Quorum Sensing Inhibitors Increase the Susceptibility of Bacterial Biofilms to Antibiotics In Vitro and In Vivo (original) (raw)
Abstract
Although the exact role of quorum sensing (QS) in various stages of biofilm formation, maturation, and dispersal and in biofilm resistance is not entirely clear, the use of QS inhibitors (QSI) has been proposed as a potential antibiofilm strategy. We have investigated whether QSI enhance the susceptibility of bacterial biofilms to treatment with conventional antimicrobial agents. The QSI used in our study target the acyl-homoserine lactone-based QS system present in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia cepacia complex organisms (baicalin hydrate, cinnamaldehyde) or the peptide-based system present in Staphylococcus aureus (hamamelitannin). The effect of tobramycin (P. aeruginosa, B. cepacia complex) and clindamycin or vancomycin (S. aureus), alone or in combination with QSI, was evaluated in various in vitro and in vivo biofilm model systems, including two invertebrate models and one mouse pulmonary infection model. In vitro the combined use of an antibiotic and a QSI generally resulted in increased killing compared to killing by an antibiotic alone, although reductions were strain and model dependent. A significantly higher fraction of infected Galleria mellonella larvae and Caenorhabditis elegans survived infection following combined treatment, compared to treatment with an antibiotic alone. Finally, the combined use of tobramycin and baicalin hydrate reduced the microbial load in the lungs of BALB/c mice infected with Burkholderia cenocepacia more than tobramycin treatment alone. Our data suggest that QSI may increase the success of antibiotic treatment by increasing the susceptibility of bacterial biofilms and/or by increasing host survival following infection.
INTRODUCTION
Biofilm-associated infections are often very difficult to treat with conventional antibiotics (7, 17, 28, 38). Hence, novel targets are needed to combat biofilm infections. One of them could be the bacterial communication system (quorum sensing [QS]). Bacteria coordinate their cell-density-dependent gene expression by excreting small signaling molecules (26). When a certain extracellular threshold concentration is reached, these molecules bind to a receptor, thereby activating the QS system. The typical QS system in Gram-negative bacteria consists of three components: a LuxI synthase homolog, acyl-homoserine-lactone (AHL) signaling molecules, and a LuxR receptor homolog (10). Gram-positive bacteria generally use small peptide signaling molecules, which are transported out of the cell and bind to a membrane-associated two-component receptor (42). Binding to the receptor activates a signal transduction system leading to the transcription of QS-regulated genes. A third QS system using autoinducer 2 (AI-2) as signaling molecule is widespread in both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and is considered to be responsible for interspecies communication (43). QS has been shown to regulate biofilm formation in several bacterial species (15, 20). AHL QS mutants of Burkholderia cenocepacia and Pseudomonas aeruginosa form biofilms with a drastically altered structure and are impaired in their ability to maintain cells within the biofilm (18, 39, 44). Similar results were observed when Burkholderia multivorans, B. cenocepacia, and P. aeruginosa biofilms were treated with QS inhibitors (QSI) such as baicalin hydrate (BH) or cinnamaldehyde (CA) (4, 44, 45). Biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus is enhanced by the agr QS system, while hamamelitannin (HAM; a nonpeptide analog of the RNAIII inhibiting peptide) decreases S. aureus attachment in vitro and in vivo (3, 21, 22). Due to the apparent role of QS in biofilm formation, QSI are proposed as promising antibiofilm agents (9). However, little is known about the relationship between the antibiofilm effect of QSI and the susceptibility of biofilms to antibiotics. In addition, biofilm model-dependent differences in susceptibility may affect the outcome. In the present study, we selected several QSI targeting the AHL-QS system or the QS system of Gram-positive bacteria and evaluated their effects on the susceptibility of medically important bacterial biofilms using in vitro and in vivo model systems.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Strains and culture conditions.
B. cenocepacia LMG 16656, LMG 16659, and LMG 18828, B. multivorans LMG 13010, LMG 17588, and LMG 18822, P. aeruginosa PAO1, ATCC 9027, MH340, and MH710 (Δ_rhlI_ Δ_lasI_) (2), and S. aureus LMG 10147, Mu50 (methicillin-resistant S. aureus [MRSA]), and CS1 (a recent clinical MRSA isolate) were cultured in Mueller-Hinton broth (MH; Oxoid, Basingstoke, England). Escherichia coli OP50 and ATCC 25922 were grown in TSB (Oxoid) at 37°C.
Caenorhabditis elegans N2 (glp-4; sek-1) was propagated under standard conditions, synchronized by hypochlorite bleaching, and cultured on nematode growth medium using E. coli OP50 as a food source (5, 36). Adult Galleria mellonella larvae (Krekelonline, Turnhout, Belgium) were stored in wood chips at 15°C in darkness prior to use. Larvae weighing between 200 and 300 mg were used throughout.
Antibiotics and QSI.
The following antibiotics were used: tobramycin (TOB; Sigma-Aldrich, Bornem, Belgium), vancomycin (VAN; Sigma-Aldrich), and clindamycin (CLI; Certa, Braine-l'Alleud, Belgium). The QSI baicalin hydrate (BH), cinnamaldehyde (CA), and hamamelitannin (HAM) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich.
Determination of the MIC.
MICs of antibiotics were determined in triplicate according to the EUCAST broth microdilution protocol, using flat-bottom 96-well microtiter plates (TPP, Trasadingen, Switzerland) (31). The inoculum was standardized to approximately 5 × 105 CFU/ml. The plates were incubated at 37°C for 20 h, and the optical density at 590 nm was determined by using a multilabel microtiter plate reader (Envision; Perkin-Elmer LAS, Waltham, MA). The lowest concentration of antibiotic for which a similar optical density was observed in the inoculated and the blank wells was recorded as the MIC. Test performance was monitored using E. coli ATCC 25922 and S. aureus LMG 10147 as control strains. For each antibiotic, the MIC was determined in the presence or absence of QSI. If the MIC determined in both conditions differed, checkerboard testing (34) was performed to determine whether the interaction is synergistic (fractional inhibitory concentration [FIC] index ≤ 0.5) or indifferent (FIC index > 0.5).
Biofilm formation on medical-grade silicone disks.
Biofilms were grown on medical grade silicone disks (Q7-4735; Dow Corning, Midland, MI) placed in the wells of a 24-well microtiter plate (TPP) as previously described (31), using MH medium, synthetic cystic fibrosis medium (29) supplemented with mucin (SCFMM), or Bolton broth with 50% plasma (Sigma-Aldrich) and 5% freeze-thaw laked horse blood (Lubbock chronic wound pathogenic biofilm medium [LCWPB]) (37). Inocula of 108 CFU/ml for MH medium and 104 CFU/ml for the other two media were used. Cell suspensions made in MH medium were incubated at 37°C for 4 h. After this adhesion step, wells were rinsed with physiological saline (PS), fresh sterile MH medium was added, and the biofilms were allowed to grow for an additional 20 h. Biofilms in the SCFMM and LCWPB media were incubated at 37°C for 24 h.
Biofilm formation in a collagen matrix.
A collagen wound biofilm model (CWB) mimicking conditions in chronic wound and soft tissue infections was used (41). In brief, collagen matrices of polymerized rat-tail collagen type I (BD Biosciences, Erembodegem, Belgium) were prepared in 15-ml tubes. For 10 ml of collagen solution (2 mg/ml), 1 ml of 10× phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) was mixed with 0.125 ml of NaOH (1 M) and 3.475 ml of simulated wound fluid (SWF; 50% fetal calf serum and 50% PS in 0.1% peptone) and kept on ice. Cold collagen stock solution (3.68 mg/ml) was added and, after mixing, 350 μl of the collagen solution was added to each tube. To achieve polymerization of the collagen, tubes were placed in an incubator at 37°C for 1 h. After polymerization, 350 μl of a bacterial suspension (105 CFU/ml in SWF) was added, and the biofilms were incubated for 24 h at 37°C.
Biofilm formation on RHE.
Reconstituted human epithelium (RHE) tissue was obtained from SkinEthic Laboratories (Nice, France). For the biofilm assay, 0.5-cm2 RHE surfaces were infected with a 50-μl suspension containing 2 × 106 CFU/ml and incubated in maintenance medium (SkinEthic Laboratories) at 37°C with 5% CO2 at 100% humidity for 24 h.
Treatment of 24-h-old biofilms and quantification of cells.
For all strains, the bactericidal effect of the antibiotics alone or in combination with QSI was determined using concentrations of 12 μg/ml for CLI, 20 μg/ml for VAN, and 8 μg/ml for TOB. Against the three B. cenocepacia and three B. multivorans strains, TOB was used at four times the MIC. The QSI were added in sub-MICs, i.e., a concentration that did not affect growth (100 μM for BH and 250 μM for CA and HAM). Antibiotics and QSI were dissolved in sterile PS for the MH model system, in PBS for the RHE model, and in the respective biofilm growth media for the other model systems. After 24 h of biofilm formation, biofilms were rinsed once with PS and subsequently treated with an antibiotic alone, a QSI alone, a combination of an antibiotic and a QSI, or a blank control solution. After 24 h at 37°C, the biofilms were rinsed with PS. Sessile cells were removed from the disks or the RHE cells by three cycles of vortexing (30 s) and sonication (30 s; Branson 3510; Branson Ultrasonics Corp., Danbury, CT), and the number of CFU/biofilm was determined by plating the resulting suspensions. The bacteria present in the collagen matrices were quantified as previously described (41). In brief, 350 μl of collagenase solution (500 μg/ml) was added to the matrices, and the tubes were incubated for 30 min at 37°C, mixed, and incubated again for 60 min. Cells were washed twice by adding 700 μl of PS and vortexing and were collected by centrifugation. The pellet was resuspended in 700 μl of PS, and the number of CFU was determined by plating.
C. elegans survival assay.
For the C. elegans survival assay, synchronized worms (L4 stage) were suspended in a medium containing 95% M9 buffer (3 g of KH2PO4, 6 g of Na2HPO4, 5 g of NaCl, and 1 ml of 1 M MgSO4 · 7H2O in 1 liter of water), 5% brain heart infusion broth (Oxoid), and 10 μg of cholesterol (Sigma-Aldrich)/ml. Then, 0.5 ml of this suspension of nematodes was transferred to the wells of a 24-well microtiter plate. An overnight bacterial culture was centrifuged, resuspended in the assay medium, and standardized to 108 CFU/ml. Next, 250-μl aliquots of this standardized suspension were added to each well, while 250 μl of sterile medium was added to the positive control. QSI and/or antibiotics were added to the test wells in the same concentrations as were added to the ones used in the biofilm experiments. The assay plates were incubated at 25°C for up to 2 days. The fraction of dead worms was determined by counting the number of dead worms and the total number of worms in each well, using a dissecting microscope. Compounds were tested three times in each assay, and each assay was repeated at least six times (n ≥ 18).
G. mellonella survival assay.
Prior to inoculation into G. mellonella, bacterial cells were washed with PBS and then diluted to an appropriate cell density (108, 104, and 107 CFU/ml for the S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, and B. cenocepacia/B. multivorans strains, respectively). A Hamilton syringe was used to inject 10-μl aliquots in the G. mellonella last left proleg. The antibiotics, QSI, or both were administered by a 10-μl injection into a different proleg within 1 h. The injected solution contained the compounds in the concentrations used in the biofilm experiments. Two control groups were used: the first group included larvae inoculated with PBS to monitor killing due to physical trauma; the second group included larvae receiving no injection. Experiments that had one or more dead larvae in either control group were discarded and repeated. For each treatment, at least 15 larvae were injected. Larvae were placed in the dark at 37°C and were scored as dead or alive every 24 h until 144 h postinfection. Larvae were considered dead when they displayed no movement in response to shaking or touch. For each treatment, data from at least four independent experiments were combined.
Mouse lung infection model.
All experiments and procedures were approved by the ethical committee of the University of Antwerp. Female BALB/c mice were used. The mice were immunosuppressed by intraperitoneal injection of cyclophosphamide 24 h before infection (150 mg/kg; Endoxan; Baxter) and at 24 and 48 h postinfection (25 mg/kg). Before intranasal challenge with B. cenocepacia LMG 16656, the mice were anesthetized with ketamine hydrochloride (60 mg/kg subcutaneously; Anesketin; Eurovet). The challenge inoculum was prepared by diluting frozen stock cultures in PBS (5 × 107 CFU/ml). The mice were inoculated with a 10-μl suspension in one nostril (5 × 105 CFU/10 μl), followed by intranasal administration of 20 μl of PBS or BH (2 mg/kg) at 24 and 48 h postinfection. The mice were sacrificed at 3 days postinfection by cervical dislocation, and the lungs were excised, weighed, and homogenized in 3 ml of PBS. A serial dilution of the lung homogenate was plated on B. cepacia selective agar (16) to enumerate the number of CFU.
Statistics.
The normal distribution of the data was checked by using the Shapiro-Wilk test. Normally and non-normally distributed data were analyzed by using an independent sample t test and the Mann-Whitney U test, respectively. Statistics were determined using SPSS software, version 17.0. Survival curves were analyzed by using a log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test.
RESULTS
Effect of QSI on the susceptibility of planktonic cells.
All QSI (BH, CA, and HAM) were used in concentrations below the MICs (see Table S1 in the supplemental material) for all strains. MICs of TOB were determined for planktonic B. cenocepacia LMG 16656 (256 μg/ml), LMG 16659 (512 μg/ml), and LMG 18828 (256 μg/ml), B. multivorans LMG 13010 (64 μg/ml), LMG 17588 (64 μg/ml), and LMG 18822 (128 μg/ml), and P. aeruginosa PAO1 (2 μg/ml) and ATCC 9027 (1 μg/ml). The MICs of VAN and CLI were determined for planktonic S. aureus Mu50 (8 and 512 μg/ml, respectively) and CS1 (4 and 0.256 μg/ml, respectively). CA and BH did not alter the susceptibility of B. cenocepacia, B. multivorans, and P. aeruginosa strains toward TOB when grown planktonically. For VAN and CLI, minor differences in MIC toward S. aureus were observed depending on the presence or absence of QSI, but these differences were within the acceptable margin of error and were not considered relevant (see Table S1 in the supplemental material). The FIC indices were >0.5 for all combinations, indicating that there was no synergistic activity and that the interactions observed are indifferent (data not shown).
Effect of QSI on the susceptibility of B. multivorans and B. cenocepacia biofilms.
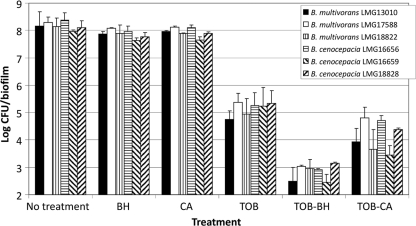
When used alone, BH or CA resulted in a minor reduction in the number of sessile B. multivorans and B. cenocepacia cells (Fig. 1). Treatment of the 24-h-old biofilms with TOB in combination with BH or CA resulted in significantly (P < 0.05) more killing of B. cenocepacia and B. multivorans biofilm cells relative to treatment with TOB alone (Fig. 1). Similar results were obtained for B. cenocepacia and B. multivorans biofilms grown in SCFMM medium (see Table S2 in the supplemental material).
Fig. 1.
Log CFU/biofilm (average ± the SD) in untreated 24-h-old B. multivorans and B. cenocepacia biofilms in MH medium and in biofilms treated with TOB or a QSI (BH or CA) alone or a combination of TOB and a QSI. Combined treatment was significantly more effective than treatment with TOB alone for both QSI and for all strains investigated (P < 0.05).
Effect of QSI on the susceptibility of P. aeruginosa biofilms.
Use of BH and CA did not result in a significant decrease of the number of P. aeruginosa PAO1 and P. aeruginosa ATCC 9027 biofilm cells in any of the in vitro biofilm models (see Table S2 in the supplemental material). However, the susceptibility of the P. aeruginosa biofilms toward TOB was model and strain dependent (Table 1). TOB treatment decreased the number of living P. aeruginosa PAO1 cells by ca. 85% for biofilms grown in LCWPB medium and by ca. 40% when grown in the other three media (Table 1). For P. aeruginosa ATCC 9027, significant killing by TOB was only observed in the CWB medium (Table 1). Compared to TOB alone, treatment of 24-h-old biofilms with TOB in combination with BH or CA led to significantly (P < 0.05) more killing of biofilm cells of both P. aeruginosa strains in all in vitro biofilm model systems (Table 1). In addition, P. aeruginosa MH710 (Δ_rhlI_ Δ_lasI_) was more susceptible to TOB compared to the corresponding WT strain MH340, even in the absence of QSI (see Table S3 in the supplemental material); BH or CA did not increase the susceptibility of the mutant strain toward TOB (see Table S3 in the supplemental material).
Table 1.
Percent decrease in the number of CFU per biofilm when 24-h-old P. aeruginosa biofilms grown in different model systems were treated with TOB or a combination of TOB and a QSI (BH or CA)
| P. aeruginosa strain | Treatment | Avg % decrease ± SD in CFU obtained in different model systemsa | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MH | SCFMM | LCWPB | CWB | ||
| PAO1 | TOB | 45.5 ± 14.2 | 39.9 ± 18.9 | 83.3 ± 7.8 | 35.2 ± 21.7 |
| TOB-BH | 88.6 ± 7.2 | 80.9 ± 4.9 | 97.0 ± 2.4 | 80.6 ± 11.4 | |
| TOB-CA | 89.4 ± 1.9 | 86.9 ± 11.2 | 93.3 ± 3.7 | 77.0 ± 5.0 | |
| ATCC 9027 | TOB | 6.3 ± 10.3 | 5.8 ± 7.6 | 2.1 ± 17.8 | 34.6 ± 18.9 |
| TOB-BH | 82.3 ± 10.3 | 72.9 ± 4.5 | 44.9 ± 7.6 | 89.5 ± 3.2 | |
| TOB-CA | 90.2 ± 1.5 | 76.3 ± 9.5 | 42.9 ± 13.7 | 80.2 ± 2.2 |
Effect of QSI on the susceptibility of S. aureus biofilms.
When used alone, HAM resulted only in a minor reduction in the number of S. aureus sessile cells (see Table S2 in the supplemental material). The effect of VAN or CLI alone was model system and strain dependent (Table 2). Combined treatment with HAM and VAN resulted in significantly more killing of S. aureus Mu50 biofilm cells in all in vitro models tested (Table 2). Similar results were observed for the combination of HAM and VAN or CLI for S. aureus CS1 in all biofilm model systems tested (Table 2).
Table 2.
Percent decrease in the number of CFU per biofilm when 24-h-old S. aureus biofilms grown in different model systems were treated with VAN or CLI or a combination of an antibiotic and HAM
| S. aureus strain | Treatment | Avg % decrease ± SD in CFU obtained in different model systemsa | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MH | SCFMM | LCWPB | CWB | RHE | ||
| CS1 | VAN | 2.2 ± 11.2 | 78.9 ± 7.8 | 2.0 ± 12.9 | 94.2 ± 1.5 | 84.1 ± 4.4 |
| VAN-HAM | 68.4 ± 10.1* | 94.0 ± 3.0* | 95.0 ± 1.0* | 99.2 ± 0.2* | 99.1 ± 1.2* | |
| CLI | 13.5 ± 9.5 | 68.3 ± 18.4 | 4.6 ± 11.2 | 74.9 ± 18.0 | 75.2 ± 2.9 | |
| CLI-HAM | 69.0 ± 8.8* | 97.8 ± 1.7* | 63.0 ± 8.8* | 96.8 ± 0.9* | 98.8 ± 1.0* | |
| Mu50 | VAN | 2.6 ± 11.7 | 65.9 ± 6.7 | 4.4 ± 13.4 | 66.9 ± 32.4 | 91.2 ± 2.3 |
| VAN-HAM | 71.3 ± 6.9* | 99.8 ± 0.1* | 82.4 ± 7.7* | 99.6 ± 1.7* | 99.6 ± 0.1* | |
| CLI | 8.3 ± 17.4 | 8.4 ± 10.2 | 5.3 ± 11.2 | 6.8 ± 9.2 | ND | |
| CLI-HAM | 6.2 ± 21.0 | 15.1 ± 12.2 | 12.1 ± 8.9 | 6.1 ± 8.5 | ND |
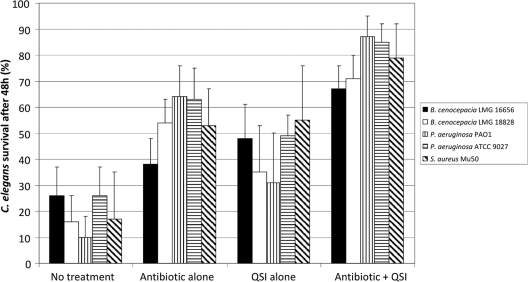
Effect of the combination of QSI and antibiotics on survival of infected C. elegans.
The in vivo effect of a combined treatment with QSI and antibiotics was evaluated by using a C. elegans model system. None of the QSI alone affected the survival of uninfected C. elegans (data not shown). Infection of C. elegans with B. cenocepacia LMG 16656, B. cenocepacia LMG 18828, P. aeruginosa PAO1, P. aeruginosa ATCC 9027, or S. aureus Mu50 significantly (P < 0.01) decreased the number of living nematodes after 48 h (Fig. 2). A significantly (P < 0.01) higher fraction survived infection with B. cenocepacia LMG 16656, B. cenocepacia LMG 18828, P. aeruginosa PAO1, or P. aeruginosa ATCC 9027 after treatment with TOB compared to no treatment (Fig. 2). Increased survival was also observed after BH treatment of C. elegans nematodes infected with B. cenocepacia LMG 16656, B. cenocepacia LMG 18828, and P. aeruginosa ATCC 9027 (Fig. 2). Similar results were obtained for CA treatment (data not shown). In addition, a significantly (P < 0.01) higher survival was observed for all BH/TOB combinations compared to treatment with TOB alone (Fig. 2). Similar results were obtained for B. cenocepacia LMG 16656, B. cenocepacia LMG 18828, and both P. aeruginosa strains treated with a TOB-CA combination (data not shown).
Fig. 2.
Percent survival of infected C. elegans (average ± the SD) after treatment with antibiotics (TOB for the B. cenocepacia and P. aeruginosa strains and VAN for S. aureus Mu50), QSI (BH for the B. cenocepacia and P. aeruginosa strains and HAM for S. aureus Mu50), or combinations of the respective compounds. The results are expressed as the percent survival after 48 h of infection and treatment. All combined treatments were significantly more effective than treatment with antibiotic alone (P < 0.01).
Both HAM and VAN alone significantly (P < 0.01) increased the survival of C. elegans infected with S. aureus Mu50 (Fig. 2). Further, the combination HAM-VAN significantly (P < 0.01) enhanced survival compared to VAN alone (79% ± 13% versus 53% ± 14%).
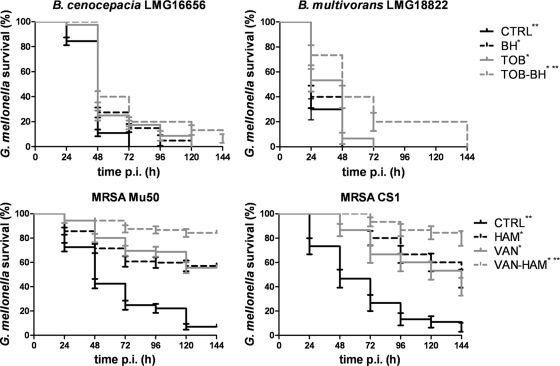
Effect of the combination of QSI and antibiotics on survival of infected G. mellonella.
None of the QSI or antibiotics was toxic for G. mellonella at the concentrations used (data not shown). All test strains significantly decreased G. mellonella survival within a 144-h postinfection time period (Fig. 3). A significantly higher percentage of G. mellonella larvae survived infection with B. multivorans LMG 18822 and B. cenocepacia LMG 16656 after treatment with TOB or BH compared to no treatment. Similar results were obtained for CA treatment (data not shown). A significantly (P < 0.05) enhanced survival was observed for the combination BH-TOB compared to TOB treatment alone for infections with B. cenocepacia LMG 16656 and B. multivorans LMG 18822 (Fig. 3). Similar results were obtained for CA-TOB (data not shown). Both HAM and VAN significantly (P < 0.05) enhanced G. mellonella survival after infection with S. aureus Mu50 or CS1. In addition, the combination VAN-HAM significantly (P < 0.05) increased survival compared to either of the compounds used alone (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3.
Kaplan-Meier survival-curve of infected G. mellonella receiving no treatment (CTRL) or a treatment with an antibiotic (TOB or VAN), a QSI (BH or HAM), or a combination of both. *, Significantly different compared to no treatment (P < 0.05); **, significantly increased survival compared to antibiotic treatment alone (P < 0.05).
Effect of BH in combination with TOB for the treatment of mice infected with B. cenocepacia LMG 16656.
The results of the in vitro and in vivo studies presented above, warranted further exploration of the therapeutic effect of BH in combination with TOB in a murine B. cenocepacia lung infection model. Significantly fewer B. cenocepacia LMG 16656 cells were recovered from TOB-treated mice than from the control mice (decreases of 47.5, 88.8, and 91.9% for the 10-, 20-, and 30-mg/kg TOB doses, respectively) (Table 3). At lower concentrations of TOB (10 or 20 mg/kg), the addition of BH to the treatment had no effect. However, the combination of a higher dose of TOB (30 mg/kg) with BH (2 mg/kg) resulted in a significantly (P < 0.05) reduced pulmonary bacterial load compared to the TOB treatment alone (Table 3).
Table 3.
Number of B. cenocepacia LMG 16656 CFU in the lungs of mice after treatment with TOB alone or in combination with BHa
| Treatment (mg/kg) | No. of mice | CFU/g of lung (avg ± SEM) | Reduction in bacterial load (%) compared to untreated control mice | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TOB | BH | |||
| 0 | 0 | 18 | 56,752 ± 13,003 | |
| 10 | 0 | 14 | 29,233 ± 3,753 | 47.5 |
| 10 | 2 | 11 | 26,793 ± 3,561 | 52.1 |
| 20 | 0 | 7 | 6,267 ± 1,813 | 88.8 |
| 20 | 2 | 4 | 8,128 ± 4,609 | 85.9 |
| 30 | 0 | 10 | 4,560 ± 1,714 | 91.9 |
| 30 | 2 | 7 | 559 ± 119* | 99.0* |
DISCUSSION
The biofilm mode of living of bacteria is associated with an increased resistance toward antibacterials, making successful treatment of biofilm-related infections difficult (17). Although much remains to be learned about the involvement of QS in biofilm formation, maintenance, and dispersal, QSI have been proposed as promising antibiofilm agents (24). In the present study we evaluated the potential of combining antibiotics with QSI. We selected various bacteria known to form clinically relevant biofilms and evaluated them under conditions mimicking the in vivo situation. B. multivorans, B. cenocepacia, P. aeruginosa, and S. aureus often infect cystic fibrosis patients and were consequently evaluated in SCFMM medium mimicking the conditions found in the cystic fibrosis lung (13, 29, 35). Both P. aeruginosa and S. aureus cause soft tissue infections (23, 25), and for this reason the biofilm susceptibility of these species was evaluated in two in vitro wound models and on RHE (36, 40). QSI targeting different QS systems and different classes of antibiotics were included, the latter in clinically relevant concentrations (8, 12). Although QSI and antibiotics did not act synergistically against planktonic cells, a different picture was observed for biofilm cells. Although there were considerable differences in results obtained in various model systems, overall, the use of QSI increased the effect of the antibiotic. QSI, such as BH, CA, and HAM, do not kill or inhibit the growth of bacterial cells but may influence biofilm formation and/or matrix production, which may lead to the altered susceptibility of these biofilms. To rule out the possibility that other processes besides QS are involved in this, we used a P. aeruginosa mutant incapable of QS (due to a disruption of both rhlI and lasI this strain cannot produce AHL signaling molecules) (2). Compared to the wild type, this mutant was much more susceptible toward TOB, which confirms the role of a functional QS system in resistance. In addition, while BH or CA resulted in an increased susceptibility of the wild-type strain toward TOB, this increase was not observed in the QS mutant strain, indicating that a functional QS system is required for the QSI to exert their effect. Although we cannot exclude that the QSI have other effects, our data strongly suggest that these are minor at best and that the increased antibiofilm effect is due to QS inhibition. However, since effects obtained in in vitro model systems cannot always be reproduced under in vivo conditions (1, 9, 14, 30), it was unclear whether combination therapy would also improve survival in vivo. For this reason, we investigated the effect of combined treatments on the survival of infected C. elegans and G. mellonella. These invertebrates have been shown to be good models for studying the pathogenicity of B. cenocepacia, P. aeruginosa, and S. aureus (5, 6, 11, 27, 32, 33, 40). Biofilm formation is also an important factor in staphylococcal virulence against C. elegans (1). A significantly higher fraction of G. mellonella larvae and C. elegans survived bacterial infection after treatment with a combination of QSI and antibiotics compared to treatment with an antibiotic alone. However, QSI alone also resulted in an increased survival, indicating that these compounds probably interfere with other cellular processes besides biofilm formation. QS is known to be involved in the production of virulence factors. For example, the production of the nematocidal protein AidA in B. cenocepacia is regulated by QS, and QS inhibition interferes with the swarming motility of bacteria and possibly affecting their dissemination in the host during infection (18, 19). RIP and its nonpeptide analog hamamelitannin were previously shown to affect S. aureus virulence factor production (21). In addition, bacterial QS mutants were observed to be significantly less virulent in several in vivo models (22, 40). For this reason, the increased survival in the presence of QSI is probably not only the result of an increased susceptibility of the bacteria to the antibiotic. Despite this, the effect observed in several in vitro and in vivo model systems encouraged us to further explore the potential effect of BH-TOB in a BALB/c lung infection model. Significantly fewer B. cenocepacia LMG 16656 cells were recovered from the lungs of mice treated with a combination of TOB-BH (30 and 2 mg/kg) compared to TOB (30 mg/kg) alone. Although the results from the present study seem promising, it will be important to determine whether similar results can be obtained for other organisms in other in vivo infection models. Altogether, our data suggest that combining antibiotics with QSI may increase the success of a treatment by increasing the efficacy of the former against biofilm-related infections and/or by increasing host survival after infection.
Supplementary Material
[Supplemental material]
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank K. Thevissen for kindly providing the C. elegans mutant, L. Eberl and L. Weisskopf for providing P. aeruginosa MH340 and MH710, and B. Martens and S. Braet for excellent technical assistance.
This study was supported by the Institute for the Promotion of Innovation through Science and Technology in Flanders (IWT-Vlaanderen) (G.B.), by the Special Research Fund (BOF) of Ghent University (T.C.), and by the Fund for Scientific Research (FWO-Flanders, Belgium) (T.C. and P.C.).
Footnotes
▿
Published ahead of print on 21 March 2011.
REFERENCES
- 1.Begun J., et al. 2007. Staphylococcal biofilm exopolysaccharide protects against Caenorhabditis elegans immune defenses. PLoS Pathog. 3:e57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Blom D., Fabbri C., Eberl L., Weisskopf L. 2011. Volatile-mediated killing of Arabidopsis thaliana by bacteria is mainly due to hydrogen cyanide. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77:1000–1008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Boles B. R., Horswill A. R. 2008. Agr-mediated dispersal of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. PLoS Pathog. 4:e1000052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Brackman G., Hillaert U., Van Calenbergh S., Nelis H. J., Coenye T. 2009. Use of quorum sensing inhibitors to interfere with biofilm formation and development in Burkholderia multivorans and Burkholderia cenocepacia. Res. Microbiol. 160:144–151 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cooper V. S., Carlson W. A., LiPuma J. J. 2009. Susceptibility of Caenorhabditis elegans to Burkholderia infection depends on prior diet and secreted bacterial attractants. PLoS One 4:e7961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dhakal B. K., et al. 2006. Caenorhabditis elegans as a simple model host for Vibrio vulnificus infection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 346:751–757 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Donlan R. M., Costerton J. W. 2002. Biofilms: survival mechanisms of clinically relevant microorganisms. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 15:167–193 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Elborn J. S., Hodson M., Bertram C. 2009. Implementation of European standards of care for cystic fibrosis-control and treatment of infection. J. Cyst. Fibrosis 8:211–217 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Estrela A. B., Heck M. G., Abraham W. R. 2009. Novel approaches to control biofilm infections. Curr. Med. Chem. 16:1512–1530 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Fuqua C., Greenberg E. P. 2002. Listening in on bacteria: acyl-homoserine lactone signaling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 3:685–695 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gao W., et al. 2010. Two novel point mutations in clinical Staphylococcus aureus reduce linezolid susceptibility and switch on the stringent response to promote persistent infection. PLoS Pathog. 6:e1000944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gemmell C. G., et al. 2006. Guidelines for the prophylaxis and treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections in the UK. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 57:589–608 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.George A. M., Jones P. M., Middleton P. G. 2009. Cystic fibrosis infections: treatment strategies and prospects. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 300:153–164 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hall-Stoodley L., Costerton J. W., Stoodley P. 2004. Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2:95–108 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hardie K. R., Heurlier K. 2008. Establishing bacterial communities by ‘word of mouth’: LuxS and autoinducer 2 in biofilm development. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6:635–643 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Henry D., et al. 1999. Comparison of isolation media for the recovery of Burkholderia cepacia complex from respiratory secretions of patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 37:1004–1007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Høiby N., Bjarnsholt T., Givskov M., Molin S., Ciofu O. 2010. Antibiotic resistance of bacterial biofilms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 35:322–332 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Huber B., et al. 2001. The cep quorum-sensing system of Burkholderia cepacia H111 controls biofilm formation and swarming motility. Microbiology 147:2517–2528 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Huber B., et al. 2004. Identification of a novel virulence factor in Burkholderia cenocepacia H111 required for efficient slow killing of Caenorhabditis elegans. Infect. Immun. 72:7220–7230 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Irie Y., Parsek M. R. 2008. Quorum sensing and microbial biofilms. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 322:67–84 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kiran M. D., et al. 2008. Discovery of a quorum sensing inhibitor of drug-resistant staphylococcal infections by structure-based virtual screening. Mol. Pharmacol. 73:1578–1586 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kong K. F., Vuong C., Otto M. 2006. Staphylococcus quorum sensing in biofilm formation and infection. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 296:133–139 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lipsky B. A., Hoey C. 2009. Topical antimicrobial therapy for treating chronic wounds. Clin. Infect. Dis. 49:1541–1549 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Macedo A. J., Abraham W. R. 2009. Can. infectious biofilm be controlled by blocking bacterial communication? Med. Chem. 5:517–528 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Martin J. M., Zenilman J. M., Lazarus G. S. 2010. Molecular microbiology: new dimensions for cutaneous biology and wound healing. J. Invest. Dermatol. 130:38–48 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Miller M. B., Bassler B. L. 2001. Quorum sensing in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 55:165–199 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Moy T. I., et al. 2009. High-throughput screen for novel antimicrobial using a whole animal infection model. ACS Chem. Biol. 4:527–533 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Musk D. J., Jr., Hergenrother P. J. 2006. Chemical countermeasures for the control of bacterial biofilms: effective compounds and promising targets. Curr. Med. Chem. 13:2163–2177 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Palmer K. L., Aye L. M., Whiteley M. 2007. Nutritional cues control Pseudomonas aeruginosa multicellular behavior in cystic fibrosis sputum. J. Bacteriol. 189:8079–8087 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Parsek M. R., Singh P. K. 2003. Bacterial biofilms: an emerging link to disease pathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 57:677–701 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Peeters E., Nelis H. J., Coenye T. 2009. In vitro activity of ceftazidime, ciprofloxacin, meropenem, minocycline, tobramycin and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole against planktonic and sessile Burkholderia cepacia complex bacteria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 64:801–809 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Rau M. H., et al. 2010. Early adaptive developments of Pseudomonas aeruginosa after the transition from life in the environment to persistent colonization in the airways of human cystic fibrosis hosts. Environ. Microbiol. 12:1643–1658 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sifri C. D., Begun J., Ausubel F. M., Calderwood S. B. 2003. Caenorhabditis elegans as a model for Staphylococcal aureus pathogenesis. Infect. Immun. 71:2208–2217 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sopirala M. M., et al. 2010. Synergy testing by Etest, microdilution checkerboard, and time-kill methods for pan-drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 54:4678–4683 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sriramulu D. D., Lünsdorf H., Lam J. S., Römling U. 2005. Microcolony formation: a novel biofilm model of Pseudomonas aeruginosa for the cystic fibrosis lung. J. Med. Microbiol. 54:667–676 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Stiernagle T. 2006. Maintenance of C. elegans. Wormbook 11:1–11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sun Y., Dowd S. E., Smith E., Rhoads D. D., Wolcott R. D. 2008. In vitro multispecies Lubbock chronic wound biofilm model. Wound Repair Regen. 16:805–813 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sutherland I. 2001. Biofilm exopolysaccharides: a strong and sticky framework. Microbiology 147:3–9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Tomlin K. L., et al. 2005. Quorum-sensing mutations affect attachment and stability of Burkholderia cenocepacia biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71:5208–5218 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Uehlinger S., et al. 2009. Identification of specific and universal virulence factors in Burkholderia cenocepacia strains by using multiple infection hosts. Infect. Immun. 77:4102–4110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Werthén M., et al. 2010. An in vitro model of bacterial infections in wounds and other soft tissues. APMIS 118:156–164 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Williams P. 2007. Quorum sensing, communication and cross-kingdom signaling in the bacterial world. Microbiology 153:3923–3938 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Xavier K. B., Bassler B. L. 2003. LuxS quorum sensing: more than just a numbers game. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 6:191–197 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Yang L., et al. 2009. Computer-aided identification of recognized drugs as Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing inhibitors. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53:2432–2443 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Zeng L., et al. 2008. Virtual screening for novel quorum sensing inhibitors to eradicate biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 79:119–126 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
[Supplemental material]