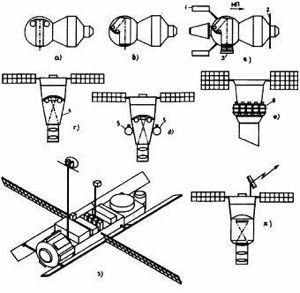
Zenit-2 satellite (original) (raw)

Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Zenit-2 satellite
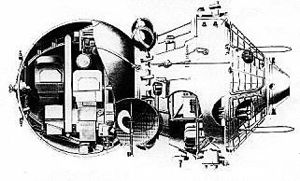
Zenit 2
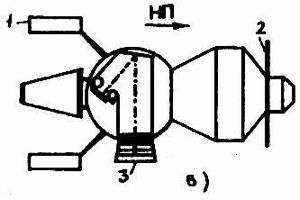
Zenit-2. Later improved version Zenit-2M commonly had a Nauka module mounted on the forward end of the sphere.
Russian military surveillance satellite. The Zenit-2 was a derivative of the manned Vostok, and the Soviet Union's first spy satellite. Reconnaissance, photo (low resolution, film return type), ELINT satellite built by OKB-1 for GRU, Russia. Launched 1961 - 1970. Used Zenit bus.
AKA: 11F61;2K;Vostok 2;Zenit-2. Status: Operational 1961. First Launch: 1961-12-11. Last Launch: 1970-05-12. Number: 81 . Gross mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb).
It fulfilled the Soviet military's unmanned photo reconnaissance satellite requirement, and later versions remained in use into the 21st Century.
The Zenit spacecraft had its origins before Sputnik. In 1956, the Soviet military identified a requirement for a photo-reconnaissance satellite (see Zenit). Sergei Korolev, flushed after the success of Sputnik, instead advocated that manned spaceflight should have first priority. After bitter disputes, a compromise solution was reached. Korolev was authorized to proceed with development of a spacecraft to achieve manned flights at the earliest possible date. However the design would be such that the same spacecraft could be used to fulfill the military's unmanned photo reconnaissance satellite requirement. A series of 1K prototypes would prove the essential design; the 2K and 4K versions would be unmanned spy satellites, and the 3K the manned spaceship. The military resisted, but in November 1958 Korolev won, and the Council of Chief designers approved the Vostok manned space program, in combination with Zenit spy satellite program.
Development work was begun in May 1959. Project leader was Ryazanov until 1961; thereafter Tsybin. Section heads were Yu M Frumkin for the spacecraft and Ts V Solovyov for the communications. The agreed technical specifications for the 2K satellite (given the code name Zenit-2) were for a photo apparatus with a focal length of not less than a meter, limited only by the size of the spacecraft itself. Electronics were to include secure radio systems that would only transmit and receive data when the spacecraft was over the territory of the USSR. These included transmission of photo-television images and receipt of secure command and programming data.
There were many difficult problems during development. The requirement for 10-15 m camera resolution from 200-400 km altitude and a speed of 8,000 m/s meant that a motion compensation system was needed. Pointing requirements were very demanding, resulting in the first Soviet use of a gyroscopic platform, infrared horizon sensors, and integration of the sensors into an automated orientation system. Technical challenges existed not just in the spacecraft but in the ground control center, which had to generate spacecraft command sequences. This was the first development of an on0board system to execute complex commands from the ground. The spacecraft optics required that internal temperatures be kept within 1 degree Centigrade, and that temperature variations be no more than 0.1 degrees/hour. Since the spacecraft was normally oriented to the sun, an active thermal regulation system was needed.
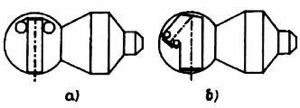
The Vostok and Zenit satellites differed from each other as follows:
- The Zenit had an extended cylindrical section in the PAO instrument/propulsion module, and lacked the aft communication antennae of the Vostok;
- The SA descent capsule and the PAO of the Zenit had large directional dish antennae for use with the secure radio-command system;
- Zenit deleted man-related life support systems, the ejection seat, and the systems for manual control of the spacecraft.
- Added were specialized intelligence systems, telemetry systems, and information systems control electronics. The Zenit-2 needed its own radio-guidance system. It couldn't use Vostok systems, since it needed to upload all instructions for the entire daily work program of automatically-controlled photography over enemy territory within a five minute pass over USSR ground stations. All communications also had to be encrypted.
The radio control system was to have been developed on the basis of preliminary work on the Podsnezhnik radio control system. A competitor was the Kub system developed by OKB-1. The conflict between the two systems was elevated to Marshal Moskalenko. The matter was decided at a meeting between Moskalenko, Korolev, and Chertok. Korolev was very possessive, and argued the case not on the technical merits but rather on keeping all Zenit-2 work within OKB-1. Moskalenko finally decided to develop both systems. Mikhail Pavlovich Petelin was the Chief Designer of Podsnezhnik and Armen Sergeyevich Mnatsoskanian was Chief Designer of Kub. Kub was finally selected as having nearly competed development. - While the Vostok needed to control its orientation only during descent, the photographic mission required constant 3-axis high precision control. For successful photography it needed to very precisely determine its position in orbit and point its camera at the correct target
- While the life support system was not required, control of the internal temperature of the capsule was even more critical than on the Vostok, due to the temperature sensitivity of the camera optics.
- To guarantee the security of the secret equipment aboard Zenit, the APO-2 automatic destruct system was installed. The APO-2 could not only operate on command but would also automatically destroy the spacecraft if certain complex logical parameters were met - for example, if it determined that the capsule was going to land on enemy territory. The spherical SA descent capsule contained all of the specialized classified apparatus (the camera, the photo-television, the radio apparatus). The Zenit camera was mounted perpendicular to the long axis of the spacecraft. Exposures were made through multiple lens cameras, shooting through one of two large diameter hatches.
The first Zenits were fitted out with the SA-20 camera, with a focal length of 1 meter, the SA-10 camera, with a focal length of 0.2 m, the Baikal photo-television device, and the Kust-12M ELINT radio apparatus (developed by M E Zaslavskiy). Baikal was installed in Zenit serial numbers 1, 2, 3,4, 7 and 8. However after four successful trial flights (Cosmos 4, 7, 9, and 15) it became clear that the Baikal did not live up to its expected specifications (the United States had a similar experience with its early electro-optical systems on the Samos series). Subsequent Zenits dropped the Baikal and used the Ftor-2P, which combined the SA-20 and SA-10 cameras and the Kust-12M ELINT apparatus into a single system. The Ftor-2P was designed to photograph, from altitudes of 180 to 200 km, 1500 frames of film, each frame covering a 60 x 60 km area, for a total coverage per mission of 5.4 million square kilometers. The system could not only take photographs at the nadir but also at oblique angles to the side of the flight path. Yu V Ryabushkin of the Krasnogorsk Mechanical Factory was chief designer of the camera.
Zenits from the beginning carried small supplemental experimental packages, for example meteoroid or cosmic particle detectors. On Zenit number 80 the Nauka autonomous sub-satellite was flown. The Nauka containers served a dual purpose. Mounted on the forward end of the re-entry sphere, they provided ballast on the spacecraft during its mission. When the Zenit had completed its work, the Nauka would be released for autonomous flight. Over 40 Nauka containers were installed on Zenit-2 and Zenit-2M spacecraft, and they achieved noteworthy results in scientific and military space research.
Flight trials (LKI) Zenit-2s had a mass of 4,610 to 4,760 kg, and production models ranged from 4,700 to 4,740 kg.
Five prototype Vostok 1K spacecraft were launched in May to December 1960; only one of the flights was completely successful. These were followed two entirely successful Vostok 3KA launches in March 1961. The third Vostok 3KA, on 12 April 1961, put the first human into space. This was followed by Gherman Titov's day-long flight in August of the same year.
Focus now turned to testing of the 2K spacecraft, code named Zenit-2. A modification of the 8K72 three-stage launch vehicle, the 8A92, was developed for Zenit. The first launch on 11 December 1961 was a failure, due to a fault in the third stage.
The first flight trials Zenit-2 was launched on 11 December 1961. However the launch ended in failure of the launch vehicle upon ignition of the third stage. The spacecraft APO destruct system at least proved its operation by detecting the shut down and automatically destroying the spacecraft.
The second Zenit-2 successful reached orbit on 26 April 1962, officially being designated Cosmos 4. However leaks from the oxygen system tanks used for the orientation system resulted in the premature return of the spacecraft after three days of flight. During most of the flight the spacecraft was uncontrollable, although the photographic material returned could be used to determine the performance of the Baikal and SA-10 systems. In all 13 LKI trials launches were made of Zenit-2, three of which ended in failure of the launch vehicle. Each flight was used methodically to test all systems, verify guidance commands, etc. Lessons learned were applied to the modernized spacecraft, which had improved cameras, on-board systems, and autonomous guidance methods. The ineffective television system was deleted.
Zenit-2 number 14 began the production flights of the spacecraft. Production and design responsibility was moved at that point from Korolev's main OKB-1 facility near Moscow to OKB-1 Filial No.3 in Samara, headed by D I Kozlov. Later Kozlov was also given responsibility for the R-7 ICBM and its space-launch derivatives. Filial No. 3 was made a separate organization, the TsKB Central Specialized Construction Bureau, which incorporated the Progress production factory in Samara. The TsKB to this day has been the leading supplier to the Soviet military of imaging spacecraft, all of them using Soyuz launch vehicles produced at the same factory.
The first two Zenits were launched by the same 8K72K launcher used for the Vostok manned spacecraft. The rest, from 1962 to 1967, used productionized Vostok 8A92 launchers. The Zenit-2, given article number 11F61, and the 8A92 launchers, were adopted as armament of the Soviet Army on 10 March 1964 by decree of the Defense Ministry of the USSR number 0045.
From 1967 launch of most Zenit-2's was moved to the northern Plesetsk cosmodrome. To reach the higher-inclination orbits required use of a more powerful launch vehicle, the Soyuz 11A57. Decree no 0015 of 1967 amended the earlier decree to add to the Zenit-2 complex the 11A57 and the newer APO-4B destruct system.
From 1968 flights gradually transitioned to the modernized spacecraft Zenit-2M. The last launch of a Zenit-2 was on 12 May 1970. In all, including the state trials launches, 81 Zenit-2's were launched, of which 7 were lost on launch vehicle failures. Of the 74 that reached orbit, 13 had only partially successful missions due to various equipment failures; three were complete failures, with the spacecraft being destroyed. Notable Zenit flights included:
- Cosmos 12, the first successful full-duration flight;
- Cosmos 48, which resulted in the spacecraft returning two days early when the thermo-regulation system failed and internal temperature rose to 43 degrees C;
- Cosmos 50, which completed a full duration mission, but was destroyed by the APO system when the braking engine failed at retrofire;
- Cosmos 66, which suffered a parachute deployment failure. The spacecraft was destroyed in the crash.
- Cosmos 199, which failed to separate from Block I stage. An attempt was made to conduct the mission without the orientation system. The APO self destruct system destroyed the spacecraft on its 126th revolution over the Sea of Okhotsk
- Cosmos 216, which landed in River Volga 1 km from shore and sank after 42 minutes. 85% of the data was ruined.
- Cosmos 235, which suffered a hard landing due to parachute system failure. 30% of the film was damaged.
- Cosmos 253, where on the 13th orbit the SA-20-1 camera's shutter responded to an uncommanded order to open. Radiation levels inside reached 3 times normal levels. 53% of the data was lost.
Typical orbital profile: inclination 65 degrees with an altitude of 197-318 km; inclination 51.8 degrees with an altitude of 200-272 km; inclination 72.8 degrees with an altitude of 203-337 km; inclination 81.3 degrees with an altitude of 201-368 km. Transmission frequencies observed in West: 19.995 PDM; sometimes 19.990 PDM.
More at: Zenit-2 satellite.
Family: Military surveillance sat, Surveillance, Surveillance orbit. Country: Russia. Engines: TDU-1. Launch Vehicles: R-7, Vostok 8K72K, Voskhod 11A57, Vostok 8A92. Launch Sites: Baikonur, Baikonur LC1, Plesetsk, Baikonur LC31, Plesetsk LC41/1, Plesetsk LC43/4. Agency: Korolev bureau, MOM. Bibliography: 102, 110, 175, 2, 367, 376, 42, 445, 474, 6, 93, 99.
Photo Gallery
 |
Zenit 2 ReconnsatCredit: © Mark Wade |
|---|
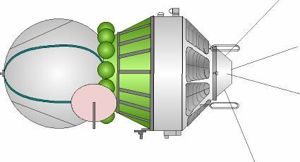
 |
Zenit Optical Paths |
|---|
 |
Zenit AerosurfaceZenit Reconnaissance satellite with aerodynamic control services for orientation in orbit. |
|---|
 |
Zenit-4MTCredit: Manufacturer Image |
|---|
1956 September 30 - .
- First official plan for future Soviet spaceflight - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft: Sputnik 3, Vostok, Zenit-2 satellite.
This set forth the following objectives: orbiting of satellites of 1.8 to 2.5 tonnes mass by 1958; one week flight of a manned spacecraft by 1964; unmanned reconnaissance satellite by 1970; rocket capable of 12 tonne escape velocity payload by 1970; rocket with 100 tonne low earth orbit payload to be developed, capable of placing 2 to 3 men on the moon (no date set).
1957 Spring - .
- Soviet reconnaisance system designs continue - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit satellite, Zenit-2 satellite. Studies were undertaken for military reconnaissance satellites. Code names for these studies were: Shchit - military reconnaissance systems; Osnova - military reconnaissance equipment; Ediniy KIK - military reconnaissance control systems..
1958 November 1 - .
- Vostok spacecraft and Zenit spy satellite authorised. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Korolev. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Vostok, Zenit-2 satellite, Zenit-4.
Council of Chief Designers Decree 'On course of work on the piloted spaceship' was issued. Council of Chief designers approved the Vostok manned space program, in combination with Zenit spy satellite program Korolev was authorised to proceed with development of a spacecraft to achieve manned flights at the earliest possible date. However the design would be such that the same spacecraft could be used to fulfil the military's unmanned photo reconnaissance satellite requirement. The military resisted, but Korolev won. This was formalised in a decree of 25 May 1959.
1959 May 22 - .
- Production of Vostok and Zenit-2 authorised. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Vostok, Zenit-2 satellite, Zenit-4.
Central Committee of the Communist Party and Council of Soviet Ministers Decree 569-264 'On work on a reconnaissance satellite and piloted spaceship' was issued. Due to a bitter fight with the military over the nature and priority of the manned spacecraft and photo-reconnaissance space programs, the final decree for the Vostok manned spacecraft was delayed until seven months after drawing release began. This authorised production of a single design that could be used either as a manned spacecraft or as a military reconnaissance satellite. These were the Zenit-2 and Zenit-4 spacecraft based on the Vostok design. This marked the end of the original Zenit configuration. The military had to develop the recovery forces and techniques for both spacecraft, including appropriate aircraft, helicopters, and handling equipment. At that time it was felt that there was a 60% chance on each launch of an abort requiring rescue operations for the cosmonaut.
1959 May 22 - .
- Vostok / Zenit-3 decree issued. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Vostok, Zenit-2 satellite, Zenit-4.
Due to a bitter fight with the military over the nature and priority of the manned spacecraft and photo-reconnaissance space programs, the final decree for the Vostok manned spacecraft was delayed until seven months after drawing release began. This authorised production of a single design that could be used either as a manned spacecraft or as a military reconnaissance satellite. These were the Zenit-2 and Zenit-4 spacecraft based on the Vostok design. This marked the end of the original Zenit configuration.
1961 February 22 - .
- Zenit project review - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Alekseyev, Semyon, Ustinov, Voronin. Program: Vostok. Flight: Vostok 1. Spacecraft: Vostok, Zenit-2 satellite, Zenit-4.
Ustinov heads a review of the reconnaissance satellite program, at that time still referred to as the Vostok-2 and Vostok-4 spacecraft. Thirty staff are working on it full time at OKB-1, but Korolev says that due to delays in the photographic, television, and radar equipment for the spacecraft the first launch will be delayed two to three months. But he points out that since Vostok-1 has already proven the recovery systems, the first Vostok-2 should still be ready for launch in June-July 1961. Ustinov notes that the Ministry of Defence has had little input or understanding of the specification for the spacecraft. The launch of the first Vostok-3 is delayed to March due to the need to fully test all systems. The life support system (Vornonin) and the ejection seat (Alekseyev) are the pacing items. The next meeting is set for 27 February. Kustanin testifies as to the readiness of the spacecraft and the cosmonauts.
1961 October 28 - .
- Zenit-2 priority delays manned space flights - . Nation: Russia. Program: Vostok. Flight: Vostok 3, Vostok 4. Spacecraft: Vostok, Zenit-2 satellite. Plans for a November group flight are delayed due to the priority of the spy satellite program. Korolev wants to fly manned Vostoks in December 1961/January 1962, but Kamanin and the VVS oppose this due to poor weather during that period..
1961 December 11 - . 09:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8K72K. FAILURE: RO-7 engine of block E upper stage cutoff prematurely. Spacecraft liquidated by self destruct system APO in 407th second of flight. Debris landed 100 km north of Vilyuisk.. Failed Stage: 2.
- Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 1 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 1. Mass: 4,610 kg (10,160 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Decay Date: 1961-12-11 .
First attempted launch of Zenit photo-reconnaisance satellite. According to Kamanin, there was a problem with the third stage, and the capsule landed between Novosibirsk and Yakutsk, but could not be located. There was no information on the nature of the problem. Korolev stayed at Tyuratam, preparing for the next launch attempt.
1962 March 5 - .
- Vostok 3/4 delayed - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Bykovsky, Gagarin, Nelyubov, Nikolayev, Popovich, Titov. Program: Vostok. Flight: Vostok 3, Vostok 4. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite.
Due to technical problems and the launch failure of a Zenit spy satellite, the launch of the dual Vostoks is pushed back to April. Therefore a trip to New York by the cosmonauts in March will not be possible. In any case the Presidium has decided against allowing them to address the United Nations.
1962 April 26 - . 10:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8K72K.
- Cosmos 4 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 2. Mass: 4,610 kg (10,160 lb). Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Nikolayev, Popovich. Agency: RVSN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Flight: Vostok 3, Vostok 4. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 3.00 days. Decay Date: 1962-04-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 287 . COSPAR: 1962-Xi-1. Apogee: 317 km (196 mi). Perigee: 285 km (177 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 90.50 min.
Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Program partially completed. Failure of primary spacecraft orientation system. It was to spend four days in space, to be followed by another mission during 5-10 May. This meant that Vostok 3/4 could not be launched before 20-30 May. The cosmonaut prime crew returned from their in-suit parachute training at Fedosiya.
1962 June 1 - . 09:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92. FAILURE: Shutdown of Block B strap-on engine stage 1.8 seconds after liftoff. The booster crashed 300 m from the pad. Pad damaged.. Failed Stage: 0.
- Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 3 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 3. Mass: 4,610 kg (10,160 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Decay Date: 1962-06-01 .
Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Third attempted launch of Zenit photo-reconnaissance satellite. It blew up 300 m from the pad, and did enough damage to put the launch complex out of operation for a month. Therefore the Vostok 3/4 launches could not take place until the end of July at the earliest.
1962 June 22 - .
- Zenit booster failure damages pad, delays Vostok 3/4 - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Gagarin, Keldysh, Korolev, Titov, Vershinin. Program: Vostok. Flight: Vostok 3, Vostok 4. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite.
A briefing by engineer V A Smirnov predicts that the Americans will make a 17-18 revolution flight of the earth by the end of 1962. Kamanin disagrees, believing they will not achieve this until the second half of 1963. Another Zenit-2 spy satellite has failed to achieve orbit. The first had failed due to a third stage problem, and now the third attempt failed due to a first stage problem. It blew up 300 m from the pad, and did enough damage to put the launch complex out of operation for a month. Therefore the Vostok 3/4 launches cannot now take place until the end of July at the earliest.
Kamanin has continued arguments over the reorganisation of VVS space units and the role of IAKM. Korolev has never supported a leading role for the VVS or Kamanin in the Soviet space program. He is complaining about the 'offences' of the VVS, Kamanin, and the cosmonauts. Korolev cites Gagarin's trauma and Titov's motor accidents. He believes cosmonauts should be selected only from OKB-1 engineers. He also believes the cosmonauts are wasting too much time on publicity tours. Vershinin and Keldysh are hearing all of these complaints.
1962 July 28 - . 09:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 7 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 4. Mass: 4,610 kg (10,160 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 4.00 days. Decay Date: 1962-08-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 346 . COSPAR: 1962-A-Iota-1. Apogee: 356 km (221 mi). Perigee: 197 km (122 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 90.00 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Also performed radiation measurements..
1962 August 4 - .
- Launch preparations - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Korolev, Nikolayev, Popovich. Program: Vostok. Flight: Vostok 3, Vostok 4. Spacecraft: Vostok, Zenit-2 satellite.
Kamanin is at the Syr Darya River at 06:50, and arrives at Area 2 at 09:00. Suit communications tests are underway. From 11:00 to 13:00 there is a discussion on how the cosmonauts will observe the third stage of their booster, and how the spacecraft will be oriented. To stay pointed, they will need to put the spacecraft in a very slow maneuver of 0.06 deg/sec, or one revolution in 1.8 hours. Once they have achieved this, they have to put the spacecraft in a roll of 0.5 deg/sec, or one revolution in 12 minutes, in order to maintain the spacecraft's thermal balance due to solar heating. Kamanin does not understand why this is necessary - the Cosmos 4 spy satellite, of the same design, spent all four days of its mission in stabilised flight, using infrared horizon trackers, and maintained a stable internal temperature of 17 deg C. Korolev mentions that Cosmos 4 could distinguish types of aircraft on airfields, and the form and tonnage of ships at sea.
1962 September 27 - . 09:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 9 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 7. Mass: 4,700 kg (10,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 4.00 days. Decay Date: 1962-10-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 422 . COSPAR: 1962-A-Omega-1. Apogee: 981 km (609 mi). Perigee: 829 km (515 mi). Inclination: 67.60 deg. Period: 103.10 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Also performed radiation measurements..
1962 October 17 - . 09:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 10 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 5. Mass: 4,700 kg (10,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 4.00 days. Decay Date: 1962-10-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 437 . COSPAR: 1962-B-Zeta-1. Apogee: 376 km (233 mi). Perigee: 178 km (110 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 90.00 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Also performed radiation measurements..
1962 December 6 - .
- Soviet Space Plans for 1963-1964 - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Korolev, Smirnov, Ustinov. Program: Soyuz, Vostok, DS. Flight: Vostok 7, Vostok 8, Vostok 9. Spacecraft: Soyuz A, Soyuz B, Soyuz V, Vostok, Zenit-2 satellite, Zenit-4.
Meeting of the Interdepartmental Soviet of the Academy of Sciences reviews space exploration plans. In the next two years, 5-6 Luna probes will be sent to the moon, including soft landers with a mass of 100 kg, and orbiters to map the surface. There will be flybys and landings of Mars and Venus. Two Zond spacecraft will study the space environment out to 20 million kilometres from the earth. In earth orbit, 10 Zenit spy satellites, 10 to 12 Vostok manned spacecraft, 4 to 6 Soyuz spacecraft, and 10 to 12 Kosmos satellites will be launched. The Kosmos will fly missions in meteorology, communications, television transmission, and heliographic, and geological studies. Kamanin finds this a good program, but it nearly all relies on a single launch pad and one-time transmission of data from a few satellites. The military plan is not reviewed; it must go through the VPK Military-Industrial Commission first. An Expert Commission is to be formed on the Soyuz spacecraft. Smirnov and Korolev have dictated a letter to Ustinov asking that eight more Vostoks be built. On the other hand, some on the general staff want 60 cosmonauts trained in the next two to three years, to support 8 to 10 flights of single-place spacecraft and 7 to 8 flights of multiplace spacecraft.
1962 December 22 - . 09:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 12 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 6. Mass: 4,700 kg (10,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1962-12-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 517 . COSPAR: 1962-B-Omega-1. Apogee: 385 km (239 mi). Perigee: 202 km (125 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 90.40 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Also performed radiation measurements..
1963 March 21 - . 08:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 13 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 9. Mass: 4,700 kg (10,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: Korolev bureau. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1963-03-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 554 . COSPAR: 1963-006A. Apogee: 303 km (188 mi). Perigee: 214 km (132 mi). Inclination: 65.20 deg. Period: 89.60 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Also performed radiation measurements..
1963 April 22 - . 08:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 15 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 8. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: Korolev bureau. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 5.00 days. Decay Date: 1963-04-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 569 . COSPAR: 1963-011A. Apogee: 336 km (208 mi). Perigee: 194 km (120 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 89.80 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Also carried weather, radiation experiments..
1963 April 28 - . 08:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 16 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 10. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: Korolev bureau. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 10.00 days. Decay Date: 1963-05-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 571 . COSPAR: 1963-012A. Apogee: 379 km (235 mi). Perigee: 201 km (124 mi). Inclination: 64.70 deg. Period: 90.30 min. Program partially completed. Part of the information lost due to failure of engine block stabilization system. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Also performed radiation measurements..
1963 May 24 - . 10:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 18 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 11. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: Korolev bureau. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 9.00 days. Decay Date: 1963-06-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 586 . COSPAR: 1963-018A. Apogee: 269 km (167 mi). Perigee: 212 km (131 mi). Inclination: 64.60 deg. Period: 89.30 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Also performed radiation measurements..
1963 July 10 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92. FAILURE: Shutdown of Block B strap-on engine stage 1.9 seconds after liftoff. Pad damaged.. Failed Stage: 0.
- Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 12 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 12. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Decay Date: 1963-07-10 . Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1963 October 18 - . 09:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 20 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 13. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: Korolev bureau. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1963-10-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 673 . COSPAR: 1963-040A. Apogee: 296 km (183 mi). Perigee: 201 km (124 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 89.40 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1963 November 28 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92. FAILURE: Failure of block E upper stage. Spacecraft liquidated by APO destruct system.. Failed Stage: 2.
- Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 14 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 14. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Decay Date: 1963-11-28 . Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1963 December 19 - . 09:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 24 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 15. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: Korolev bureau. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 9.00 days. Decay Date: 1963-12-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 712 . COSPAR: 1963-052A. Apogee: 391 km (242 mi). Perigee: 204 km (126 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 90.50 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1964 March 10 - . LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Zenit-2 spy satellite accepted into mlitary service - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Defence Ministry of the USSR decree 0045 'On adopting the Zenit-2 satellite launched on the 8A92 into armaments' was issued..
1964 April 4 - . 09:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 28 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 16. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: Korolev bureau. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1964-04-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 779 . COSPAR: 1964-017A. Apogee: 373 km (231 mi). Perigee: 213 km (132 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 90.40 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1964 April 25 - . 10:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 29 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 19. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: Korolev bureau. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 7.00 days. Decay Date: 1964-05-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 791 . COSPAR: 1964-021A. Apogee: 292 km (181 mi). Perigee: 203 km (126 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 89.50 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1964 June 10 - . 10:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 32 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 18. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: Korolev bureau. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1964-06-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 807 . COSPAR: 1964-029A. Apogee: 322 km (200 mi). Perigee: 205 km (127 mi). Inclination: 51.30 deg. Period: 89.80 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1964 June 23 - . 10:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 33 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 20. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: Korolev bureau. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1964-07-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 816 . COSPAR: 1964-033A. Apogee: 279 km (173 mi). Perigee: 205 km (127 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 89.40 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1964 July 15 - . 11:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 35 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 21. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: Korolev bureau. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1964-07-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 833 . COSPAR: 1964-039A. Apogee: 258 km (160 mi). Perigee: 218 km (135 mi). Inclination: 51.30 deg. Period: 89.20 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1964 August 14 - . 09:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 37 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 22. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: Korolev bureau. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1964-08-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 848 . COSPAR: 1964-044A. Apogee: 240 km (140 mi). Perigee: 208 km (129 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 88.90 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Program partially completed. Break in the film fof the SA-10 camera..
1964 September 24 - . 12:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 46 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 23. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: Korolev bureau. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1964-10-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 885 . COSPAR: 1964-059A. Apogee: 264 km (164 mi). Perigee: 211 km (131 mi). Inclination: 51.30 deg. Period: 89.20 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Demonstration launch witnessed by Khrushchev..
1964 October 14 - . 09:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 48 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 24. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: Korolev bureau. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 6.00 days. Decay Date: 1964-10-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 908 . COSPAR: 1964-066A. Apogee: 284 km (176 mi). Perigee: 204 km (126 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 89.30 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Program partially completed. Returned early due to failure of spacecraft thermoregulation system; internal temperature rose to 43 degrees C..
1964 October 28 - . 10:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 50 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 25. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: Korolev bureau. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1964-11-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 919 . COSPAR: 1964-070A. Apogee: 232 km (144 mi). Perigee: 190 km (110 mi). Inclination: 51.20 deg. Period: 88.70 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Unsuccessful mission. Failure of the braking engine system. Spacecraft ordered to self destruct..
1965 January 11 - . 09:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 52 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 26. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: Korolev bureau. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1965-01-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 968 . COSPAR: 1965-001A. Apogee: 298 km (185 mi). Perigee: 203 km (126 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 89.50 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1965 March 25 - . 10:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 64 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 17. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1965-04-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 1305 . COSPAR: 1965-025A. Apogee: 250 km (150 mi). Perigee: 205 km (127 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 89.10 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1965 May 7 - . 09:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 66 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 27. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1965-05-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 1362 . COSPAR: 1965-035A. Apogee: 397 km (246 mi). Perigee: 285 km (177 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 91.30 min. Returned after 8 days. Unsuccessful mission. Parachute deployment failure. Spacecraft destroyed in crash..
1965 June 15 - . 10:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 68 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 29. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1965-06-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 1404 . COSPAR: 1965-046A. Apogee: 306 km (190 mi). Perigee: 208 km (129 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 89.70 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1965 July 13 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92. FAILURE: Second stage guidance failure.. Failed Stage: 2.
- Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 28 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 28. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Decay Date: 1965-07-13 . Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1965 August 14 - . 11:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 78 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 30. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1965-08-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 1505 . COSPAR: 1965-066A. Apogee: 379 km (235 mi). Perigee: 330 km (200 mi). Inclination: 69.00 deg. Period: 91.60 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1965 November 27 - . 08:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 98 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 31. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1965-12-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 1780 . COSPAR: 1965-097A. Apogee: 547 km (339 mi). Perigee: 205 km (127 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 92.10 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1965 December 10 - . 08:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 99 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 32. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1965-12-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 1817 . COSPAR: 1965-103A. Apogee: 309 km (192 mi). Perigee: 203 km (126 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 89.60 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1966 January 7 - . 08:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 104 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 36. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1966-01-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 1903 . COSPAR: 1966-001A. Apogee: 379 km (235 mi). Perigee: 195 km (121 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 90.20 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Program not completely met. Spacecraft put into incorrect orbit by abnormal function of second and third stages of booster..
1966 January 22 - . 08:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 105 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 38. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1966-01-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 1945 . COSPAR: 1966-003A. Apogee: 311 km (193 mi). Perigee: 203 km (126 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 89.60 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1966 February 10 - . 08:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 107 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 34. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1966-02-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 1998 . COSPAR: 1966-010A. Apogee: 313 km (194 mi). Perigee: 216 km (134 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 89.70 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1966 March 17 - . 10:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 112 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 37. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1966-03-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 2107 . COSPAR: 1966-021A. Apogee: 664 km (412 mi). Perigee: 214 km (132 mi). Inclination: 72.00 deg. Period: 93.30 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1966 April 20 - . 10:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 115 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 35. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1966-04-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 2147 . COSPAR: 1966-033A. Apogee: 283 km (175 mi). Perigee: 189 km (117 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 89.20 min. . Program partially completed. Abnormal operation of SA-10 camera..
1966 May 6 - . 11:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 117 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 39. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1966-05-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 2163 . COSPAR: 1966-037A. Apogee: 314 km (195 mi). Perigee: 200 km (120 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 89.60 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1966 June 8 - . 11:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 120 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 41. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1966-06-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 2196 . COSPAR: 1966-050A. Apogee: 331 km (205 mi). Perigee: 201 km (124 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 89.80 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1966 July 14 - . 10:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 124 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 42. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1966-07-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 2325 . COSPAR: 1966-064A. Apogee: 282 km (175 mi). Perigee: 205 km (127 mi). Inclination: 51.80 deg. Period: 89.40 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1966 September 16 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92. FAILURE: Launch vehicle destroyed. Failure of Block D core stage.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 40 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 40. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Decay Date: 1966-09-16 . Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1966 October 14 - . 12:13 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 129 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 33. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 7.00 days. Decay Date: 1966-10-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 2491 . COSPAR: 1966-091A. Apogee: 288 km (178 mi). Perigee: 199 km (123 mi). Inclination: 65.40 deg. Period: 89.40 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1966 November 19 - . 08:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 132 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 46. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1966-11-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 2599 . COSPAR: 1966-106A. Apogee: 257 km (159 mi). Perigee: 202 km (125 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 89.10 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1966 December 19 - . 12:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 136 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 47. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1966-12-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 2624 . COSPAR: 1966-115A. Apogee: 281 km (174 mi). Perigee: 197 km (122 mi). Inclination: 64.60 deg. Period: 89.30 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Also carried science package..
1967 January 1 - . LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Zenit-2 spysat moved to more powerful Voskhod launcher. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Ministry of Defence Decree 15 'On transfer of Zenit-2 from the 8A92 to the 11A57 launcher' was issued..
1967 January 19 - . 12:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 138 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 43. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1967-01-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 2646 . COSPAR: 1967-004A. Apogee: 273 km (169 mi). Perigee: 190 km (110 mi). Inclination: 64.60 deg. Period: 89.10 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1967 February 27 - . 08:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 143 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 45. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1967-03-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 2693 . COSPAR: 1967-017A. Apogee: 390 km (240 mi). Perigee: 202 km (125 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 90.50 min. Placed into orbit with 22.8 second period different from that planned. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Also carried science package..
1967 March 13 - . 12:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 147 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 44. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1967-03-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 2710 . COSPAR: 1967-022A. Apogee: 298 km (185 mi). Perigee: 195 km (121 mi). Inclination: 64.50 deg. Period: 89.40 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Program partially completed..
1967 April 4 - . 14:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 153 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 48. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1967-04-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 2740 . COSPAR: 1967-030A. Apogee: 279 km (173 mi). Perigee: 199 km (123 mi). Inclination: 64.60 deg. Period: 89.30 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Program partially completed. Failure of primary SA-20 camera..
1967 May 12 - . 10:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Vostok 8A92.
- Cosmos 157 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 49. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1967-05-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 2781 . COSPAR: 1967-044A. Apogee: 262 km (162 mi). Perigee: 249 km (154 mi). Inclination: 51.30 deg. Period: 89.60 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Program partially completed. Bad quality film loaded into SA-20 camera..
1967 June 8 - . 13:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 164 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 50. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 6.00 days. Decay Date: 1967-06-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 2836 . COSPAR: 1967-057A. Apogee: 317 km (196 mi). Perigee: 185 km (114 mi). Inclination: 65.60 deg. Period: 89.50 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1967 July 4 - . 05:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 168 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 52. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1967-07-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 2869 . COSPAR: 1967-067A. Apogee: 230 km (140 mi). Perigee: 223 km (138 mi). Inclination: 51.80 deg. Period: 89.10 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1967 September 1 - . 10:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57. FAILURE: Failure of Block I stage at 296 seconds. Remnants of spacecraft and stage fell near Novaya Zemlya.. Failed Stage: 2.
- Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 51 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 51. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Decay Date: 1967-09-01 . Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1967 September 16 - . 06:06 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 177 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 53. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1967-09-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 2947 . COSPAR: 1967-088A. Apogee: 267 km (165 mi). Perigee: 201 km (124 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 89.10 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1967 September 26 - . 10:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 180 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 54. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1967-10-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 2966 . COSPAR: 1967-093A. Apogee: 350 km (210 mi). Perigee: 206 km (128 mi). Inclination: 72.80 deg. Period: 90.10 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1967 October 11 - . 11:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 181 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 55. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1967-10-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 2981 . COSPAR: 1967-097A. Apogee: 325 km (201 mi). Perigee: 198 km (123 mi). Inclination: 65.60 deg. Period: 89.70 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1967 November 25 - . 11:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 193 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 58. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1967-12-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 3052 . COSPAR: 1967-117A. Apogee: 756 km (469 mi). Perigee: 745 km (462 mi). Inclination: 74.00 deg. Period: 99.90 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1967 December 16 - . 12:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 195 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 57. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1967-12-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 3071 . COSPAR: 1967-124A. Apogee: 352 km (218 mi). Perigee: 204 km (126 mi). Inclination: 65.60 deg. Period: 90.00 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1968 January 16 - . 12:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 199 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 59. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 16.00 days. Decay Date: 1968-02-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 3099 . COSPAR: 1968-003C. Apogee: 363 km (225 mi). Perigee: 206 km (128 mi). Inclination: 65.60 deg. Period: 90.20 min.
Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Unsuccessful mission. Spacecraft failed to separate from Block I stage. Attempt was made to conduct mission without orientation system. APO self destruct system destroyed spacecraft on 126th revolution over Sea of Okhotsk. First generation, low resolution photo surveillance; recovery probably failed.
1968 March 5 - . 12:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 205 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 56. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1968-03-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 3140 . COSPAR: 1968-016A. Apogee: 293 km (182 mi). Perigee: 197 km (122 mi). Inclination: 65.70 deg. Period: 89.40 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1968 April 3 - . 11:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 210 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 60. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1968-04-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 3168 . COSPAR: 1968-024A. Apogee: 373 km (231 mi). Perigee: 200 km (120 mi). Inclination: 81.40 deg. Period: 90.30 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1968 April 20 - . 10:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 216 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 62. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1968-04-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 3207 . COSPAR: 1968-034A. Apogee: 267 km (165 mi). Perigee: 198 km (123 mi). Inclination: 51.00 deg. Period: 89.20 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Unsuccessful mission. Spacecraft landed in River Volga 1 km from shore and sank after 42 minutes. 85% of the data was ruined..
1968 June 1 - . 10:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 223 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 63. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Completed Operations Date: 1968-06-09 . Decay Date: 1968-06-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 3274 . COSPAR: 1968-045A. Apogee: 317 km (196 mi). Perigee: 221 km (137 mi). Inclination: 72.90 deg. Period: 89.90 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1968 July 10 - . 19:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 231 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 64. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1968-07-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 3316 . COSPAR: 1968-058A. Apogee: 311 km (193 mi). Perigee: 206 km (128 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 89.60 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1968 August 9 - . 07:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 235 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 61. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1968-08-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 3339 . COSPAR: 1968-067A. Apogee: 281 km (174 mi). Perigee: 201 km (124 mi). Inclination: 51.80 deg. Period: 89.30 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Partially successful. Hard landing due to parachute sytem failure. 30% of the film damaged..
1968 September 14 - . 06:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 240 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 66. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 7.00 days. Decay Date: 1968-09-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 3388 . COSPAR: 1968-075A. Apogee: 283 km (175 mi). Perigee: 203 km (126 mi). Inclination: 51.80 deg. Period: 89.30 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1968 October 11 - . 12:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 247 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 65. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1968-10-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 3484 . COSPAR: 1968-088A. Apogee: 345 km (214 mi). Perigee: 199 km (123 mi). Inclination: 65.40 deg. Period: 89.90 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1968 November 13 - . 12:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 253 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 67. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 5.00 days. Decay Date: 1968-11-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 3542 . COSPAR: 1968-102A. Apogee: 337 km (209 mi). Perigee: 216 km (134 mi). Inclination: 65.40 deg. Period: 90.00 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Unsuccessful mission. On 13th orbit the SA-20-1 camera's shutter responded to an uncommanded order to open. Radiation levels inside reached 3 times normal levels. 53% of the data was lost..
1968 November 29 - . 12:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 255 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 68. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1968-12-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 3574 . COSPAR: 1968-105A. Apogee: 317 km (196 mi). Perigee: 197 km (122 mi). Inclination: 65.40 deg. Period: 89.60 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1968 December 10 - . 08:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 258 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 69. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1968-12-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 3602 . COSPAR: 1968-111A. Apogee: 298 km (185 mi). Perigee: 205 km (127 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 89.60 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1969 January 12 - . 12:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 263 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 70. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1969-01-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 3651 . COSPAR: 1969-003A. Apogee: 325 km (201 mi). Perigee: 200 km (120 mi). Inclination: 65.40 deg. Period: 89.70 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1969 February 25 - . 10:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 266 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 71. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1969-03-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 3761 . COSPAR: 1969-015A. Apogee: 336 km (208 mi). Perigee: 202 km (125 mi). Inclination: 72.00 deg. Period: 89.80 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1969 March 22 - . 12:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 273 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 77. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1969-03-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 3831 . COSPAR: 1969-027A. Apogee: 336 km (208 mi). Perigee: 200 km (120 mi). Inclination: 65.40 deg. Period: 89.80 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1969 April 9 - . 13:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 278 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 78. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1969-04-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 3883 . COSPAR: 1969-034A. Apogee: 310 km (190 mi). Perigee: 198 km (123 mi). Inclination: 65.40 deg. Period: 89.60 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1969 May 13 - . 09:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 281 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 72. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1969-05-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 3939 . COSPAR: 1969-042A. Apogee: 303 km (188 mi). Perigee: 191 km (118 mi). Inclination: 65.40 deg. Period: 89.40 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1969 June 24 - . 06:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 287 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 76. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1969-07-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 3991 . COSPAR: 1969-054A. Apogee: 265 km (164 mi). Perigee: 189 km (117 mi). Inclination: 51.80 deg. Period: 89.00 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1969 July 22 - . 12:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 290 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 75. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1969-07-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 4042 . COSPAR: 1969-060A. Apogee: 332 km (206 mi). Perigee: 195 km (121 mi). Inclination: 65.40 deg. Period: 89.70 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1969 September 24 - . 12:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 301 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 79. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1969-10-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 4106 . COSPAR: 1969-081A. Apogee: 271 km (168 mi). Perigee: 203 km (126 mi). Inclination: 65.40 deg. Period: 89.30 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1969 November 12 - . 11:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 309 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 80. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1969-11-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 4223 . COSPAR: 1969-098A. Apogee: 364 km (226 mi). Perigee: 185 km (114 mi). Inclination: 64.50 deg. Period: 90.00 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. First flight with Nauka external experiment container..
1970 March 4 - . 12:14 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC43/4. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 325 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 73. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1970-03-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 4340 . COSPAR: 1970-015A. Apogee: 327 km (203 mi). Perigee: 200 km (120 mi). Inclination: 65.40 deg. Period: 89.80 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1970 March 13 - . 08:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC43/4. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 326 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 74. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1970-03-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 4346 . COSPAR: 1970-018A. Apogee: 232 km (144 mi). Perigee: 208 km (129 mi). Inclination: 81.30 deg. Period: 88.90 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite..
1970 May 12 - . 10:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Plesetsk. Launch Complex: Plesetsk LC41/1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Cosmos 344 - . Payload: Zenit-2 11F61 s/n 81. Mass: 4,720 kg (10,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok. Spacecraft: Zenit-2 satellite. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1970-05-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 4401 . COSPAR: 1970-038A. Apogee: 326 km (202 mi). Perigee: 204 km (126 mi). Inclination: 72.90 deg. Period: 89.80 min. Area survey photo reconnaissance satellite. Partially successful. Failure of SA-10B camera on 42nd orbit..
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use