outerjoin - Outer join between two tables or timetables - MATLAB (original) (raw)
Outer join between two tables or timetables
Syntax
Description
[T](#btx2ndz-1-C) = outerjoin([Tleft](#mw%5Ff8c603e5-ef85-494d-acfd-ed1e5afc1daf),[Tright](#mw%5Ff6023fff-36da-477c-b657-ea48af2f2fb3)) creates the table or timetable, T, as the outer join of Tleft and Tright usingkey variables. An outer join combines table rows where the key variables have matching values, but it also includes rows where the key variables from one input table have no matches in the other input table. For example, if Tleft has variables namedKey1 and Var1, andTright has variables Key1 andVar2, then T=outerjoin(Tleft,Tright) usesKey1 as a key variable.

By default, the key variables are:
- Variables that have the same names in
TleftandTright, if both inputs are tables, or ifTleftis a timetable andTrightis a table. - Vectors of row times, if both
TleftandTrightare timetables.
The matching values of the key variables in the left and right tables do not have to be in the same order. Outer joins can perform one-to-many and many-to-one matches between the key variables of the two tables. That is, a value that occurs once in a key variable of the left table can have multiple matches in the right table. Similarly, a value that occurs once in a key variable of the right table can have multiple matches in the left table.
You can perform outer joins only on certain combinations of tables and timetables.
- If
Tleftis a table, thenTrightmust be a table.outerjoinreturnsTas a table. - If
Tleftis a timetable, thenTrightcan be either a table or a timetable.outerjoinreturnsTas a timetable for either combination of inputs.
[T](#btx2ndz-1-C) = outerjoin([Tleft](#mw%5Ff8c603e5-ef85-494d-acfd-ed1e5afc1daf),[Tright](#mw%5Ff6023fff-36da-477c-b657-ea48af2f2fb3),[Name,Value](#namevaluepairarguments)) performs the outer-join operation with additional options specified by one or moreName,Value pair arguments.
[[T](#btx2ndz-1-C),[ileft](#btx2ndz-1-ia),[iright](#btx2ndz-1-ib)] = outerjoin(___) also returns index vectors, ileft andiright, indicating the correspondence between rows inT and rows in Tleft andTright respectively. You can use this syntax with any of the input arguments in the previous syntaxes.
Examples
Create a table, Tleft.
Tleft = table([5;12;23;2;15;6],... {'cheerios';'pizza';'salmon';'oreos';'lobster';'pizza'},... 'VariableNames',{'Age','FavoriteFood'},... 'RowNames',{'Amy','Bobby','Holly','Harry','Marty','Sally'})
Tleft=6×2 table Age FavoriteFood ___ ____________
Amy 5 {'cheerios'}
Bobby 12 {'pizza' }
Holly 23 {'salmon' }
Harry 2 {'oreos' }
Marty 15 {'lobster' }
Sally 6 {'pizza' }Create a table, Tright, with one variable in common with Tleft, called FavoriteFood.
Tright = table({'cheerios';'oreos';'pizza';'salmon';'cake'},... [110;160;140;367;243],... {'A-';'D';'B';'B';'C-'},... 'VariableNames',{'FavoriteFood','Calories','NutritionGrade'})
Tright=5×3 table FavoriteFood Calories NutritionGrade ____________ ________ ______________
{'cheerios'} 110 {'A-'}
{'oreos' } 160 {'D' }
{'pizza' } 140 {'B' }
{'salmon' } 367 {'B' }
{'cake' } 243 {'C-'} Use the outerjoin function to create a new table, T, with data from tables Tleft and Tright.
T = outerjoin(Tleft,Tright)
T=7×5 table Age FavoriteFood_Tleft FavoriteFood_Tright Calories NutritionGrade ___ __________________ ___________________ ________ ______________
NaN {0×0 char } {'cake' } 243 {'C-' }
5 {'cheerios'} {'cheerios'} 110 {'A-' }
15 {'lobster' } {0×0 char } NaN {0×0 char}
2 {'oreos' } {'oreos' } 160 {'D' }
12 {'pizza' } {'pizza' } 140 {'B' }
6 {'pizza' } {'pizza' } 140 {'B' }
23 {'salmon' } {'salmon' } 367 {'B' } Table T contains a separate variable for the key variable from Tleft, called FavoriteFood_Tleft, and the key variable from Tright, called FavoriteFood_Tright.
Create a table, Tleft.
Tleft = table({'a' 'b' 'c' 'e' 'h'}',[1 2 3 11 17]',... 'VariableNames',{'Key1' 'Var1'})
Tleft=5×2 table Key1 Var1 _____ ____
{'a'} 1
{'b'} 2
{'c'} 3
{'e'} 11
{'h'} 17 Create a table, Tright, with common values in the variable Key1 between tables Tleft and Tright, but also containing rows with values of Key1 not present in Tleft.
Tright = table({'a','b','d','e'}',[4;5;6;7],... 'VariableNames',{'Key1' 'Var2'})
Tright=4×2 table Key1 Var2 _____ ____
{'a'} 4
{'b'} 5
{'d'} 6
{'e'} 7 Use the outerjoin function to create a new table, T, with data from tables Tleft and Tright. Merge the key values into a single variable in the output table, T.
T = outerjoin(Tleft,Tright,'MergeKeys',true)
T=6×3 table Key1 Var1 Var2 _____ ____ ____
{'a'} 1 4
{'b'} 2 5
{'c'} 3 NaN
{'d'} NaN 6
{'e'} 11 7
{'h'} 17 NaN Variables in table T that came from Tleft contain missing values in the rows that have no match from Tright. Similarly, variables in T that came from Tright contain missing values in those rows that had no match from Tleft.
Create a table, Tleft.
Tleft = table({'a' 'b' 'c' 'e' 'h'}',[1 2 3 11 17]',... 'VariableNames',{'Key1' 'Var1'})
Tleft=5×2 table Key1 Var1 _____ ____
{'a'} 1
{'b'} 2
{'c'} 3
{'e'} 11
{'h'} 17 Create a table, Tright, with common values in the variable Key1 between tables Tleft and Tright, but also containing rows with values of Key1 not present in Tleft.
Tright = table({'a','b','d','e'}',[4;5;6;7],... 'VariableNames',{'Key1' 'Var2'})
Tright=4×2 table Key1 Var2 _____ ____
{'a'} 4
{'b'} 5
{'d'} 6
{'e'} 7 Use the outerjoin function to create a new table, T, with data from tables Tleft and Tright. Match up rows with common values in the key variable, Key1, but also retain rows whose key values don’t have a match.
Also, return index vectors, ileft and iright indicating the correspondence between rows in T and rows in Tleft and Tright respectively.
[T,ileft,iright] = outerjoin(Tleft,Tright)
T=6×4 table Key1_Tleft Var1 Key1_Tright Var2 __________ ____ ___________ ____
{'a' } 1 {'a' } 4
{'b' } 2 {'b' } 5
{'c' } 3 {0×0 char} NaN
{0×0 char} NaN {'d' } 6
{'e' } 11 {'e' } 7
{'h' } 17 {0×0 char} NaN The index vectors ileft and iright contain zeros to indicate the rows in table T that do not correspond to rows in tables Tleft or Tright, respectively.
Create a table, Tleft.
Tleft = table({'a' 'b' 'c' 'e' 'h'}',[1 2 3 11 17]',... 'VariableNames',{'Key1' 'Var1'})
Tleft=5×2 table Key1 Var1 _____ ____
{'a'} 1
{'b'} 2
{'c'} 3
{'e'} 11
{'h'} 17 Create a table, Tright, with common values in the variable Key1 between tables Tleft and Tright, but also containing rows with values of Key1 not present in Tleft.
Tright = table({'a','b','d','e'}',[4;5;6;7],... 'VariableNames',{'Key1' 'Var2'})
Tright=4×2 table Key1 Var2 _____ ____
{'a'} 4
{'b'} 5
{'d'} 6
{'e'} 7 Use the outerjoin function to create a new table, T, with data from tables Tleft and Tright. Ignore rows in Tright whose key values do not match any rows in Tleft.
Also, return index vectors, ileft and iright indicating the correspondence between rows in T and rows in Tleft and Tright respectively.
[T,ileft,iright] = outerjoin(Tleft,Tright,'Type','left')
T=5×4 table Key1_Tleft Var1 Key1_Tright Var2 __________ ____ ___________ ____
{'a'} 1 {'a' } 4
{'b'} 2 {'b' } 5
{'c'} 3 {0×0 char} NaN
{'e'} 11 {'e' } 7
{'h'} 17 {0×0 char} NaN All values of ileft are nonzero indicating that all rows in T have corresponding rows in Tleft.
Create two timetables, Tleft and Tright. They have some row times in common, but each also includes row times that are not in the other timetable.
Tleft = timetable(seconds([1;2;4;6]),[1 2 3 11]')
Tleft=4×1 timetable Time Var1 _____ ____
1 sec 1
2 sec 2
4 sec 3
6 sec 11 Tright = timetable(seconds([2;4;6;7]),[4 5 6 7]')
Tright=4×1 timetable Time Var1 _____ ____
2 sec 4
4 sec 5
6 sec 6
7 sec 7 Combine Tleft and Tright with an outer join. T1 matches up the rows with common row times, but also includes the rows that do not have matches.
T1 = outerjoin(Tleft,Tright)
T1=5×2 timetable Time Var1_Tleft Var1_Tright _____ __________ ___________
1 sec 1 NaN
2 sec 2 4
4 sec 3 5
6 sec 11 6
7 sec NaN 7 Combine Tleft and Tright, but ignore rows in Tright whose row times do not match any row times in Tleft.
T2 = outerjoin(Tleft,Tright,'Type','left')
T2=4×2 timetable Time Var1_Tleft Var1_Tright _____ __________ ___________
1 sec 1 NaN
2 sec 2 4
4 sec 3 5
6 sec 11 6 Input Arguments
Left table, specified as a table or a timetable.
Right table, specified as a table or a timetable.
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments asName1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is the argument name and Value is the corresponding value. Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the pairs does not matter.
Before R2021a, use commas to separate each name and value, and enclose Name in quotes.
Example: 'Keys',2 uses the second variable in Tleft and the second variable in Tright as key variables.
Variables to use as keys, specified as the comma-separated pair consisting of'Keys' and a positive integer, vector of positive integers, string array, character vector, cell array of character vectors, pattern scalar, or logical vector.
You cannot use the 'Keys' name-value pair argument with the 'LeftKeys' and 'RightKeys' name-value pair arguments.
The vector of row labels can be a key. For more information, see the Algorithms section.
Example: 'Keys',[1 3] uses the first and third variables inTleft and Tright as key variables.
Example: 'Keys',{'X','Y'} uses the variables namedX and Y inTleft and Tright as key variables.
Example: 'Keys','Row' uses the vectors of row names of Tleft and Tright as key variables, if both Tleft andTright are tables with row names.
Variables to use as keys in Tleft, specified as the comma-separated pair consisting of 'LeftKeys' and a positive integer, vector of positive integers, string array, character vector, cell array of character vectors, pattern scalar, or logical vector.
You must use the 'LeftKeys' name-value pair argument in conjunction with the 'RightKeys' name-value pair argument. 'LeftKeys' and'RightKeys' both must specify the same number of key variables. outerjoin pairs key values based on their order.
The vector of row labels can be a key. For more information, see theAlgorithms section.
Example: 'LeftKeys',1 uses only the first variable in Tleft as a key variable.
Variables to use as keys in Tright, specified as the comma-separated pair consisting of 'RightKeys' and a positive integer, vector of positive integers, string array, character vector, cell array of character vectors, pattern scalar, or logical vector.
You must use the 'RightKeys' name-value pair argument in conjunction with the 'LeftKeys' name-value pair argument. 'LeftKeys' and'RightKeys' both must specify the same number of key variables. outerjoin pairs key values based on their order.
The vector of row labels can be a key. For more information, see theAlgorithms section.
Example: 'RightKeys',3 uses only the third variable in Tright as a key variable.
Merge keys flag, specified as the comma-separated pair consisting of 'MergeKeys' and either false, true, 0 or 1.
| false | outerjoin includes two separate variables in the output table,T, for each key variable pair from tables Tleft andTright.This behavior is the default behavior. |
|---|---|
| true | outerjoin includes a single variable in the output table,T, for each key variable pair from tables Tleft andTright.outerjoin creates the single variable by merging the key values from Tleft andTright, taking values fromTleft where a corresponding row exists in Tleft, and taking values from Tright otherwise.If you specify'LeftVariables' or'RightVariables' to include only one key from a key variable pair, thenouterjoin includes the merged key—containing values from both key variables—in the output table.If you specify'LeftVariables' and'RightVariables' to exclude both keys from a key variable pair, thenouterjoin does not include the merged key variable in the output table. |
Variables from Tleft to include inT, specified as the comma-separated pair consisting of 'LeftVariables' and a positive integer, vector of positive integers, string array, character vector, cell array of character vectors, pattern scalar, or logical vector.
You can use 'LeftVariables' to include or exclude key variables as well as nonkey variables from the output,T.
By default, outerjoin includes all variables fromTleft.
Variables from Tright to include inT, specified as the comma-separated pair consisting of 'RightVariables' and a positive integer, vector of positive integers, string array, character vector, cell array of character vectors, pattern scalar, or logical vector.
You can use 'RightVariables' to include or exclude key variables as well as nonkey variables from the output,T.
By default, outerjoin includes all the variables from Tright.
Type of outer join operation, specified as the comma-separated pair consisting of'Type' and either 'full' (meaning a full outer join), 'left' (left outer join), or 'right' (right outer join).
- For a full outer join of inputs
TleftandTright, the outputTcombines all rows from both inputs, filling empty table elements with missing values.
- For a left outer join, the output
Tincludes all rows fromTleft, but excludes rows ofTrightwhose key values do not match any key values fromTleft.
- For a right outer join,
Tincludes all rows fromTright, but excludes rows ofTleftwhose key values do not match any key values fromTright.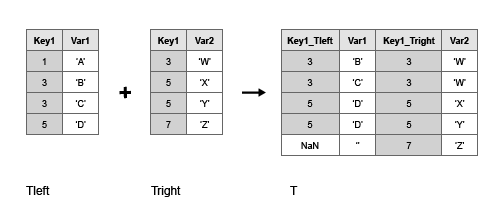
By default, outerjoin does a full outer join and includes unmatched rows from both Tleft and Tright.
Output Arguments
Outer join from Tleft and Tright, returned as a table. The output table, T, contains one row for each pair of rows in tables Tleft andTright that share the same combination of key values. If Tleft and Tright contain variables with the same name, outerjoin adds a unique suffix to the corresponding variable names in T. Variables inT that came from Tleft contain missing values in those rows that had no match fromTright. Similarly, variables in T that came from Tright contain missing values in those rows that had no match from Tleft.
(A missing value is equivalent to "Not-a-Number" for various data types, such as a NaN, NaT, empty string, or undefined categorical value.)
In general, if there are m rows in tableTleft and n rows in tableTright that all contain the same combination of values in the key variables, table T containsm*n rows for that combination. T also contains rows corresponding to key value combinations in one input table that do not match any row the other input table.
T contains the horizontal concatenation ofTleft(ileft,LeftVars) andTright(iright,RightVars) sorted by the values in the key variables. By default, LeftVars consists of all the variables of Tleft, and RightVars consists of all the variables from Tright. Otherwise,LeftVars consists of the variables specified by the'LeftVariables' name-value pair argument, andRightVars consists of the variables specified by the'RightVariables' name-value pair argument.
You can store additional metadata such as descriptions, variable units, variable names, and row names in the table. For more information, see the Properties section of table.
Index to Tleft, returned as a column vector. Each element of ileft identifies the row in tableTleft that corresponds to that row in the output table, T. The vector ileft contains zeros to indicate the rows in T that do not correspond to rows in Tleft.
Index to Tright, returned as a column vector. Each element of iright identifies the row in tableTright that corresponds to that row in the output table, T. The vector iright contains zeros to indicate the rows in T that do not correspond to rows in Tright.
More About
Variable used to match and combine data between the input tables,Tleft and Tright.
Algorithms
- The vector of row labels from an input table or timetable can be used as a key variable. Row labels are the row names of a table or the row times of a timetable. To use this vector as a key, specify it as
'Row'(for the row names of a table), as the name of a timetable vector of row times, or as the value of_`T`_.Properties.DimensionNames{1}, where_`T`_is the table or timetable.
In general,outerjoincopies row labels from the input tableTleftto the output tableT.- If
Tlefthas no row labels, thenThas no row labels. - If
Tlefthas row labels, thenouterjoincopies row labels fromTleftto create row labels inT.
* If you specify row labels from bothTleftandTrightas a key pair, thenouterjoinmerges row labels fromTrightinto row labels ofTwhere needed.
* If you specify row labels ofTleftas a key, but do not specify row labels ofTrightas the matching key, thenouterjoincreates default row labels inTwhere needed. Typically, default row labels areNaNs or missing values
* If bothTleftandTrightare tables, but you do not specify either input’s row names as a key, thenouterjoindoes not create row names inT.
* If bothTleftandTrightare timetables, but you do not specify either input’s row times as a key, thenouterjoincopies row times fromTlefttoT. It also fills inNaNs orNaTs as row times where needed.
- If
You cannot perform an outer join using the row labels ofTleft as the left key and a variable ofTright as the right key. To perform the outer join, convert the row labels of Tleft to a table variable and use the new table variable as a key.
Extended Capabilities
Theouterjoin function fully supports tall arrays. For more information, see Tall Arrays.
Usage notes and limitations:
- Input tables cannot have key variables with the same names unless the value of
'MergeKeys'istrue(logical1). - In general, the input tables cannot have any nonkey variables with the same names. However, you can join subsets of the input tables if you specify the
'LeftVariables'and'RightVariables'name-value arguments. Specify these arguments so that no variable name appears in both'LeftVariables'and'RightVariables'. - The values of these name-value arguments must be constant:
'Keys''LeftKeys''RightKeys''MergeKeys''LeftVariables''RightVariables''Type'
- The values of these name-value arguments do not support pattern expressions:
'Keys''LeftKeys''RightKeys''LeftVariables''RightVariables'
- Nested tables and timetables are not supported.
Version History
Introduced in R2013b