CalibrationDisplay (original) (raw)
class sklearn.calibration.CalibrationDisplay(prob_true, prob_pred, y_prob, *, estimator_name=None, pos_label=None)[source]#
Calibration curve (also known as reliability diagram) visualization.
It is recommended to usefrom_estimator orfrom_predictionsto create a CalibrationDisplay. All parameters are stored as attributes.
Read more about calibration in the User Guide and more about the scikit-learn visualization API in Visualizations.
For an example on how to use the visualization, seeProbability Calibration curves.
Added in version 1.0.
Parameters:
prob_truendarray of shape (n_bins,)
The proportion of samples whose class is the positive class (fraction of positives), in each bin.
prob_predndarray of shape (n_bins,)
The mean predicted probability in each bin.
y_probndarray of shape (n_samples,)
Probability estimates for the positive class, for each sample.
estimator_namestr, default=None
Name of estimator. If None, the estimator name is not shown.
pos_labelint, float, bool or str, default=None
The positive class when computing the calibration curve. By default, pos_label is set to estimators.classes_[1] when usingfrom_estimator and set to 1 when using from_predictions.
Added in version 1.1.
Attributes:
**line_**matplotlib Artist
Calibration curve.
**ax_**matplotlib Axes
Axes with calibration curve.
**figure_**matplotlib Figure
Figure containing the curve.
See also
Compute true and predicted probabilities for a calibration curve.
CalibrationDisplay.from_predictions
Plot calibration curve using true and predicted labels.
CalibrationDisplay.from_estimator
Plot calibration curve using an estimator and data.
Examples
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression from sklearn.calibration import calibration_curve, CalibrationDisplay X, y = make_classification(random_state=0) X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split( ... X, y, random_state=0) clf = LogisticRegression(random_state=0) clf.fit(X_train, y_train) LogisticRegression(random_state=0) y_prob = clf.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1] prob_true, prob_pred = calibration_curve(y_test, y_prob, n_bins=10) disp = CalibrationDisplay(prob_true, prob_pred, y_prob) disp.plot() <...>
classmethod from_estimator(estimator, X, y, *, n_bins=5, strategy='uniform', pos_label=None, name=None, ax=None, ref_line=True, **kwargs)[source]#
Plot calibration curve using a binary classifier and data.
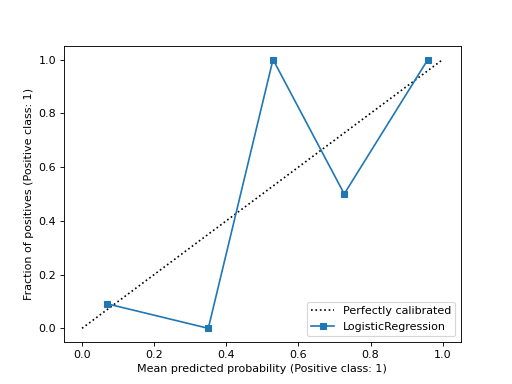
A calibration curve, also known as a reliability diagram, uses inputs from a binary classifier and plots the average predicted probability for each bin against the fraction of positive classes, on the y-axis.
Extra keyword arguments will be passed tomatplotlib.pyplot.plot.
Read more about calibration in the User Guide and more about the scikit-learn visualization API in Visualizations.
Added in version 1.0.
Parameters:
estimatorestimator instance
Fitted classifier or a fitted Pipelinein which the last estimator is a classifier. The classifier must have a predict_proba method.
X{array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Input values.
yarray-like of shape (n_samples,)
Binary target values.
n_binsint, default=5
Number of bins to discretize the [0, 1] interval into when calculating the calibration curve. A bigger number requires more data.
strategy{‘uniform’, ‘quantile’}, default=’uniform’
Strategy used to define the widths of the bins.
'uniform': The bins have identical widths.'quantile': The bins have the same number of samples and depend on predicted probabilities.
pos_labelint, float, bool or str, default=None
The positive class when computing the calibration curve. By default, estimators.classes_[1] is considered as the positive class.
Added in version 1.1.
namestr, default=None
Name for labeling curve. If None, the name of the estimator is used.
axmatplotlib axes, default=None
Axes object to plot on. If None, a new figure and axes is created.
ref_linebool, default=True
If True, plots a reference line representing a perfectly calibrated classifier.
**kwargsdict
Keyword arguments to be passed to matplotlib.pyplot.plot.
Returns:
displayCalibrationDisplay.
Object that stores computed values.
See also
CalibrationDisplay.from_predictions
Plot calibration curve using true and predicted labels.
Examples
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.datasets import make_classification from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression from sklearn.calibration import CalibrationDisplay X, y = make_classification(random_state=0) X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split( ... X, y, random_state=0) clf = LogisticRegression(random_state=0) clf.fit(X_train, y_train) LogisticRegression(random_state=0) disp = CalibrationDisplay.from_estimator(clf, X_test, y_test) plt.show()
classmethod from_predictions(y_true, y_prob, *, n_bins=5, strategy='uniform', pos_label=None, name=None, ax=None, ref_line=True, **kwargs)[source]#
Plot calibration curve using true labels and predicted probabilities.
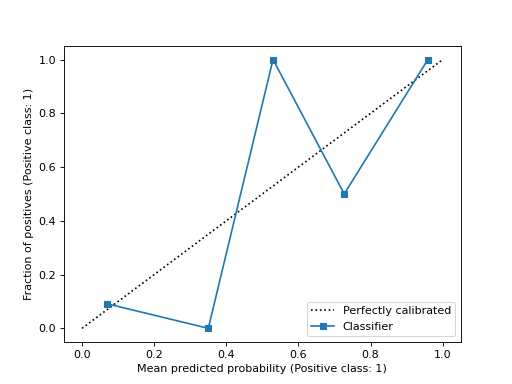
Calibration curve, also known as reliability diagram, uses inputs from a binary classifier and plots the average predicted probability for each bin against the fraction of positive classes, on the y-axis.
Extra keyword arguments will be passed tomatplotlib.pyplot.plot.
Read more about calibration in the User Guide and more about the scikit-learn visualization API in Visualizations.
Added in version 1.0.
Parameters:
y_truearray-like of shape (n_samples,)
True labels.
y_probarray-like of shape (n_samples,)
The predicted probabilities of the positive class.
n_binsint, default=5
Number of bins to discretize the [0, 1] interval into when calculating the calibration curve. A bigger number requires more data.
strategy{‘uniform’, ‘quantile’}, default=’uniform’
Strategy used to define the widths of the bins.
'uniform': The bins have identical widths.'quantile': The bins have the same number of samples and depend on predicted probabilities.
pos_labelint, float, bool or str, default=None
The positive class when computing the calibration curve. By default pos_label is set to 1.
Added in version 1.1.
namestr, default=None
Name for labeling curve.
axmatplotlib axes, default=None
Axes object to plot on. If None, a new figure and axes is created.
ref_linebool, default=True
If True, plots a reference line representing a perfectly calibrated classifier.
**kwargsdict
Keyword arguments to be passed to matplotlib.pyplot.plot.
Returns:
displayCalibrationDisplay.
Object that stores computed values.
See also
CalibrationDisplay.from_estimator
Plot calibration curve using an estimator and data.
Examples
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.datasets import make_classification from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression from sklearn.calibration import CalibrationDisplay X, y = make_classification(random_state=0) X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split( ... X, y, random_state=0) clf = LogisticRegression(random_state=0) clf.fit(X_train, y_train) LogisticRegression(random_state=0) y_prob = clf.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1] disp = CalibrationDisplay.from_predictions(y_test, y_prob) plt.show()
plot(*, ax=None, name=None, ref_line=True, **kwargs)[source]#
Plot visualization.
Extra keyword arguments will be passed tomatplotlib.pyplot.plot.
Parameters:
axMatplotlib Axes, default=None
Axes object to plot on. If None, a new figure and axes is created.
namestr, default=None
Name for labeling curve. If None, use estimator_name if not None, otherwise no labeling is shown.
ref_linebool, default=True
If True, plots a reference line representing a perfectly calibrated classifier.
**kwargsdict
Keyword arguments to be passed to matplotlib.pyplot.plot.
Returns:
displayCalibrationDisplay
Object that stores computed values.