N1M (original) (raw)

Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
N1M
Russian heavy-lift orbital launch vehicle. The N1M was to be the first Soviet launch vehicle to use liquid oxygen/liquid hydrogen high energy cryogenic propellants. It was designed to launch payloads in support of the LEK lunar expeditions (two cosmonauts on the surface), the DLB (long-duration lunar base), and heavy unmanned satellites into geosynchronous and interplanetary trajectories. As originally conceived, the advanced propellants would be used in all upper stages. However due to delays in Kuznetsov development of a 200 metric ton thrust LOx/LH2 engine, the final version used an N1 first stage, with a Block V-III second stage, and Blocks S and R third and fourth stages.
Status: Development ended 1971. Thrust: 43,295.50 kN (9,733,216 lbf). Gross mass: 2,348,000 kg (5,176,000 lb). Height: 96.00 m (314.00 ft). Diameter: 10.00 m (32.00 ft).
Stage Data - N1M
- Stage 1. 1 x N1 Block A. Gross Mass: 1,880,000 kg (4,140,000 lb). Empty Mass: 130,000 kg (280,000 lb). Thrust (vac): 50,300.000 kN (11,307,800 lbf). Isp: 330 sec. Burn time: 125 sec. Isp(sl): 284 sec. Diameter: 10.30 m (33.70 ft). Span: 16.90 m (55.40 ft). Length: 30.10 m (98.70 ft). Propellants: Lox/Kerosene. No Engines: 30. Engine: NK-15. Status: Out of Production. Comments: Includes 14,000 kg for Stage 1-2 interstage and payload fairing. Compared to total fuelled mass excludes 15,000 kg propellant expended in thrust build-up and boil-off prior to liftoff. Values as in draft project as defended on 2-16 July 1962.
- Stage 2. 1 x N1 Block V-III. Gross Mass: 325,000 kg (716,000 lb). Empty Mass: 35,000 kg (77,000 lb). Thrust (vac): 2,350.000 kN (528,300 lbf). Isp: 440 sec. Burn time: 510 sec. Diameter: 8.00 m (26.20 ft). Span: 8.00 m (26.20 ft). Length: 27.00 m (88.00 ft). Propellants: Lox/LH2. No Engines: 6. Engine: RD-57. Status: Study 1965. Comments: N1 improvement study, 1965. Lox/LH2 replacement for Block V third stage. Pursued into 1966 and later, but later efforts concentrated on Block S, R, and SR cryogenic stages.
- Stage 3. 1 x N1 Block S. Gross Mass: 58,000 kg (127,000 lb). Empty Mass: 8,000 kg (17,600 lb). Thrust (vac): 392.000 kN (88,125 lbf). Isp: 440 sec. Burn time: 540 sec. Diameter: 6.70 m (21.90 ft). Span: 6.70 m (21.90 ft). Length: 16.00 m (52.00 ft). Propellants: Lox/LH2. No Engines: 1. Engine: RD-57. Status: Study 1967. Comments: Designed 1965-1971 as replacement for N-1 Blok G. Cancelled in 1971 in favor of development of single stage, Block Sr.
- Stage 4. 1 x N1 Block R. Gross Mass: 23,000 kg (50,000 lb). Empty Mass: 4,300 kg (9,400 lb). Thrust (vac): 73.500 kN (16,523 lbf). Isp: 440 sec. Burn time: 1,080 sec. Diameter: 4.10 m (13.40 ft). Span: 4.10 m (13.40 ft). Length: 8.70 m (28.50 ft). Propellants: Lox/LH2. No Engines: 1. Engine: RD-56. Status: Development 1976. Comments: Designed 1965-1971 as replacement for N-1 Blok D. Cancelled 1971 in favor of Blok Sr; revived and developed in 1974-1976. First static test Oct 12 1976. Two stages tested 1976-1977. Strangely never replaced Blok D on Proton.
Family: heavy-lift, orbital launch vehicle. Country: Russia. Engines: RD-57, NK-15, RD-56. Spacecraft: L3M-1970. Stages: N1 Block R, N1 Block S, N1 Block A, N1 Block V-III. Agency: Korolev bureau.
Photo Gallery
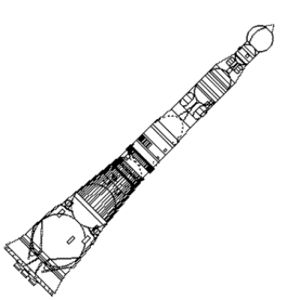 |
N1M cutawayCredit: © Mark Wade |
|---|
 |
N1 and N-1MN1 and N-1M Dynamic test modelsCredit: © Mark Wade |
|---|
1967 June 15 - . LV Family: N1. Launch Vehicle: N1M.
- First test of liquid hydrogen/LOX engine for N1M - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. First test of the 11D56 in an iron stand version. First test of an engine with these propellants in USSR for use in a space launch vehicle..
1971 May 15 - . LV Family: N1. Launch Vehicle: N1M.
- Go-ahead to develop LH2/LOX stage for N1M - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3.
Decision made to proceed with development of the multi-engined stage Block Sr with a propellant mass of 66.4 tonnes. This single stage would be used in place of the previously-planned Blocks S and R to insert the modernized Lunar Expeditionary Complex (LEK) into low lunar orbit. It was also to be used to insert heavy spacecraft into geosynchronous orbit and on interplanetary trajectories.
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use
