A reverse-phase protein microarray-based screen identifies host signaling dynamics upon Burkholderia spp. infection - PubMed (original) (raw)
A reverse-phase protein microarray-based screen identifies host signaling dynamics upon Burkholderia spp. infection
Chih-Yuan Chiang et al. Front Microbiol. 2015.
Abstract
Burkholderia is a diverse genus of gram-negative bacteria that causes high mortality rate in humans, equines and cattle. The lack of effective therapeutic treatments poses serious public health threats. Developing insights toward host-Burkholderia spp. interaction is critical for understanding the pathogenesis of infection as well as identifying therapeutic targets for drug development. Reverse-phase protein microarray technology was previously proven to identify and characterize novel biomarkers and molecular signatures associated with infectious disease and cancer. In the present study, this technology was utilized to interrogate changes in host protein expression and phosphorylation events in macrophages infected with a collection of geographically diverse strains of Burkholderia spp. The expression or phosphorylation state of 25 proteins was altered during Burkholderia spp. infections of which eight proteins were selected for further characterization by immunoblotting. Increased phosphorylation of AMPK-α1, Src, and GSK3β suggested the importance of their roles in regulating Burkholderia spp. mediated innate immune response. Modulating the inflammatory response by perturbing their activities may provide therapeutic routes for future treatments.
Keywords: Burkholderia mallei; Burkholderia pseudomallei; lipopolysaccharide; reverse-phase protein microarrays.
Figures
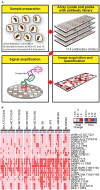
FIGURE 1
A schematic diagram of the experimental design and overview of the results. (A) Lysates harvested from Burkholderia spp. infected RAW264.7 macrophages were arrayed on nitrocellulose coated slides. Each slide was incubated with one primary antibody with a total of 114 antibodies in the library. The primary antibody was detected by biotin-labeled secondary antibody, which, in turn, was recognized by IRDye680 fluorophore conjugated streptavidin. Signals were acquired, quantified, and analyzed according to materials and methods section. (B) RAW264.7 macrophages were infected at multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 10 with indicated Burkholderia spp. for 0.5, 1, 4, and 8 h. Lysates were harvested and subjected to reverse-phase protein microarray (RPMA) studies. A heat map of fold changes over untreated samples is depicted. Experiments were performed on two independent days and data from these repeat studies are shown.
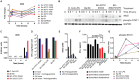
FIGURE 2
Induction of iNOS and activation of STAT1 in response to Burkholderia spp. infection. A) The expression pattern of iNOS obtained from RPMA study. (B) RAW264.7 macrophages were infected with Burkholderia pseudomallei (Bp) E8, Burkholderia mallei (Bm) 23344, and Bm 2002721278 at MOI of 10, or treated with LPS at 100 ng/ml. Samples were collected at 0.5, 1, 4, and 8 h post treatments. The amount of iNOS and phosphorylated STAT1 was evaluated by immunoblotting, followed by (C) densitometric quantification of iNOS. N.D. indicates signal was not detectable. (D) Colony forming unit (CFU) was determined 3 and 24 h post Burkholderia spp. infection of RAW264.7 cells, with and without aminoguanidine (AG) treatment. Culture supernatants harvested at 24 h post infection from mock-infected and Burkholderia spp. infected RAW264.7 macrophages were assayed for the production of (E) nitrite and (F) IFN-β. _P_-values between species were calculated by Mann–Whitney U test. ∗∗∗_p_-value < 0.001. (G) densitometric quantification of phosphorylated STAT1. Immunoblots in Figures 2–4 were performed concurrently from the same samples and loading control, GAPDH. The immunoblot data is representative of three independent trials. Bacterial CFUs represent the average of two biological replicates. Nitrite and IFN-β levels were computed by averaging three biological replicates.
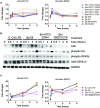
FIGURE 3
Burkholderia spp. induces NF-κB mediated responses. (A) The phosphorylation state of indicated proteins acquired by RPMA. (B) Samples were prepared as described in Figure 2B. The expression or phosphorylation state of indicated proteins was evaluated by immunoblotting, followed by (C) densitometry quantification. Immunoblots in Figures 2–4 were performed concurrently with the same sample and loading control, GAPDH. The immunoblot data is representative of three independent trials.
FIGURE 4
AMPK-α1 is phosphorylated upon Burkholderia spp. infection. (A) The phosphorylation state of AMPK-α1 acquired by RPMA. (B) Samples were prepared as described in Figure 2B. The phosphorylation state of AMPK-α1 was evaluated by immunoblotting, followed by (C) densitometry quantification. Immunoblots in Figures 2–4 were performed concurrently with the same sample and loading control, GAPDH. The immunoblot data is representative of three independent trials.
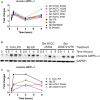
FIGURE 5
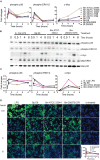
Activation of MAPK pathway components upon Burkholderia spp. infection. (A) The expression and phosphorylation states of indicated proteins acquired by RPMA. (B) Samples were prepared as described in Figure 2B. The expression and phosphorylation states of indicated proteins were evaluated by immunoblotting, followed by (C) densitometry quantification. (D) RAW264.7 macrophages were stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or infected with Burkholderia spp. at indicated time points. Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 was visualized by indirect immuno-fluorescent staining. Expression of phosphorylated ERK1/2 was subsequently quantified using the Opera confocal system. Phosphorylated ERK1/2 is pseudocolored green and nuclear stain is colored blue. The immunoblot data is representative of three independent trials.
FIGURE 6
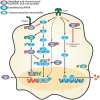
Activation of signaling cascades in response to Burkholderia spp. infection. A signaling network was constructed based on current knowledge of signal transduction pathways and our survey of host protein expression and phosphorylation profiles in response to Burkholderia spp. infection. Proteins identified in the RPMA screen (green circle) and/or characterized by immunoblotting are designated by color coding (gold circle, confirmed by immunoblot; red, confirmed by RPMA and immunoblot). Red bold arrow represents potential therapeutic routes.
Similar articles
- Innate immune response to Burkholderia mallei.
Saikh KU, Mott TM. Saikh KU, et al. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2017 Jun;30(3):297-302. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000000362. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28177960 Free PMC article. Review. - Characterization of the murine macrophage response to infection with virulent and avirulent Burkholderia species.
Chiang CY, Ulrich RL, Ulrich MP, Eaton B, Ojeda JF, Lane DJ, Kota KP, Kenny TA, Ladner JT, Dickson SP, Kuehl K, Raychaudhuri R, Sun M, Bavari S, Wolcott MJ, Covell D, Panchal RG. Chiang CY, et al. BMC Microbiol. 2015 Nov 6;15:259. doi: 10.1186/s12866-015-0593-3. BMC Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26545875 Free PMC article. - PKC-η-MARCKS Signaling Promotes Intracellular Survival of Unopsonized Burkholderia thailandensis.
Micheva-Viteva SN, Shou Y, Ganguly K, Wu TH, Hong-Geller E. Micheva-Viteva SN, et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Jun 7;7:231. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00231. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28638804 Free PMC article. - Characterization of cellular immune response and innate immune signaling in human and nonhuman primate primary mononuclear cells exposed to Burkholderia mallei.
Alam S, Amemiya K, Bernhards RC, Ulrich RG, Waag DM, Saikh KU. Alam S, et al. Microb Pathog. 2015 Jan;78:20-8. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2014.11.009. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Microb Pathog. 2015. PMID: 25450887 - Molecular insights into Burkholderia pseudomallei and Burkholderia mallei pathogenesis.
Galyov EE, Brett PJ, DeShazer D. Galyov EE, et al. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2010;64:495-517. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.112408.134030. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20528691 Review.
Cited by
- Proteomic Analysis of Non-human Primate Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells During Burkholderia mallei Infection Reveals a Role of Ezrin in Glanders Pathogenesis.
Chiang CY, Zhong Y, Ward MD, Lane DJ, Kenny T, Rosario-Acevedo R, Eaton BP, Treviño SR, Chance TB, Hu M, Worsham PL, Waag DM, Moore RT, Cazares LH, Cote CK, Zhou Y, Panchal RG. Chiang CY, et al. Front Microbiol. 2021 Apr 22;12:625211. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.625211. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33967974 Free PMC article. - Mitigating the Impact of Antibacterial Drug Resistance through Host-Directed Therapies: Current Progress, Outlook, and Challenges.
Chiang CY, Uzoma I, Moore RT, Gilbert M, Duplantier AJ, Panchal RG. Chiang CY, et al. mBio. 2018 Jan 30;9(1):e01932-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01932-17. mBio. 2018. PMID: 29382729 Free PMC article. Review. - Innate immune response to Burkholderia mallei.
Saikh KU, Mott TM. Saikh KU, et al. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2017 Jun;30(3):297-302. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000000362. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28177960 Free PMC article. Review. - Proteomic discovery of host kinase signaling in bacterial infections.
Richter E, Mostertz J, Hochgräfe F. Richter E, et al. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2016 Oct;10(9-10):994-1010. doi: 10.1002/prca.201600035. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2016. PMID: 27440122 Free PMC article. Review. - Rapid and Sensitive Multiplex Detection of Burkholderia pseudomallei-Specific Antibodies in Melioidosis Patients Based on a Protein Microarray Approach.
Kohler C, Dunachie SJ, Müller E, Kohler A, Jenjaroen K, Teparrukkul P, Baier V, Ehricht R, Steinmetz I. Kohler C, et al. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016 Jul 18;10(7):e0004847. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004847. eCollection 2016 Jul. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016. PMID: 27427979 Free PMC article.
References
- Alam S., Amemiya K., Bernhards R. C., Ulrich R. G., Waag D. M., Saikh K. U. (2014). Characterization of cellular immune response and innate immune signaling in human and nonhuman primate primary mononuclear cells exposed to Burkholderia mallei. Microb. Pathog. 78 20–28. 10.1016/j.micpath.2014.11.009 - DOI - PubMed
- Alem F., Yao K., Lane D., Calvert V., Petricoin E. F., Kramer L., et al. (2015). Host response during Yersinia pestis infection of human bronchial epithelial cells involves negative regulation of autophagy and suggests a modulation of survival-related and cellular growth pathways. Front. Microbiol. 6:50 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00050 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous