join - Combine two tables or timetables by rows using key variables - MATLAB (original) (raw)
Combine two tables or timetables by rows using key variables
Syntax
Description
[T](#d126e1784712) = join([Tleft](#mw%5F408a130e-438a-4df0-9f84-79f9fc456187),[Tright](#mw%5Ffd2815b3-8905-4c1e-9623-9bc16b389101)) combines the tables or timetables Tleft andTright by merging rows from the two inputs. Thejoin function performs a simple form of the join operation where each row of Tleft must match exactly one row inTright. Rows match where the corresponding values in thekey variables are the same. The output combines all rows from Tleft with the rows fromTright where the key variables have matching values.
For example, if Tleft has variables namedKey1 and Var1, andTright has variables Key1 andVar2, then T=join(Tleft,Tright) usesKey1 as a key variable.
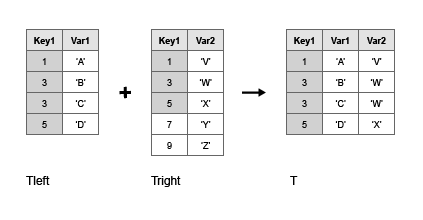
By default, the key variables are:
- Variables that have the same names in
TleftandTright, if both inputs are tables, or ifTleftis a timetable andTrightis a table. - Vectors of row times, if both
TleftandTrightare timetables.
The matching values of the key variables do not have to be in the same orders in the left and right inputs. Also, the key variables of Tright must contain all values in the key variables of Tleft. Each value must occur only once in the key variables of Tright, but can occur multiple times in the key variables of Tleft. Therefore, the join operation replicates any row from Tright that matches multiple rows from Tleft.
The inputs can be tables, timetables, or one of each.
- If
Tleftis a table, thenjoinreturnsTas a table. - If
Tleftis a timetable, thenjoinreturnsTas a timetable.
[T](#d126e1784712) = join([Tleft](#mw%5F408a130e-438a-4df0-9f84-79f9fc456187),[Tright](#mw%5Ffd2815b3-8905-4c1e-9623-9bc16b389101),[Name,Value](#namevaluepairarguments)) joins the tables or timetables with additional options specified by one or moreName,Value pair arguments.
For example, you can specify which variables to use as key variables.
[[T](#d126e1784712),[iright](#d126e1784808)] = join(___) also returns an index vectoriright such that each element of iright identifies the row in Tright that corresponds to that row inT. You can use this syntax with any of the input arguments of the previous syntaxes.
Examples
Append Values from One Table to Another
Create a table, Tleft.
Tleft = table({'Janice','Jonas','Javier','Jerry','Julie'}',[1;2;1;2;1],... 'VariableNames',{'Employee' 'Department'})
Tleft=5×2 table Employee Department __________ __________
{'Janice'} 1
{'Jonas' } 2
{'Javier'} 1
{'Jerry' } 2
{'Julie' } 1 Create a table, Tright, with a variable in common with Tleft.
Tright = table([1 2]',{'Mary' 'Mona'}',... 'VariableNames',{'Department' 'Manager'})
Tright=2×2 table Department Manager __________ ________
1 {'Mary'}
2 {'Mona'}Create a new table, T, containing data from tables Tleft and Tright. Use the join function to repeat and append Manager data from table Tright to the data from table Tleft, based on the key variable, Department.
T=5×3 table Employee Department Manager __________ __________ ________
{'Janice'} 1 {'Mary'}
{'Jonas' } 2 {'Mona'}
{'Javier'} 1 {'Mary'}
{'Jerry' } 2 {'Mona'}
{'Julie' } 1 {'Mary'}Merge Tables with One Variable in Common
Create a table, Tleft.
Tleft = table([5;12;23;2;6],... {'cereal';'pizza';'salmon';'cookies';'pizza'},... 'VariableNames',{'Age','FavoriteFood'},... 'RowNames',{'Amy','Bobby','Holly','Harry','Sally'})
Tleft=5×2 table Age FavoriteFood ___ ____________
Amy 5 {'cereal' }
Bobby 12 {'pizza' }
Holly 23 {'salmon' }
Harry 2 {'cookies'}
Sally 6 {'pizza' } Create a table, Tright, with one variable in common with Tleft.
Tright = table({'cereal';'cookies';'pizza';'salmon';'cake'},... [110;160;140;367;243],... {'B';'D';'B-';'A';'C-'},... 'VariableNames',{'FavoriteFood','Calories','NutritionGrade'})
Tright=5×3 table FavoriteFood Calories NutritionGrade ____________ ________ ______________
{'cereal' } 110 {'B' }
{'cookies'} 160 {'D' }
{'pizza' } 140 {'B-'}
{'salmon' } 367 {'A' }
{'cake' } 243 {'C-'} Create a new table, T, with data from tables Tleft and Tright. The variable in common, FavoriteFood, is used as a key variable by the join function.
T=5×4 table Age FavoriteFood Calories NutritionGrade ___ ____________ ________ ______________
Amy 5 {'cereal' } 110 {'B' }
Bobby 12 {'pizza' } 140 {'B-'}
Holly 23 {'salmon' } 367 {'A' }
Harry 2 {'cookies'} 160 {'D' }
Sally 6 {'pizza' } 140 {'B-'} Table T does not include information from the last row of table Tright about 'cake' because there is no corresponding entry in table Tleft.
Merge Tables by Specifying One Key Variable
Create a table, Tleft.
Tleft = table([10;4;2;3;7],[5;4;9;6;1],[10;3;8;8;4])
Tleft=5×3 table Var1 Var2 Var3 ____ ____ ____
10 5 10
4 4 3
2 9 8
3 6 8
7 1 4 Create a table, Tright, giving Var2 of table Tright the same contents as Var2 from table Tleft.
Tright = table([6;1;1;6;8],[5;4;9;6;1])
Tright=5×2 table Var1 Var2 ____ ____
6 5
1 4
1 9
6 6
8 1 Create a new table, T, containing data from tables Tleft and Tright. Use Var2 in tables Tleft and Tright as the key variable to the join function.
T = join(Tleft,Tright,'Keys','Var2')
T=5×4 table Var1_Tleft Var2 Var3 Var1_Tright __________ ____ ____ ___________
10 5 10 6
4 4 3 1
2 9 8 1
3 6 8 6
7 1 4 8 join adds a unique suffix to the nonkey variable, Var1, to distinguish the data from tables Tleft and Tright.
Keep One Copy of Nonkey Variables
Create a new table with data from tables Tleft and Tright. If any nonkey variables have the same name in both tables, keep only the copy from table Tleft.
Create a table, Tleft.
Tleft = table([10;4;2;3;7],[5;4;9;6;1])
Tleft=5×2 table Var1 Var2 ____ ____
10 5
4 4
2 9
3 6
7 1 Create a table, Tright, giving Var2 of table Tright the same contents as Var2 from table Tleft.
Tright = table([6;1;1;6;8],[5;4;9;6;1],[10;3;8;8;4])
Tright=5×3 table Var1 Var2 Var3 ____ ____ ____
6 5 10
1 4 3
1 9 8
6 6 8
8 1 4 Create a new table, T, with data from tables Tleft and Tright. Use Var2 as a key variable to the join function and keep only the copy of Var1 from table Tleft. The output table T does not contain the Var1 data from table Tright.
T = join(Tleft,Tright,'Keys','Var2','KeepOneCopy','Var1')
T=5×3 table Var1 Var2 Var3 ____ ____ ____
10 5 10
4 4 3
2 9 8
3 6 8
7 1 4 Merge Tables Using Row Names as Keys
Create a table, Tleft.
Tleft = table(['M';'M';'F';'F';'F'],[38;43;38;40;49],... 'VariableNames',{'Gender' 'Age'},... 'RowNames',{'Smith' 'Johnson' 'Williams' 'Jones' 'Brown'})
Tleft=5×2 table Gender Age ______ ___
Smith M 38
Johnson M 43
Williams F 38
Jones F 40
Brown F 49 Create a table, Tright, such that the rows of Tleft and the rows of Tright have a one-to-one correspondence.
Tright = table([64;69;67;71;64],... [119;163;133;176;131],... [122 80; 109 77; 117 75; 124 93; 125 83],... 'VariableNames',{'Height' 'Weight' 'BloodPressure'},... 'RowNames',{'Brown' 'Johnson' 'Jones' 'Smith' 'Williams'})
Tright=5×3 table Height Weight BloodPressure ______ ______ _____________
Brown 64 119 122 80
Johnson 69 163 109 77
Jones 67 133 117 75
Smith 71 176 124 93
Williams 64 131 125 83 Create a new table, T, with data from tables Tleft and Tright. Use the vectors of row names as key variables. (The name of the vector of row names of a table is 'Row', as shown by Tleft.Properties.DimensionNames{1}.)
T = join(Tleft,Tright,'Keys','Row')
T=5×5 table Gender Age Height Weight BloodPressure ______ ___ ______ ______ _____________
Smith M 38 71 176 124 93
Johnson M 43 69 163 109 77
Williams F 38 64 131 125 83
Jones F 40 67 133 117 75
Brown F 49 64 119 122 80 The rows of T are in the same order as Tleft.
Merge Tables Using Left and Right Keys
Create a table, Tleft.
Tleft = table([10;4;2;3;7],[5;4;9;6;1],[10;3;8;8;4])
Tleft=5×3 table Var1 Var2 Var3 ____ ____ ____
10 5 10
4 4 3
2 9 8
3 6 8
7 1 4 Create a table, Tright, giving Var2 of table Tright the same contents as Var1 from table Tleft, but in a different order.
Tright = table([6;1;1;6;8],[2;3;4;7;10])
Tright=5×2 table Var1 Var2 ____ ____
6 2
1 3
1 4
6 7
8 10 Create a new table, T, containing data from tables Tleft and Tright. Use Var1 from table Tleft with Var2 from table Tright as key variables to the join function.
[T,iright] = join(Tleft,Tright,'LeftKeys',1,'RightKeys',2)
T=5×4 table Var1_Tleft Var2 Var3 Var1_Tright __________ ____ ____ ___________
10 5 10 8
4 4 3 1
2 9 8 6
3 6 8 1
7 1 4 6 T is the horizontal concatenation of Tleft and Tright(iright,1).
Merge Timetables
Create two timetables that have the same row times but different variables.
Traffic = [0.8 0.9 0.1 0.7 0.9]'; Noise = [0 1 1.5 2 2.3]'; Tleft = timetable(hours(1:5)',Traffic,Noise)
Tleft=5×2 timetable Time Traffic Noise ____ _______ _____
1 hr 0.8 0
2 hr 0.9 1
3 hr 0.1 1.5
4 hr 0.7 2
5 hr 0.9 2.3 Distance = [0.88 0.86 0.91 0.9 0.86]'; Tright = timetable(hours(1:5)',Distance)
Tright=5×1 timetable Time Distance ____ ________
1 hr 0.88
2 hr 0.86
3 hr 0.91
4 hr 0.9
5 hr 0.86 Merge the timetables. join uses the row times as the key variables.
T=5×3 timetable Time Traffic Noise Distance ____ _______ _____ ________
1 hr 0.8 0 0.88
2 hr 0.9 1 0.86
3 hr 0.1 1.5 0.91
4 hr 0.7 2 0.9
5 hr 0.9 2.3 0.86 Merge Timetable and Table
Create a timetable and a table.
Measurements = [0.13 0.22 0.31 0.42 0.53 0.57 0.67 0.81 0.90 1.00]'; Device = ['A';'B';'A';'B';'A';'B';'A';'B';'A';'B']; Tleft = timetable(seconds(1:10)',Measurements,Device)
Tleft=10×2 timetable Time Measurements Device ______ ____________ ______
1 sec 0.13 A
2 sec 0.22 B
3 sec 0.31 A
4 sec 0.42 B
5 sec 0.53 A
6 sec 0.57 B
7 sec 0.67 A
8 sec 0.81 B
9 sec 0.9 A
10 sec 1 B Device = ['A';'B']; Accuracy = [0.023;0.037]; Tright = table(Device,Accuracy)
Tright=2×2 table Device Accuracy ______ ________
A 0.023
B 0.037 Merge the timetable and table. Device is the key variable because both Tleft and Tright have a variable with that name. T is a timetable.
T=10×3 timetable Time Measurements Device Accuracy ______ ____________ ______ ________
1 sec 0.13 A 0.023
2 sec 0.22 B 0.037
3 sec 0.31 A 0.023
4 sec 0.42 B 0.037
5 sec 0.53 A 0.023
6 sec 0.57 B 0.037
7 sec 0.67 A 0.023
8 sec 0.81 B 0.037
9 sec 0.9 A 0.023
10 sec 1 B 0.037 Input Arguments
Tleft — Left table
table | timetable
Left table, specified as a table or a timetable. For all key variables, each row of Tleft must match exactly one row inTright.
Tright — Right table
table | timetable
Right table, specified as a table or a timetable. For all key variables, each row of Tright must match exactly one row inTleft.
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments asName1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is the argument name and Value is the corresponding value. Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the pairs does not matter.
Before R2021a, use commas to separate each name and value, and enclose Name in quotes.
Example: 'Keys',2 uses the second variable inTleft and the second variable in Tright as key variables.
Keys — Variables to use as keys
positive integer | vector of positive integers | string array | character vector | cell array of character vectors | pattern scalar | logical vector
Variables to use as keys, specified as the comma-separated pair consisting of 'Keys' and a positive integer, vector of positive integers, string array, character vector, cell array of character vectors, pattern scalar, or logical vector.
You cannot use the 'Keys' name-value pair argument with the 'LeftKeys' and'RightKeys' name-value pair arguments.
The vector of row labels from an input table or timetable can be a key, alone or in combination with other key variables. Row labels are the row names of a table or the row times of a timetable. To use this vector as a key, specify it as 'Row' (for the row names of a table), as the name of a timetable vector of row times, or as the value of_`T`_.Properties.DimensionNames{1}, where _`T`_ is the table or timetable.
For backward compatibility, you can also specify the value of'Keys' as 'RowNames' whenTleft and Tright are tables with row names. However, the best practice is to specify the value of'Keys' as the name of the vector of row names.
Example: 'Keys',[1 3] uses the first and third variables from Tleft and Tright as key variables.
Example: 'Keys',{'X','Y'} uses the variables namedX and Y inTleft and Tright as key variables.
Example: 'Keys','Row' uses the vectors of row names of Tleft and Tright as key variables, if both Tleft andTright are tables with row names.
LeftKeys — Variables to use as keys in Tleft
positive integer | vector of positive integers | string array | character vector | cell array of character vectors | pattern scalar | logical vector
Variables to use as keys in Tleft, specified as the comma-separated pair consisting of 'LeftKeys' and a positive integer, vector of positive integers, string array, character vector, cell array of character vectors, pattern scalar, or logical vector.
You must use the 'LeftKeys' name-value pair argument in conjunction with the 'RightKeys' name-value pair argument. 'LeftKeys' and'RightKeys' both must specify the same number of key variables. join pairs key values inTleft and Tright based on their order.
The vector of row labels from an input table or timetable can be a key, alone or in combination with other key variables. Row labels are the row names of a table or the row times of a timetable. To use this vector as a key, specify it as 'Row' (for the row names of a table), as the name of a timetable vector of row times, or as the value of_`T`_.Properties.DimensionNames{1}, where _`T`_ is the table or timetable.
Example: 'LeftKeys',1 uses only the first variable in Tleft as a key variable.
RightKeys — Variables to use as keys in Tright
positive integer | vector of positive integers | string array | character vector | cell array of character vectors | pattern scalar | logical vector
Variables to use as keys in Tright, specified as the comma-separated pair consisting of 'RightKeys' and a positive integer, vector of positive integers, string array, character vector, cell array of character vectors, pattern scalar, or logical vector.
You must use the 'RightKeys' name-value pair argument in conjunction with the 'LeftKeys' name-value pair argument. 'LeftKeys' and'RightKeys' both must specify the same number of key variables. join pairs key values inTleft and Tright based on their order.
The vector of row labels from an input table or timetable can be a key, alone or in combination with other key variables. Row labels are the row names of a table or the row times of a timetable. To use this vector as a key, specify it as 'Row' (for the row names of a table), as the name of a timetable vector of row times, or as the value of_`T`_.Properties.DimensionNames{1}, where _`T`_ is the table or timetable.
Example: 'RightKeys',3 uses only the third variable in Tright as a key variable.
LeftVariables — Variables from Tleft to include in T
positive integer | vector of positive integers | string array | character vector | cell array of character vectors | pattern scalar | logical vector
Variables from Tleft to include inT, specified as the comma-separated pair consisting of 'LeftVariables' and a positive integer, vector of positive integers, string array, character vector, cell array of character vectors, pattern scalar, or logical vector.
You can use 'LeftVariables' to include or exclude key variables, as well as nonkey variables, from T. However, you cannot include row names or row times fromTleft, because they are not variables.
By default, join includes all variables fromTleft.
RightVariables — Variables from Tright to include in T
positive integer | vector of positive integers | string array | character vector | cell array of character vectors | pattern scalar | logical vector
Variables from Tright to include inT, specified as the comma-separated pair consisting of 'RightVariables' and a positive integer, vector of positive integers, string array, character vector, cell array of character vectors, pattern scalar, or logical vector.
You can use 'RightVariables' to include or exclude key variables, as well as nonkey variables, from T. However, you cannot include row names or row times fromTright, because they are not variables.
By default, join includes all variables fromTright except the key variables.
KeepOneCopy — Variables for which join retains only the copy from Tleft
string array | character vector | cell array of character vectors | pattern scalar
Variables for which join retains only the copy fromTleft, specified as the comma-separated pair consisting of 'KeepOneCopy' and a string array, character vector, cell array of character vectors, or pattern scalar that specifies variable names.
Key variables appear once in T, but if nonkey variables with identical names occur in Tleft andTright, then join retains both copies in T by default. Use the'KeepOneCopy' name-value pair to retain only the copy from Tleft.
Example: 'KeepOneCopy',Var2 keeps only the copy fromTleft of the nonkey variableVar2.
Output Arguments
T — Merged data from Tleft and Tright
table | timetable
Merged data from Tleft and Tright, returned as a table or a timetable. The table, T, contains one row for each row in Tleft, appearing in the same order.
join creates T by horizontally concatenating Tleft(:,LeftVars) andTright(iright,RightVars). By default,LeftVars is all the variables ofTleft, and RightVars is all the nonkey variables from Tright. Otherwise,LeftVars consists of the variables specified by the'LeftVariables' name-value pair argument, andRightVars consists of the variables specified by the'RightVariables' name-value pair argument.
If Tleft and Tright contain nonkey variables with the same name, join adds a unique suffix to the corresponding variable names in T, unless you specify the 'KeepOneCopy' name-value pair argument.
If Tleft is a table, then T is also a table. If Tleft is a timetable andTright is either a timetable or a table, thenT is a timetable.
You can store additional metadata in T, such as descriptions, variable units, variable names, and row names. For more information, see the Properties sections of table or timetable.
iright — Index to Tright
column vector
Index to Tright, returned as a column vector. Each element of iright identifies the row inTright that corresponds to that row in the output table or timetable, T.
More About
Key Variable
Variable used to match and combine data between input tablesTleft and Tright.
Key Value
Value in a key variable of Tleft orTright.
Algorithms
The join function first finds one or more key variables. Then,join uses the key variables to find the row in input tableTright that matches each row in input tableTleft, and combines those rows to create a row in output tableT.
- If there is a one-to-one mapping between key values in
TleftandTright, thenjoinsorts the data inTrightand appends it to tableTleft. - If there is a many-to-one mapping between key values in
TleftandTright, thenjoinsorts and repeats the data inTrightbefore appending it to tableTleft. - If there is data in a key variable of
Trightthat does not map to a key value inTleft, thenjoindoes not include that data in the output table,T.
Extended Capabilities
Tall Arrays
Calculate with arrays that have more rows than fit in memory.
Thejoin function supports tall arrays with the following usage notes and limitations:
- To join a tall timetable and a tall table, the timetable must be the first input to
join.
For more information, see Tall Arrays.
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using MATLAB® Coder™.
Usage notes and limitations:
- In general, input tables cannot have nonkey variables with the same names. However, you can join subsets of the input tables if you specify the name-value arguments:
'KeepOneCopy', where you list variables to take from the left input table only.'LeftVariables'and'RightVariables', where you list variables to take from either the left input table or the right input table, but not both.
- The values of these name-value arguments must be constant:
'Keys''LeftKeys''RightKeys''LeftVariables''RightVariables''KeepOneCopy'
- The values of these name-value arguments do not support pattern expressions:
'Keys''LeftKeys''RightKeys''LeftVariables''RightVariables''KeepOneCopy'
- Nested tables and timetables are not supported.
Thread-Based Environment
Run code in the background using MATLAB® backgroundPool or accelerate code with Parallel Computing Toolbox™ ThreadPool.
This function fully supports thread-based environments. For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions in Thread-Based Environment.
Version History
Introduced in R2013b