Soyuz 7K-TM (original) (raw)

Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Soyuz 7K-TM

Soyuz ASTP in Orbit
Credit: NASA
Russian manned spacecraft. The Soyuz 7K-T as modified for the docking with Apollo. Launched 1974 - 1975.
AKA: 11F615A12;7K-TM/F/;Soyuz M. Status: Operational 1974. First Launch: 1974-04-03. Last Launch: 1975-07-15. Number: 4 . Thrust: 4.09 kN (919 lbf). Gross mass: 6,680 kg (14,720 lb). Unfuelled mass: 6,180 kg (13,620 lb). Specific impulse: 282 s. Height: 7.48 m (24.54 ft). Span: 8.37 m (27.46 ft).
The spacecraft included some systems developed for the cancelled Soyuz S, including a new launch escape tower. Other changes included new lightweight solar panels to increase endurance; an androgynous universal docking mechanism in place of standard Soyuz male mechanism; unique radio aerials for common communications; optical docking targets for manual docking with Apollo; and modifications to the environmental control system to lower the cabin pressure to 0.68 atmospheres prior to docking with Apollo..
Crew Size: 2. Orbital Storage: 7.00 days. Habitable Volume: 9.00 m3. Spacecraft delta v: 215 m/s (705 ft/sec). Electric System: 8.00 kWh. Electric System: 0.50 average kW.
More at: Soyuz 7K-TM.
Family: Manned spacecraft, Space station orbit. Country: Russia. Engines: KTDU-35. Spacecraft: Soyuz ASTP SA, Soyuz ASTP BO, Soyuz ASTP PAO. Flights: Soyuz 16, Soyuz 19 (ASTP). Launch Vehicles: R-7, Soyuz-U. Propellants: Nitric acid/Hydrazine. Projects: ASTP. Launch Sites: Baikonur, Baikonur LC1, Baikonur LC31. Agency: Korolev bureau, MOM. Bibliography: 185, 186, 187, 188, 2, 21, 32, 33, 367, 376, 452, 51, 6, 60, 89, 6904, 13132.
Photo Gallery
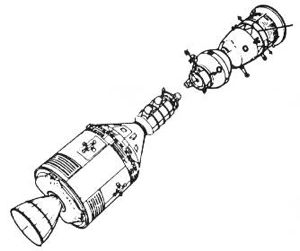 |
Soyuz ASTPUnusual 1972 illustration of Soyuz ASTP without solar panels.Credit: NASA |
|---|
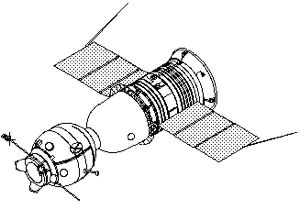 |
Soyuz ASTPCredit: © Mark Wade |
|---|
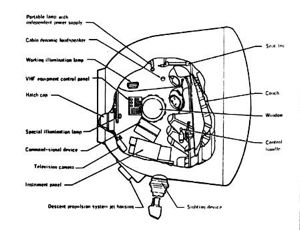 |
Soyuz ASTP SACutaway of Soyuz re-entry capsule. |
|---|
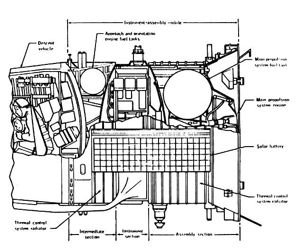 |
Soyuz ASTP POCutaway of Soyuz equipment / propulsion module. |
|---|
 |
Soyuz ASTP in Orbit Soyuz ASTP in Orbit 3Credit: NASA |
|---|
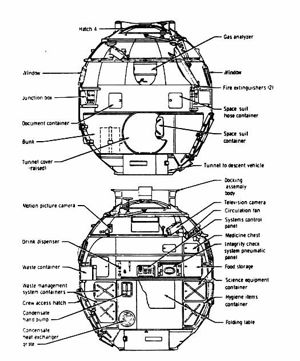 |
Soyuz ASTP BOCutaway of Soyuz orbital module. |
|---|
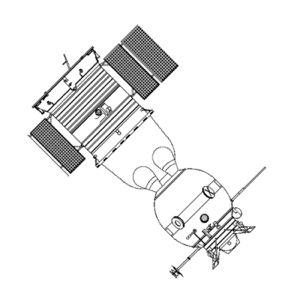 |
Soyuz ASTPCredit: © Mark Wade |
|---|
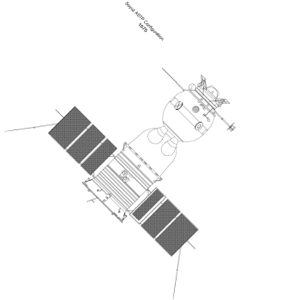 |
Soyuz ASTPCredit: © Mark Wade |
|---|
 |
Soyuz ASTP in Orbit Soyuz ASTP in Orbit 4Credit: NASA |
|---|
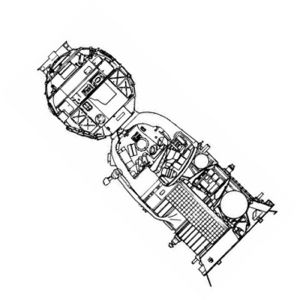 |
Soyuz ASTP Cutaway |
|---|
 |
APAS-75 docking unitAPAS-75 docking unit as used in ASTP project.Credit: Andy Salmon |
|---|
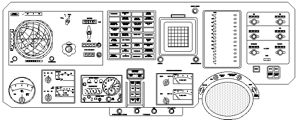 |
Panel Soyuz 7K-OKControl panel of the initial earth orbit version of Soyuz.Credit: © Mark Wade |
|---|
 |
Soyuz 16Credit: Manufacturer Image |
|---|
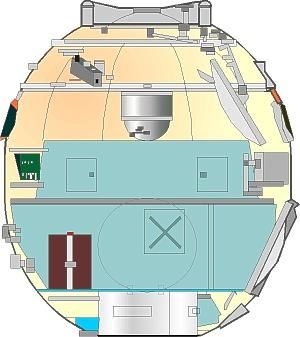 |
Soyuz OMDetailed cutaway of standard Soyuz orbital module, as flown on ASTP mission.Credit: © Mark Wade |
|---|
1970 October 14 - .
- Contacts on join USA/USSR docking system. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Keldysh, Nikolayev, Sevastyanov. Program: ASTP. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-TM.
Communist Party Meeting at the cosmonaut centre. Keldysh calls later. Six specialists are to be sent to the United States to discuss design of a common USA/USSR docking system. Kamanin yet again goes through the correct answers and prepared speeches to be given to the press by Nikolayev and Sevastyanov on their visit to West Germany.
1972 January 1 - .
- TsKBEM reorganised - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Bushuyev, Dorofeyev, Mishin, Semenov, Shabarov. Program: Lunar L3, Soyuz, Almaz. Spacecraft: LK, Mars 5NM, MKBS, Soyuz 7K-LOK, Soyuz 7K-OK, Soyuz 7K-S, Soyuz 7K-T, Soyuz 7K-TM.
TsKBEM was given a completely new structure as a result of the findings of the expert commissions on the disasters for the previous year, Mishin remained as the Chief Designer for the organisation, but each programme now had its own chief designer:- N1: Boris Dorofeyev
- 8K98P solid propellant ICBM: Igor Sadovskiy
- N1 payloads: Vladimir Brorov [check]
- Soyuz 7K-TM, or Soyuz M, for Soyuz-Apollo: Konstantin Bushuyev
- Soyuz 7K-T: Yuri Semenov
- Soyuz 7K-S or Soyuz VI: Yevgeni Shabarov
Additional Details: here....
1974 April 3 - . 07:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Cosmos 638 - . Payload: Soyuz ASTP s/n 71-EPSA. Mass: 6,570 kg (14,480 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: ASTP. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-TM. Duration: 9.89 days. Decay Date: 1974-04-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 7234 . COSPAR: 1974-018A. Apogee: 309 km (192 mi). Perigee: 187 km (116 mi). Inclination: 51.80 deg. Period: 89.40 min.
Unmanned Soyuz test flight. Recovered April 13, 1974 5:05 GMT. Soyuz ASTP Test.
Maneuver Summary:
190km X 309km orbit to 190km X 266km orbit. Delta V: 12 m/s
190km X 266km orbit to 240km X 300km orbit. Delta V: 23 m/s
240km X 300km orbit to 258km X 274km orbit. Delta V: 12 m/s
Total Delta V: 47 m/s.
Officially: Investigation of the upper atmosphere and outer space.
1974 August 12 - . 06:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Cosmos 672 - . Payload: Soyuz ASTP s/n 72-EPSA. Mass: 6,570 kg (14,480 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: ASTP. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-TM. Duration: 5.94 days. Decay Date: 1974-08-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 7413 . COSPAR: 1974-064A. Apogee: 226 km (140 mi). Perigee: 222 km (137 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 88.90 min.
ASTP precursor. Recovered August 18, 1974 5:02 GMT. Soyuz ASTP test.
Maneuver Summary:
195km X 305km orbit to 195km X 221km orbit. Delta V: 24 m/s
195km X 221km orbit to 223km X 223km orbit. Delta V: 8 m/s
231km X 231km orbit to 231km X 231km orbit. Delta V: 1 m/s
223km X 223km orbit to 231km X 231km orbit. Delta V: 4 m/s
231km X 231km orbit to 227km X 237km orbit. Delta V: 2 m/s
Total Delta V: 39 m/s.
Officially: Investigation of the upper atmosphere and outer space.
1974 December 2 - . 09:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz 16 - . Call Sign: Buran (Snowstorm ). Crew: Filipchenko, Rukavishnikov. Backup Crew: Andreyev, Dzhanibekov. Support Crew: Ivanchenkov, Romanenko. Payload: Soyuz ASTP s/n 73-EPSA. Mass: 6,800 kg (14,900 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: ASTP. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 16. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-TM. Duration: 5.93 days. Decay Date: 1974-12-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 7561 . COSPAR: 1974-096A. Apogee: 291 km (180 mi). Perigee: 184 km (114 mi). Inclination: 51.80 deg. Period: 89.20 min.
ASTP Manned Test Flight. Check-out of the Soyuz space craft's on-board systems which had been modernized to meet the requirements of the 1975 joint flight in accordance with the programme of the Soviet-United States experiment; conduct of scientific and technical investigations.
1975 July 15 - . 12:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz 19 (ASTP) - . Call Sign: Soyuz (Union ). Crew: Kubasov, Leonov. Backup Crew: Filipchenko, Rukavishnikov. Support Crew: Andreyev, Dzhanibekov, Ivanchenkov, Romanenko. Payload: Soyuz ASTP s/n 75 (EPSA). Mass: 6,790 kg (14,960 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: ASTP. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Apollo (ASTP), Soyuz 19 (ASTP). Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-TM. Duration: 5.94 days. Decay Date: 1975-07-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 8030 . COSPAR: 1975-065A. Apogee: 220 km (130 mi). Perigee: 186 km (115 mi). Inclination: 51.80 deg. Period: 88.50 min.
Soyuz 19 initial orbital parameters were 220.8 by 185.07 kilometres, at the desired inclination of 51.80�, while the period of the first orbit was 88.6 minutes. On 17 July the two spacecraft docked. The crew members rotated between the two spacecraft and conducted various mainly ceremonial activities. Leonov was on the American side for 5 hours, 43 minutes, while Kubasov spent 4:57 in the command and docking modules.
After being docked for nearly 44 hours, Apollo and Soyuz parted for the first time and were station-keeping at a range of 50 meters. The Apollo crew placed its craft between Soyuz and the sun so that the diameter of the service module formed a disk which blocked out the sun. After this experiment Apollo moved towards Soyuz for the second docking.
Three hours later Apollo and Soyuz undocked for the second and final time. The spacecraft moved to a 40 m station-keeping distance so that an ultraviolet absorption experiment could be performed. With all the joint flight activities completed, the ships went on their separate ways.
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use