Unstack Table Variables - Distribute values from one table variable to multiple table variables in the Live
Editor - MATLAB ([original](https://in.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/unstacktablevariables.html)) ([raw](?raw))Main Content
Distribute values from one table variable to multiple table variables in the Live Editor
Description
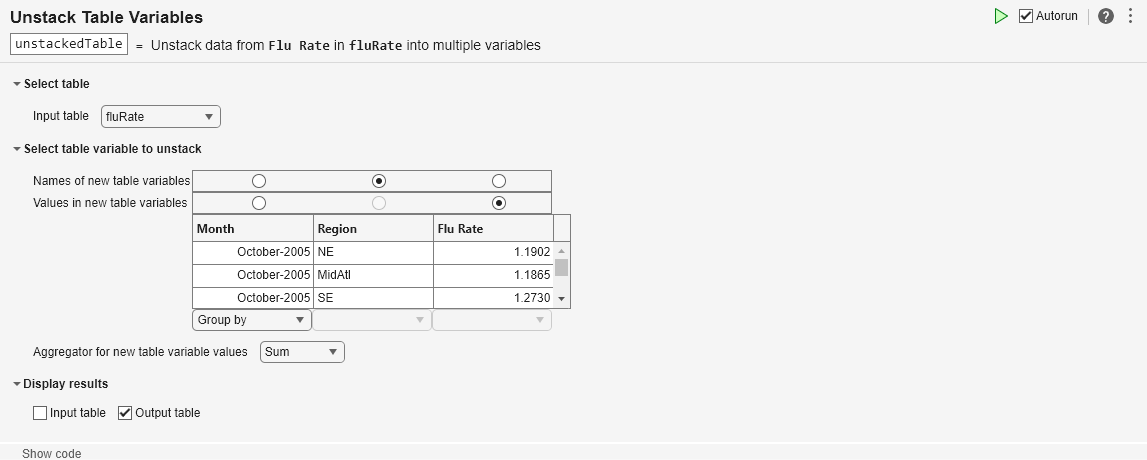
The Unstack Table Variables task lets you interactively unstack, or distribute, values in a table or timetable from one variable to multiple variables. The task automatically generates MATLAB® code for your live script. The generated code uses the unstack function.
To unstack variables means to distribute values from specified variables into multiple variables of the output. You must specify that one input variable is the indicator variable, whose unique values indicate the corresponding variables of the output. Other variables of the input can be grouping variables or constant variables, whose values determine the rows of the output. The diagram shows the result of unstacking a table using indicator and grouping variables.
Open the Task
To add the Unstack Table Variables task to a live script in the MATLAB Editor:
- On the Live Editor tab, select > .
- Or, in a code block in the script, type a relevant keyword, such as
unstack. Select from the suggested command completions.
Examples
This example shows how to unstack values from one variable in an input table and distribute them to multiple variables in an output table by using the Unstack Table Variables Live Editor task.
First, load a table from a sample file that lists the number of power company customers who experienced electric power outages. The table lists the number of customers by month and by region of the United States.
load customersOutage.mat customersOutage
customersOutage=18×3 table Month Region CustomersOutage _____________ _________ _______________
October-2023 NorthEast 3492
October-2023 MidWest 565
October-2023 SouthEast 1027
November-2023 NorthEast 2944
November-2023 MidWest 1293
November-2023 SouthEast 834
December-2023 NorthEast 2559
December-2023 MidWest 936
December-2023 SouthEast 1412
January-2024 NorthEast 12045
January-2024 MidWest 50117
January-2024 SouthEast 0
February-2024 NorthEast 4931
February-2024 MidWest 1089
February-2024 SouthEast 137
March-2024 NorthEast 3018
⋮Add the Unstack Table Variables task to your live script. Unstack the CustomersOutage variable so that the output table has variables named NorthEast, MidWest, and SouthEast.
- To group the data by month, select the
Group bymenu item below theMonthvariable in the task. - To select the names of the output variables, click the radio button
Names of new table variablesabove theRegionvariable. For each unique value inRegion, there is a corresponding variable in the output table. - To distribute values from the
CustomersOutagevariable into theNorthEast,Midwest, andSouthEastvariables in the output, click the radio buttonValues in new table variablesaboveCustomersOutage.
unstackedTable=6×4 table Month NorthEast MidWest SouthEast _____________ _________ _______ _________
October-2023 3492 565 1027
November-2023 2944 1293 834
December-2023 2559 936 1412
January-2024 12045 50117 0
February-2024 4931 1089 137
March-2024 3018 942 870 Related Examples
Version History
Introduced in R2020a
When you select the Custom function option for theAggregator for new table variable values method, you can generate template code that can help you write your own custom aggregation function.
- Select
Custom function. - Select
Local functionfrom the next menu. - Click New to add a new local function to the script.
- Select the name of the new local function from the next menu.
The live task generates template code and places it within the live script. To customize this code, edit it in the live script.
This Live Editor task does not run automatically if the inputs have more than 1 million elements. In previous releases, the task always ran automatically for inputs of any size. If the inputs have a large number of elements, then the code generated by this task can take a noticeable amount of time to run (more than a few seconds).
When a task does not run automatically, the Autorun indicator is disabled. You can either run the task manually when needed or choose to enable the task to run automatically.