Symmetric matrix eigendecomposition (original) (raw)
Next: Accumulated symmetric matrix eigendecomposition Up: General size matrices Previous: Cholesky factorising a general Contents
Symmetric matrix eigendecomposition
#include <gandalf/linalg/mat_symmetric.h>Gandalf has a routine for computing the real eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a general size symmetric matrix, based on either the CLAPACK routine dspev() or the CCMath routine eigval(). A symmetric matrix  can be written as
can be written as
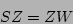
where 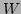 is a diagonal matrix of real eigenvalues and
is a diagonal matrix of real eigenvalues and 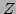 is a square matrix of orthognal eigenvectors, unique if the eigenvalues are distinct. If the matrix is positive definite (or semi-definite) then all the eigenvalues will be
is a square matrix of orthognal eigenvectors, unique if the eigenvalues are distinct. If the matrix is positive definite (or semi-definite) then all the eigenvalues will be 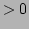 (or
(or 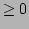 ). Here is an example code fragment using the Gandalf routine to compute
). Here is an example code fragment using the Gandalf routine to compute 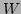 and (optionally)
and (optionally) 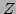 .
.
Gan_SquMatrix smS; /* declare symmetric matrix */
Gan_SquMatrix smW; /* declare matrix of eigenvalues W */
Gan_Matrix mZ; /* declare matrix of eigenvectors */
/* create and fill S */
gan_symmat_form ( &smS, 5 );
gan_symmat_fill_va ( &smS, 5,
1.0,
2.0, 3.0,
4.0, 5.0, 6.0,
7.0, 8.0, 9.0, 10.0,
11.0, 12.0, 13.0, 14.0, 15.0 );
/* create Z and W */
gan_mat_form ( &mZ, 5, 5 );
gan_diagmat_form ( &smW, 0 );
/* compute sigenvalues and eigenvectors of S */
gan_symmat_eigen ( &smS, &smW, &mZ, GAN_TRUE, NULL, 0 );After calling this routine smW will contain the computed eigenvalues, and mZ the eigenvectors. If the eigenvector matrix is passed asNULL, the eigenvectors are not computed. The boolean fourth argument indicates whether the eigenvectors should be sorted into ascending order. The fifth and sixth arguments define a workspace array of doubles, and the size of the array, which can be used by LAPACK. If passed asNULL, 0 as above, the workspace is allocated inside the function.
Next: Accumulated symmetric matrix eigendecomposition Up: General size matrices Previous: Cholesky factorising a general Contents
2006-03-17