arviz.plot_dist — ArviZ dev documentation (original) (raw)
arviz.plot_dist(values, values2=None, color='C0', kind='auto', cumulative=False, label=None, rotated=False, rug=False, bw='default', quantiles=None, contour=True, fill_last=True, figsize=None, textsize=None, plot_kwargs=None, fill_kwargs=None, rug_kwargs=None, contour_kwargs=None, contourf_kwargs=None, pcolormesh_kwargs=None, hist_kwargs=None, is_circular=False, ax=None, backend=None, backend_kwargs=None, show=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Plot distribution as histogram or kernel density estimates.
By default continuous variables are plotted using KDEs and discrete ones using histograms
Parameters:
valuesarray_like
Values to plot from an unknown continuous or discrete distribution.
values2array_like, optional
Values to plot. If present, a 2D KDE or a hexbin will be estimated.
colorstr
valid matplotlib color.
kindstr, default “auto”
By default (“auto”) continuous variables will use the kind defined by rcParamplot.density_kind and discrete ones will use histograms. To override this use “hist” to plot histograms and “kde” for KDEs.
If true plot the estimated cumulative distribution function. Defaults to False. Ignored for 2D KDE.
labelstr
Text to include as part of the legend.
Whether to rotate the 1D KDE plot 90 degrees.
Add a rug plot for a specific subset of values. Ignored for 2D KDE.
If numeric, indicates the bandwidth and must be positive. If str, indicates the method to estimate the bandwidth and must be one of “scott”, “silverman”, “isj” or “experimental” when is_circular is False and “taylor” (for now) when is_circular is True. Defaults to “experimental” when variable is not circular and “taylor” when it is.
quantileslist, optional
Quantiles in ascending order used to segment the KDE. Use [.25, .5, .75] for quartiles.
If True plot the 2D KDE using contours, otherwise plot a smooth 2D KDE.
If True fill the last contour of the 2D KDE plot.
figsize(float, float), optional
Figure size. If None it will be defined automatically.
textsizefloat, optional
Text size scaling factor for labels, titles and lines. If None it will be autoscaled based on figsize. Not implemented for bokeh backend.
plot_kwargsdict
Keywords passed to the pdf line of a 1D KDE. Passed to arviz.plot_kde() asplot_kwargs.
fill_kwargsdict
Keywords passed to the fill under the line (use fill_kwargs={‘alpha’: 0} to disable fill). Ignored for 2D KDE. Passed to arviz.plot_kde() as fill_kwargs.
rug_kwargsdict
Keywords passed to the rug plot. Ignored if rug=False or for 2D KDE Use space keyword (float) to control the position of the rugplot. The larger this number the lower the rugplot. Passed toarviz.plot_kde() as rug_kwargs.
contour_kwargsdict
Keywords passed to the contourplot. Ignored for 1D KDE.
contourf_kwargsdict
Keywords passed to matplotlib.axes.Axes.contourf(). Ignored for 1D KDE.
pcolormesh_kwargsdict
Keywords passed to matplotlib.axes.Axes.pcolormesh(). Ignored for 1D KDE.
hist_kwargsdict
Keyword arguments used to customize the histogram. Ignored when plotting a KDE. They are passed to matplotlib.axes.Axes.hist() if using matplotlib, or to bokeh.plotting.figure.quad() if using bokeh. In bokeh case, the following extra keywords are also supported:
color: replaces thefill_colorandline_colorof thequadmethodbins: taken fromhist_kwargsand passed to numpy.histogram() insteaddensity: normalize histogram to represent a probability density function, Defaults toTruecumulative: plot the cumulative counts. Defaults toFalse.
is_circular{False, True, “radians”, “degrees”}, default False
Select input type {“radians”, “degrees”} for circular histogram or KDE plot. If True, default input type is “radians”. When this argument is present, it interprets the values passed are from a circular variable measured in radians and a circular KDE is used. Inputs in “degrees” will undergo an internal conversion to radians. Only valid for 1D KDE.
axmatplotlib Axes or Bokeh Figure, optional
Matplotlib or bokeh targets on which to plot. If not supplied, Arviz will create its own plot area (and return it).
backend{“matplotlib”, “bokeh”}, default “matplotlib”
Select plotting backend.
backend_kwargs :dict, optional
These are kwargs specific to the backend being used, passed tomatplotlib.pyplot.subplots() or bokeh.plotting.figure. For additional documentation check the plotting method of the backend.
showbool, optional
Call backend show function.
Returns:
axesmatplotlib axes or bokeh figure
See also
Plot Posterior densities in the style of John K. Kruschke’s book.
Generate KDE plots for continuous variables and histograms for discrete ones.
1D or 2D KDE plot taking into account boundary conditions.
Examples
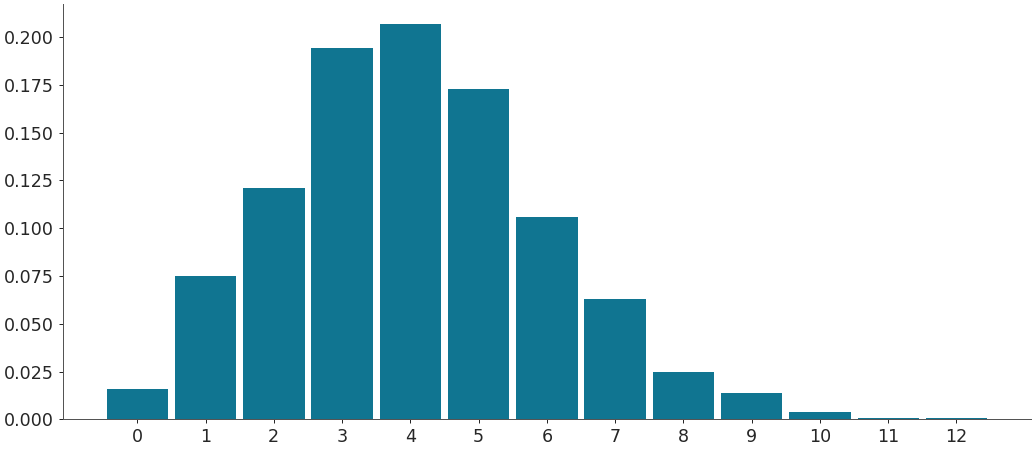
Plot an integer distribution
import numpy as np import arviz as az a = np.random.poisson(4, 1000) az.plot_dist(a)
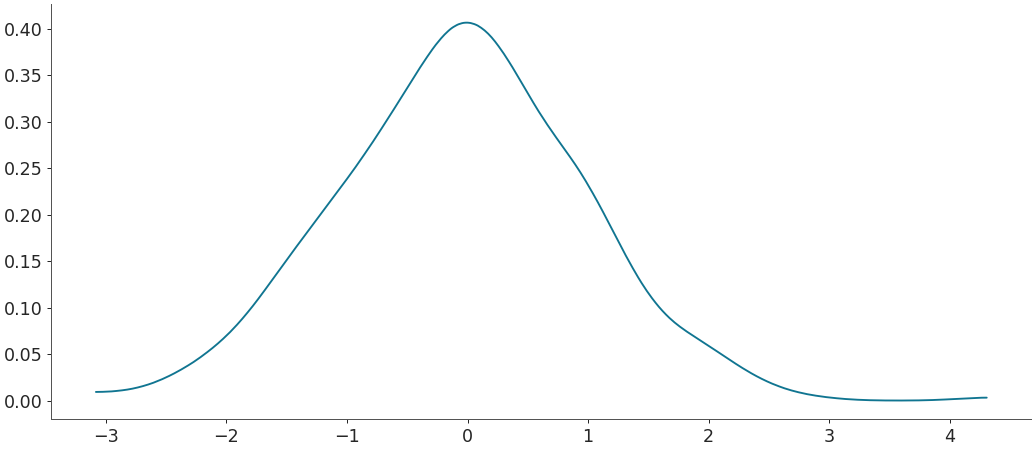
Plot a continuous distribution
b = np.random.normal(0, 1, 1000) az.plot_dist(b)
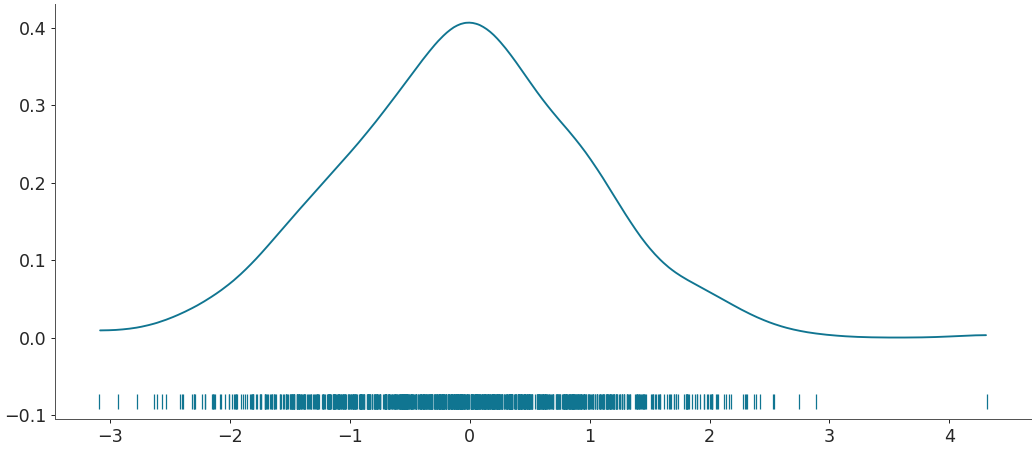
Add a rug under the Gaussian distribution
az.plot_dist(b, rug=True)
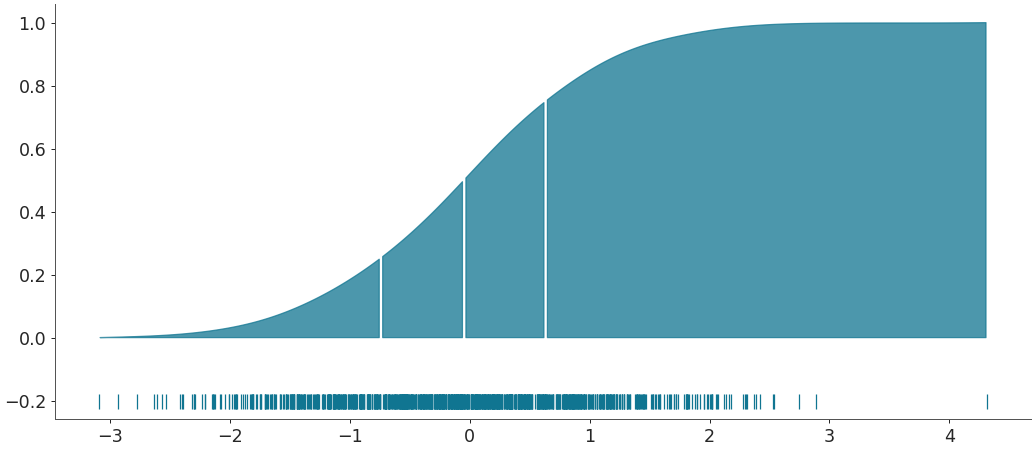
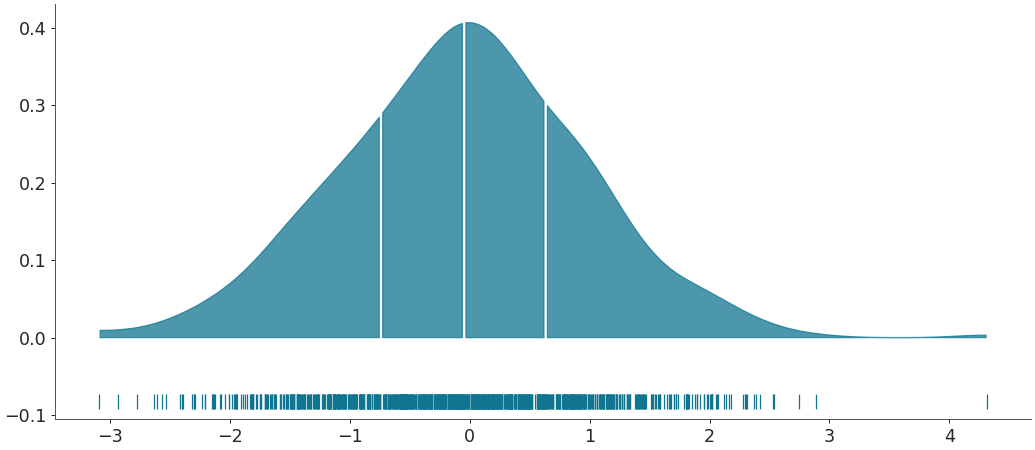
Segment into quantiles
az.plot_dist(b, rug=True, quantiles=[.25, .5, .75])
Plot as the cumulative distribution
az.plot_dist(b, rug=True, quantiles=[.25, .5, .75], cumulative=True)