structfun - Apply function to each field of scalar structure - MATLAB (original) (raw)
Apply function to each field of scalar structure
Syntax
Description
[A](#d126e1756708) = structfun([func](#d126e1756490),[S](#d126e1756520)) applies the function func to each field of scalar structureS, one field at a time. structfun then concatenates the outputs from func into the column vectorA. The input argument func is a function handle to a function that takes one input argument and returns a scalar. The output from func must always be the same data type to use this syntax. If the function outputs have different data types, you must set theUniformOutput name-value argument tofalse. The number of elements in A equals the number of fields in S.
You cannot specify the order in which structfun calculates the elements of A or rely on them being done in any particular order.
[A](#d126e1756708) = structfun([func](#d126e1756490),[S](#d126e1756520),[Name,Value](#namevaluepairarguments)) applies func with additional options specified by one or moreName,Value pair arguments. For example, to return output values in a structure, specify 'UniformOutput',false. You can return A as a structure when func returns values that cannot be concatenated into an array. The returned structure has the same fields as S.
[A1,...,Am] = structfun(___) returns multiple output arrays A1,...,Am when func returnsm output values. func can return output arguments that have different data types, but the data type of each output must be the same each time func is called. You can use this syntax with any of the input arguments of the previous syntaxes.
Examples
Create a scalar structure with fields that contain numeric arrays of different sizes.
S.f1 = 1:10; S.f2 = [2; 4; 6]; S.f3 = []
S = struct with fields: f1: [1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10] f2: [3×1 double] f3: []
Calculate the mean of each numeric array, and return the means in an array.
A = 3×1
5.5000
4.0000
NaNCreate a scalar structure in which each field contains an array of random numbers.
S.X = rand(1,10); S.Y = rand(1,10); S.Z = rand(1,10)
S = struct with fields: X: [0.8147 0.9058 0.1270 0.9134 0.6324 0.0975 0.2785 0.5469 0.9575 0.9649] Y: [0.1576 0.9706 0.9572 0.4854 0.8003 0.1419 0.4218 0.9157 0.7922 0.9595] Z: [0.6557 0.0357 0.8491 0.9340 0.6787 0.7577 0.7431 0.3922 0.6555 0.1712]
Plot the arrays. Return an array of chart line objects from the plot function and use them to add different markers to each set of data points. structfun can return arrays of any data type, so long as objects of that data type can be concatenated.
figure hold on p = structfun(@plot,S); p(1).Marker = 'o'; p(2).Marker = '+'; p(3).Marker = 's'; hold off
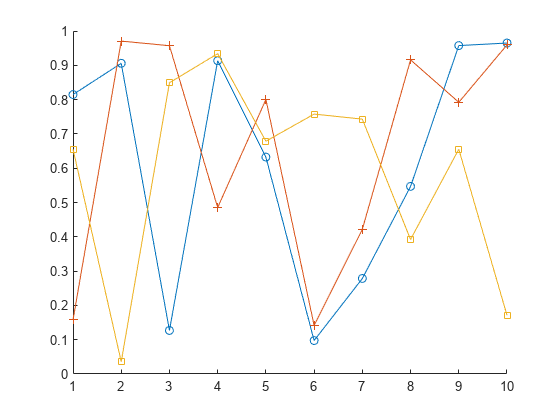
Create a scalar structure with fields that contain matrices.
S.f1 = 1:10; S.f2 = [2 3; 4 5; 6 7]; S.f3 = rand(4,4)
S = struct with fields: f1: [1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10] f2: [3×2 double] f3: [4×4 double]
Calculate the means of each matrix. mean returns vectors containing the mean of each column, so the means cannot be returned as an array. To return the means in a structure, specify the 'UniformOutput',false name-value pair.
A = structfun(@mean,S,'UniformOutput',false)
A = struct with fields: f1: 5.5000 f2: [4 5] f3: [0.6902 0.3888 0.7627 0.5962]
Create a scalar structure.
S.f1 = 1:10; S.f2 = [2 3; 4 5; 6 7]; S.f3 = rand(4,4)
S = struct with fields: f1: [1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10] f2: [3×2 double] f3: [4×4 double]
Calculate the sizes of each array in S. The number of rows and columns are each in 3-by-1 numeric arrays.
[nrows,ncols] = structfun(@size,S)
Input Arguments
Function to apply to the fields of the input scalar structure, specified as a function handle.
func can correspond to more than one function file and therefore can represent a set of overloaded functions. In these cases, MATLAB® determines which function to call based on the class of the input arguments.
Example: A = structfun(@max,S) returns the maximum of each field of S.
Input structure, specified as a scalar structure.
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments asName1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is the argument name and Value is the corresponding value. Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the pairs does not matter.
Before R2021a, use commas to separate each name and value, and enclose Name in quotes.
Example: A = structfun(@mean,S,'UniformOutput',false) returns the outputs from mean in a structure with the same fields asS.
True or false, specified as the comma-separated pair consisting of'UniformOutput' and eithertrue (1) orfalse (0).
| Value of'UniformOutput' | Description |
|---|---|
| true (1) | func must return scalars that structfun concatenates into a column vector. The outputs forfunc must be the same data type, or structfun errors with this option. |
| false (0) | structfun returns the outputs of func in one or more scalar structures. The output scalar structures have the same fields as the input scalar structure. The outputs of func can have any data type. |
Function to catch errors, specified as the comma-separated pair consisting of'ErrorHandler' and a function handle. If func throws an error, then the error handler specified by 'ErrorHandler' catches the error and takes the action specified in the function. The error handler either must throw an error or return the same number of outputs asfunc. If the value of 'UniformOutput' is true, then the output arguments of the error handler must be scalars and have the same data type as the outputs of func.
The first input argument of the error handler is a structure with these fields:
identifier— Error identifiermessage— Error message textindex— Linear index into the input arrays at whichfuncthrew the error
The remaining input arguments to the error handler are the input arguments for the call to func that made func throw the error.
Suppose func returns two doubles as output arguments. You can specify the error handler as 'ErrorHandler',@errorFunc, whereerrorFunc is a function that raises a warning and returns two output arguments.
function [A,B] = errorFunc(S,varargin) warning(S.identifier, S.message); A = NaN; B = NaN; end
If you do not specify 'ErrorHandler', then structfun rethrows the error thrown by func.
Output Arguments
Output array, returned as a column vector of any data type or as a scalar structure.
By default, structfun concatenates the outputs fromfunc into a column vector. func must return scalars. If func returns objects, then the class that the objects belong to must meet these requirements.
- Support assignment by linear indexing into the object array
- Have a
reshapemethod that returns an array that has the same size as the input
If the value of the 'UniformOutput' name-value pair argument is false (0), thenstructfun returns outputs as fields of a scalar structure. In that case, the outputs from func can have any sizes and different data types.
Extended Capabilities
Usage notes and limitations:
- The
ErrorHandleroption is not supported. - The number of outputs must be less than or equal to three.
Version History
Introduced before R2006a