ftell - Current location of file position pointer in file - MATLAB (original) (raw)
Main Content
Current location of file position pointer in file
Syntax
Description
position = ftell([fileID](#d126e602673)) returns the current location of the position pointer in the specified file.
- If the query is successful, then
positionis a zero-based integer that indicates the number of bytes from the beginning of the file. - If the query is unsuccessful, then
positionis-1.
Examples
When you open a file, MATLAB® creates a pointer to indicate the current position within the file. Open the following badpoem.txt file and perform a read operation (which advances the position pointer). Then, query the final position in the file after the read operation.
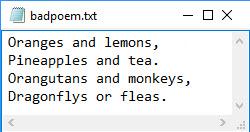
Use fopen to open the file. Then, use ftell to query the current position.
fid = fopen('badpoem.txt'); ftell(fid)
Using fgetl, read the first line and examine the current position after the read operation.
tline1 = fgetl(fid) % read the first line
tline1 = 'Oranges and lemons,'
Read the second line and examine the current position.
tline2 = fgetl(fid) % read the second line
tline2 = 'Pineapples and tea.'
Close the file.
Input Arguments
File identifier of an open file, specified as an integer. To open a file and obtain its identifier, use the fopen function.
Data Types: double
Extended Capabilities
Usage notes and limitations:
When the MATLAB® behavior differs from the C compiler behavior, the generated code usually matches the C compiler behavior. For example, if you usefseek to seek past the end of a file, the behavior offtell in the generated code matches the C compiler behavior.
Version History
Introduced before R2006a
You can read data from primary online sources by performing low-level file read operations over an internet URL.
This function supports thread-based environments.