tanh - Hyperbolic tangent - MATLAB (original) (raw)
Main Content
Syntax
Description
Y = tanh([X](#d126e1815853)) returns the hyperbolic tangent of the elements of X. The tanh function operates element-wise on arrays. The function accepts both real and complex inputs. All angles are in radians.
Examples
Create a vector and calculate the hyperbolic tangent of each value.
X = [0 pi 2pi 3pi]; Y = tanh(X)
Y = 1×4
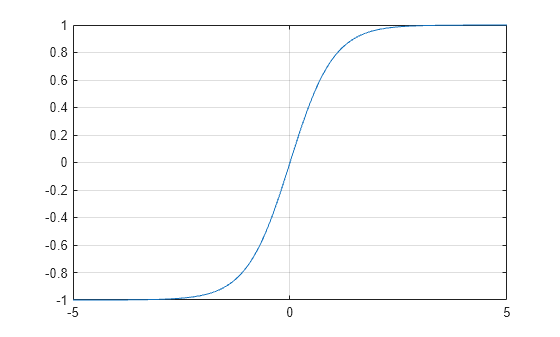
0 0.9963 1.0000 1.0000Plot the hyperbolic tangent function over the domain -5≤x≤5.
x = -5:0.01:5; y = tanh(x); plot(x,y) grid on
Input Arguments
Input angles in radians, specified as a scalar, vector, matrix, multidimensional array, table, or timetable.
Data Types: single | double | table | timetable
Complex Number Support: Yes
More About
The hyperbolic tangent of an angle x is the ratio of the hyperbolic sine and hyperbolic cosine
In terms of the traditional tangent function with a complex argument, the identity is
Extended Capabilities
Thetanh function fully supports tall arrays. For more information, see Tall Arrays.
The tanh function fully supports GPU arrays. To run the function on a GPU, specify the input data as a gpuArray (Parallel Computing Toolbox). For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions on a GPU (Parallel Computing Toolbox).
Version History
Introduced before R2006a
The tanh function can calculate on all variables within a table or timetable without indexing to access those variables. All variables must have data types that support the calculation. For more information, see Direct Calculations on Tables and Timetables.