afterEach - Run function after each function finishes running in the background - MATLAB (original) (raw)
Run function after each function finishes running in the background
Syntax
Description
[B](#mw%5F246a6227-31b7-4a73-bb93-554a26bc91e9) = afterEach([A](#mw%5F568d326c-59ee-483b-bee6-3cf7414dd621),[fcn](#mw%5F83b760b7-250b-48db-b5eb-4c833bc19a57),[n](#mw%5F1bdc7797-9ff0-4ef7-824b-891b2e6a551b)) runs the function fcn automatically after each element in theFuture array A finishes and returns aFuture object B.
MATLAB® runs the function fcn using the outputs from each element in Future array A. IfFuture array A has M elements, MATLAB runs the function M times. When the scheduled function fcn finishes for theMth time, theFuture object B finishes.
For more information about using afterEach to run functions after they finish running on a parallel pool, see afterEach (Parallel Computing Toolbox).
If the computations for any elements in A result in an error, by default, afterEach does not run fcn on the elements that failed.
[B](#mw%5F246a6227-31b7-4a73-bb93-554a26bc91e9) = afterEach([A](#mw%5F568d326c-59ee-483b-bee6-3cf7414dd621),[fcn](#mw%5F83b760b7-250b-48db-b5eb-4c833bc19a57),[n](#mw%5F1bdc7797-9ff0-4ef7-824b-891b2e6a551b),[PassFuture](#mw%5F38693cd9-c2b1-4abe-baae-ff3b448afebc)=true) runs fcn using each Future element inA instead of the outputs of each element inA. Use this syntax if you want to handle error fromFuture objects.
Examples
Run Callback Function After Function Finishes Running in the Background
This example shows how to use afterEach to schedule a callback function to run after a function finishes running in the background.
Use parfeval to run the function rand(1) and retrieve one output. Specify backgroundPool as the first argument to run the function in the background. Repeat 10 times to create 10 Future objects.
for i = 1:10 f(i) = parfeval(backgroundPool,@rand, 1, 1); end
After each Future finishes, display the value using the disp function. The input arguments for disp are the output arguments from each Future. Specify the third argument to the afterEach function as 0 to return no outputs from the callback.
Handle Errors from Functions Running in the Background
This example shows how to use afterEach to handle errors from a function that runs in the background.
When computations for Future objects result in an error, by default, afterEach does not evaluate its function on the elements that failed. If you want to handle any errors, for example, when you have a user interface that you want to update, you can use the PassFuture argument. When you set PassFuture to true, MATLAB passes the Future object to the callback function. You can call fetchOutputs on it, process the outputs, and handle any possible errors.
Send a computation to the background using parfeval. The computation results in an error. You can view the error message using the Error property of the future.
errorFuture = parfeval(backgroundPool, ... @(n,k) factorial(n)/(factorial(k)*factorial(n-k)),1,4,8); wait(errorFuture); errorFuture.Error
ans = ParallelException with properties:
identifier: 'MATLAB:factorial:NNegativeInt'
message: 'N must be an array of real non-negative integers.'
cause: {}
remotecause: {[1×1 MException]}
stack: [2×1 struct]
Correction: []If you use afterEach on a future that results in an error, the callback function is not evaluated. In the code below, MATLAB does not execute the displayResult function because the future errors.
afterEach(errorFuture,@displayResult,0);
Write a callback function to handle futures that result in errors. If the error property of the future variable is empty, the handleError helper function calls fetchOutputs on the future variable, and process its outputs. If the error property of the future variable is not empty, the handleError helper function displays an error dialog box.
function handleError(f) fig = uifigure(Position=[100 100 425 275]); if isempty(f.Error) output = fetchOutputs(f); message = strcat("Computation complete: Result = ",num2str(output)); uialert(fig,message,"Sucess",Icon="success") else message = "Computation failed!"; uialert(fig,message,"Error",Icon="error") end end
Call afterEach with the handleError function and set PassFuture to true.
afterEach(errorFuture,@handleError,0,PassFuture=true);

function displayResult(output) fig = uifigure(Position=[100 100 425 275]); message = strcat("Computation complete: Result = ",num2str(output)); uialert(fig,message,"Sucess",Icon="success") end
Update Wait Bar While Functions Run in the Background
This example shows how to use afterEach to update a wait bar with the progress of functions running in the background.
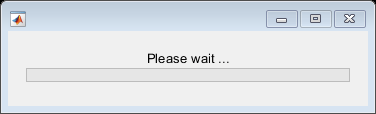
Create a wait bar, w.
w = waitbar(0,'Please wait ...');
Set the number of iterations for your for-loop, N. Store the current number of completed iterations, 0, and the total number of iterations, N, in the UserData property of the wait bar.
N = 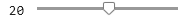 20;
w.UserData = [0 N];
20;
w.UserData = [0 N];
Run a for-loop with N iterations. In each iteration, use parfeval and backgroundPool to run pause in the background for a random number of seconds. Store each Future object in an array.
for i = 1:N delay = rand; f(i) = parfeval(backgroundPool,@pause,0,delay); end
Use the helper function updateWaitbar to update the waitbar after each Future finishes.
afterEach(f,@(~)updateWaitbar(w),0);
Use delete to close the wait bar after all the Future objects finish.
afterAll(f,@(~)delete(w),0);
Define Helper Function
Define the helper function updateWaitbar. The function increments the first element of the UserData property, then uses the vector to calculate the progress.
function updateWaitbar(w) % Update a waitbar using the UserData property.
% Check if the waitbar is a reference to a deleted object
if isvalid(w)
% Increment the number of completed iterations
w.UserData(1) = w.UserData(1) + 1;
% Calculate the progress
progress = w.UserData(1) / w.UserData(2);
% Update the waitbar
waitbar(progress,w);
endend
Input Arguments
A — Input Future
parallel.Future scalar | parallel.Future array
Input Future object, specified as a parallel.Future scalar or array.
MATLAB runs the function fcn after each element in A finishes.
- By default
PassFutureis false and MATLAB runsfcn(X1,...,Xm)using the outputsX1,...,Xmfrom eachFutureelement inAas the elements finish.
If any of the elements inAencounters an error, by default,afterEachdoes not runfcnon the elements that failed. - If you specify
PassFutureastrue, MATLAB runsfcn(A(j))after eachFutureelement inAfinishes.
If any of the elements inAencounters an errorafterEachrunsfcnon the elements that failed.
If the Future array has M elements, MATLAB runs the function M times. When the scheduled function fcn finishes, theFuture object B finishes.
Example: A = parfeval(backgroundPool,@magic,1,3);
fcn — Callback function to run
function handle
Callback function to run, specified as a function handle.
Example: fcn = @magic
n — Number of output arguments
nonnegative integer scalar
Number of output arguments, specified as a nonnegative integer scalar.
- By default
PassFutureis false, andnis the number of output arguments requested from runningfcn(X1,...,Xm)using the outputsX1,...,Xmfrom each element in theFuturearray A. - If you specify
PassFutureastrue,nis the number of output arguments requested from runningfcn(A(j))using each elementA(j)in theFuturearrayA.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
PassFuture — Pass Future elements in array A to callback function
falseor 0 (default) | true or 1
Pass the Future elements in array A to the callback function, specified as true orfalse.
- By default
PassFutureis false and MATLAB runsfcn(X1,...,Xm)using the outputsX1,...,Xmfrom eachFutureelement inAas the elements finish.
If any of the elements inAencounters an error, by default,afterEachdoes not runfcn on the elements that failed. - If you specify
PassFutureastrue, MATLAB runsfcn(A(j))after eachFutureelement inAfinishes, instead of the outputs of theFutureelements inA.
If any of the elements inAencounters an errorafterEachrunsfcnon the elements that failed.
Data Types: logical
Output Arguments
B — Output Future
parallel.Future object
Output Future object, returned as aparallel.Future object.
- Use fetchOutputs to retrieve results from
B. - Use
afterEachor afterAll to run a function whenBcompletes.
When you set PassFuture, you change theError property of B ifafterEach does not result in an error:
- By default,
PassFutureisfalseand if any of the elements inA encounters an error, theErrorproperty ofBis a cell array with the same number of elements asA. - If you set
PassFuturetotrue, theErrorproperty ofBis an empty cell array, even if one or more elements inAencounter an error.
If afterEach results in an error, theError property of B is anMException object.
Version History
Introduced in R2018a