imageDataAugmenter - Configure image data augmentation - MATLAB (original) (raw)
Configure image data augmentation
Creation
Syntax
Description
aug = imageDataAugmenter creates animageDataAugmenter object with default property values consistent with the identity transformation.
aug = imageDataAugmenter(`Name,Value`) configures a set of image augmentation options using name-value pairs to setproperties. You can specify multiple name-value pairs. Enclose each property name in quotes.
Properties
FillValue — Fill value
numeric scalar | numeric vector
Fill value used to define out-of-bounds points when resampling, specified as a numeric scalar or numeric vector.
- If the augmented images are single channel, then
FillValuemust be a scalar. - If the augmented images are multichannel, then
FillValuecan be a scalar or a vector with length equal to the number of channels of the input image. For example, if the input image is an RGB image,FillValuecan be a vector of length 3.
For grayscale and color images, the default fill value is0. For categorical images, the default fill value is an '<undefined>' label and thetrainnet function ignores filled pixels when training.
Example: 128
RandXReflection — Random reflection
false (default) | true
Random reflection in the left-right direction, specified as a logical scalar. When RandXReflection is true (1), each image is reflected horizontally with 50% probability. When RandXReflection isfalse (0), no images are reflected.
RandYReflection — Random reflection
false (default) | true
Random reflection in the top-bottom direction, specified as a logical scalar. When RandYReflection is true (1), each image is reflected vertically with 50% probability. When RandYReflection isfalse (0), no images are reflected.
RandRotation — Range of rotation
[0 0] (default) | 2-element numeric vector | function handle
Range of rotation, in degrees, applied to the input image, specified as one of the following.
- 2-element numeric vector. The second element must be larger than or equal to the first element. The rotation angle is picked randomly from a continuous uniform distribution within the specified interval.
- function handle. The function must accept no input arguments and return the rotation angle as a numeric scalar. Use a function handle to pick rotation angles from a disjoint interval or using a nonuniform probability distribution. For more information about function handles, see Create Function Handle.
By default, augmented images are not rotated.
Example: [-45 45]
RandScale — Range of uniform scaling
[1 1] (default) | 2-element numeric vector | function handle
Range of uniform (isotropic) scaling applied to the input image, specified as one of the following.
- 2-element numeric vector. The second element must be larger than or equal to the first element. The scale factor is picked randomly from a continuous uniform distribution within the specified interval.
- function handle. The function must accept no input arguments and return the scale factor as a numeric scalar. Use a function handle to pick scale factors from a disjoint interval or using a nonuniform probability distribution. For more information about function handles, see Create Function Handle.
By default, augmented images are not scaled.
Example: [0.5 4]
RandXScale — Range of horizontal scaling
[1 1] (default) | 2-element vector of positive numbers | function handle
Range of horizontal scaling applied to the input image, specified as one of the following.
- 2-element numeric vector. The second element must be larger than or equal to the first element. The horizontal scale factor is picked randomly from a continuous uniform distribution within the specified interval.
- function handle. The function must accept no input arguments and return the horizontal scale factor as a numeric scalar. Use a function handle to pick horizontal scale factors from a disjoint interval or using a nonuniform probability distribution. For more information about function handles, seeCreate Function Handle.
By default, augmented images are not scaled in the horizontal direction.
Note
If you specify RandScale, thenimageDataAugmenter ignores the value ofRandXScale when scaling images.
Example: [0.5 4]
RandYScale — Range of vertical scaling
[1 1] (default) | 2-element vector of positive numbers | function handle
Range of vertical scaling applied to the input image, specified as one of the following.
- 2-element numeric vector. The second element must be larger than or equal to the first element. The vertical scale factor is picked randomly from a continuous uniform distribution within the specified interval.
- function handle. The function must accept no input arguments and return the vertical scale factor as a numeric scalar. Use a function handle to pick vertical scale factors from a disjoint interval or using a nonuniform probability distribution. For more information about function handles, see Create Function Handle.
By default, augmented images are not scaled in the vertical direction.
Note
If you specify RandScale, thenimageDataAugmenter ignores the value ofRandYScale when scaling images.
Example: [0.5 4]
RandXShear — Range of horizontal shear
[0 0] (default) | 2-element numeric vector | function handle
Range of horizontal shear applied to the input image, specified as one of the following. Shear is measured as an angle in degrees, and is in the range (–90, 90).
- 2-element numeric vector. The second element must be larger than or equal to the first element. The horizontal shear angle is picked randomly from a continuous uniform distribution within the specified interval.
- function handle. The function must accept no input arguments and return the horizontal shear angle as a numeric scalar. Use a function handle to pick horizontal shear angles from a disjoint interval or using a nonuniform probability distribution. For more information about function handles, see Create Function Handle.
By default, augmented images are not sheared in the horizontal direction.
Example: [0 45]
RandYShear — Range of vertical shear
[0 0] (default) | 2-element numeric vector | function handle
Range of vertical shear applied to the input image, specified as one of the following. Shear is measured as an angle in degrees, and is in the range (–90, 90).
- 2-element numeric vector. The second element must be larger than or equal to the first element. The vertical shear angle is picked randomly from a continuous uniform distribution within the specified interval.
- function handle. The function must accept no input arguments and return the vertical shear angle as a numeric scalar. Use a function handle to pick vertical shear angles from a disjoint interval or using a nonuniform probability distribution. For more information about function handles, see Create Function Handle.
By default, augmented images are not sheared in the vertical direction.
Example: [0 45]
RandXTranslation — Range of horizontal translation
[0 0] (default) | 2-element numeric vector | function handle
Range of horizontal translation applied to the input image, specified as one of the following. Translation distance is measured in pixels.
- 2-element numeric vector. The second element must be larger than or equal to the first element. The horizontal translation distance is picked randomly from a continuous uniform distribution within the specified interval.
- function handle. The function must accept no input arguments and return the horizontal translation distance as a numeric scalar. Use a function handle to pick horizontal translation distances from a disjoint interval or using a nonuniform probability distribution. For more information about function handles, see Create Function Handle.
By default, augmented images are not translated in the horizontal direction.
Example: [-5 5]
RandYTranslation — Range of vertical translation
[0 0] (default) | 2-element numeric vector | function handle
Range of vertical translation applied to the input image, specified as one of the following. Translation distance is measured in pixels.
- 2-element numeric vector. The second element must be larger than or equal to the first element. The vertical translation distance is picked randomly from a continuous uniform distribution within the specified interval.
- function handle. The function must accept no input arguments and return the vertical translation distance as a numeric scalar. Use a function handle to pick vertical translation distances from a disjoint interval or using a nonuniform probability distribution. For more information about function handles, see Create Function Handle.
By default, augmented images are not translated in the vertical direction.
Example: [-5 5]
Object Functions
| augment | Apply identical random transformations to multiple images |
|---|
Examples
Create Image Data Augmenter to Resize and Rotate Images
Create an image data augmenter that preprocesses images before training. This augmenter rotates images by random angles in the range [0, 360] degrees and resizes images by random scale factors in the range [0.5, 1].
augmenter = imageDataAugmenter( ... 'RandRotation',[0 360], ... 'RandScale',[0.5 1])
augmenter = imageDataAugmenter with properties:
FillValue: 0
RandXReflection: 0
RandYReflection: 0
RandRotation: [0 360]
RandScale: [0.5000 1]
RandXScale: [1 1]
RandYScale: [1 1]
RandXShear: [0 0]
RandYShear: [0 0]
RandXTranslation: [0 0]
RandYTranslation: [0 0]Create an augmented image datastore using the image data augmenter. The augmented image datastore also requires sample data, labels, and an output image size.
[XTrain,YTrain] = digitTrain4DArrayData; imageSize = [56 56 1]; auimds = augmentedImageDatastore(imageSize,XTrain,YTrain,'DataAugmentation',augmenter)
auimds = augmentedImageDatastore with properties:
NumObservations: 5000
MiniBatchSize: 128
DataAugmentation: [1x1 imageDataAugmenter]
ColorPreprocessing: 'none'
OutputSize: [56 56]
OutputSizeMode: 'resize'
DispatchInBackground: 0Preview the random transformations applied to the first eight images in the image datastore.
minibatch = preview(auimds); imshow(imtile(minibatch.input));
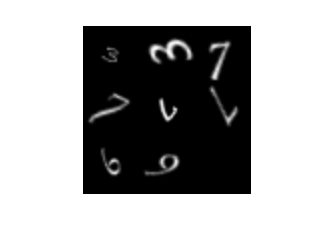
Preview different random transformations applied to the same set of images.
minibatch = preview(auimds); imshow(imtile(minibatch.input));

Train Network with Augmented Images
Train a convolutional neural network using augmented image data. Data augmentation helps prevent the network from overfitting and memorizing the exact details of the training images.
Load the sample data, which consists of synthetic images of handwritten digits. XTrain is a 28-by-28-by-1-by-5000 array, where:
- 28 is the height and width of the images.
- 1 is the number of channels.
- 5000 is the number of synthetic images of handwritten digits.
labelsTrain is a categorical vector containing the labels for each observation.
Set aside 1000 of the images for network validation.
idx = randperm(size(XTrain,4),1000); XValidation = XTrain(:,:,:,idx); XTrain(:,:,:,idx) = []; TValidation = labelsTrain(idx); labelsTrain(idx) = [];
Create an imageDataAugmenter object that specifies preprocessing options for image augmentation, such as resizing, rotation, translation, and reflection. Randomly translate the images up to three pixels horizontally and vertically, and rotate the images with an angle up to 20 degrees.
imageAugmenter = imageDataAugmenter( ... 'RandRotation',[-20,20], ... 'RandXTranslation',[-3 3], ... 'RandYTranslation',[-3 3])
imageAugmenter = imageDataAugmenter with properties:
FillValue: 0
RandXReflection: 0
RandYReflection: 0
RandRotation: [-20 20]
RandScale: [1 1]
RandXScale: [1 1]
RandYScale: [1 1]
RandXShear: [0 0]
RandYShear: [0 0]
RandXTranslation: [-3 3]
RandYTranslation: [-3 3]Create an augmentedImageDatastore object to use for network training and specify the image output size. During training, the datastore performs image augmentation and resizes the images. The datastore augments the images without saving any images to memory. trainnet updates the network parameters and then discards the augmented images.
imageSize = [28 28 1]; augimds = augmentedImageDatastore(imageSize,XTrain,labelsTrain,'DataAugmentation',imageAugmenter);
Specify the convolutional neural network architecture.
layers = [ imageInputLayer(imageSize)
convolution2dLayer(3,8,'Padding','same')
batchNormalizationLayer
reluLayer
maxPooling2dLayer(2,'Stride',2)
convolution2dLayer(3,16,'Padding','same')
batchNormalizationLayer
reluLayer
maxPooling2dLayer(2,'Stride',2)
convolution2dLayer(3,32,'Padding','same')
batchNormalizationLayer
reluLayer
fullyConnectedLayer(10)
softmaxLayer];Specify the training options. Choosing among the options requires empirical analysis. To explore different training option configurations by running experiments, you can use the Experiment Manager app.
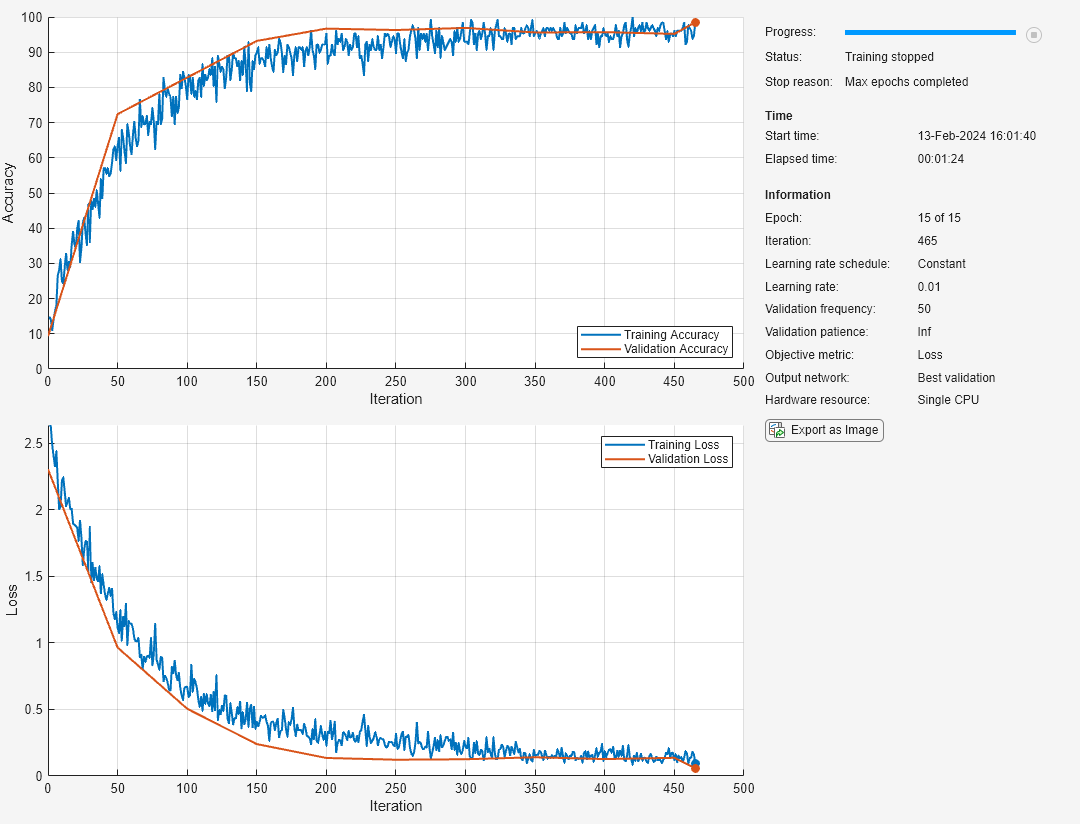
opts = trainingOptions('sgdm', ... 'MaxEpochs',15, ... 'Shuffle','every-epoch', ... 'Plots','training-progress', ... 'Metrics','accuracy', ... 'Verbose',false, ... 'ValidationData',{XValidation,TValidation});
Train the neural network using the trainnet function. For classification, use cross-entropy loss. By default, the trainnet function uses a GPU if one is available. Training on a GPU requires a Parallel Computing Toolbox™ license and a supported GPU device. For information on supported devices, see GPU Computing Requirements (Parallel Computing Toolbox). Otherwise, the trainnet function uses the CPU. To specify the execution environment, use the ExecutionEnvironment training option.
net = trainnet(augimds,layers,"crossentropy",opts);
Tips
- To preview the transformations applied to sample images, use the augment function.
- To perform image augmentation during training, create an augmentedImageDatastore and specify preprocessing options by using the
'DataAugmentation'name-value pair with an imageDataAugmenter. The augmented image datastore automatically applies random transformations to the training data.
Version History
Introduced in R2017b