MySQL :: MySQL 5.7 Reference Manual :: 14.5.1 Buffer Pool (original) (raw)
14.5.1 Buffer Pool
The buffer pool is an area in main memory whereInnoDB caches table and index data as it is accessed. The buffer pool permits frequently used data to be accessed directly from memory, which speeds up processing. On dedicated servers, up to 80% of physical memory is often assigned to the buffer pool.
For efficiency of high-volume read operations, the buffer pool is divided into pages that can potentially hold multiple rows. For efficiency of cache management, the buffer pool is implemented as a linked list of pages; data that is rarely used is aged out of the cache using a variation of the least recently used (LRU) algorithm.
Knowing how to take advantage of the buffer pool to keep frequently accessed data in memory is an important aspect of MySQL tuning.
Buffer Pool LRU Algorithm
The buffer pool is managed as a list using a variation of the LRU algorithm. When room is needed to add a new page to the buffer pool, the least recently used page is evicted and a new page is added to the middle of the list. This midpoint insertion strategy treats the list as two sublists:
- At the head, a sublist of new (“young”) pages that were accessed recently
- At the tail, a sublist of old pages that were accessed less recently
Figure 14.2 Buffer Pool List
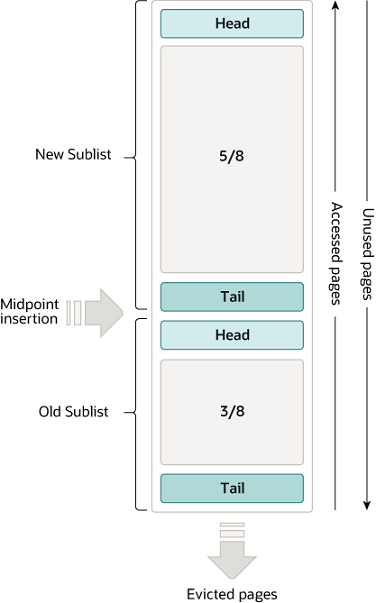
The algorithm keeps frequently used pages in the new sublist. The old sublist contains less frequently used pages; these pages are candidates for eviction.
By default, the algorithm operates as follows:
- 3/8 of the buffer pool is devoted to the old sublist.
- The midpoint of the list is the boundary where the tail of the new sublist meets the head of the old sublist.
- When
InnoDBreads a page into the buffer pool, it initially inserts it at the midpoint (the head of the old sublist). A page can be read because it is required for a user-initiated operation such as an SQL query, or as part of aread-ahead operation performed automatically byInnoDB. - Accessing a page in the old sublist makes it“young”, moving it to the head of the new sublist. If the page was read because it was required by a user-initiated operation, the first access occurs immediately and the page is made young. If the page was read due to a read-ahead operation, the first access does not occur immediately and might not occur at all before the page is evicted.
- As the database operates, pages in the buffer pool that are not accessed “age” by moving toward the tail of the list. Pages in both the new and old sublists age as other pages are made new. Pages in the old sublist also age as pages are inserted at the midpoint. Eventually, a page that remains unused reaches the tail of the old sublist and is evicted.
By default, pages read by queries are immediately moved into the new sublist, meaning they stay in the buffer pool longer. A table scan, performed for a mysqldump operation or aSELECT statement with noWHERE clause, for example, can bring a large amount of data into the buffer pool and evict an equivalent amount of older data, even if the new data is never used again. Similarly, pages that are loaded by the read-ahead background thread and accessed only once are moved to the head of the new list. These situations can push frequently used pages to the old sublist where they become subject to eviction. For information about optimizing this behavior, seeSection 14.8.3.3, “Making the Buffer Pool Scan Resistant”, andSection 14.8.3.4, “Configuring InnoDB Buffer Pool Prefetching (Read-Ahead)”.
InnoDB Standard Monitor output contains several fields in the BUFFER POOL AND MEMORY section regarding operation of the buffer pool LRU algorithm. For details, see Monitoring the Buffer Pool Using the InnoDB Standard Monitor.
Buffer Pool Configuration
You can configure the various aspects of the buffer pool to improve performance.
- Ideally, you set the size of the buffer pool to as large a value as practical, leaving enough memory for other processes on the server to run without excessive paging. The larger the buffer pool, the more
InnoDBacts like an in-memory database, reading data from disk once and then accessing the data from memory during subsequent reads. SeeSection 14.8.3.1, “Configuring InnoDB Buffer Pool Size”. - On 64-bit systems with sufficient memory, you can split the buffer pool into multiple parts to minimize contention for memory structures among concurrent operations. For details, see Section 14.8.3.2, “Configuring Multiple Buffer Pool Instances”.
- You can keep frequently accessed data in memory regardless of sudden spikes of activity from operations that would bring large amounts of infrequently accessed data into the buffer pool. For details, seeSection 14.8.3.3, “Making the Buffer Pool Scan Resistant”.
- You can control how and when to perform read-ahead requests to prefetch pages into the buffer pool asynchronously in anticipation that the pages are needed soon. For details, seeSection 14.8.3.4, “Configuring InnoDB Buffer Pool Prefetching (Read-Ahead)”.
- You can control when background flushing occurs and whether or not the rate of flushing is dynamically adjusted based on workload. For details, seeSection 14.8.3.5, “Configuring Buffer Pool Flushing”.
- You can configure how
InnoDBpreserves the current buffer pool state to avoid a lengthy warmup period after a server restart. For details, seeSection 14.8.3.6, “Saving and Restoring the Buffer Pool State”.
Monitoring the Buffer Pool Using the InnoDB Standard Monitor
InnoDB Standard Monitor output, which can be accessed usingSHOW ENGINE INNODB STATUS, provides metrics regarding operation of the buffer pool. Buffer pool metrics are located in the BUFFER POOL AND MEMORY section ofInnoDB Standard Monitor output:
----------------------
BUFFER POOL AND MEMORY
----------------------
Total large memory allocated 2198863872
Dictionary memory allocated 776332
Buffer pool size 131072
Free buffers 124908
Database pages 5720
Old database pages 2071
Modified db pages 910
Pending reads 0
Pending writes: LRU 0, flush list 0, single page 0
Pages made young 4, not young 0
0.10 youngs/s, 0.00 non-youngs/s
Pages read 197, created 5523, written 5060
0.00 reads/s, 190.89 creates/s, 244.94 writes/s
Buffer pool hit rate 1000 / 1000, young-making rate 0 / 1000 not
0 / 1000
Pages read ahead 0.00/s, evicted without access 0.00/s, Random read
ahead 0.00/s
LRU len: 5720, unzip_LRU len: 0
I/O sum[0]:cur[0], unzip sum[0]:cur[0] The following table describes buffer pool metrics reported by theInnoDB Standard Monitor.
Per second averages provided in InnoDB Standard Monitor output are based on the elapsed time sinceInnoDB Standard Monitor output was last printed.
Table 14.2 InnoDB Buffer Pool Metrics
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Total memory allocated | The total memory allocated for the buffer pool in bytes. |
| Dictionary memory allocated | The total memory allocated for the InnoDB data dictionary in bytes. |
| Buffer pool size | The total size in pages allocated to the buffer pool. |
| Free buffers | The total size in pages of the buffer pool free list. |
| Database pages | The total size in pages of the buffer pool LRU list. |
| Old database pages | The total size in pages of the buffer pool old LRU sublist. |
| Modified db pages | The current number of pages modified in the buffer pool. |
| Pending reads | The number of buffer pool pages waiting to be read into the buffer pool. |
| Pending writes LRU | The number of old dirty pages within the buffer pool to be written from the bottom of the LRU list. |
| Pending writes flush list | The number of buffer pool pages to be flushed during checkpointing. |
| Pending writes single page | The number of pending independent page writes within the buffer pool. |
| Pages made young | The total number of pages made young in the buffer pool LRU list (moved to the head of sublist of “new” pages). |
| Pages made not young | The total number of pages not made young in the buffer pool LRU list (pages that have remained in the “old” sublist without being made young). |
| youngs/s | The per second average of accesses to old pages in the buffer pool LRU list that have resulted in making pages young. See the notes that follow this table for more information. |
| non-youngs/s | The per second average of accesses to old pages in the buffer pool LRU list that have resulted in not making pages young. See the notes that follow this table for more information. |
| Pages read | The total number of pages read from the buffer pool. |
| Pages created | The total number of pages created within the buffer pool. |
| Pages written | The total number of pages written from the buffer pool. |
| reads/s | The per second average number of buffer pool page reads per second. |
| creates/s | The average number of buffer pool pages created per second. |
| writes/s | The average number of buffer pool page writes per second. |
| Buffer pool hit rate | The buffer pool page hit rate for pages read from the buffer pool vs from disk storage. |
| young-making rate | The average hit rate at which page accesses have resulted in making pages young. See the notes that follow this table for more information. |
| not (young-making rate) | The average hit rate at which page accesses have not resulted in making pages young. See the notes that follow this table for more information. |
| Pages read ahead | The per second average of read ahead operations. |
| Pages evicted without access | The per second average of the pages evicted without being accessed from the buffer pool. |
| Random read ahead | The per second average of random read ahead operations. |
| LRU len | The total size in pages of the buffer pool LRU list. |
| unzip_LRU len | The length (in pages) of the buffer pool unzip_LRU list. |
| I/O sum | The total number of buffer pool LRU list pages accessed. |
| I/O cur | The total number of buffer pool LRU list pages accessed in the current interval. |
| I/O unzip sum | The total number of buffer pool unzip_LRU list pages decompressed. |
| I/O unzip cur | The total number of buffer pool unzip_LRU list pages decompressed in the current interval. |
Notes:
- The
youngs/smetric is applicable only to old pages. It is based on the number of page accesses. There can be multiple accesses for a given page, all of which are counted. If you see very lowyoungs/svalues when there are no large scans occurring, consider reducing the delay time or increasing the percentage of the buffer pool used for the old sublist. Increasing the percentage makes the old sublist larger so that it takes longer for pages in that sublist to move to the tail, which increases the likelihood that those pages are accessed again and made young. SeeSection 14.8.3.3, “Making the Buffer Pool Scan Resistant”. - The
non-youngs/smetric is applicable only to old pages. It is based on the number of page accesses. There can be multiple accesses for a given page, all of which are counted. If you do not see a highernon-youngs/svalue when performing large table scans (and a higheryoungs/svalue), increase the delay value. SeeSection 14.8.3.3, “Making the Buffer Pool Scan Resistant”. - The
young-makingrate accounts for all buffer pool page accesses, not just accesses for pages in the old sublist. Theyoung-makingrate andnotrate do not normally add up to the overall buffer pool hit rate. Page hits in the old sublist cause pages to move to the new sublist, but page hits in the new sublist cause pages to move to the head of the list only if they are a certain distance from the head. not (young-making rate)is the average hit rate at which page accesses have not resulted in making pages young due to the delay defined byinnodb_old_blocks_time not being met, or due to page hits in the new sublist that did not result in pages being moved to the head. This rate accounts for all buffer pool page accesses, not just accesses for pages in the old sublist.
Buffer pool server status variables and theINNODB_BUFFER_POOL_STATS table provide many of the same buffer pool metrics found inInnoDB Standard Monitor output. For more information, seeExample 14.10, “Querying the INNODB_BUFFER_POOL_STATS Table”.