strategic planning (original) (raw)
What is strategic planning?
Strategic planning is a process in which an organization's leaders define their vision for the future and identify their organization's goals and objectives. The process includes establishing the sequence in which those goals should be realized so the organization can reach its stated vision.
Strategic planning is forward looking. It differs from traditional business planning, which typically focuses on short-term, tactical goals, such as how a budget is divided up. The time covered by a business plan can range from several months to several years.
The product of strategic planning is a strategic plan. It is often reflected in a plan document or other media. These plans can be easily shared, understood and followed by various people including employees, customers, business partners and investors.
Organizations conduct strategic planning periodically to consider the effect of changing business, industry, and legal and regulatory conditions. A strategic plan may be updated and revised at that time to reflect any strategic changes.

Chief information officers use strategic planning to determine how IT can be best used to further an organization's business goals.
Why is strategic planning important?
Businesses need direction and organizational goals to work toward. Strategic planning offers that type of guidance. Essentially, a strategic plan is a roadmap to get to business goals. Without such guidance, there is no way to tell whether a business is on track to reach its goals.
The following four aspects of strategy development are worth attention:
- The mission. Strategic planning starts with a mission that offers a company a sense of purpose and direction. The organization's mission statement describes who it is, what it does and where it wants to go. Missions are typically broad but actionable. For example, a business in the education industry might seek to be a leader in online virtual educational tools and services.
- The goals. Strategic planning involves selecting goals. Most planning uses SMART goals -- specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound -- or other objectively measurable goals. Measurable goals are important because they enable business leaders to determine how well the business is performing against goals and the overall mission. Goal setting for the fictitious educational business might include releasing the first version of a virtual classroom platform within two years or increasing sales of an existing tool by 30% in the next year.
- Alignment with short-term goals. Strategic planning relates directly to short-term, tactical business planning and can help business leaders with everyday decision-making that better aligns with business strategy. For the fictitious educational business, leaders might choose to make strategic investments in communication and collaboration technologies, such as virtual classroom software and services but decline opportunities to establish physical classroom facilities.
- Evaluation and revision. Strategic planning helps business leaders periodically evaluate progress against the plan and make changes or adjustments in response to changing conditions. For example, a business may seek a global presence, but legal and regulatory restrictions could emerge that affect its ability to operate in certain geographic regions. As a result, business leaders might have to revise the strategic plan to redefine objectives or change progress metrics.
Modern considerations for strategic planning
While strategic planning has been a cornerstone of organizational management for decades, the landscape of strategic planning has undergone significant shifts in recent years.
Innovations in technology and socioeconomic upheavals, most notably the COVID-19 pandemic, have fundamentally altered the calculus of strategic planning. These modern considerations underscore the evolving nature of strategic planning in today's world.
The importance of strategic planning in an evolving society
The advent of the COVID-19 pandemic has starkly highlighted the importance of flexibility and resilience in strategic planning. Organizations worldwide have faced the stark reality that the ability to pivot quickly in response to rapidly changing external conditions is not just advantageous but essential for survival.
This period has reinforced the concept that strategic plans must be living documents -- adaptable, dynamic and responsive to unforeseen challenges and opportunities. The traditional view of strategic planning as a set of fixed guidelines has given way to an understanding of strategic plans as fluid frameworks that guide organizational response to a volatile environment.
Embracing digital transformation
The swift pace of technological evolution has made the incorporation of digital transformation strategies a critical component of strategic planning.
Digital capabilities are now at the heart of operational success and competitive differentiation. Organizations can integrate data analytics and AI into strategic planning processes to help them innovate, boost efficiency, enhance customer experiences and maintain a competitive edge.
Agility and adaptability
Modern strategic planning is characterized by an emphasis on agility and the capacity for rapid adaptation. In an era marked by constant change, organizations must be prepared to navigate through a sea of change, adjusting their course in response to market dynamics and environmental shifts.
This necessitates a continuous reassessment of the strategic plan and a willingness to recalibrate goals and tactics in alignment with the evolving external landscape. The agility to adapt strategic priorities swiftly is now a critical competency for organizational resilience and long-term success.
Sustainability and social responsibility
Sustainability and social responsibility have emerged as central considerations in strategic planning. As societal expectations evolve, there is an increasing demand for organizations to align their strategies with environmental, social and governance (ESG) criteria.
This alignment reflects a broader commitment to sustainable development and responsible corporate citizenship. Incorporating sustainability and social responsibility into strategic planning not only meets regulatory and societal expectations but also opens new avenues for innovation and connects organizations with eco-conscious consumers and stakeholders.
Cultivating organizational culture and employee engagement
A strategic plan that resonates with an organization's culture and actively engages employees is more likely to succeed. Cultivating a supportive culture that aligns with the strategic vision is crucial for fostering organizational alignment and buy-in.
Engaging employees in the strategic planning process instills a sense of ownership and commitment to the organization's goals, thereby driving collective effort toward their realization. Modern strategic planning recognizes the value of employee engagement and organizational culture as foundational elements that underpin the successful implementation of strategic objectives.
What are the steps in the strategic planning process?
There are myriad different ways to approach strategic planning depending on the type of business and the granularity required. Most strategic planning cycles can be summarized in these five steps:
Identify. A strategic planning cycle starts with the determination of a business's current strategic position. This is where stakeholders use the existing strategic plan -- including the mission statement and long-term strategic goals -- to perform assessments of the business and its environment. These assessments can include a needs assessment or a SWOT analysis (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats analysis) to understand the state of the business and the path ahead.
Prioritize. Next, strategic planners set objectives and initiatives that line up with the company mission and goals and will move the business toward achieving its goals. There may be many potential goals, so planning prioritizes the most important, relevant and urgent ones. Goals may include a consideration of resource requirements -- such as budgets and equipment -- and they often involve a timeline and business metrics or KPIs for measuring progress.
Develop. This is the main thrust of strategic planning in which stakeholders collaborate to formulate the steps or tactics necessary to attain a stated strategic objective. This may involve creating numerous short-term tactical business plans that fit into the overarching strategy. Stakeholders involved in plan development use various tools such as a strategy map to help visualize and tweak the plan. Developing the plan may involve cost and opportunity tradeoffs that reflect business priorities. Developers may reject some initiatives if they don't support the long-term strategy.
Implement. Once the strategic plan is developed, it's time to put it in motion. This requires clear communication across the organization to set responsibilities, make investments, adjust policies and processes, and establish measurement and reporting. Implementation typically includes strategic management with regular strategic reviews to ensure that plans stay on track.
Update. A strategic plan is periodically reviewed and revised to adjust priorities and reevaluate goals as business conditions change and new opportunities emerge. Quick reviews of metrics can happen quarterly, and adjustments to the strategic plan can occur annually. Stakeholders may use balanced scorecards and other tools to assess performance against goals.

A balanced scorecard focuses on four key parts of a business's strategic plan: financial, customer, internal business processes, and learning and growth.
Who does the strategic planning in a business?
A committee typically leads the strategic planning process. Planning experts recommend the committee include representatives from all areas within the enterprise and work in an open and transparent way where information is documented from start to finish.
The committee researches and gathers the information needed to understand the organization's status and factors that will affect it in the future. The committee should solicit input and feedback to validate or challenge its assessment of the information.
The committee can opt to use one of many methodologies or strategic frameworks that have been developed to guide leaders through this process. These methodologies take the committee through a series of steps that include an analysis or assessment, strategy formulation, and the articulation and communication of the actions needed to move the organization toward its strategic vision.
The committee creates benchmarks that will enable the organization to determine how well it is performing against its goals as it implements the strategic plan. The planning process should also identify which executives are accountable for ensuring that benchmarking activities take place at planned times and that specific objectives are met.
How often should strategic planning be done?
There are no uniform requirements to dictate the frequency of a strategic planning cycle. However, there are common approaches.
- Quarterly reviews. Once per quarter is usually a convenient time frame to revisit assumptions made in the planning process and gauge progress by checking metrics against the plan.
- Annual reviews. A yearly review lets business leaders assess metrics for the previous four quarters and make informed adjustments to the plan.
Timetables are always subject to change. Timing should be flexible and tailored to the needs of a company. For example, a startup in a dynamic industry might revisit its strategic plan monthly. A mature business in a well-established industry might opt to revisit the plan less frequently.
Types of strategic plans
Strategic planning activities typically focus on three areas: business, corporate or functional. They break out as follows:
- Business. A business-centric strategic plan focuses on the competitive aspects of the organization -- creating competitive advantages and opportunities for growth. These plans adopt a mission evaluating the external business environment, setting goals, and allocating financial, human and technological resources to meet those goals. This is the typical strategic plan and the main focus of this article.
- Corporate. A corporate-centric plan defines how the company works. It focuses on organizing and aligning the structure of the business, its policies and processes and its senior leadership to meet desired goals. For example, the management of a research and development skunkworks might be structured to function dynamically and on an ad hoc basis. It would look different from the management team in finance or HR.
- Functional. Function-centric strategic plans fit within corporate-level strategies and provide a granular examination of specific departments or segments such as marketing, HR, finance and development. Functional plans focus on policy and process -- such as security and compliance -- while setting budgets and resource allocations.
In most cases, a strategic plan will involve elements of all three focus areas. But the plan may lean toward one focus area depending on the needs and type of business.
What is strategic management?
Organizations that are best at aligning their actions with their strategic plans engage in strategic management. A strategic management process establishes ongoing practices to ensure that an organization's processes and resources support the strategic plan's mission and vision statement.
In simple terms, strategic management is the implementation of the strategy. As such, strategic management is sometimes referred to as strategy execution. Strategy execution involves identifying benchmarks, allocating financial and human resources and providing leadership to realize established goals.
Strategic management may involve a prescriptive or descriptive approach. A prescriptive approach focuses on how strategies should be created. It often uses an analytical approach -- such as SWOT or balanced scorecards -- to account for risks and opportunities. A descriptive approach focuses on how strategies should be implemented and typically relies on general guidelines or principles.
Given the similarities between strategic planning and strategic management, the two terms are sometimes used interchangeably.
What is a strategy map?
A strategy map is a planning tool or template used to help stakeholders visualize the complete strategy of a business as one interrelated graphic. These visualizations offer a powerful way for understanding and reviewing the cause-and-effect relationships among the elements of a business strategy.
While a map can be drawn in a number of ways, all strategy maps focus on four major business areas or categories: financial, customer, internal business processes, and learning and growth. Goals sort into those four areas, and relationships or dependencies among those goals can be established.
For example, a strategy map might include a financial goal of reducing costs and a business process goal to improve operational efficiency. These two goals are related and can help stakeholders understand that tasks such as improving operational workflows can reduce company costs and meet two elements of the strategic plan.
A strategy map can help translate overarching goals into an action plan and goals that can be aligned and implemented.
Strategy mapping can also help to identify strategic challenges that might not be obvious. For example, one learning and growth goal may be to increase employee expertise but that may expose unexpected challenges in employee retention and compensation, which affects cost reduction goals.
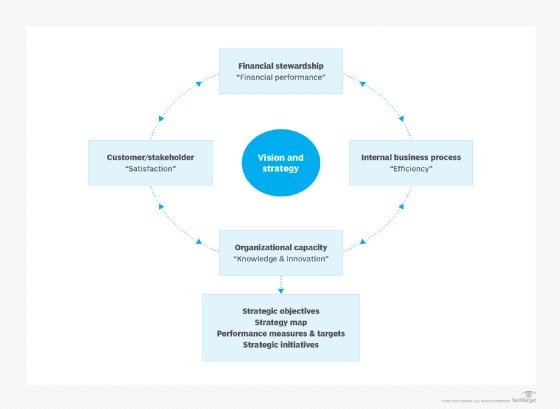
Strategy mapping as part of strategic planning assists organizations by helping detect strategic challenges that might otherwise not be obvious.
Benefits of strategic planning
Effective strategic planning has many benefits. It forces organizations to be aware of the future state of opportunities and challenges. It also forces them to anticipate risks and understand what resources will be needed to seize opportunities and overcome strategic issues.
Strategic planning also gives individuals a sense of direction and marshals them around a common mission. It creates standards and accountability. Strategic planning can enhance operational plans and efficiency. It also helps organizations limit time spent on crisis management, where they're reacting to unexpected changes that they failed to anticipate and prepare for.
Information technology is a key part of developing an effective strategic plan. Look at these eight free IT strategic planning templates that can help make IT a driving force in a business. Learn how to assess an organization's needs and implement a technology strategy and see how to set business goals in these step-by-step guides.