Augmented reality vs. virtual reality vs. mixed reality (original) (raw)
Learn about AR vs. VR vs. MR as well as how companies in various industries are using these extended reality technologies to potentially improve their operations.
Advancements in immersive technologies continue, changing how various industries operate. Extended reality can potentially benefit companies in various ways, so IT leaders should learn how the technologies can potentially apply to their industry.
Understanding the differences between augmented reality vs. virtual reality vs. mixed reality can seem challenging, but the technologies' appearances in pop culture mean that many people are familiar with them already. Each immersive technology can potentially improve the digital experiences of a company's consumers and employees.
Here's more about each type of technology as well as some potential real-life use cases and applications.
What is augmented reality?
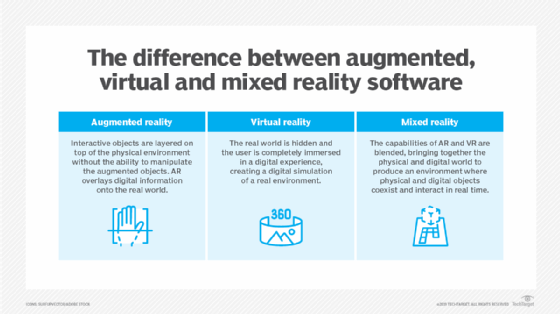
Augmented reality (AR) layers a digital display onto the view of a user's physical surroundings.
The screen in Tony Stark's Iron Man helmet is the perfect example. It shows important information, such as the distance of other objects, his altitude and how fast an opponent is moving.
Another entertainment-based AR example is the popular app Pokemon Go, which allows players to use their smartphones to interact with digital characters in the real world.
However, augmented reality has also crossed over to the business world. Some manufacturers are using AR to train workers and perform maintenance.
Use cases for augmented reality
- An augmented reality headset can display useful information in the manufacturing setting, such as a machine's model and serial number and its instruction manual and repair procedures. The AR headset can synchronize with a tablet or computer so a supervisor can see what the worker is seeing and offer verbal instructions on how to use or repair a piece of equipment if needed. The AR headset can also display animated instructions for how to perform a certain task or repair a piece of machinery.
- Restaurants can give diners the option of viewing menu items using AR technology when ordering in-person or via their mobile phones. AR can give a customer more insight into details about the food, like the size of a particular order, potentially improving customer satisfaction. AR could also potentially save restaurants money because of a reduced need for paper menu reprints.
- AR can also potentially improve warehouse logistics. Warehouse workers can use AR smart glasses to discover the shortest route within the warehouse to pick an item for a customer. The smart glasses can then notify the employee that they've arrived at the correct location and can confirm the physical location of items on the shelves.
What is virtual reality?
Virtual reality (VR) is a 3D computer-simulated environment where users can interact with digital objects, either by clicking a mouse or using wearable devices, such as headsets and special gloves.
Hollywood's version of virtual reality -- as seen in films like The Matrix and Ready Player One -- is a fully immersive, computer-generated world that perfectly mimics all the physical sensations of the real world. While we're a long way off from being able to experience taste, touch and smell in VR, it's still a useful -- if only partially immersive -- technology.
Some consumer VR products include Google's Cardboard, Meta's Oculus Rift and Sony's PlayStation VR2.
Use cases for virtual reality
- Manufacturers can use a special virtual reality headset to analyze equipment, evaluate production processes and train workers. For example, workers can virtually re-create the manufacturing process and study it in a VR simulation to see if there is a more efficient way to run certain machines.
- Manufacturers can also create a virtual model, or digital twin, of a specific product to monitor its lifecycle and gain insight into its inner workings.
- Healthcare can potentially find uses for VR. The technology can be helpful for exposure therapy for veterans with PTSD and for rehabilitation treatments for patients with neurological disorders.
Key differences between AR and VR
Confusion can arise over the difference between augmented reality and virtual reality. Some of the key areas where AR and VR differ include the following:
- Equipment. Smartphones can deliver AR experiences, but VR requires a headset, adding to a user's upfront investment.
- Environment. AR allows a user to connect a virtual world to the real world, while VR users inhabit a fictional world. A Pokemon Go user sees creatures appearing in the real world -- for example, an imaginary Pikachu standing next to a real tree -- while a user playing a VR video game sees only the fictional VR world while wearing the headset.
- Interactions. AR involves the virtual world and the real world coexisting together, while VR involves the user participating in a completely virtual world. For example, a VR game could place a user in the middle of the French Revolution to participate in the Storming of the Bastille. Their in-game interactions all take place within the fictional world.
What is mixed reality?
Mixed reality (MR) takes augmented reality a step further and allows users to manipulate and interact with virtual objects and information. A mixed reality headset displays information that aligns or synchronizes with specific areas in users' physical environments that they can then interact with in a digital environment. For example, an MR headset can project a virtual keyboard onto a desk that the wearer can then use to type.
The key difference between mixed reality and augmented reality is the user's ability to interact with the digital display. For example, a technician wearing an AR headset can view the holographic image of the engine but can't virtually take it apart.
Use cases for mixed reality
- A technician wearing an MR headset can view a holographic image of a piece of equipment, such as an engine, and take it apart virtually to examine its inner workings. Using MR to do so saves time and doesn't require the tools that the technician would need to inspect the physical equipment.
- Retail merchandisers can use MR to help them visualize a store layout before carrying it out in the real world. A hologram can display how it will look to add, for example, a promotional display at the front of the store.
- Students can potentially enhance their learning by interacting with virtual content through 3D projections and simulations. MR helps reinforce educational concepts without the risk that real-life learning can bring. For example, a student learning the skills for working in a museum can use MR to practice cleaning an ancient artifact without potentially damaging a valuable item.
What does extended reality mean?
Extended reality, or XR, is a computer-generated experience that unites aspects of both the real and virtual worlds. XR encompasses augmented reality, virtual reality and mixed reality and can also include other immersive technology, such as the metaverse.
Users access the metaverse through XR.
 By: Martin Schwirn
By: Martin Schwirn  augmented reality (AR)
augmented reality (AR)  By: Alexander Gillis
By: Alexander Gillis  What is a VR developer and how do you become one?
What is a VR developer and how do you become one?  By: Esther Shein
By: Esther Shein  Qualcomm claims new wave of mixed reality experiences with Snapdragon XR2+ Gen 2
Qualcomm claims new wave of mixed reality experiences with Snapdragon XR2+ Gen 2  By: Joe O’Halloran
By: Joe O’Halloran