Data Alignment for Code Replacement - MATLAB & Simulink (original) (raw)
Main Content
Code replacement libraries can align data objects passed into a replacement function to a specified boundary.
Code Replacement Data Alignment
You can take advantage of function implementations that require aligned data to optimize application performance when using MATLAB® Coder™. To configure data alignment for a function implementation:
- Specify the data alignment requirements in a code replacement entry. Specify alignment separately for each implementation function argument or collectively for all function arguments. See Specify Data Alignment Requirements for Function Arguments.
- Specify the data alignment capabilities and syntax for one or more compilers. Include the alignment specifications in a library registration entry in the
rtwTargetInfo.mfile. See Provide Data Alignment Specifications for Compilers. - Register the library containing the table entry and alignment specification object.
- Configure the code generator to use the code replacement library and generate code. Observe the results.
For examples, see Programmatically Develop a Code Replacement Library Using Data Alignment and the “Data Alignment for Function Implementations” section of the Optimize Generated Code by Developing and Using Code Replacement Libraries - Simulink example page.
Specify Data Alignment Requirements for Function Arguments
To specify the data alignment requirement for an argument in a code replacement entry:
- If you are defining a replacement function in a code replacement table registration file, create an argument descriptor object (
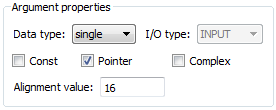
RTW.ArgumentDescriptor). Use itsAlignmentBoundaryproperty to specify the required alignment boundary and assign the object to the argumentDescriptorproperty. - If you are defining a replacement function using the Code Replacement Tool, on the Mapping Information tab, in the Argument properties section for the replacement function, enter a value for the Alignment value parameter.

The AlignmentBoundary property (or Alignment value parameter) specifies the alignment boundary for data passed to a function argument, in number of bytes. The AlignmentBoundary property is valid only for addressable objects, including matrix and pointer arguments. It is not applicable for value arguments. Valid values are:
-1(default) — If the data is aSimulink.Bus,Simulink.Signal, orSimulink.Parameterobject, specifies that the code generator determines an optimal alignment based on usage. Otherwise, specifies that there is not an alignment requirement for this argument.- Positive integer that is a power of 2 — Specifies number of bytes in the boundary. The starting memory address for the data allocated for the function argument is a multiple of the specified value. If you specify an alignment boundary that is less than the natural alignment of the argument data type, the alignment directive is emitted in the generated code. However, the target compiler ignores the directive.
The following code specifies the AlignmentBoundary for an argument as 16 bytes.
hLib = RTW.TflTable; entry = RTW.TflCOperationEntry; arg = getTflArgFromString(hLib, 'u1','single*'); desc = RTW.ArgumentDescriptor; desc.AlignmentBoundary = 16; arg.Descriptor = desc; entry.Implementation.addArgument(arg);
The equivalent alignment boundary specification in the Code Replacement Tool dialog box is in this figure.
Note
If your model imports Simulink.Bus, Simulink.Parameter, or Simulink.Signal objects, specify an alignment boundary in the object properties, using the Alignment property. For more information, see Simulink.Bus, Simulink.Parameter, and Simulink.Signal.
Provide Data Alignment Specifications for Compilers
To support data alignment in generated code, describe the data alignment capabilities and syntax for your compilers in the code replacement library registration. Provide one or more alignment specifications for each compiler in a library registry entry.
- If you are defining a code replacement library registration entry in a
rtwTargetInfo.mcustomization file, add one or moreAlignmentSpecificationobjects to anRTW.DataAlignmentobject. Attach theRTW.DataAlignmentobject to theTargetCharacteristicsobject of the registry entry.
TheRTW.DataAlignmentobject also has the propertyDefaultMallocAlignment, which specifies the default alignment boundary, in bytes, that the compiler uses for dynamically allocated memory. If the code generator uses dynamic memory allocation for a data object involved in a code replacement, this value determines if the memory satisfies the alignment requirement of the replacement. If not, the code generator does not use the replacement. The default value forDefaultMallocAlignmentis-1, indicating that the default alignment boundary used for dynamically allocated memory is unknown. In this case, the code generator uses the natural alignment of the data type to determine whether to allow a replacement.
Additionally, you can specify the alignment boundary for complex types by using the addComplexTypeAlignment function. - If you are generating a customization file function using the Code Replacement Tool, fill out the following fields for each compiler.
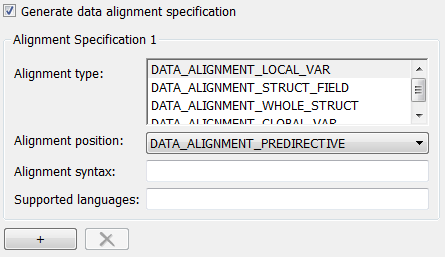
Click the plus (+) symbol to add additional compiler specifications.
For each data alignment specification, provide the following information.
| AlignmentSpecification Property | Dialog Box Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| AlignmentType | Alignment type | Cell array of predefined enumerated strings specifyingthe types of alignment this specification supports.DATA_ALIGNMENT_LOCAL_VAR — Local variablesDATA_ALIGNMENT_GLOBAL_VAR — Global variablesDATA_ALIGNMENT_STRUCT_FIELD — Individual structure fieldsDATA_ALIGNMENT_WHOLE_STRUCT — Whole structure, with padding (individual structure field alignment, if specified, is favored by the code generator and takes precedence over whole structure alignment)Each alignment specification must specify at leastDATA_ALIGNMENT_GLOBAL_VAR andDATA_ALIGNMENT_STRUCT_FIELD. |
| AlignmentPosition | Alignment position | Predefined enumerated string specifying the position in which you must place the compiler alignment directive for the alignment typeDATA_ALIGNMENT_WHOLE_STRUCT:DATA_ALIGNMENT_PREDIRECTIVE — The alignment directive is emitted beforestruct st_tag{…} as part of the type definition statement (for example, MSVC).DATA_ALIGNMENT_POSTDIRECTIVE — The alignment directive is emitted afterstruct st_tag{…} as part of the type definition statement (for example, gcc).DATA_ALIGNMENT_PRECEDING_STATEMENT — The alignment directive is emitted as a standalone statement immediately preceding the definition of the structure type. A semicolon (;) must terminate the registered alignment syntax.DATA_ALIGNMENT_FOLLOWING_STATEMENT — The alignment directive is emitted as a standalone statement immediately following the definition of the structure type. A semicolon (;) must terminate the registered alignment syntax.For alignment types other thanDATA_ALIGNMENT_WHOLE_STRUCT, code generation uses the alignment positionDATA_ALIGNMENT_PREDIRECTIVE. |
| AlignmentSyntaxTemplate | Alignment syntax | Specify the alignment directive string that the compiler supports. The string is registered as a syntax template that has placeholders in it. These placeholders are supported:%n — Replaced by the alignment boundary for the replacement function argument.%s — Replaced by the aligned symbol, usually the identifier of a variable.For example, for the gcc compiler, you can specify__attribute__((aligned(%n))), or for the MSVC compiler,__declspec(align(%n)). |
| SupportedLanguages | Supported languages | Cell array specifying the languages to which this alignment specification applies, among c andc++. Sometimes, alignment syntax and position differ between languages for a compiler. |
An example of a data alignment specification for the GCC compiler follows.
da = RTW.DataAlignment;
as = RTW.AlignmentSpecification; as.AlignmentType = {'DATA_ALIGNMENT_LOCAL_VAR', ... 'DATA_ALIGNMENT_STRUCT_FIELD', ... 'DATA_ALIGNMENT_GLOBAL_VAR'}; as.AlignmentSyntaxTemplate = 'attribute((aligned(%n)))'; as.AlignmentPosition = 'DATA_ALIGNMENT_PREDIRECTIVE'; as.SupportedLanguages = {'c', 'c++'}; da.addAlignmentSpecification(as);
tc = RTW.TargetCharacteristics; tc.DataAlignment = da;
Here is the corresponding specification in the Generate registration file dialog box of the Code Replacement Tool.

Specify Data Alignment in MATLAB Code for Imported Data
If MATLAB Coder code replacements that require data alignment use imported data, such as an entry-point or exported function I/O, specify data alignment to external code with coder.dataAlignment statements in the MATLAB code.
If MATLAB Coder code replacements occur that require data alignment (uses imported data), such as an entry-point or exported function with I/O, specify code replacement data alignment with coder.DataAlignment statements in the MATLAB code.
To specify the data alignment requirements for imported data in a MATLAB code:
- For each instance of imported data that requires data alignment, specify the alignment in the function with a
coder.dataAlignmentstatement of the form:coder.dataAlignment('_`varName`_', _`alignvalue`_) - The
varNameis a character array of the variable name that requires alignment information specification. The_alignvalue_ is an integer number which should be a power of 2. This number specifies the power-of-2 byte alignment boundary. - An example function that specifies data alignment is:
function y = testFunction(x1,x2)
coder.dataAlignment('x1',16); % Specifies information
coder.dataAlignment('x2',16); % Specifies information
coder.dataAlignment('y',16); % Specifies information
y = x1 + x2;
end
If testFunction is an entry-point or exported function, imported data x1, x2, and y are not aligned automatically by the code generator. The coder.DataAlignment statements for these variables are only meant as information for the code generator. The call sites allocating memory for the data need to ensure that the data is aligned as specified.
You also can specify code replacement data alignment for exported data, such as aglobal variable or an ExportedGlobal storage class. For more information, see Choose Storage Class for Controlling Data Representation in Generated Code.