Design and Create a Custom Block - MATLAB & Simulink (original) (raw)
Setup Working Environment to Design and Create a Custom Block
This example open a directory containing the following files required for this topic.
ex_customsat_lib.slxsldemo_customsat.slxmsfuntmpl.mcustom_sat.mcustom_sat_final.mcustomsat_callback.mcustomsat_plotcallback.mcustom_sat_plot.mplotsat.m
How to Design a Custom Block
In general, use the following process to design a custom block:
- Defining Custom Block Behavior
- Deciding on a Custom Block Type
- Placing Custom Blocks in a Library
- Adding a User Interface to a Custom Block
Suppose you want to create a customized saturation block that limits the upper and lower bounds of a signal based on either a block parameter or the value of an input signal. In a second version of the block, you want the option to plot the saturation limits after the simulation is finished. The following tutorial steps you through designing these blocks. The library [ex_customsat_lib](https://mdsite.deno.dev/matlab:open%5Fsystem%28'ex%5Fcustomsat%5Flib'%29;) contains the two versions of the customized saturation block.
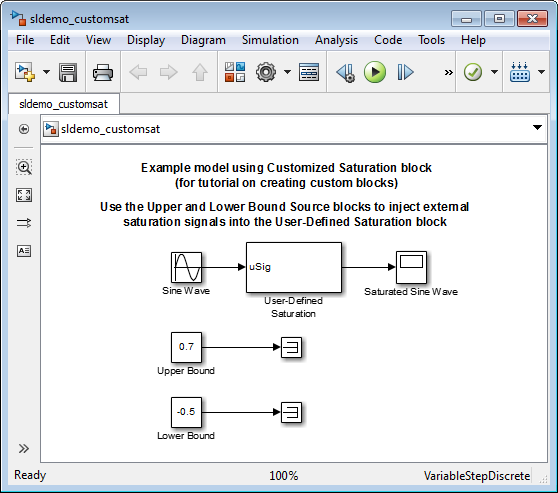
The example model [sldemo_customsat](https://mdsite.deno.dev/matlab:open%5Fsystem%28'sldemo%5Fcustomsat'%29;) uses the basic version of the block.
Defining Custom Block Behavior
Begin by defining the features and limitations of your custom block. In this example, the block supports the following features:
- Turning on and off the upper or lower saturation limit.
- Setting the upper and/or lower limits via a block parameters.
- Setting the upper and/or lower limits using an input signal.
It also has the following restrictions:
- The input signal under saturation must be a scalar.
- The input signal and saturation limits must all have a data type of double.
- Code generation is not required.
Deciding on a Custom Block Type
Based on the custom block features, the implementation needs to support the following:
- Multiple input ports
- A relatively simple algorithm
- No continuous or discrete system states
Therefore, this tutorial implements the custom block using a Level-2 MATLAB® S-function. MATLAB S-functions support multiple inputs and, because the algorithm is simple, do not have significant overhead when updating the diagram or simulating the model. See Comparison of Custom Block Functionality for a description of the different functionality provided by MATLAB S-functions as compared to other types of custom blocks.
Parameterizing the MATLAB S-Function
Begin by defining the S-function parameters. This example requires four parameters:
- The first parameter indicates how the upper saturation limit is set. The limit can be off, set via a block parameter, or set via an input signal.
- The second parameter is the value of the upper saturation limit. This value is used only if the upper saturation limit is set via a block parameter. In the event this parameter is used, you should be able to change the parameter value during the simulation, i.e., the parameter is tunable.
- The third parameter indicates how the lower saturation limit is set. The limit can be off, set via a block parameter, or set via an input signal.
- The fourth parameter is the value of the lower saturation limit. This value is used only if the lower saturation limit is set via a block parameter. As with the upper saturation limit, this parameter is tunable when in use.
The first and third S-function parameters represent modes that must be translated into values the S-function can recognize. Therefore, define the following values for the upper and lower saturation limit modes:
1indicates that the saturation limit is off.2indicates that the saturation limit is set via a block parameter.3indicates that the saturation limit is set via an input signal.
Writing the MATLAB S-Function
After you define the S-function parameters and functionality, write the S-function. The template msfuntmpl.m provides a starting point for writing a Level-2 MATLAB S-function. You can find a completed version of the custom saturation block in the file custom_sat.m. Open this file before continuing with this tutorial.
This S-function modifies the S-function template as follows:
- The
setupfunction initializes the number of input ports based on the values entered for the upper and lower saturation limit modes. If the limits are set via input signals, the method adds input ports to the block. Thesetupmethod then indicates there are four S-function parameters and sets the parameter tunability. Finally, the method registers the S-function methods used during simulation.
function setup(block)
% The Simulink engine passes an instance of the Simulink.MSFcnRunTimeBlock
% class to the setup method in the input argument "block". This is known as
% the S-function block's run-time object.
% Register original number of input ports based on the S-function
% parameter values
try % Wrap in a try/catch, in case no S-function parameters are entered
lowMode = block.DialogPrm(1).Data;
upMode = block.DialogPrm(3).Data;
numInPorts = 1 + isequal(lowMode,3) + isequal(upMode,3);
catch
numInPorts=1;
end % try/catch
block.NumInputPorts = numInPorts;
block.NumOutputPorts = 1;
% Setup port properties to be inherited or dynamic
block.SetPreCompInpPortInfoToDynamic;
block.SetPreCompOutPortInfoToDynamic;
% Override input port properties
block.InputPort(1).DatatypeID = 0; % double
block.InputPort(1).Complexity = 'Real';
% Override output port properties
block.OutputPort(1).DatatypeID = 0; % double
block.OutputPort(1).Complexity = 'Real';
% Register parameters. In order:
% -- If the upper bound is off (1) or on and set via a block parameter (2)
% or input signal (3)
% -- The upper limit value. Should be empty if the upper limit is off or
% set via an input signal
% -- If the lower bound is off (1) or on and set via a block parameter (2)
% or input signal (3)
% -- The lower limit value. Should be empty if the lower limit is off or
% set via an input signal
block.NumDialogPrms = 4;
block.DialogPrmsTunable = {'Nontunable','Tunable','Nontunable', ...
'Tunable'};
% Register continuous sample times [0 offset]
block.SampleTimes = [0 0];
%% -----------------------------------------------------------------
%% Options
%% -----------------------------------------------------------------
% Specify if Accelerator should use TLC or call back into
% MATLAB script
block.SetAccelRunOnTLC(false);
%% -----------------------------------------------------------------
%% Register methods called during update diagram/compilation
%% -----------------------------------------------------------------
block.RegBlockMethod('CheckParameters', @CheckPrms);
block.RegBlockMethod('ProcessParameters', @ProcessPrms);
block.RegBlockMethod('PostPropagationSetup', @DoPostPropSetup);
block.RegBlockMethod('Outputs', @Outputs);
block.RegBlockMethod('Terminate', @Terminate);
%end setup function
- The
CheckParametersmethod verifies the values entered into the Level-2 MATLAB S-Function block.
function CheckPrms(block)
lowMode = block.DialogPrm(1).Data;
lowVal = block.DialogPrm(2).Data;
upMode = block.DialogPrm(3).Data;
upVal = block.DialogPrm(4).Data;
% The first and third dialog parameters must have values of 1-3
if ~any(upMode == [1 2 3]);
error('The first dialog parameter must be a value of 1, 2, or 3');
end
if ~any(lowMode == [1 2 3]);
error('The first dialog parameter must be a value of 1, 2, or 3');
end
% If the upper or lower bound is specified via a dialog, make sure there
% is a specified bound. Also, check that the value is of type double
if isequal(upMode,2),
if isempty(upVal),
error('Enter a value for the upper saturation limit.');
end
if ~strcmp(class(upVal), 'double')
error('The upper saturation limit must be of type double.');
end
end
if isequal(lowMode,2),
if isempty(lowVal),
error('Enter a value for the lower saturation limit.');
end
if ~strcmp(class(lowVal), 'double')
error('The lower saturation limit must be of type double.');
end
end
% If a lower and upper limit are specified, make sure the specified
% limits are compatible.
if isequal(upMode,2) && isequal(lowMode,2),
if lowVal >= upVal,
error('The lower bound must be less than the upper bound.');
end
end
%end CheckPrms function - The
ProcessParametersandPostPropagationSetupmethods handle the S-function parameter tuning.
function ProcessPrms(block)
%% Update run time parameters
block.AutoUpdateRuntimePrms;
%end ProcessPrms function
function DoPostPropSetup(block)
%% Register all tunable parameters as runtime parameters.
block.AutoRegRuntimePrms;
%end DoPostPropSetup function - The
Outputsmethod calculates the block's output based on the S-function parameter settings and any input signals.
function Outputs(block)
lowMode = block.DialogPrm(1).Data;
upMode = block.DialogPrm(3).Data;
sigVal = block.InputPort(1).Data;
lowPortNum = 2; % Initialize potential input number for lower saturation limit
% Check upper saturation limit
if isequal(upMode,2), % Set via a block parameter
upVal = block.RuntimePrm(2).Data;
elseif isequal(upMode,3), % Set via an input port
upVal = block.InputPort(2).Data;
lowPortNum = 3; % Move lower boundary down one port number
else
upVal = inf;
end
% Check lower saturation limit
if isequal(lowMode,2), % Set via a block parameter
lowVal = block.RuntimePrm(1).Data;
elseif isequal(lowMode,3), % Set via an input port
lowVal = block.InputPort(lowPortNum).Data;
else
lowVal = -inf;
end
% Assign new value to signal
if sigVal > upVal,
sigVal = upVal;
elseif sigVal < lowVal,
sigVal=lowVal;
end
block.OutputPort(1).Data = sigVal;
%end Outputs function
Placing Custom Blocks in a Library
Libraries allow you to share your custom blocks with other users, easily update the functionality of copies of the custom block, and collect blocks for a particular project into a single location. If your custom block requires a bus as an interface, you can share the bus object with library users by creating the bus object in a data dictionary and attaching the dictionary to the library (See Link Data Dictionary to Custom Libraries).
This example places the custom saturation block into a library.
- In the Simulink® Editor, in the Simulation tab, select > .
- From the User-Defined Functions library, drag a Level-2 MATLAB S-Function block into your new library.

- Save your library with the filename
saturation_lib. - Double-click the block to open its Function Block Parameters dialog box.
- In the S-function name field, enter the name of the S-function. For example, enter
custom_sat. In theParameters field enter2,-1,2,1.
- Click OK.
You have created a custom saturation block that you can share with other users.
You can make the block easier to use by adding a customized user interface.
Adding a User Interface to a Custom Block
You can create a block dialog box for a custom block using the masking features of Simulink. Masking the block also allows you to add port labels to indicate which ports corresponds to the input signal and the saturation limits.
- Open the library
saturation_libthat contains the custom block you created. - Right-click the Level-2 MATLAB S-Function block and select > .
- On the Icon & Ports pane in theIcons drawing commands box, enter
port_label('input',1,'uSig'), and then click .
This command labels the default port as the input signal under saturation.
- In the Parameters & Dialog pane, add four parameters corresponding to the four S-Function parameters. For each new parameter, drag a popup or edit control to the Dialog box section, as shown in the table. Drag each parameter into the Parameters group.
Type Prompt Name Evaluate Tunable Popup options Callback popup Upper boundary: upMode ✓ No limitEnter limit as parameterLimit using input signal customsat_callback('upperbound_callback', gcb) edit Upper limit: upVal ✓ ✓ N/A customsat_callback('upperparam_callback', gcb) Type Prompt Name Evaluate Tunable Popup options Callback ----- --------------- ------- -------- ------- -------------------------------------------------------- ------------------------------------------------ popup Lower boundary: lowMode ✓ No limitEnter limit as parameterLimit using input signal customsat_callback('lowerbound_callback', gcb) edit Lower limit: lowVal ✓ ✓ N/A customsat_callback('lowerparam_callback', gcb) The MATLAB S-Function script custom_sat_final.m contains the mask parameter callbacks. Find custom_sat_final.min your working folder to define the callbacks in this example. This MATLAB script has two input arguments. The first input argument is a character vector indicating which mask parameter invoked the callback. The second input argument is the handle to the associated Level-2 MATLAB S-Function block.The figure shows the completed Parameters & Dialog pane in the Mask Editor. 
- In the Initialization pane, select theAllow library block to modify its contents check box. This setting allows the S-function to change the number of ports on the block.
- In the Documentation pane:
- In the Mask type field, enter
- In the Mask description field, enter
Limit the input signal to an upper and lower saturation value
set either through a block parameter or input signal.
- Click OK.
- To map the S-function parameters to the mask parameters, right-click the Level-2 MATLAB S-Function block and select > .
- Change the S-function name field to
custom_sat_finaland theParameters field tolowMode,lowVal,upMode,upVal.
The figure shows the Function Block Parameters dialog box after the changes.
- Click OK. Save and close the library to exit the edit mode.
- Reopen the library and double-click the customized saturation block to open the masked parameter dialog box.

To create a more complicated user interface, place a MATLAB graphics user interface on top of the masked block. The blockOpenFcn invokes the MATLAB graphics user interface, which uses calls toset_param to modify the S-function block parameters based on settings in the user interface.
Writing the Mask Callback
The function customsat_callback.m contains the mask callback code for the custom saturation block mask parameter dialog box. This function invokes local functions corresponding to each mask parameter through a call to feval.
The following local function controls the visibility of the upper saturation limit's field based on the selection for the upper saturation limit's mode. The callback begins by obtaining values for all mask parameters using a call to get_param with the property nameMaskValues. If the callback needed the value of only one mask parameter, it could call get_param with the specific mask parameter name, for example, get_param(block,'upMode'). Because this example needs two of the mask parameter values, it uses theMaskValues property to reduce the calls toget_param.
The callback then obtains the visibilities of the mask parameters using a call to get_param with the property nameMaskVisbilities. This call returns a cell array of character vectors indicating the visibility of each mask parameter. The callback alters the values for the mask visibilities based on the selection for the upper saturation limit's mode and then updates the port label text.
The callback finally uses the set_param command to update the block's MaskDisplay property to label the block's input ports.
function customsat_callback(action,block) % CUSTOMSAT_CALLBACK contains callbacks for custom saturation block
% Copyright 2003-2007 The MathWorks, Inc.
%% Use function handle to call appropriate callback feval(action,block)
%% Upper bound callback function upperbound_callback(block)
vals = get_param(block,'MaskValues'); vis = get_param(block,'MaskVisibilities'); portStr = {'port_label(''input'',1,''uSig'')'}; switch vals{1} case 'No limit' set_param(block,'MaskVisibilities',[vis(1);{'off'};vis(3:4)]); case 'Enter limit as parameter' set_param(block,'MaskVisibilities',[vis(1);{'on'};vis(3:4)]); case 'Limit using input signal' set_param(block,'MaskVisibilities',[vis(1);{'off'};vis(3:4)]); portStr = [portStr;{'port_label(''input'',2,''up'')'}]; end if strcmp(vals{3},'Limit using input signal'), portStr = [portStr;{['port_label(''input'',',num2str(length(portStr)+1), ... ',''low'')']}]; end set_param(block,'MaskDisplay',char(portStr));
The final call to set_param invokes thesetup function in the MATLAB S-function custom_sat.m. Therefore, thesetup function can be modified to set the number of input ports based on the mask parameter values instead of on the S-function parameter values. This change to the setup function keeps the number of ports on the Level-2 MATLAB S-Function block consistent with the values shown in the mask parameter dialog box.
The modified MATLAB S-function custom_sat_final.m contains the following newsetup function. If you are stepping through this tutorial, open the file.
%% Function: setup =================================================== function setup(block)
% Register original number of ports based on settings in Mask Dialog ud = getPortVisibility(block); numInPorts = 1 + isequal(ud(1),3) + isequal(ud(2),3);
block.NumInputPorts = numInPorts; block.NumOutputPorts = 1;
% Setup port properties to be inherited or dynamic block.SetPreCompInpPortInfoToDynamic; block.SetPreCompOutPortInfoToDynamic;
% Override input port properties block.InputPort(1).DatatypeID = 0; % double block.InputPort(1).Complexity = 'Real';
% Override output port properties block.OutputPort(1).DatatypeID = 0; % double block.OutputPort(1).Complexity = 'Real';
% Register parameters. In order: % -- If the upper bound is off (1) or on and set via a block parameter (2) % or input signal (3) % -- The upper limit value. Should be empty if the upper limit is off or % set via an input signal % -- If the lower bound is off (1) or on and set via a block parameter (2) % or input signal (3) % -- The lower limit value. Should be empty if the lower limit is off or % set via an input signal block.NumDialogPrms = 4; block.DialogPrmsTunable = {'Nontunable','Tunable','Nontunable','Tunable'};
% Register continuous sample times [0 offset] block.SampleTimes = [0 0];
%% ----------------------------------------------------------------- %% Options %% ----------------------------------------------------------------- % Specify if Accelerator should use TLC or call back into % MATLAB script block.SetAccelRunOnTLC(false);
%% ----------------------------------------------------------------- %% Register methods called during update diagram/compilation %% -----------------------------------------------------------------
block.RegBlockMethod('CheckParameters', @CheckPrms); block.RegBlockMethod('ProcessParameters', @ProcessPrms); block.RegBlockMethod('PostPropagationSetup', @DoPostPropSetup); block.RegBlockMethod('Outputs', @Outputs); block.RegBlockMethod('Terminate', @Terminate); %endfunction
The getPortVisibility local function incustom_sat_final.m uses the saturation limit modes to construct a flag that is passed back to the setup function. The setup function uses this flag to determine the necessary number of input ports.
%% Function: Get Port Visibilities ======================================= function ud = getPortVisibility(block)
ud = [0 0];
vals = get_param(block.BlockHandle,'MaskValues'); switch vals{1} case 'No limit' ud(2) = 1; case 'Enter limit as parameter' ud(2) = 2; case 'Limit using input signal' ud(2) = 3; end
switch vals{3} case 'No limit' ud(1) = 1; case 'Enter limit as parameter' ud(1) = 2; case 'Limit using input signal' ud(1) = 3; end
Adding Block Functionality Using Block Callbacks
The User-Defined Saturation with Plotting block inex_customsat_lib uses block callbacks to add functionality to the original custom saturation block. This block provides an option to plot the saturation limits when the simulation ends. The following steps show how to modify the original custom saturation block to create this new block.
Add a check box to the mask parameter dialog box to toggle the plotting option on and off.
- Right-click the Level-2 MATLAB S-Function block in
saturation_liband select + Create Mask. - On the Mask Editor Parameters pane, add a fifth mask parameter with the following properties.
Prompt Name Type Tunable Type options Callback Plot saturation limits plotcheck checkbox No NA customsat_callback('plotsaturation',gcb) - Click OK.

- Right-click the Level-2 MATLAB S-Function block in
Write a callback for the new check box. The callback initializes a structure to store the saturation limit values during simulation in the Level-2 MATLAB S-Function block
UserData. The MATLAB script[customsat_plotcallback.m](https://mdsite.deno.dev/matlab:edit%28'customsat%5Fplotcallback.m'%29;)contains this new callback, as well as modified versions of the previous callbacks to handle the new mask parameter. If you are following through this example, open[customsat_plotcallback.m](https://mdsite.deno.dev/matlab:edit%28'customsat%5Fplotcallback.m'%29;)and copy its local functions over the previous local functions incustomsat_callback.m.
%% Plotting checkbox callback
function plotsaturation(block)
% Reinitialize the block's userdata
vals = get_param(block,'MaskValues');
ud = struct('time',[],'upBound',[],'upVal',[],'lowBound',[],'lowVal',[]);
if strcmp(vals{1},'No limit'),
ud.upBound = 'off';
else
ud.upBound = 'on';
end
if strcmp(vals{3},'No limit'),
ud.lowBound = 'off';
else
ud.lowBound = 'on';
end
set_param(gcb,'UserData',ud);Update the MATLAB S-function
Outputsmethod to store the saturation limits, if applicable, as done in the new MATLAB S-function[custom_sat_plot.m](https://mdsite.deno.dev/matlab:edit%28'custom%5Fsat%5Fplot.m'%29;). If you are following through this example, copy theOutputsmethod incustom_sat_plot.mover the originalOutputsmethod incustom_sat_final.m
%% Function: Outputs ===================================================
function Outputs(block)
lowMode = block.DialogPrm(1).Data;
upMode = block.DialogPrm(3).Data;
sigVal = block.InputPort(1).Data;
vals = get_param(block.BlockHandle,'MaskValues');
plotFlag = vals{5};
lowPortNum = 2;
% Check upper saturation limit
if isequal(upMode,2)
upVal = block.RuntimePrm(2).Data;
elseif isequal(upMode,3)
upVal = block.InputPort(2).Data;
lowPortNum = 3; % Move lower boundary down one port number
else
upVal = inf;
end
% Check lower saturation limit
if isequal(lowMode,2),
lowVal = block.RuntimePrm(1).Data;
elseif isequal(lowMode,3)
lowVal = block.InputPort(lowPortNum).Data;
else
lowVal = -inf;
end
% Use userdata to store limits, if plotFlag is on
if strcmp(plotFlag,'on');
ud = get_param(block.BlockHandle,'UserData');
ud.lowVal = [ud.lowVal;lowVal];
ud.upVal = [ud.upVal;upVal];
ud.time = [ud.time;block.CurrentTime];
set_param(block.BlockHandle,'UserData',ud)
end
% Assign new value to signal
if sigVal > upVal,
sigVal = upVal;
elseif sigVal < lowVal,
sigVal=lowVal;
end
block.OutputPort(1).Data = sigVal;
%endfunctionWrite the function
[plotsat.m](https://mdsite.deno.dev/matlab:edit%28'plotsat.m'%29;)to plot the saturation limits. This function takes the handle to the Level-2 MATLAB S-Function block and uses this handle to retrieve the block'sUserData. If you are following through this tutorial, saveplotsat.mto your working folder.
function plotSat(block)
% PLOTSAT contains the plotting routine for custom_sat_plot
% This routine is called by the S-function block's StopFcn.
ud = get_param(block,'UserData');
fig=[];
if ~isempty(ud.time)
if strcmp(ud.upBound,'on')
fig = figure;
plot(ud.time,ud.upVal,'r');
hold on
end
if strcmp(ud.lowBound,'on')
if isempty(fig),
fig = figure;
end
plot(ud.time,ud.lowVal,'b');
end
if ~isempty(fig)
title('Upper bound in red. Lower bound in blue.')
end% Reinitialize userdata
ud.upVal=[];
ud.lowVal=[];
ud.time = [];
set_param(block,'UserData',ud);
end
5. Right-click the Level-2 MATLAB S-Function block and select . The Block Properties dialog box opens. On the Callbacks pane, modify theStopFcn to call the plotting callback as shown in the following figure, then click OK.