Density Estimation for a Gaussian mixture (original) (raw)
Note
Go to the endto download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via JupyterLite or Binder
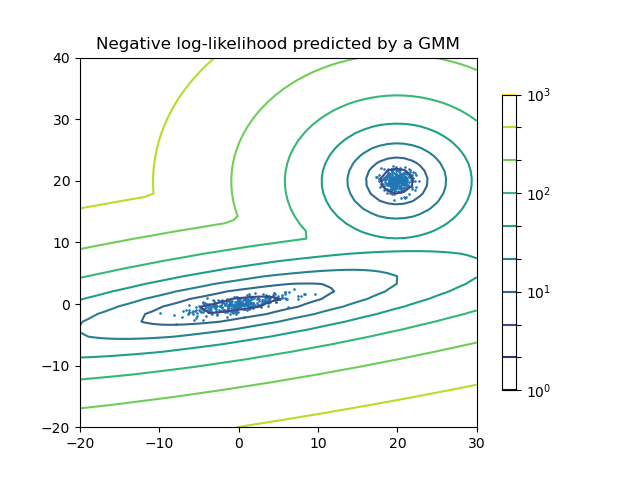
Plot the density estimation of a mixture of two Gaussians. Data is generated from two Gaussians with different centers and covariance matrices.
Authors: The scikit-learn developers
SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np from matplotlib.colors import LogNorm
from sklearn import mixture
n_samples = 300
generate random sample, two components
generate spherical data centered on (20, 20)
shifted_gaussian = np.random.randn(n_samples, 2) + np.array([20, 20])
generate zero centered stretched Gaussian data
C = np.array([[0.0, -0.7], [3.5, 0.7]]) stretched_gaussian = np.dot(np.random.randn(n_samples, 2), C)
concatenate the two datasets into the final training set
X_train = np.vstack([shifted_gaussian, stretched_gaussian])
fit a Gaussian Mixture Model with two components
clf = mixture.GaussianMixture(n_components=2, covariance_type="full") clf.fit(X_train)
display predicted scores by the model as a contour plot
x = np.linspace(-20.0, 30.0) y = np.linspace(-20.0, 40.0) X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y) XX = np.array([X.ravel(), Y.ravel()]).T Z = -clf.score_samples(XX) Z = Z.reshape(X.shape)
CS = plt.contour( X, Y, Z, norm=LogNorm(vmin=1.0, vmax=1000.0), levels=np.logspace(0, 3, 10) ) CB = plt.colorbar(CS, shrink=0.8, extend="both") plt.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], 0.8)
plt.title("Negative log-likelihood predicted by a GMM") plt.axis("tight") plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.121 seconds)
Related examples