Fizeau interferometers (original) (raw)
Definition: interferometers for investigating optical surfaces
Categories:  photonic devices,
photonic devices,  optical metrology
optical metrology
- interferometers
- etalons
- common-path interferometers
- Fabry–Perot interferometers
- Fizeau interferometers
- Gires–Tournois interferometers
- Mach–Zehnder interferometers
- Michelson interferometers
- Twyman–Green interferometers
- white light interferometers
- (more topics)
Related: interferometersMichelson interferometersTwyman–Green interferometersoptical flats
Page views in 12 months: 1547
DOI: 10.61835/di9 Cite the article: BibTex BibLaTex plain textHTML Link to this page! LinkedIn
Content quality and neutrality are maintained according to our editorial policy.
📦 For purchasing Fizeau interferometers, use the RP Photonics Buyer's Guide — an expert-curated directory for finding all relevant suppliers, which also offers advanced purchasing assistance.
Contents
What is a Fizeau Interferometer?
Fizeau interferometers, named after Hippolyte Fizeau, are a common type of interferometers which are used for characterizing optical surfaces, e.g. of mirrors or prisms.
Operation Principle
One exploits interference between reflections at a test surface and a nearby reference surface, as shown in Figure 1. The reference surface in Figure 1 is the right surface of an optical flat, having a particularly high flatness and also otherwise high surface quality. Normally, the reference surface is slightly tilted (e.g. controlled with a micrometer screw) against the test surface, so that for ideal surface quality one would obtain a regular pattern of straight interference fringes (stripes). Any deviations between the surface shapes lead to distortions of those stripes (Fizeau curves).
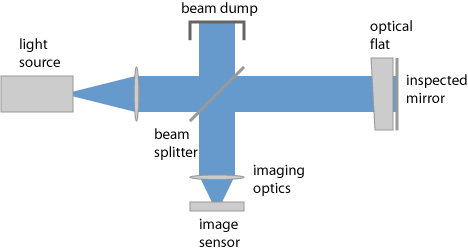
Figure 1: Setup of a Fizeau interferometer. Depending on the application, one may omit the imaging optics or directly observe the output with the eye.
The test surface does not need to be highly reflective; its reflectivity should just be high enough to produce a clear interference pattern.
Influences of reflections from the left side of the optical flat may be minimized with an anti-reflection coating, with a wedge shape of the optical flat and in addition sometimes exploiting the limited coherence length of the light.
The used light source can be a laser, but one can also use other light sources such as gas discharge lamps. The light does not need to be highly monochromatic if the distance between the test surface and the reference surface is small.
Comparison with Other Interferometers
A Fizeau interferometer can be seen as a simpler alternative to a Twyman–Green interferometer. Its advantage is that interference occurs only between two closely spaced parts, and only the relative distance of those must be carefully controlled. The orientation of the beam splitter, for example, is not critical. On the other hand, the Twyman–Green interferometer is more flexible, for example concerning the optimization of fringe contrast for different reflectivities of the investigated samples.
There is also a similarity to a Fabry–Pérot interferometer. The Fizeau interferometer can be considered as a Fabry–Pérot interferometer made for surface characterizations. Typically, it does not exhibit sharp resonances due to low surface reflectivities.
Frequently Asked Questions
This FAQ section was generated with AI based on the article content and has been reviewed by the article’s author (RP).
What is a Fizeau interferometer?
A Fizeau interferometer, named after Hippolyte Fizeau, is a type of interferometer commonly used to characterize the surface shape and quality of optical components like mirrors or prisms.
How does a Fizeau interferometer work?
It operates by generating an interference pattern from two light reflections: one from a high-quality reference surface and one from the test surface. Deviations in the test surface's shape cause distortions in the otherwise regular pattern of interference fringes.
What is the main advantage of a Fizeau interferometer over a Twyman–Green type?
Its main advantage is simplicity. Interference occurs between two closely spaced surfaces, so only their relative position needs precise control. This makes it less sensitive to the alignment of other components compared to a Twyman–Green interferometer.
What kind of light source is required for a Fizeau interferometer?
A laser can be used, but other sources such as gas discharge lamps are also suitable. Highly monochromatic light is not necessary if the distance between the reference and test surfaces is small.
Suppliers
Bibliography
| [1] | Y. H. Meyer, “Fringe shape with an interferential wedge”, J. Opt. Soc. Am. 71 (10), 1255 (1981); doi:10.1364/JOSA.71.001255 |
|---|---|
| [2] | T. T. Kajava, H. M. Lauranto and A. T. Friberg, “ Interference pattern of the Fizeau interferometer”, J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 11 (7), 2045 (1994); doi:10.1364/JOSAA.11.002045 |
(Suggest additional literature!)
Questions and Comments from Users
Here you can submit questions and comments. As far as they get accepted by the author, they will appear above this paragraph together with the author’s answer. The author will decide on acceptance based on certain criteria. Essentially, the issue must be of sufficiently broad interest.
Please do not enter personal data here. (See also our privacy declaration.) If you wish to receive personal feedback or consultancy from the author, please contact him, e.g. via e-mail.
By submitting the information, you give your consent to the potential publication of your inputs on our website according to our rules. (If you later retract your consent, we will delete those inputs.) As your inputs are first reviewed by the author, they may be published with some delay.