Enrichment of super-sized resequencing targets from the human genome (original) (raw)
- News & Views
- Published: November 2007
Nature Methods volume 4, pages 891–892 (2007)Cite this article
- 337 Accesses
- 29 Citations
- 3 Altmetric
- Metrics details
Methods relying on dense arrays of synthetic oligodeoxynucleotides to target specific subsets of the human genome may enable routine resequencing of all human exons or multi-megabase-pair chromosomal regions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Relevant articles
Open Access articles citing this article.
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
Figure 1: Two ways to use high-density arrays of custom-synthesized oligodeoxynucleotides to target subsets of the human genome.
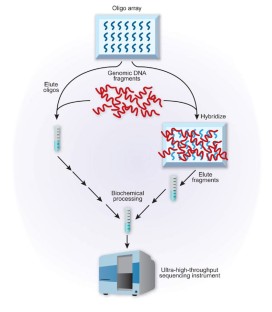
Kim Caesar
References
- Porreca, J.G. et al. Nat. Methods 4, 931–936 (2007).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Okou, T.D. et al. Nat. Methods 4, 907–909 (2007).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Albert, T.J. et al. Nat. Methods 4, 903–905 (2007).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Shendure, J. et al. Nat. Rev. Genet. 5, 335–344 (2004).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Nilsson, M. et al. Science 265, 2085–2088 (1994).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Hardenbol, P. et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 673–678 (2003).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Bashiardes, S. et al. Nat. Methods 2, 63–69 (2005).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Guo, Z. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 6964–6969 (2006).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Department of Genome Science and Medicine, Maynard Olson is at the University of Washington, Seattle, Washington 98195, USA. mvo@u.washington.edu,
Maynard Olson
Authors
- Maynard Olson
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olson, M. Enrichment of super-sized resequencing targets from the human genome.Nat Methods 4, 891–892 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth1107-891
- Issue Date: November 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth1107-891