pie - Legacy pie chart - MATLAB (original) (raw)
Syntax
Description
Note
piechart is recommended over pie because it enables you to create aPieChart object, which provides more customization options. For example, PieChart objects have properties for changing the slice colors, the arrangement of the slices around the circle (clockwise or counterclockwise), and the location of the first slice. (since R2023b)
pie([X](#buiol%5Fj-1-X)) draws a pie chart using the data in X. Each slice of the pie chart represents an element inX.
- If
sum(X) ≤ 1, then the values inXdirectly specify the areas of the pie slices.piedraws only a partial pie ifsum(X) < 1. - If
sum(X) > 1, thenpienormalizes the values byX/sum(X)to determine the area of each slice of the pie. - If
Xis of data typecategorical, the slices correspond to categories. The area of each slice is the number of elements in the category divided by the number of elements inX.
pie([X](#buiol%5Fj-1-X),[explode](#buiol%5Fj-1-explode)) offsets slices from the pie. explode is a vector or matrix of zeros and nonzeros that correspond to X. The pie function offsets slices for the nonzero elements only in explode.
If X is of data type categorical, then explode can be a vector of zeros and nonzeros corresponding to categories, or a cell array of the names of categories to offset.
pie([X](#buiol%5Fj-1-X),[labels](#buiol%5Fj-1-labels)) specifies options for labeling the pie slices. In this case, X must be numeric.
pie([X](#buiol%5Fj-1-X),[explode](#buiol%5Fj-1-explode),[labels](#buiol%5Fj-1-labels)) offsets slices and specifies the text labels. X can be numeric or categorical.
pie([ax](#buiol%5Fj-1-ax),___) plots into the axes specified by ax instead of into the current axes (gca). The option ax can precede any of the input argument combinations in the previous syntaxes.
[p](#buiol%5Fj-1-p) = pie(___) returns a vector of patch and text graphics objects. The input can be any of the input argument combinations in the previous syntaxes.
Examples
Create a pie chart of vector X.
X = [1 3 0.5 2.5 2]; pie(X)

Offset the second and fourth pie slices by setting the corresponding explode elements to 1.
explode = [0 1 0 1 0]; pie(X,explode)

Create a pie chart of vector X and label the slices.
X = 1:3; labels = {'Taxes','Expenses','Profit'}; pie(X,labels)

Create a labeled pie chart, and then modify the color and font size of the text labels.
X = 1:3; labels = {'Taxes','Expenses','Profit'}; p = pie(X,labels)

p = 1×6 graphics array:
Patch Text Patch Text Patch Text Get the text object for the label 'Profit'. Change its color and font size. Use dot notation to set properties.
t = p(6); t.BackgroundColor = 'cyan'; t.EdgeColor = 'red'; t.FontSize = 14;

Create a pie chart, and specify a format expression to display each label with three digits after the decimal point. To include a percent sign in the labels, specify '%%' at the end of the expression.
X = [1/3 2/3]; pie(X,'%.3f%%')

Create a pie chart of vector X where the sum of the elements is less than 1.
X = [0.19 0.22 0.41]; pie(X)

pie draws a partial pie because the sum of the elements is less than 1.
Create vectors y2010 and y2011, that contain financial data for two years. Then create a cell array containing the labels for the values.
y2010 = [50 0 100 95]; y2011 = [65 22 97 120]; labels = {'Investments','Cash','Operations','Sales'};
Create a 1-by-2 tiled chart layout, and display two pie charts that each have a title. Then display a shared legend in the east tile of the layout. To do this, call the legend function with a return argument to store the legend object. Then move the legend to the east tile by setting the Layout.Tile property to 'east'.
t = tiledlayout(1,2,'TileSpacing','compact');
% Create pie charts ax1 = nexttile; pie(ax1,y2010) title('2010')
ax2 = nexttile; pie(ax2,y2011) title('2011')
% Create legend lgd = legend(labels); lgd.Layout.Tile = 'east';

Plot a categorical pie chart with offset slices corresponding to categories.
X = categorical({'North','South','North','East','South','West'}); explode = {'North','South'}; pie(X,explode)

Now, use a logical vector to offset the same slices.
explode = [0 1 1 0]; pie(X,explode)

Plot a categorical pie chart without any offset slices and label the slices. When X is of data type categorical you must specify the input argument explode. To specify labels without any offset slices, specify explode as an empty cell array, and labels as the labels.
X = categorical({'North','South','North','East','South','West'}); explode = {}; labels = {'E','N','S','W'}; pie(X,explode,labels)

Now, offset a slice and label all slices.
X = categorical({'North','South','North','East','South','West'}); explode = {'West'}; labels = {'E','N','S','W'}; pie(X,explode,labels)

Define x and create a pie chart.

Specify the description for each pie slice in the cell array labels. Specify the descriptions in the order that you specified the data in x.
labels = ["Product A","Product B","Product C"];
Display a horizontal legend below the pie chart. Pass the descriptions contained in labels to the legend function. Set the legend's Location property to "southoutside" and its Orientation property to "horizontal".
legend(labels,"Location","southoutside","Orientation","horizontal")

Input Arguments
Input vector or matrix.
- If
Xis numeric, then all values inXmust be finite. - If
Xis categorical, thenpieignores undefined elements.
Data Types: double|categorical
Offset slices, specified as a numeric vector or matrix, logical vector or matrix, string array, or cell array of character vectors.
- If
Xis numeric, thenexplodemust be a logical or numeric vector or matrix of zeros and nonzeros that correspond toX. A true (nonzero) value offsets the corresponding slice from the center of the pie chart, so thatX(i,j)is offset from the center ifexplode(i,j)is nonzero.explodemust be the same size asX. - If
Xis categorical, thenexplodecan be a string array or cell array of category names.pieoffsets slices corresponding to categories inexplode. - If
Xis categorical, thenexplodealso can be a logical or numeric vector with elements that correspond to each category inX. Thepiefunction offsets slices corresponding to true (nonzero) in category order.
Label options, specified as an array of text labels or a format expression. Use this argument to display custom text labels with the pie slices, or to display the percentage values that MATLAB® provides in a specific format.
Note
To specify the label options when X contains categorical values, you must specify the explode argument before the label options.
Display Text Labels
Specify the labels as a cell array of character vectors or as a string array.
When X contains numeric values, the number of elements inlabels must equal the number of elements inX.
When X contains categorical values, the number and order of the elements in labels must equal the number and order of the categories in X. To determine the number and order of the categories, use the categories function.
Display Percentages in a Specific Format
Specify a format expression as a character vector or as a string scalar. The format expression begins with a percent symbol (%) followed by a series of identifiers.
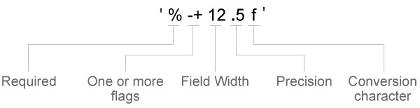
All the identifiers are optional except for the conversion character. Specify the identifiers in this order:
- One or more flags — Options for displaying plus signs, decimal points, and justifying the labels.
- Plus sign (
+) — Display a plus sign next to positive values. - Hash symbol (
#) — Display the decimal point even when the precision is0, such as in'50.'. - Minus sign (
–) — Left justify the labels and pad the ends of the labels with spaces instead of padding them at the beginning.
- Plus sign (
- Field width — Minimum number of characters to display in the label. Specify the field width as an integer value. If the number of digits in a label is smaller than the field width, then the label is padded with spaces.
- Precision — Number of digits to the right of the decimal point. Specify the precision as a decimal point followed by an integer value.
- Conversion character — Fixed-point or exponential notation. For a list of conversion characters, see the table below. If you specify a conversion character that does not fit the data, MATLAB uses
%einstead.
| Conversion Character | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| f | Fixed-point notation. The precision value indicates the number of decimal places. | '%.4f%%' displays the label for a slice that is 6.25% of the pie as 6.2500%. |
| e | Exponential notation. The precision value indicates the number of decimal places. | '%.4e%%' displays the label for a slice that is 6.25% of the pie as 6.2500e+00%. |
| g | The more compact version of e or f, with no trailing zeros. The precision value indicates the maximum number of decimal places. | '%.4g%%'displays the label for a slice that is 6.25% of the pie as 6.25%. |
In addition to the identifiers listed above, you can also specify literal text at the beginning or end of the format expression. To display a single quotation mark, use''. To display a percent symbol, use %%. For example, '%.2f%%' displays the labels with two trailing decimal places followed by a percent symbol.
Axes object. Use ax to plot the pie chart in a specific axes instead of the current axes (gca).
Output Arguments
Extended Capabilities
This function supports tall arrays with the following limitations:
X must be a tall categorical array.
For more information, see Tall Arrays.
The pie function supports GPU array input with these usage notes and limitations:
- This function accepts GPU arrays, but does not run on a GPU.
For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions on a GPU (Parallel Computing Toolbox).
Version History
Introduced before R2006a
When you call the pie function, and specify data that contains zero values, your pie chart shows the zero values and corresponding labels. If you callpie with an output argument, the output includes objects for each zero value.
In previous releases, pie omitted the zero values from the chart, and it did not return any objects that corresponded to those values. If you do not want to display zero values or return the corresponding objects, then remove the zeros from your data.
