Function Caller - Call a Simulink function - Simulink (original) (raw)
Libraries:
Simulink / User-Defined Functions
Description
A Function Caller block calls and executes a Simulink® function. Simulink functions specify a function prototype which includes the function name and input and output arguments. For example, when a Function Caller block calls a function with prototype y = f(u), the input of theFunction Caller block is the input argument, u, of the Simulink function and the output argument, y, of the Simulink function is the output of the Function Caller block.
In this example, a Function Caller block is configured to call and execute the Simulink function, y = timestwo(x), defined in aSimulink Function block. To test the function call, a Sine Wave block is connected to the input port x to provide input data and a Scope block is connected to the output porty to view results from the output.
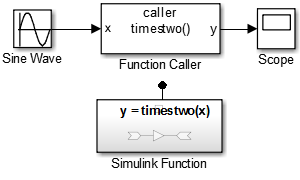
You can call a Simulink function defined in a Simulink Function block, Stateflow® Chart (Stateflow) as an exported function, or anS-Function block. For more information on defining a Simulink function, see Define a Simulink Function in a Model.
For more information, see Simulink Functions Overview.
Examples
Ports
Input
Input signal for an input argument that is sent to the function.
The function prototype determines the number and name of input ports that appear on the Function Caller block. Connect signal lines to the input ports to send data to a function through the function input arguments.
For example, y = myfunction(u) creates one input port (u) on the Function Caller block.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | Boolean | fixed point | enumerated | bus
Output
Output signal for an output argument that the function returns.
The function prototype determines the number and name of output ports that appear on the Function Caller block. Connect signal or message lines to the output ports to receive data from a function through the function output arguments. The Function Caller block outputs messages when you select theExecute function call asynchronously check box.
For example, y = myfunction(u) creates one output port (y) on the Function Caller block.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | Boolean | fixed point | enumerated | bus
Parameters
Specify the function prototype between a Function Caller block and a Simulink function.
Note
To call a function defined in a Simulink Function block:
- Function call argument names must match the function arguments.
- Function names, input arguments, and output arguments must be valid MATLAB® identifiers.
Programmatic Use
| Block Parameter: FunctionPrototype |
|---|
| Type: character vector |
| Values: 'y=f(u)' | function prototype |
| Default:'y=f(u)' |
Qualified function name, specified as a character vector or string.
The function name is shown on the block icon. You can edit the name by clicking on the parameter value on the block icon and entering a new value.
Note
This parameter is automatically synchronized with theFunction prototype parameter of theFunction Caller block.
For more information about resolving a function through qualification, seeScoped Simulink Function Blocks in Models andScoped Simulink Function Blocks in Subsystems.
Programmatic Use
| Block Parameter: ScopedFunctionName | |
|---|---|
| Type: character vector | |
| Values: 'f' | 'Client.f' | function name |
| Default:'f' |
Specify a comma-separated list of MATLAB expressions that combine data type, dimensions, and complexity (real or imaginary) for each input argument. For examples, see Argument Specification for Simulink Function Blocks.
Note
This specification must match the Simulink Function block data type specified with the Data type parameter of the Argument Inport block.
Programmatic Use
| Block Parameter: InputArgumentSpecifications |
|---|
| Type: character vector |
| Values: '' | MATLAB expression |
| Default:'' |
Specify a comma-separated list of MATLAB expressions that combine data type, dimensions, and complexity (real or imaginary) for each output argument. For examples, see Argument Specification for Simulink Function Blocks.
Note
This specification must match the Simulink Function block data type specified with the Data type parameter of the Argument Outport block.
Programmatic Use
| Block Parameter: OutputArgumentSpecifications |
|---|
| Type: character vector |
| Values: '' | MATLAB expression |
| Default:'' |
Specify the interval of time between calls to the Simulink function.
By default, the block inherits its sample time based on the context of the block in the model. To set a different sample time, enter a value using a sample time format from the table in Specify Sample Time.
If the Function Caller block has any inputs, it is a nonsource block, and you must set the sample time to-1.
Programmatic Use
| Block Parameter:SampleTime | |
|---|---|
| Type: string | character vector | |
| Values: scalar | vector | sample time |
| Default:'-1' |
Specify whether to execute the Simulink Function block associated with this Function Caller block asynchronously.
- Select Execute function call asynchronously to enable asynchronous execution.
Asynchronous execution is when the caller invokes a function, the function executes based on the priority order, and returns the output arguments to the caller. The function executes based on the ordering defined in the Schedule Editor and then returns the output arguments to the caller. The block outputs these arguments using a message output port.- If there is one function output argument, the output argument becomes the message payload.
- If there is more than one function output argument, the Function Caller block bundles the output arguments as a structure that becomes the message payload.
Connect the message output port to a Message Triggered Subsystem block in immediate mode. The Message Triggered Subsystem block acts as a callback for the function.
- Clear Execute function call asynchronously to enable synchronous execution.
Synchronous execution is when the caller invokes a function, the function runs immediately, and returns the output arguments to the caller.
Programmatic Use
| Block Parameter:AsynchronousCaller |
|---|
| Type: character vector |
| Values: 'on' | 'off' |
| Default:'off' |
Block Characteristics
| Data Types | Boolean | bus | double | enumerated | fixed point | integer | single |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Feedthrough | yes | |||||
| Multidimensional Signals | yes | |||||
| Variable-Size Signals | no | |||||
| Zero-Crossing Detection | no |
Extended Capabilities
To generate code for a model that uses the Function Caller block to call and execute a Simulink function asynchronously:
- Select the Execute function call asynchronously parameter in the Function Caller block parameters.
- Set the System target file parameter in Configuration Parameters. For more information, see Configure a System Target File (Embedded Coder).
Version History
Introduced in R2014b
Starting in R2025a, the Function Caller block supports editing the qualified function name with the Function name parameter. Use one of these methods.
- Use set_param to set
ScopedFunctionNameblock parameter. - Click on the parameter value on the block icon and enter a new value.
Starting in R2022b, when you select a Function Caller block whose related Simulink Function block is in a referenced model, both theSimulink Function block and the Model block of the referenced model are highlighted.
Starting in R2022b, you can specify a Simulink function to be executed asynchronously by selecting the newExecute function call asynchronously parameter in theTrigger block inside of the Simulink Function block and in the Function Caller block.