General size matrix/matrix multiplication (original) (raw)
Next: Inverting a general size Up: General size matrices Previous: General size matrix/vector multiplication Contents
General size matrix/matrix multiplication
Similar options are available to matrix/matrix multiplication as with matrix/vector multiplication, with the added complication that either or both if the matrices may have an implicit transpose or (for square matrices) inverse applied to them. Firstly we list the routines available when both input matrices are general rectangular matrices. In this case only implicit transpose is of relevance to us, and we can write the operations we need to implement as
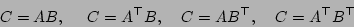
To right-multiply a matrix 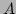 by another matrix
by another matrix 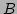 , with all the above transpose combinations, the Gandalf routines are
, with all the above transpose combinations, the Gandalf routines are
Gan_Matrix mA, mB, mC; /* matrices A, B & C */
/* ... create and fill matrices A, B, create matrix C ... */
gan_mat_rmult_q ( &mA, &mB, &mC ); /* C = A*B, OR */
gan_mat_rmultT_q ( &mA, &mB, &mC ); /* C = A*B^T, OR */
gan_matT_rmult_q ( &mA, &mB, &mC ); /* C = A^T*B, OR */
gan_matT_rmultT_q ( &mA, &mB, &mC ); /* C = A^T*B^T, OR */with similar routines to create the result matrix  from scratch:
from scratch:
Gan_Matrix mA, mB, *pmC; /* matrices A, B & C */
/* ... create and fill matrices A, B ... */
pmC = gan_mat_rmult_s ( &mA, &mB ); /* C = A*B, OR */
pmC = gan_mat_rmultT_s ( &mA, &mB ); /* C = A*B^T, OR */
pmC = gan_matT_rmult_s ( &mA, &mB ); /* C = A^T*B, OR */
pmC = gan_matT_rmultT_s ( &mA, &mB ); /* C = A^T*B^T, OR */The next set of routines deals with the case where it is known that the result of multiplying matrices 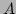 and
and 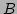 is symmetric. In that case we can use the routines
is symmetric. In that case we can use the routines
Gan_Matrix mA, mB; /* matrices A & B */
Gan_SquMatrix smC; /* matrix C */
/* ... create and fill matrices A, B, create matrix C ... */
gan_mat_rmult_sym_q ( &mA, &mB, &mC ); /* C = A*B, OR */
gan_mat_rmultT_sym_q ( &mA, &mB, &mC ); /* C = A*B^T, OR */
gan_matT_rmult_sym_q ( &mA, &mB, &mC ); /* C = A^T*B, OR */
gan_matT_rmultT_sym_q ( &mA, &mB, &mC ); /* C = A^T*B^T */with the alternatives
Gan_Matrix mA, mB; /* matrices A & B */
Gan_SquMatrix *psmC; /* matrix C */
/* ... create and fill matrices A, B ... */
psmC = gan_mat_rmult_sym_s ( &mA, &mB ); /* C = A*B, OR */
psmC = gan_mat_rmultT_sym_s ( &mA, &mB ); /* C = A*B^T, OR */
psmC = gan_matT_rmult_sym_s ( &mA, &mB ); /* C = A^T*B, OR */
psmC = gan_matT_rmultT_sym_s ( &mA, &mB ); /* C = A^T*B^T */In the case that 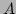 and
and 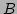 are the same matrix, we can be sure that both
are the same matrix, we can be sure that both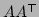 and
and 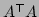 are symmetric, and there are special Gandalf routines for these cases, distinguished according to whether
are symmetric, and there are special Gandalf routines for these cases, distinguished according to whether 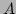 is multiplied by its own transpose on the right or left:
is multiplied by its own transpose on the right or left:
Gan_Matrix mA; /* matrix A */
Gan_SquMatrix smC; /* matrix C */
/* ... create and fill matrix A, create matrix C ... */
gan_mat_srmultT_q ( &mA, &mC ); /* C = A*A^T, OR */
gan_mat_slmultT_q ( &mA, &mC ); /* C = A^T*A */with the alternatives
Gan_Matrix mA; /* matrix A */
Gan_SquMatrix *psmC; /* matrix C */
/* ... create and fill matrix A ... */
psmC = gan_mat_srmultT_s ( &mA ); /* C = A*A^T, OR */
psmC = gan_mat_slmultT_s ( &mA ); /* C = A^T*A */If one or both of the input matrices is a special square matrix, there are many more combinations available. First consider a square matrix 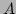 being multiplied on left or right by a general rectangular matrix
being multiplied on left or right by a general rectangular matrix 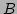 , giving a result matrix
, giving a result matrix 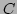 . Given the possibility of both implicit transpose and inverse of the square matrix, we need to consider the operations
. Given the possibility of both implicit transpose and inverse of the square matrix, we need to consider the operations
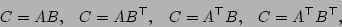
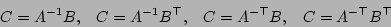
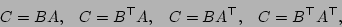
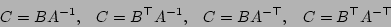
These operations are implemented by the following Gandalf routines:
Gan_SquMatrix smA; /* square matrix A */
Gan_Matrix mB, mC; /* matrices B & C */
/* ... create and fill matrices A, B, create matrix C ... */
/* routines right-multipling A by B */
gan_squmat_rmult_q ( &smA, &mB, &mC ); /* C = A*B, OR */
gan_squmat_rmultT_q ( &smA, &mB, &mC ); /* C = A*B^T, OR */
gan_squmatT_rmult_q ( &smA, &mB, &mC ); /* C = A^T*B, OR */
gan_squmatT_rmultT_q ( &smA, &mB, &mC ); /* C = A^T*B^T, OR */
gan_squmatI_rmult_q ( &smA, &mB, &mC ); /* C = A^-1*B, OR */
gan_squmatI_rmultT_q ( &smA, &mB, &mC ); /* C = A^-1*B^T, OR */
gan_squmatIT_rmult_q ( &smA, &mB, &mC ); /* C = A^-T*B, OR */
gan_squmatIT_rmultT_q ( &smA, &mB, &mC ); /* C = A^-T*B^T */
/* routines left-multipling A by B */
gan_squmat_lmult_q ( &smA, &mB, &mC ); /* C = B*A, OR */
gan_squmat_lmultT_q ( &smA, &mB, &mC ); /* C = B^T*A, OR */
gan_squmatT_lmult_q ( &smA, &mB, &mC ); /* C = B*A^T, OR */
gan_squmatT_lmultT_q ( &smA, &mB, &mC ); /* C = B^T*A^T, OR */
gan_squmatI_lmult_q ( &smA, &mB, &mC ); /* C = B*A^-1, OR */
gan_squmatI_lmultT_q ( &smA, &mB, &mC ); /* C = B^T*A^-1, OR */
gan_squmatIT_lmult_q ( &smA, &mB, &mC ); /* C = B*A^-T, OR */
gan_squmatIT_lmultT_q ( &smA, &mB, &mC ); /* C = B^T*A^-T */These routines have the alternative form
Gan_SquMatrix smA; /* square matrix A */
Gan_Matrix mB, *pmC; /* matrices B & C */
/* ... create and fill matrices A, B ... */
/* routines right-multipling A by B */
pmC = gan_squmat_rmult_s ( &smA, &mB ); /* C = A*B, OR */
pmC = gan_squmat_rmultT_s ( &smA, &mB ); /* C = A*B^T, OR */
pmC = gan_squmatT_rmult_s ( &smA, &mB ); /* C = A^T*B, OR */
pmC = gan_squmatT_rmultT_s ( &smA, &mB ); /* C = A^T*B^T, OR */
pmC = gan_squmatI_rmult_s ( &smA, &mB ); /* C = A^-1*B, OR */
pmC = gan_squmatI_rmultT_s ( &smA, &mB ); /* C = A^-1*B^T, OR */
pmC = gan_squmatIT_rmult_s ( &smA, &mB ); /* C = A^-T*B, OR */
pmC = gan_squmatIT_rmultT_s ( &smA, &mB ); /* C = A^-T*B^T */
/* routines left-multipling A by B */
pmC = gan_squmat_lmult_s ( &smA, &mB ); /* C = B*A, OR */
pmC = gan_squmat_lmultT_s ( &smA, &mB ); /* C = B^T*A, OR */
pmC = gan_squmatT_lmult_s ( &smA, &mB ); /* C = B*A^T, OR */
pmC = gan_squmatT_lmultT_s ( &smA, &mB ); /* C = B^T*A^T, OR */
pmC = gan_squmatI_lmult_s ( &smA, &mB ); /* C = B*A^-1, OR */
pmC = gan_squmatI_lmultT_s ( &smA, &mB ); /* C = B^T*A^-1, OR */
pmC = gan_squmatIT_lmult_s ( &smA, &mB ); /* C = B*A^-T, OR */
pmC = gan_squmatIT_lmultT_s ( &smA, &mB ); /* C = B^T*A^-T */The in-place versions will overwrite the contents of matrix 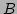 with the result, and work fine unless
with the result, and work fine unless 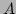 is of symmetric type (in which case the error handler is invoked and NULL returned):
is of symmetric type (in which case the error handler is invoked and NULL returned):
Gan_SquMatrix smA; /* square matrix A */
Gan_Matrix mB; /* matrix B */
/* ... create and fill matrices A, B ... */
/* routines right-multipling A by B */
gan_squmat_rmult_i ( &smA, &mB ); /* replace B = A*B, OR */
gan_squmat_rmultT_i ( &smA, &mB ); /* replace B = A*B^T, OR */
gan_squmatT_rmult_i ( &smA, &mB ); /* replace B = A^T*B, OR */
gan_squmatT_rmultT_i ( &smA, &mB ); /* replace B = A^T*B^T, OR */
gan_squmatI_rmult_i ( &smA, &mB ); /* replace B = A^-1*B, OR */
gan_squmatI_rmultT_i ( &smA, &mB ); /* replace B = A^-1*B^T, OR */
gan_squmatIT_rmult_i ( &smA, &mB ); /* replace B = A^-T*B, OR */
gan_squmatIT_rmultT_i ( &smA, &mB ); /* replace B = A^-T*B^T */
/* routines left-multipling A by B */
gan_squmat_lmult_i ( &smA, &mB ); /* replace B = B*A, OR */
gan_squmat_lmultT_i ( &smA, &mB ); /* replace B = B^T*A, OR */
gan_squmatT_lmult_i ( &smA, &mB ); /* replace B = B*A^T, OR */
gan_squmatT_lmultT_i ( &smA, &mB ); /* replace B = B^T*A^T, OR */
gan_squmatI_lmult_i ( &smA, &mB ); /* replace B = B*A^-1, OR */
gan_squmatI_lmultT_i ( &smA, &mB ); /* replace B = B^T*A^-1, OR */
gan_squmatIT_lmult_i ( &smA, &mB ); /* replace B = B*A^-T, OR */
gan_squmatIT_lmultT_i ( &smA, &mB ); /* replace B = B^T*A^-T */Now we consider multiplying a square matrix 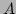 by its own transpose, producing a symmetric matrix
by its own transpose, producing a symmetric matrix 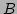 . This operation will most often be applied to triangular matrices, and in Gandalf implicit transpose and inverse of the input matrix are supported, giving rise to the operations
. This operation will most often be applied to triangular matrices, and in Gandalf implicit transpose and inverse of the input matrix are supported, giving rise to the operations
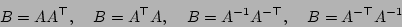
which are implemented by the routines
Gan_SquMatrix smA, smB; /* declare matrices A & B */
/* ... create & fill matrix A, create (& optionally fill) matrix B ... */
gan_squmat_srmultT_squ_q ( &smA, &smB ); /* set B = A*A^T, OR */
gan_squmatT_srmult_squ_q ( &smA, &smB ); /* set B = A^T*A, OR */
gan_squmatI_srmultIT_squ_q ( &smA, &smB ); /* set B = A^-1*A^-T, OR */
gan_squmatIT_srmultI_squ_q ( &smA, &smB ); /* set B = A^-T*A^-1 */There are also routines to build the result matrix 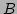 from scratch:
from scratch:
Gan_SquMatrix smA, *psmB; /* declare matrices A & B */
/* ... create & fill matrix A ... */
psmB = gan_squmat_srmultT_squ_s ( &smA ); /* create B = A*A^T, OR */
psmB = gan_squmatT_srmult_squ_s ( &smA ); /* create B = A^T*A, OR */
psmB = gan_squmatI_srmultIT_squ_s ( &smA ); /* create B = A^-1*A^-T, OR */
psmB = gan_squmatIT_srmultI_squ_s ( &smA ); /* create B = A^-T*A^-1 */and in-place versions of these operations are also available:
Gan_SquMatrix smA; /* declare matrix A */
/* ... create & fill matrix A ... */
gan_squmat_srmultT_squ_i ( &smA ); /* replace A = A*A^T, OR */
gan_squmatT_srmult_squ_i ( &smA ); /* replace A = A^T*A, OR */
gan_squmatI_srmultIT_squ_i ( &smA ); /* replace A = A^-1*A^-T, OR */
gan_squmatIT_srmultI_squ_i ( &smA ); /* replace A = A^-T*A^-1 */Finally, there is a set of routines that multiply a symmetric matrix on left and right by a rectangular matrix and its transpose, producing another symmetric matrix. The operations implemented are

This triple product is implemented as two matrix multiplications, and the matrix to hold the intermediate result is also passed in to the routines, so that it is also available on output. The routines are
Gan_SquMatrix smS, smSp; /* declare matrices S & S' */
Gan_Matrix mA, mB; /* declare matrices A & B */
/* ... create & fill matrices S & A, create (& optionally fill) matrices B & Sp ... */
gan_symmat_lrmult_q ( &smS, &mA, &mB, &smSp ); /* set B = S*A^T and Sp = A*S*A^T, OR */
gan_symmat_lrmultT_q ( &smS, &mA, &mB, &smSp ); /* set B = S*A and Sp = A^T*S*A */with alternative versions that create the result matrix 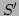 from scratch:
from scratch:
Gan_SquMatrix smS, *psmSp; /* declare matrices S & S' */
Gan_Matrix mA, mB; /* declare matrices A & B */
/* ... create & fill matrices S & A, create (& optionally fill) matrix B ... */
psmSp = gan_symmat_lrmult_s ( &smS, &mA, &mB ); /* set B = S*A^T and Sp = A*S*A^T, OR */
psmSp = gan_symmat_lrmultT_s ( &smS, &mA, &mB ); /* set B = S*A and Sp = A^T*S*A */It is allowable to pass NULL for the 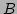 matrix (&mB in the above function calls). In that case the intermediate result is computed and thrown away.
matrix (&mB in the above function calls). In that case the intermediate result is computed and thrown away.
Next: Inverting a general size Up: General size matrices Previous: General size matrix/vector multiplication Contents
2006-03-17