issorted - Determine if array is sorted - MATLAB (original) (raw)
Determine if array is sorted
Syntax
Description
TF = issorted([A](#bvcule5-A)) returns logical1 (true) when the elements ofA are in sorted order and logical 0 (false) otherwise.
- If
Ais a vector, thenissortedreturns 1 when the vector elements are in ascending order. - If
Ais a matrix, thenissortedreturns 1 when each column ofAis in ascending order. - If
Ais a multidimensional array, thenissortedreturns 1 whenAis in ascending order along the first dimension whose size does not equal 1. - If
Ais a timetable, thenissortedreturns 1 when its row time vector is in ascending order. To check the ordering of row times or variables of a timetable with additional options, use theissortedrowsfunction.
TF = issorted([A](#bvcule5-A),[dim](#bvcule5-dim)) returns 1 when A is sorted along dimension dim. For example, if A is a matrix, then issorted(A,2) returns 1 when each row of A is in ascending order.
TF = issorted(___,[direction](#bvcule5-direction)) returns 1 when A is sorted in the order specified by direction for any of the previous syntaxes. For example, issorted(A,'monotonic') returns 1 if the elements of A are ascending or descending.
TF = issorted(___,[Name,Value](#namevaluepairarguments)) specifies additional parameters for checking sort order. For example, issorted(A,'ComparisonMethod','abs') checks if A is sorted by magnitude.
TF = issorted([A](#bvcule5-A),'rows') returns 1 when the elements of the first column of a matrix are sorted. If the first column contains repeated elements, then issorted looks at the ordering of the second column to determine TF. In general, issorted looks to the column immediately to the right to determine TF when the current and previous columns have repeated elements.
- If
Ais a timetable, thenissortedchecks if the row time vector is in ascending order. - This syntax is not supported for a matrix of character vectors.
Note
This syntax is not recommended. Use issortedrows instead.
Examples
Sorted Vector
Create a vector and check if it is sorted in ascending order.
A = [5 12 33 39 78 90 95 107]; issorted(A)
Sorted Matrix Rows
Create a 5-by-5 matrix and check if each row is sorted in descending order.
A = 5×5
17 24 1 8 15
23 5 7 14 16
4 6 13 20 22
10 12 19 21 3
11 18 25 2 9Sort each row of A in descending order using the sort function, and check that the result has descending rows.
B = 5×5
24 17 15 8 1
23 16 14 7 5
22 20 13 6 4
21 19 12 10 3
25 18 11 9 22-D Array of Strings
Create a 2-D array of strings and determine if each column is sorted.
str = ["Horse","Chicken";"cow","Goat"]
str = 2x2 string "Horse" "Chicken" "cow" "Goat"
Determine if the rows are sorted from left to right.
Determine if each row is sorted in descending order from left to right.
issorted(str,2,'descend')
Complex Vector with NaN
Create a vector containing complex numbers and NaN values.
A = [NaN NaN 1+i 1+2i 2+2i 3+i];
Check that the NaN elements are placed first within the vector, and that the remaining elements are sorted by real part.
issorted(A,'MissingPlacement','first','ComparisonMethod','real')
Since the third and fourth elements of A have equal real part, issorted checks if the imaginary part of these elements are also sorted.
Input Arguments
A — Input array
vector | matrix | multidimensional array | cell array of character vectors | timetable
Input array, specified as a vector, matrix, multidimensional array, cell array of character vectors, or timetable.
- If
Acontains missing values, such asNaN,NaT,<undefined>, andmissing, then by default,issortedrequires that they are placed at the end to return 1. - If
Ais complex, then by default,issorteddetermines sort order by the magnitude of the elements. If there are consecutive elements with equal magnitude, thenissortedalso checks the phase angle in the interval (-π, π] to break ties. - If
Ais a cell array of character vectors or a string array, thenissorteddetermines sort order using the code order for the UTF-16 character encoding scheme. The sort is case-sensitive. For more information on sorted character and string arrays, see Sort Order for Character and String Arrays.
Data Types: double | single | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | logical | char | string | cell | categorical | datetime | duration | timetable
Complex Number Support: Yes
dim — Dimension to operate along
positive integer scalar
Dimension to operate along, specified as a positive integer scalar. If no value is specified, then the default is the first array dimension whose size does not equal 1.
Consider a matrix A. issorted(A,1) checks if the data in each column of A is sorted.
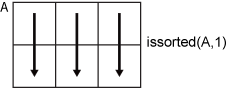
issorted(A,2) checks if the data in each row of A is sorted.
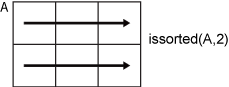
dim is not supported for timetable input.
Data Types: double | single | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
direction — Sorting direction
'ascend' (default) | 'descend' | 'monotonic' | 'strictascend' | 'strictdescend' | 'strictmonotonic'
Sorting direction, specified as one of the following:
'ascend'— Checks if data is in ascending order. Data can contain consecutive repeated elements.'descend'— Checks if data is in descending order. Data can contain consecutive repeated elements.'monotonic'— Checks if data is in descending or ascending order. Data can contain consecutive repeated elements.'strictascend'— Checks if data is in strictly ascending order. Data cannot contain duplicate or missing elements.'strictdescend'— Checks if data is in strictly descending order. Data cannot contain duplicate or missing elements.'strictmonotonic'— Checks if data is in strictly descending or strictly ascending order. Data cannot contain duplicate or missing elements.
direction is not supported for timetable input. Use issortedrows instead.
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments asName1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is the argument name and Value is the corresponding value. Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the pairs does not matter.
Before R2021a, use commas to separate each name and value, and enclose Name in quotes.
Example: issorted(A,'MissingPlacement','last')
MissingPlacement — Placement of missing values
'auto' (default) | 'first' | 'last'
Placement of missing values (NaN, NaT, <undefined>, and missing) specified as the comma-separated pair consisting of 'MissingPlacement' and one of the following:
'auto'— Missing elements are required to be placed last for ascending order and first for descending order to return 1.'first'— Missing elements are required to be placed first to return 1.'last'— Missing elements are required to be placed last to return 1.
This name-value pair is not supported for timetable input. Use issortedrows instead.
ComparisonMethod — Element comparison method
'auto' (default) | 'real' | 'abs'
Element comparison method for numeric input, specified as the comma-separated pair consisting of 'ComparisonMethod' and one of the following:
'auto'— Check ifAis sorted byreal(A)whenAis real, and check ifAis sorted byabs(A)whenAis complex.'real'— Check ifAis sorted byreal(A)whenAis real or complex. IfAhas elements with consecutive equal real parts, then checkimag(A)to break ties.'abs'— Check ifAis sorted byabs(A)whenAis real or complex. IfAhas elements with consecutive equal magnitude, then checkangle(A)in the interval (-π,π] to break ties.
More About
Sort Order for Character and String Arrays
MATLAB® stores characters as Unicode® using the UTF-16 character encoding scheme. Character and string arrays are sorted according to the UTF-16 code point order. For the characters that are also the ASCII characters, this order means that uppercase letters come before lowercase letters. Digits and some punctuation also come before letters.
Extended Capabilities
Tall Arrays
Calculate with arrays that have more rows than fit in memory.
Theissorted function fully supports tall arrays. For more information, see Tall Arrays.
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using MATLAB® Coder™.
Usage notes and limitations:
- The first input argument must not be a cell array.
- If
Ais complex with all zero imaginary parts, then MATLAB might convertAtoreal(A)before callingissorted(A). In this case, MATLAB checks thatAis sorted byreal(A), but the generated code checks thatAis sorted byabs(A). To make the generated code match MATLAB, useissorted(real(A))orissorted(A,'ComparisonMethod','real'). See Code Generation for Complex Data with Zero-Valued Imaginary Parts (MATLAB Coder). - If you supply
dim, then it must be constant. - For limitations related to variable-size inputs, see Variable-Sizing Restrictions for Code Generation of Toolbox Functions (MATLAB Coder).
Thread-Based Environment
Run code in the background using MATLAB® backgroundPool or accelerate code with Parallel Computing Toolbox™ ThreadPool.
This function fully supports thread-based environments. For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions in Thread-Based Environment.
GPU Arrays
Accelerate code by running on a graphics processing unit (GPU) using Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
The issorted function supports GPU array input with these usage notes and limitations:
- The input array
Amust be a vector. - The
MissingPlacementname-value option supports only the value'auto'.
For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions on a GPU (Parallel Computing Toolbox).
Distributed Arrays
Partition large arrays across the combined memory of your cluster using Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
This function fully supports distributed arrays. For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions with Distributed Arrays (Parallel Computing Toolbox).
Version History
Introduced before R2006a