcurrant
Blackcurrant is a strong candidate fruit to provide neuroprotection in AD. Anthocyanins are the major group of polyphenols in blackcurrant, accounting for about 80% of the total amount of quantified compounds (Ghosh and Konishi, 2007). β-Amyloid (Aβ)-induced formation of ROS is also inhibited by flavonols from blackcurrant (Li et al., 2004). Polyphenolic substances present in blackcurrant fruits have been reported for antioxidant, antimicrobial, antiviral, and antibacterial properties (Krisch et al., 2009; Molan et al., 2010; Bragoulo and Molan, 2011; Szachowicz-Peteleska et al., 2012; Tabart et al., 2012; Vepsalainen et al., 2013). Vepsalainen et al. (2013) investigated the effects of anthocyanin-rich blackcurrant extracts on neuroprotection and amyloid precursor protein (APP) expression in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells overexpressing APP751 isoform under AD-related stress conditions. They also found that the cells which were treated with anthocyanin-rich blackcurrant extracts experienced significantly reduced ROS production. These findings indicate that anthocyanin-rich blackcurrant extracts exhibit a beneficial effect through their promising antioxidant activity.
Polyphenols, which are abundant in bilberry and blackcurrant, have been shown to inhibit the formation and extension of Aβ fibrils and to destabilize the preformed Aβ fibrils in vitro (Vepsalainen et al., 2013). They also investigated the effects of both bilberry and blackcurrant-fed APdE9 mice; and found both berry extract-fed APdE9 mice showed similar reductions in total APP-normalized APP C-terminal fragments levels, while the dietary effects on soluble Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels and the ratio of Aβ42/40 in the dorsal cortex were different. Interestingly, bilberry supplementation reduced both soluble Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels as compared to blackcurrant-fed mice, whereas a reduced ratio of insoluble Aβ42/40 and moderately increased soluble APPα levels were observed in blackcurrant-fed mice, but not in bilberry-fed mice. These important findings clearly suggest that the increased ratio of Aβ42/40 is a key pathogenic feature and that soluble APPα is known to exert neuroprotective effects. Berry supplements may have an inhibitory effect on β-secretase expression, preventing cognitive decline and mitigating AD-like pathology in a mouse model of AD. On the other hand, the decreased ratio of insoluble Aβ42/40 in blackcurrant-fed mice may be attributed to the modulation of γ-secretase function than β-secretase inhibition (Vepsalainen et al., 2013).
Bilberry and blackcurrant supplemented diets also attenuated behavioral abnormalities in APdE9 mice. Under a stressful swimming condition, a black currant diet increased swimming speed, ruling out the possibility that this is derived from some kind of motor impairment. The most striking effect of berry extracts was observed in the food-motivated spatial working memory task, in which both bilberry and blackcurrant attenuated the APdE9 genotype-linked impairment. A moderate beneficial effect of the berry extracts was also observed in the strategy of solving the Morris swim task: both the time spent near the pool wall and search rotations while swimming were decreased in the bilberry and blackcurrant fed mice (Vepsäläinen et al., 2013). Interestingly, hyperactivity was alleviated to some extent by both bilberry and blackcurrant diets, but significance was found only in the blackcurrant-fed mice. These finding suggests that the flavonols and anthocyanin-rich blackcurrant extracts exert protective effects under stress conditions.
However, the fact that moderate alterations in long-lasting supplementation of APdE9 mice with bilberry or blackcurrant revealed beneficial effects on APP and Aβ metabolism. In addition, these supplementations alleviated behavioral abnormalities in a well-characterized AD mouse model. Based on these results, it is anticipated that bilberry- and blackcurrant-derived phytochemicals could display beneficial neuroprotective effects on behavioral outcome and APP processing and Aβ accumulation (Vepsalainen et al., 2013).
Blackberry
Blackberry fruits are well known to be a rich source of antioxidants, rich polyphenols (Kaume et al., 2012) manganese, folate, fibers, cyaniding-3-O-glucoside, vitamin C, salicylate and high tannin. The biological functions of blackberries include anti-hyperglycemic (Stefanut et al., 2013), antioxidative, antiseptic, antibacterial/antiviral, anticancer properties. In addition, they can normalize cholesterol, delay the process of aging, relieve pains, and strengthen blood circulation (Jiao and Wang, 2000; Siriwoharn et al., 2006).
Tavares et al. (2013) reported that wild blackberries, brigantinus and vagabundus collected from Braganc (northeast region of Portugal) demonstrated attainable neuroprotective effects by reducing intracellular ROS levels, modulating glutathione levels and inhibiting the occurrence of caspases during treatments. These effects protected neuronal cells against oxidative injury, one of the most important features of neurodegeneration. In vitro studies have also reported that blackberries have potent anti-inflammatory and antiproliferative properties (Wang and Jiao, 2000; Dai et al., 2007). In addition, the antioxidants present in these fruits improved behavioral performance in motor neuron tests in aged rats. The balance and fine motor coordination in cognitive test were also improved in the Morris water maze, demonstrating the measures of spatial working memory and learning (Shukitt-Hale et al., 2009).
Blueberry
Blueberries are a rich source of flavonoids, notably anthocyanins, caffeic acid, flavanols and hydroxycinnamates (Cao et al., 1999; Prior et al., 2001; Wu et al., 2004; Gavrilova et al., 2011; You et al., 2011). The consumption of blueberries has been reported to prevent oxidative stress, inhibit inflammation (Sweeney et al., 2002) and kidney injury (Nair et al., 2014), and improve vascular health (Erlund et al., 2008). These beneficial effects have been attributed to their relatively high flavonoid content, in particular, anthocyanins. A recent study has demonstrated that blueberry supplementation can alleviate age-related behavioral deficits and high-fat diet-related behavioral declines (Carey et al., 2014).
The protein kinases, such as MAP kinase (MAPK), extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and transcriptional activator cyclic-AMP response element binding protein (CREB), are involved to mediate the beneficial effects of learning and memory produced by various phytochemicals present in blueberries. The imbalance in calcium homeostasis and the accumulation of AB protein promote oxidative stress, aging and neurodegeneration. Aβ alone or together with glutamate, inhibits PKA and its downstream signaling target CREB, in embryonic neurons. CREB is closely associated with learning and memory at the synaptic sites that are affected in AD. It is further complicated by age-related differences in memory, signal processing, and susceptibility to ROS (Impey et al., 1999; Kuperstein and Yavin, 2002; Vitolo et al., 2002). Brewer et al. (2010) reported that blueberry extract treatment offers protection from Aβ42 in middle-aged (neurons isolated in 10–12 months) and old neurons (neurons isolated around 24 months) in a defined culture medium. Blueberry extract treatment lowered Aβ42 toxicity in middle-aged and old hippocampal neurons. Importantly, blueberry extract induces a cellular upregulation of glutathione synthesis, a major antioxidant that lowers production of cellular ROS, indicating that the blueberry extract is a potent antioxidant. This is confirmed by the findings that Aβ treatment lowered the major redox buffer, glutathione, consistent with oxidative depletion, but blueberry extract treatment reversed this loss by increasing the level of glutathione. The increase in glutathione level in old neurons after Aβ treatment is escorted by enhanced pERK signaling in an age-dependent manner, showing the greatest increase in the MAPK activity (Brewer, 1998). However, blueberry extract treatment can reduce pERK activity (Brewer et al., 2013). ERK1/2 is essential for protection against neurodegeneration because of inflammation/oxidative stress and is required for memory formation. Studies have suggested that prolonged activation of pERK signaling possibly has an adverse effect and moderate pERK activity is protective and has beneficial effects. Thus, at least in part, blueberry extract may decrease endogenous pERK expression level and its activity, because the overall oxidative stress load and Aβ levels can be reduced with blueberry extract. As mentioned above, blueberry extract treatment can increase glutathione expression and reduce ROS generation. Thus, submaximal ERK signaling may reduce endogenous stress. Brewer et al. (1998) reported that blueberry extract pretreatment prevents calcium dysregulation and inhibit CREB and ERK activities through ROS stress response, suggesting that blueberry extract can improve the cognitive function in aging rats by regulating transient stress signaling and ROS generation.
A preclinical study has demonstrated that blueberry supplementation enhances motor and memory performance in aged animals (Youdim et al., 2000; Casadesus et al., 2004). Changes in brain-derived neurotrophic factor-mediated protein synthesis, such as Arc/Arg3.1, are directly related to blueberry consumption. Inhibition of CREB/brain-derived neurotrophic factor pathway effectively blocks the changes in spatial memory in the blueberry-supplemented animals (Williams et al., 2008). Following blueberry feeding, anthocyanins have been identified in the specific cerebral regions responsible for cognitive function, including the hippocampus and neocortex (Andres-Lacueva et al., 2005). Furthermore, anthocyanins distribution in the hippocampus might be related to increased neuronal signaling in this region (Casadesus et al., 2000). Barros et al. (2006) conducted a study involving psychopharmacological screening to evaluate potential effects of a lyophilized extract of different cultivars from Vaccinium ashei, Reade (Ericaceae) berries, which are commonly known as rabbit eye blueberries and are shown to have memory-enhancing, anxiolytic and locomotion increasing properties in mice, as well as the protective effects against free radical-induced DNA damage in the brain. These results are reliable with the hypothesis that flavonoids (including anthocyanins) can show beneficial effects on cell signaling and decrease oxidative damage. These results also suggest that flavonoids might directly act on cognitive function, which may help prevent age-related and pathological degenerative processes in the brain.
Joseph et al. (1999) found that 8 week dietary supplementation of blueberry extracts was effective in reversing age-related deficits in the brain and behavioral dysfunctiond in aged (19 months) F344 rats. In addition, blueberry supplemented animals showed positive effects on cognitive behavior, motor performance (e.g., rod walking and the accelerating rotarod), carbachol-stimulated GTPase activity, and oxotremorine enhanced DA release. A study showed that after 6 weeks of blueberry-supplemented diets, neuronal loss in the hippocampus was reduced in rats with cerebral ischemia (Sweeney et al., 2002). There is evidence that in addition to Morris water maze performance, the cognitive declines in object recognition were effectively reversed by blueberry supplementation (Goyarzu et al., 2004). Animals treated with blueberry showed a significantly reduced caspase-3 activity in the ischemic hemisphere. Chronic treatment with blueberry reduces ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis and cerebral infarction (Wang et al., 2005).
Stromberg et al. (2005) show that blueberry causes a rapid but transient increase of OX-6-positive microglia in the striatum and the globus pallidus of normal F344 male rats. Additionally, the number of striatal TH-positive nerve fibers was increased in animals fed with blueberry supplemented diet. Supplementation of blueberries in adult mice (aged 3 months) improved performance in memory tasks and had a protective effect on DNA damage in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex (Barros et al., 2006). Short-term dietary supplementation of antioxidant rich blueberries can decrease the level of oxidative stress in brain regions and can ameliorate age-related deficits in neuronal and behavioral functions to generate a heat shock protein 70 mediated neuroprotective response to stress in rats. Therefore, supplementeation of blueberries shows beneficial effects by increasing antioxidant level, enhancing anti-inflammatory activities and regulating various signaling pathways at different time points (Galli et al., 2006). A 2-month dietary supplementation of blueberries alleviated deficits in learning performance induced by bilateral hippocampal injections of kainic acid, reduced the loss of CA1 pyramidal neurons (Duffy et al., 2008), and reversed the deficits in cognitive performance (Shukitt-Hale et al., 2007). Short-term blueberry-enriched diet prevents and reverses object recognition memory declines in aged Fischer-344 rats (Malin et al., 2011). Joseph et al. (2003) showed that amyloid precursor protein/presenilin-1 transgenic mice that were given a diet containing blueberry extract from 4 to 12 months of age showed no behavioral deficits in Y-maze performance. Krikorian et al. (2010) indicated that wild blueberry juice supplementation for 12 weeks improved memory function in old adults with mild memory decline.
The central cholinergic system is essential for the regulation of cognitive functions (Sarter and Bruno, 1997; Silman and Sussman, 2005; Zimmerman and Soreq, 2006). Agonists of cholinergic receptors and inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase have been extensively used to increase endogenous acetylcholine levels and thus overcome cognitive deficits. Acetylcholinesterase metabolizes acetylcholine to choline and acetyl-coenzyme A. Papandreou et al. (2009) reported that administration of polyphenol-rich wild blueberry extract to healthy adult mice attenuated brain oxidative stress (MDA levels), increased brain ascorbate and glutathione levels, and decreased acetylcholinesterase activity. Thus, supplementation of polyphenols-concentrated blueberry extract significantly enhances the cognitive function of adult mice by increasing cerebral antioxidant level and inhibiting acetylcholinesterase activity. These findings stress the critical impact of wild blueberry bioactive components on brain function.
Shukitt-Hale et al. (2008) reported that blueberry polyphenols attenuated kainic acid-induced learning impairments in rats, which were similar to those observed in aged animals. The reason for the similarity in behavioral deficits between aged and kainic acid-injected rats, as mentioned above, might be the increase in inflammation, which is a factor of inducing cognitive deficits. Blueberry polyphenols have anti-inflammatory actions. Young rats give a diet supplemented with a 2% blueberry extract for 2 months, prior to the injection of an inflammatory stimulus into the hippocampus, exhibit significantly less impairments in their spatial learning and memory abilities.
Furthermore, rats fed with the blueberry diet prior to kainic acid injection exhibited less activation of the inflammatory marker MHC class II marker (OX-6), increased expression in the neurotrophic factor insulin-like growth factor-1 along with decreased levels of inflammatory cytokines interleukin-1β, tumor necrosis factor-α, and transcription factor nuclear factor kappaB. Thus, the mechanism by which blueberry polyphenols protects the brain is to decrease the deleterious effects of an inflammatory stimulus by altering the expression of inflammation-related genes.
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis presents with pathological and clinical features similar to those of multiple sclerosis, including inflammation and neurodegeneration. A study by Xin et al. (2012) has demonstrated that in relapsing-remitting experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis models, blueberry-supplemented mice showed lower motor disability scores and improved cumulative and final motor scores compared to control diet-fed mice. These findings demonstrated that blueberry supplementation is beneficial in multiple experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis models, suggesting that blueberries, which are easily administered orally and well-tolerated, may provide benefits to multiple sclerosis patients.
Mulberry
Mulberries (Morus alba L., Moraceae) are used in oriental traditional medicine for anti-inflammatory, diuretic, antitussive, antipyretic (Asano et al., 2001) and anti-hyperglycemic purposes (Stefanut et al., 2013). High amounts of anthocyanins from berries are consumed in the common diet and used in some therapeutic applications (Mitcheva et al., 1993; Dugo et al., 2001). Cyanidin-3-O-β-d-glucopyranoside (C3G), which is an aglycon of anthocyanin, has free radical scavenging and inflammation suppressing activities and offers protection to an endothelial dysfunction (Seeram et al., 2001; Kahkonen and Heinonen, 2003; Seraino et al., 2003).
In an effort to reduce the level of ROS-induced damage, the mulberry fruit extract and C3G were evaluated to determine whether they can prevent ROS generation and reduce the degree of neuronal damage. The data show that the neuroprotective effect of the mulberry fruit extract is the result of C3G in the H2O2-induced oxidative damage in PC12 cells (Kang et al., 2006). In oxygen-glucose-deprived PC12 cells, C3G increased cell viability. In addition, C3G offered more effective neuroprotection in oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced cerebral ischemia than the mulberry fruit extract at the same concentration (Kang et al., 2006). The result suggests that C3G is a major neuroprotective compound in the mulberry fruit extract in oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced cerebral ischemic cytotoxicity in PC12 cells. In in vivo experiments, mulberry fruit extract and C3G reduce infarct volume in middle cerebral artery-occluded animal models. Additional studies have demonstrated that the mulberry fruit extract has neuroprotective effects in both in vitro and in vivo ischemic oxidative stress models, suggesting that C3G is a major neuroprotective constituent of the mulberry fruit extract (Kang et al., 2006).
Conclusion
Oxidative stress and inflammation are major factors contributing to aging and the development of age-related neurodegenerative diseases. Numerous natural antioxidant/anti-inflammatory compounds found in plant food matrices, like fruits, especially berries (such as strawberry, bilberry, blackcurrant, blackberry, blueberry and mulberry) can offer neuroprotective effects (Table 2) (Essa et al., 2012; Subash et al., 2014a,b,c). Furthermore, the berry fruit may exert their effects directly through alterations in cell signaling to improve/increase neuronal communication, calcium buffering, neuroprotective stress shock proteins, plasticity, antioxidant/anti-inflammatory action, stress signaling pathways and inhibition of acetylcholinesterase. These modifications, and others that are being studied, may mediate the enhancements in cognitive and motor behavioral performance by berries. Thus, nutritional interventions rich in phytochemicals (for example anthocyanins and caffeic acid) such as berry fruits may be a valuable asset in preventing against aging by reducing or delaying the development of age-related neurodegenerative diseases (Figure 1). Extensive clinical trials need to be done to further validate the effects of berry fruits and bring novel therapeutic agents for brain-related diseases.
Table 2.
Neuroprotective effects of berry fruits
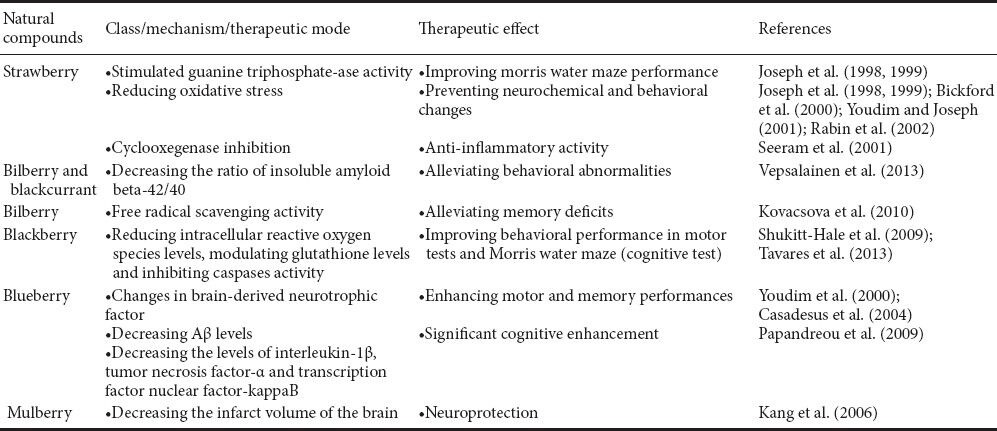
Figure 1.
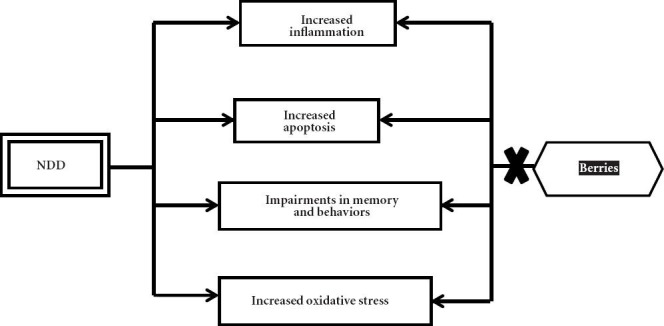
Graphic representation showing the possible mechanism of berry fruits against neurodegenerative diseases (NDD).
Footnotes
Funding: This study was supported by a grant from the Research Councial of Sultanate of Oman, No. RC/AGR/FOOD/11/01.
Conflicts of interest: None declared.
Copyedited by Pohanka M, Colangelo AM, Li CH, Song LP, Zhao M
References
- 1.Alzheimer's Association. “Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2008;8:110–133. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2008.02.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Andres-Lacueva C, Shukitt-Hale B, Galli RL, Jauregui O, Lamuela-Raventos RM, Joseph JA. Anthocyanins in aged blueberry-fed rats are found centrally and may enhance memory. Nutr Neurosci. 2005;8:111–120. doi: 10.1080/10284150500078117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Angeloni C, Pirola L, Vauzour D, Maraldi T. Dietary polyphenols and their effects on cell biochemistry and pathophysiology. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012 doi: 10.1155/2012/583901. doi:10.1155/2012/583901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Aquilano K, Baldelli S, Rotilio G, Ciriolo MR. Role of nitric oxide synthases in Parkinson's disease: a review on the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of polyphenols. Neurochem Res. 2008;33:2416–2426. doi: 10.1007/s11064-008-9697-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Asano N, Yamashita T, Yasuda K, Ikeda K, Kizu H, Kameda Y, Kato A, Nash RJ, Lee HS, Ryu KS. Polyhydroxylated alkaloids isolated from mulberry trees (Morusalba L.) and silkworms (Bombyx mori L) J Agric Food Chem. 2001;49:4208–4213. doi: 10.1021/jf010567e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Balk E, Chung M, Raman G, Tatsioni A, Chew P, Ip S, DeVine D, Lau J. B vitamins and berries and age-related neurodegenerative disorders. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep) 2006;(134):1–161. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Barros D, Amaral OB, Izquierdo I, Geracitano L, do Carmo Bassols Raseira M, Henriques AT, Ramirez MR. Behavioral and genoprotective effects of Vaccinium berries intake in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2006;84:229–234. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2006.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bastianetto S, Krantic S, Quirion R. Polyphenols as potential inhibitors of amyloid aggregation and toxicity: possible significance to Alzheimer's disease. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2008;8:429–435. doi: 10.2174/138955708784223512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Basu A, Rhone M, Lyons TJ. Berries: emerging impact on cardiovascular health. Nutr Rev. 2010;68:168–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2010.00273.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Baum M, Schantz M, Leick S, Berg S, Betz M, Frank K, Rehage H, Schwarz K, Kulozik U, Schuchmann H, Richling E. Is the antioxidative effectiveness of a bilberry extract influenced by encapsulation? J Sci Food Agric. 2014;94:2301–2307. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.6558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bickford P, Gould T, Briederick L, Chadman K, Pollock A, Young D, Shukitt-Hale B, Joseph J. Antioxidant-rich diets improve cerebellar physiology and motor learning in aged rats. Brain Res. 2000;866:211–217. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(00)02280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Brango ulo HL, Molan PC. Assay of the antioxidant capacity of foods using an iron(II)-catalysed lipid peroxidation model for greater nutritional relevance. Food Chem. 2011;125:1126–1130. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Brewer GJ. Age-related toxicity to lactate, glutamate, and beta-amyloid in cultured adult neurons. Neurobiol Aging. 1998;19:561–568. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(98)00091-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Brewer GJ, Torricelli JR, Lindsey AL, Kunz EZ, Neuman A, Fisher DR, Joseph JA. Age-related toxicity of amyloid-beta associated with increased pERK and pCREB in primary hippocampal neurons: reversal by blueberry extract. J Nutr Biochem. 2010;21:991–998. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2009.08.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Calo R, Marabini L. Protective effect of Vaccinium myrtillus extract against UVA- and UVB-induced damage in a human keratinocyte cell line (HaCaT cells) J Photoch Photobio B. 2014;132:27–35. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2014.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cao G, Shukitt-Hale B, Bickford PC, Joseph JA, McEwen J, Prior RL. Hyperoxia-induced changes in antioxidant capacity and the effect of dietary antioxidants. J Appl Physiol. 1999;86:1817–1822. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1999.86.6.1817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Carey AN, Gomes SM, Shukitt-Hale B. Blueberry supplementation improves memory in middle-aged mice fed a high-fat diet. J Agric Food Chem. 2014;62:3972–3978. doi: 10.1021/jf404565s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Casadesus G, Shukitt-Hale B, Joseph JA. Qualitative versus quantitative caloric intake: are they equivalent paths to successful aging? Neurobiol Aging. 2002;23:747–769. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(02)00079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Casadesus G, Shukitt-Hale B, Stellwagen HM, Zhu X, Lee HG, Smith MA, Joseph JA. Modulation of hippocampal plasticity and cognitive behavior by short-term blueberry supplementation in aged rats. Nutr Neurosci. 2004;7:309–316. doi: 10.1080/10284150400020482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chen L, Xin X, Zhang H, Yuon Q. Phytochemical properties and antioxidant capacities of commercial raspberry varieties. J Funct Foods. 2013;5:508–515. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Dai J, Patel JD, Mumper RJ. Characterization of blackberry extract and its antiproliferative and anti-inflammatory properties. J Med Food. 2007;10:258–265. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2006.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Davarmanesh M, Miri R, Haghnegahdar S, Tadbir AA, Tanideh N, Saghiri MA, Garcia-Godoy F, Asatourian A. Protective effect of bilberry extract as a pretreatment on induced oral mucositis in hamsters. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2013;116:702–708. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2013.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Duffy KB, Spangler EL, Devan BD, Guo Z, Bowker JL, Janas AM, Hagepanos A, Minor RK, DeCabo R, Mouton PR, Shukitt-Hale B, Joseph JA, Ingram DK. A blueberry-enriched diet provides cellular protection against oxidative stress and reduces a kainate-induced learning impairment in rats. Neurobiol Aging. 2008;29:1680–1689. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2007.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Dugo P, Mondello L, Errante G, Zappia G, Dugo G. Identification of anthocyanins in berries by narrow-bore high-performance liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization detection. J Agric Food Chem. 2001;49:3987–3992. doi: 10.1021/jf001495e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Erlund I, Koli R, Alfthan G, Marniemi J, Puukka P, Mustonen P, Mattila P, Jula A. Favorable effects of berry consumption on platelet function, blood pressure, and HDL cholesterol. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;87:323–331. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/87.2.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Esposito E, Rotilio D, Di Matteo V, Di Giulio C, Cacchio M, Algeri S. A review of specific dietary antioxidants and the effects on biochemical mechanisms related to neurodegenerative processes. Neurobiol Aging. 2012;23:719–735. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(02)00078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Essa MM, Vijayan RK, Castellano-Gonzalez G, Memon MA, Braidy N, Guillemin GJ. Neuroprotective Effect of Natural Products against Alzheimer's disease. Neurochem Res. 2012;37:1829–1842. doi: 10.1007/s11064-012-0799-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ferencik M, Novak M, Rovensky J, Rybar I. Alzheimer's disease inflammation and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2001;102:123–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Galli RL, Bielinski DF, Szprengiel A, Shukitt-Hale B, Joseph JA. Blueberry supplemented diet reverses age-related decline in hippocampal HSP70 neuroprotection. Neurobio Aging. 2006;27:344–350. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.01.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gavrilova V, Kajdzanoska M, Gjamovski V, Stefova M. Separation characterization and quantification of phenolic compounds in blueberries and red and black currants by HPLC-DAD-ESI-MSn. J Agric Food Chem. 2011;59:4009–4018. doi: 10.1021/jf104565y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ghosh D, Konishi T. Anthocyanins and anthocyanin-rich extracts: role in diabetes and eye function. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2007;16:200–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Goyarzu P, Malin DH, Lau FC, Taglialatela G, Moon WD, Jennings R, Moy E, Moy D, Lippold S, Shukitt-Hale B, Joseph JA. Blueberry supplemented diet: effects on object recognition memory and nuclear factor-kappa B levels in aged rats. Nutr Neurosci. 2004;7:75–83. doi: 10.1080/10284150410001710410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Grady CL, Craik FI. Changes in memory processing with age. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2000;10:224–231. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(00)00073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hakkinen SH, Torronen AR. Content of flavonols and selected phenolic acids in strawberries and Vaccinium species: Influence of cultivar, cultivation site and technique. Food Res Int. 2000;33:517–524. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hamaguchi T, Ono K, Yamada M. Anti-amyloidogenic therapies: strategies for prevention and treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006;63:1538–1552. doi: 10.1007/s00018-005-5599-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Impey S, Obrietan K, Storm DR. Making new connections: role of ERK/MAP kinase signaling in neuronal plasticity. Neuron. 1999;23:11–14. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80747-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Jiao H, Wang SY. Correlation of antioxidant capacities to oxygen radical scavenging enzyme activities in blackberry. J Agric Food Chem. 2000;48:5672–5676. doi: 10.1021/jf000765q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Johnson WM, Wilson-Delfosse AL, Mieyal JJ. Dysregulation of glutathione homeostasis in neurodegenerative diseases. Nutrients. 2012;4:1399–1440. doi: 10.3390/nu4101399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Joseph JA, Shukitt-Hale B, Denisova NA, Prior RL, Cao G, Martin A, Taglialatela G, Bickford PC. Long-term dietary strawberry, spinach or vitamin e supplementation retards the onset of age-related neuronal signal-transduction and cognitive behavioral deficits. J Neurosci. 1998;18:8047–8055. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-19-08047.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Joseph JA, Shukitt-Hale B, Denisova NA, Bielinski D, Martin A, McEwen JJ, Bickford PC. Reversals of age-related declines in neuronal signal transduction, cognitive, and motor behavioral deficits with blueberry, spinach, or strawberry dietary supplementation. J Neurosci. 1999;19:8114–8121. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-18-08114.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Joseph JA, Shukitt-Hale B, McEwen J, Rabin BM. CNS-induced deficits of heavy particle irradiation in space: The aging connection. Adv Space Res. 2000;25:2057–2064. doi: 10.1016/s0273-1177(99)01013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Joseph JA, Denisova NA, Arendash G, Gordon M, Diamond D, Shukitt-Hale B, Morgan D. Blueberry supplementation enhances signaling and prevents behavioral deficits in an Alzheimer disease model. Nutr Neurosci. 2003;6:153–162. doi: 10.1080/1028415031000111282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kahkonen MP, Heinonen M. Antioxidant activity of anthocyanins and their aglycons. J Agric Food Chem. 2003;51:628–633. doi: 10.1021/jf025551i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kang TH, Hur JY, Kim HB, Ryu JH, Kim SY. Neuroprotective effects of the cyanidin-3-O-beta-d-glucopyranoside isolated from mulberry fruit against cerebral ischemia. Neurosci Lett. 2006;391:122–126. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2005.08.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Karlund A, Pekka Salminen J, Koskinen P, Ahern JR, Karonen M, Tiilikkala K, Karjalainen RO. Polyphenols in strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa) leaves induced by plant activators. J Agric Food Chem. 2014;62:4592–4600. doi: 10.1021/jf405589f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kaume L, Howard LR, Devareddy L. The blackberry fruit: a review on its composition and chemistry, metabolism and bioavailability, and health benefits. J Agric Food Chem. 2012;60:5716–5727. doi: 10.1021/jf203318p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kolosova NG, Shcheglova TV, Sergeeva SV, Loskutova LV. Long-term antioxidant supplementation attenuates oxidative stress markers and cognitive deficits in senescent-accelerated OXYS rats. Neurobiol Aging. 2006;27:1289–1297. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.07.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kovacsova M, Barta A, Parohova J, Vrankova S, Pechanova O. Neuroprotective mechanisms of natural polyphenolic compounds. Act Nerv Super Rediviva. 2010;52:181–186. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Krikorian R, Shidler MD, Nash TA, Kalt W, Vinqvist-Tymchuk MR, Shukitt-Hale B, Joseph JA. Blueberry supplementation improves memory in older adults. J Agric Food Chem. 2010;58:3996–4000. doi: 10.1021/jf9029332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Krisch J, Ordogh L, Galgoczy L, Papp T, Vágvölgyi CS. Anticandidal effect of berry juices and extracts from Ribes species. Cent Eur J Biol. 2009;4:86–89. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kuperstein F, Yavin E. ERK activation and nuclear translocation in amyloid-beta peptide- and iron-stressed neuronal cell cultures. Eur J Neurosci. 2002;16:44–54. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2002.02056.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Lau FC, Shukitt-Hale B, Joseph JA. The beneficial effects of fruit polyphenols on brain aging. Neurobiol Aging. 2005;26:128–132. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Li MH, Jang JH, Sun B, Surh YJ. Protective effects of oligomers of grape seed polyphenols against beta-amyloid-induced oxidative cell death. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004;1030:317–329. doi: 10.1196/annals.1329.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Liu R, Liu IY, Bi X, Thompson RF, Doctrow SR, Malfroy B, Baudry M. Reversal of age-related learning deficits and brain oxidative stress in mice with superoxide dismutase/catalase mimetics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:8526–8531. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1332809100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Luo H, Dan Lv X, En Wang GE, Li YF, Kurihara H, He RR. Anti-inflammatory effects of anthocyanins-rich extract from bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.) on croton oil-induced ear edema and Propionibacterium acnes plus LPS-induced liver damage in mice. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2014;65:594–601. doi: 10.3109/09637486.2014.886184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Malin DH, Lee DR, Goyarzu P, Chang YH, Ennis LJ, Beckett E, Shukitt-Hale B, Joseph JA. Short-term blueberry-enriched diet prevents and reverses object recognition memory loss in aging rats. Nutrition. 2011;27:338–342. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2010.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Marambaud P, Zhao H, Davies P. Resveratrol promotes clearance of Alzheimer's disease beta-amyloid peptides. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:37377–37382. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M508246200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Mitcheva M, Astroug H, Drenska D, Popov A, Kassarova M. Biochemical and morphological studies on the effects of anthocyans and vitamin E on carbon tetrachloride induced liver injury. Cell Mol Biol. 1993;39:443–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Molan AL, Liu Z, Kruger M. The ability of blackcurrant extracts to positively modulate key markers of gastrointestinal function in rats. World J Microb Biot. 2010;26:1735–1743. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Murray A. Atheroprotective effects of bilberry extracts in Apo E-deficient mice. J Agri Food Chem. 2009;57:11106–11011. doi: 10.1021/jf9035468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Nair AR, Masson GS, Ebenezer PJ, Del Piero F, Francis J. Role of TLR4 in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury: Protection by blueberry. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014;71:16–25. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.03.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Nile SH, Park SW. Edible berries: Bioactive components and their effect on human health. Nutrition. 2014;30:134–144. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2013.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Obukhova LA, Skulachev VP, Natalia G, Kolosova NG. Mitochondria- targeted antioxidant SkQ1 inhibits age-dependent involution of the thymus in normal and senescence-prone rats. Aging. 2009;1:389–401. doi: 10.18632/aging.100043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Ono K, Yoshiike Y, Takashima A, Hasegawa K, Naiki H, Yamada M. Potent anti-amyloidogenic and fibril-destabilizing effects of polyphenols in vitro: implications for the prevention and therapeutics of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 2003;87:172–181. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01976.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Pantelidis GE, Vasilakakis M, Manganaris GA, Diamantidis Gr. Antioxidant capacity phenol anthocyanin and ascorbic acid contents in raspberries, blackberries, red currants gooseberries, and cornelian cherries. Food Chem. 2007;102:777–783. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Pandey KB, Rizvi SI. Plant polyphenols as dietary antioxidants in human health and disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2009;2:270–278. doi: 10.4161/oxim.2.5.9498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Papandreou MA, Dimakopoulou A, Linardaki ZI, Cordopatis P, Klimis-Zacas D, Margarity M, Lamari FN. Effect of a polyphenol-rich wild blueberry extract on cognitive performance of mice, brain antioxidant markers and acetylcholinesterase activity. Behav Brain Res. 2009;198:352–358. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2008.11.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Petersen PC. Mild cognitive impairment as a diagnostic entity. J Intern Med. 2004;256:183–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2004.01388.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Prior RL, Lazarus SA, Cao G, Muccitelli H, Hammerstone JF. Identification of procyanidins and anthocyanins in blueberries and cranberries (Vaccinium spp.) using high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem. 2001;49:1270–1276. doi: 10.1021/jf001211q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Rabin BM, Shukitt-Hale B, Szprengiel A, Joseph JA. Effects of heavy particle irradiation and diet on amphetamine- and lithium chloride-induced taste avoidance learning in rats. Brain Res. 2002;953:31–36. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(02)03263-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Rahman K. Studies on free radicals, antioxidants, and co-factors. Clin Interv Aging. 2007;2:219–236. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Rendeiro C, Guerreiro JD, Williams CM, Spencer JP. Flavonoids as modulators of memory and learning: molecular interactions resulting in behavioural effects. Proc Nutr Soc. 2012;71:246–262. doi: 10.1017/S0029665112000146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Rios de Souza V, Pimenta Pereira PA, Teodoro da Silva TL de Oliveira Lima LC, Pio R, Queiroz F. Determination of the bioactive compounds, antioxidant activity and chemical composition of Brazilian blackberry, red raspberry, strawberry, blueberry and sweet cherry fruits. Food Chem. 2014;156:362–368. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.01.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Sarter M, Bruno JP. Cognitive functions of cortical acetylcholine: toward a unifying hypothesis. Brain Res Rev. 1997;23:28–46. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0173(96)00009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Savaskan E, Olivieri G, Meier F Seifritz E, Wirz-Justice A, Müller-Spahn F. Red wine ingredientresveratrol protects from beta-amyloid neurotoxicity. Gerontology. 2005;49:380–383. doi: 10.1159/000073766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Sayre KM, Perry G, Smith MA. Oxidative stress and neurotoxicity. Chem Res Toxicol. 2008;21:172–188. doi: 10.1021/tx700210j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Schaffer S, Eckert GP, Schmitt-Schillig S, Müller WE. Plant foods and brain aging: a critical appraisal. Forum Nutr. 2006;59:86–115. doi: 10.1159/000095209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Seeram NP, Momin RA, Nair MG, Bourquin LD. Cyclooxygenase inhibitory and antioxidant cyanidin glycosides in cherries and berries. Phytomedicine. 2001;8:362–369. doi: 10.1078/0944-7113-00053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Serraino I, Dugo L, Dugo P, Mondello L, Mazzon E, Dugo G, Caputi AP, Cuzzocrea S. Protective effects of cyanidin-3-Oglucoside from blackberry extract against peroxynitrite-induced endothelial dysfunction and vascular failure. Life Sci. 2003;73:1097–1114. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(03)00356-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Shukitt-Hale B, Carey AN, Jenkins D, Rabin BM, Joseph JA. Beneficial effects of fruit extracts on neuronal function and behavior in a rodent model of accelerated aging. Neurobiol Aging. 2007;28:1187–1194. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.05.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Shukitt-Hale B, Lau FC, Carey AN, Galli RL, Spangler EL, Ingram DK, Joseph JA. Blueberry polyphenols attenuate kainic acid-induced decrements in cognition and alter inflammatory gene expression in rat hippocampus. Nutr Neurosci. 2008;11:172–182. doi: 10.1179/147683008X301487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Shukitt-Hale B, Cheng V, Joseph JA. Effects of blackberries on motor and cognitive function in aged rats. Nutr Neurosci. 2009;12:135–140. doi: 10.1179/147683009X423292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Silman I, Sussman JL. Acetylcholinesterase: ‘classical’ and ‘non-classical’ functions and pharmacology. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2005;5:293–302. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2005.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Simirgiotis MJ, Schmeda-Hirschmann G. Determination of phenolic composition and antioxidant activity in fruits, rhizomes and leaves of the white strawberry (Fragaria chiloensis spp. chiloensis form chiloensis) using HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS and free radical quenching techniques. J Food Compos Anal. 2010;23:545–553. [Google Scholar]
- 85.Siriwoharn T, Wrolstad RE, Durst RW. Identification of ellagic acid in blackberry juice sediment. J Food Sci. 2006;70:C189–197. [Google Scholar]
- 86.Ştefanuţ MN, Cata A, Pop R, Tănasie C, Boc D, Ienaşcu I, Ordodi V. Anti-hyperglycemic effect of bilberry, blackberry and mulberry ultrasonic extracts on diabetic rats. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2013;68:378–384. doi: 10.1007/s11130-013-0380-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Stromberg I, Gemma C, Vila J, Bickford PC. Blueberry- and spirulina-enriched diets enhance striatal dopamine recovery and induce a rapid, transient microglia activation after injury of the rat nigrostriatal dopamine system. Exp Neurol. 2005;196:298–307. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2005.08.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Subash S, Essa MM, Al-Asmi A, Al-Adawi S, Vaishnav R, Guillemin GJ. Effect of dietary supplementation of dates in Alzheimer's disease APPsw/2576 transgenic mice on oxidative stress and antioxidant status. Nutr Neurosci. 2014a doi: 10.1179/1476830514Y.0000000134. Epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Subash S, Braidy N, Essa MM, Al-Buraiki Z, Vaishnav R, Al-Adawi S, Al-Asmi A, Guillemin GJ. Long Term (15 Months) Dietary Supplementation with Pomegranates from Oman Attenuates Cognitive and Behavioural Deficts in a Transgenic Mice Model of Alzheimer's Disease. Nutrition. 2014b doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2014.06.004. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2014.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Subash S, Essa MM, Braidy N, Al-Jabri A, Vaishnav R, Al-Adawi S, Al-Asmi A, Guillemin GJ. Consumption of fig fruits grown in Oman can improve memory, anxiety, and learning skills in a transgenic mice model of Alzheimer's disease. Nutr Neurosci. 2014c doi: 10.1179/1476830514Y.0000000131. Epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Sweeney MI, Kalt W, MacKinnon SL, Ashby J, Gottschall-Pass KT. Feeding rats diets enriched in lowbush blueberries for six weeks decreases ischemia-induced brain damage. Nutr Neurosci. 2002;5:427–431. doi: 10.1080/1028415021000055970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Szachowicz-Petelska B, Dobrzynska I, Skrzydlewska E, Figaszewski Z. Protective effect of blackcurrant on liver cell membrane of rats intoxicated with ethanol. J Membr Biol. 2012;245:191–200. doi: 10.1007/s00232-012-9429-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Szajdek A, Borowska JE. Bioactive compounds and health-promoting properties of berry fruits a review. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2008;63:147–156. doi: 10.1007/s11130-008-0097-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Tabart J, Franck T, Kevers C, Pincemail J, Serteyn D, Dommes J. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of Ribes nigrum extracts. Food Chemistry. 2012;131:1116–1122. [Google Scholar]
- 95.Tavares L, Figueira I, McDougall GJ, Vieira HL, Stewart D, Alves PM, Ferreira RB, Santos CN. Neuroprotective effects of digested polyphenols from wild blackberry species. Eur J Nutr. 2013;52:225–236. doi: 10.1007/s00394-012-0307-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Tulipani S, Romandini S, Busco F, Bompadre S, Mezzetti B, Battino M. Ascorbate, not urate, modulates the plasma antioxidant capacity after strawberry intake. Food Chem. 2009;117:181–188. [Google Scholar]
- 97.Uttara B, Singh AV, Zamboni P, Mahajan RT. Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases: a review of upstream and downstream antioxidant therapeutic options. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2009;7:65–74. doi: 10.2174/157015909787602823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Vepsalainen S, Koivisto H, Pekkarinen E, Mäkinen P, Dobson G, McDougall GJ, Stewart D, Haapasalo A, Karjalainen RO, Tanila H, Hiltunen M. Anthocyanin-enriched bilberry and blackcurrant extracts modulate amyloid precursor protein processing and alleviate behavioral abnormalities in the APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J Nutr Biochem. 2013;24:360–370. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2012.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Vitolo OV, Sant Angelo A, Costanzo V, Battaglia F, Arancio O, Shelanski M. Amyloid beta-peptide inhibition of the PKA/CREB pathway and long-term potentiation: reversibility by drugs that enhance cAMP signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:13217–13221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.172504199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Wang SY, Jiao H. Scavenging capacity of berry crops on superoxide radicals, hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radicals, and singlet oxygen. J Agric Food Chem. 2000;48:5677–5684. doi: 10.1021/jf000766i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Wang Y, Chang CF, Chou J, Chen HL, Deng X, Harvey BK, Cadet JL, Bickford PC. Dietary supplementation with blueberries, spinach, or spirulina reduces ischemic brain damage. Exp Neurol. 2005;193:75–84. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2004.12.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Williams CM, El Mohsen MA, Vauzour D, Rendeiro C, Butler LT, Ellis JA, Whiteman M, Spencer JP. Blueberry induced changes in spatial working memory correlate with changes in hippocampal CREB phosphorylation and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels. Free Radical Biol Med. 2008;45:295–305. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.04.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Wu XL, Gu LW, Prior RL, McKay S. Characterization of anthocyanins and proanthocyanidins in some cultivars of Ribes, Aronia, and Sambucus and their antioxidant capacity. J Agric Food Chem. 2004;52:7846–7856. doi: 10.1021/jf0486850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Xin J, Feinstein DL, Hejna MJ, Lorens SA, McGuire SO. Beneficial Effects of Blueberries in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J Agric Food Chem. 2012;60:5743–5748. doi: 10.1021/jf203611t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.You Q, Wang BW, Chen F, Huang ZL, Wang X, Luo PG. Comparison of anthocyanins and phenolics in organically and conventionally grown blueberries in selected cultivars. Food Chem. 2011;125:201–208. [Google Scholar]
- 106.Youdim KA, Joseph JA. A possible emerging role of phytochemicals in improving age-related neurological dysfunctions: a multiplicity of effects. Free Radic Biol Med. 2001;30:583–594. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(00)00510-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Youdim KA, Shukitt-Hale B, Martin A, Wang H, Denisova N, Bickford PC, Joseph JA. Short-term dietary supplementation of blueberry polyphenolics: beneficial effects on aging brain performance and peripheral tissue function. Nutr Neurosci. 2000;3:383–397. [Google Scholar]
- 108.Zheng Z, Lee JE, Yenari MA. Stroke: molecular mechanisms and potential targets for treatment. Curr Mol Med. 2003;3:361–372. doi: 10.2174/1566524033479717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Zimmerman G, Soreq H. Termination and beyond: acetylcholinesterase as a modulator of synaptic transmission. Cell Tissue Res. 2006;326:655–669. doi: 10.1007/s00441-006-0239-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]