read - Read data from buffer - MATLAB (original) (raw)
Main Content
Syntax
Description
[out](#mw%5Febb4369d-6d09-49d1-bfdc-2edbb3426b44) = read([asyncBuff](#mw%5Fae58d9b3-cca1-4319-861d-4c601ce002ff)) returns all unread samples from the buffer, asyncBuff.
[out](#mw%5Febb4369d-6d09-49d1-bfdc-2edbb3426b44) = read([asyncBuff](#mw%5Fae58d9b3-cca1-4319-861d-4c601ce002ff),[NumRows](#d126e507142)) returns NumRows samples from each channel (column) of the buffer.
[out](#mw%5Febb4369d-6d09-49d1-bfdc-2edbb3426b44) = read([asyncBuff](#mw%5Fae58d9b3-cca1-4319-861d-4c601ce002ff),[NumRows](#d126e507142),[Overlap](#mw%5F50352d37-39ae-4ce4-94eb-a0d279e33ef8)) returns NumRows samples from each channel and overlaps previously read samples by Overlap.
[[out](#mw%5Febb4369d-6d09-49d1-bfdc-2edbb3426b44),[nUnderrun](#mw%5Fd55fa0ce-ec3f-4634-a505-119a2e72ec71)] = read(___) also returns the number of rows zero-padded if underrun occurred, using any of the previous arguments.
Examples
The dsp.AsyncBuffer System object™ supports reading variable frame sizes from the buffer.
Create a dsp.AsyncBuffer System object. The input is white Gaussian noise with a mean of 0, a standard deviation of 1, and a frame size of 512 samples. Write the input to the buffer using the write method.
asyncBuff = dsp.AsyncBuffer; input = randn(512,1); write(asyncBuff,input); plot(input) hold on

Store the data that is read from the buffer in outTotal.
Plot the input signal and data that is read from the buffer in the same plot. Read data from the buffer until all samples are read. In each iteration of the loop, randi determines the number of samples to read. Therefore, the signal is read in as a variable-size signal. The prevIndex variable keeps track of the previous index value that contains the data.
outTotal = zeros(size(input)); prevIndex = 0; while asyncBuff.NumUnreadSamples ~= 0 numToRead = randi([1,64]); out = read(asyncBuff,numToRead); outTotal(prevIndex+1:prevIndex+numToRead) = out; prevIndex = prevIndex+numToRead; end plot(outTotal,"r") hold off
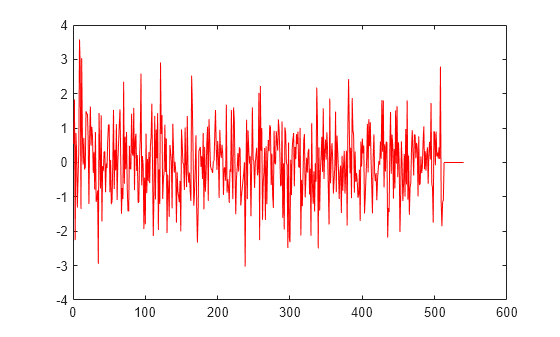
Verify that the input data and the data read from the buffer (excluding the underrun samples, if any) are the same. The cumulative number of overrun and underrun samples in the buffer is determined by the info function.
S = struct with fields: CumulativeOverrun: 0 CumulativeUnderrun: 28
The CumulativeUnderrun field shows the number of samples underrun per channel. Underrun occurs if you attempt to read more samples than available.
Input Arguments
Number of samples read from each channel (column) of the buffer, specified as a positive integer. If the requested number of samples is greater than the number of unread samples, the output is zero-padded.
The function returns NumRows samples from each channel and overlaps previously read samples by Overlap. The total number of samples read is NumRows × NumChann, where_NumChann_ is the number of channels in the buffer. The total number of new samples read is (NumRows – Overlap) × NumChann. If the overlap portion contains samples that are overwritten, and are therefore not contiguously written, the output is zero-padded.
Output Arguments
Data read from the buffer, returned as an array of NumRows × NumChann samples. If Overlap is specified, the function returns (NumRows –Overlap) × NumChann samples. If the requested number of samples is greater than the number of unread samples, the output is zero-padded.
Data Types: double
Complex Number Support: Yes
Number of samples zero-padded in each channel (column) if underrun occurred. Underrun occurs if you attempt to read more samples than available. Samples that are zero-padded in overlapped portions are not counted as underrun.
Data Types: int32
Version History
Introduced in R2017a