Hypoxia. Regulation of NFκB signalling during inflammation: the role of hydroxylases (original) (raw)
- Review
- Published: 23 February 2009
Arthritis Research & Therapy volume 11, Article number: 215 (2009)Cite this article
- 8607 Accesses
- 80 Citations
- Metrics details
Abstract
NFκB is a master regulator of innate immunity and inflammatory signalling. Microenvironmental hypoxia has long been identified as being coincident with chronic inflammation. The contribution of microenvironmental hypoxia to NFκB-induced inflammation has more recently been appreciated. Identification of the co-regulation of NFκB and hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) pathways by 2-oxo-glutarate-dependent hydroxylase family members has highlighted an intimate relationship between NFκB inflammatory signalling and HIF-mediated hypoxic signalling pathways. Adding another layer of complexity to our understanding of the role of NFκB inflammatory signalling by hypoxia is the recent recognition of the contribution of basal NFκB activity to HIF-1α transcription. This observation implicates an important and previously unappreciated role for NFκB in inflammatory disease where HIF-1α is activated. The present review will discuss recent literature pertaining to the regulation of NFκB inflammatory signalling by hypoxia and some of the inflammatory diseases where this may play an important role. Furthermore, we will discuss the potential for prolylhydroxylase inhibitors in inflammatory disease.
NFκB
The transcription factor NFκB has been investigated for its diverse range of functions in innate immunity, stress responses, cell survival and development. It is also the master regulator of the inflammatory response [1]. An in-depth review of the NFκB pathway is beyond the scope of the present article, and there are several excellent reviews dedicated specifically to this topic [2, 3].
Briefly, the NFκB family comprises five members: p65, Rel B, c-Rel, p50 and p52. These proteins share a highly conserved Rel homology domain. In order to bind DNA and modulate gene expression, family members form homodimers or heterodimers – with the exception of Rel B, which will only form heterodimers with p50 or p52 [4]. The most commonly encountered dimer complex is the p50–p65 dimer [5]. There are two primary activation pathways for NFκB: the canonical pathway, which is predominantly dependent on inhibitor of κB kinase (IKK) beta, and the IKKα-dependent noncanonical pathway [6].
Under resting conditions, NFκB is bound to its co-repressor molecule IκB in the cytosol, with which it interacts through multiple ankyrin repeats. A nuclear localisation sequence of the p65 protein is masked and it remains predominantly sequestered in the cytosolic compartment. Upon stimulation IκBα is phosphorylated at serine 32 and serine 36, targeted for ubiquitination and thereafter degraded proteolytically by the 26S proteosome [7]. A nuclear localisation sequence of NFκB is then revealed, and this is free to translocate and accumulate in the nucleus where it can become transcriptionally active by binding to specific κB sites within the promoter regions of its target genes [8]. The stimulus for IκBα to release the inhibition of NFκB has been identified as phosphorylation by the 700 kDa IKKα/β/γ protein complex.
Genes induced by NFκB include those responsible for encoding inflammatory genes such as TNFα, IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, macrophage inflammatory protein 1 alpha and methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein 1, cell surface adhesion molecules such as E-selectin, vascular adhesion molecule 1 and intracellular cell adhesion molecule 1, inducible enzymes including cyclooxygenase 2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase, and survival molecules such as cellular inhibitor of apoptosis molecule 1, cellular inhibitor of apoptosis molecule 2 and BCL-XL [9]. A number of stimuli have been shown to activate NFκB through the canonical pathway, including proinflammatory cytokines, bacterial products, growth factors [10] and hypoxia [11–13]. The convergence point for these diverse stimuli is at the level of the IKK complex. NFκB is also activated by ultraviolet light [14, 15], by oxidative stress [16], by shear stress [17] and by other mechanisms.
NFκB, hypoxia and hydroxylases
NFκB has been shown to be activated by hypoxia in a number of studies [12, 18, 19]. Cyclooxygenase 2 [20], TNFα [21], IL-6 [22] and macrophage inflammatory protein 2 [23] are among the target genes identified for hypoxia-induced NFκB, and these underline the factor's importance in inflammatory signalling. While several groups have previously identified hypoxia as playing a role in NFκB signalling, the mechanism whereby a decrease in available oxygen could elicit the activation of a transcription factor that is predominantly activated by more traditional receptor–ligand activation signalling pathways was unclear. While canonical NFκB signalling is sensitive to a diverse range of ligands and employs a plethora of signalling molecules, these signal transduction pathways converge on the IKK complex.
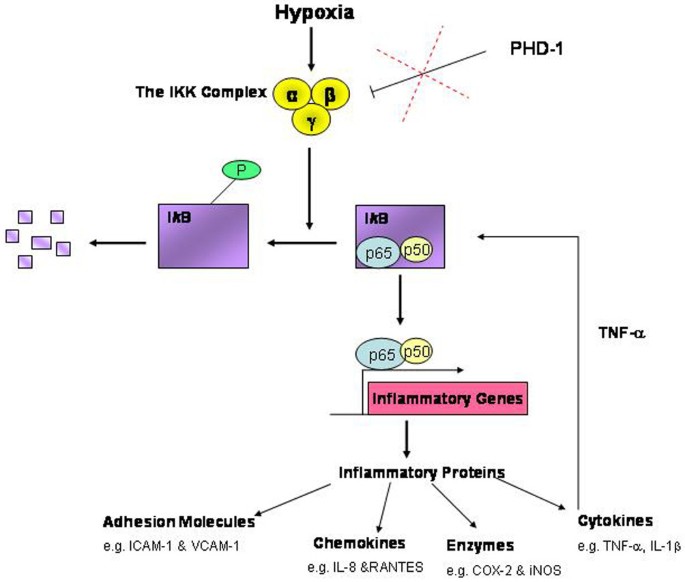
We recently demonstrated a mechanism by which hypoxia activates NFκB through IKKβ activation, leading to phosphorylation-dependent degradation of IκBα and activation of NFκB. Pharmacological hydroxylase inhibition with dimethyl-oxallylglycine (DMOG) activated NFκB signalling and defined a repressive role for prolyl hydroxylase (PHD)-1 controlling activity of NFκB. IKKβ expression and activity were found to be increased by hypoxia [11]. Interestingly, IKKβ (and IKKα) contains an evolutionarily conserved L_XX_LAP motif that resembles the prolyl hydroxylation sites in hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) alpha. In this pathway, therefore, hypoxia appears to activate NFκB through decreased PHD-dependent hydroxylation of IKKβ, although hydroxylation of IKKβ at proline 191 has yet to be demonstrated. Further work on IKKβ and the inflammatory response supports the theory that hypoxia has the potential to modulate the NFκB response to inflammatory stimuli through catalytic upregulation of IKKβ [13]. See Figure 1 for a schematic of hypoxia-induced NFκB activation.
While it has yet to be proven that IKKβ is hydroxylated by the PHDs, they do have an important role in regulating the stability of HIF, especially the PHD-2 isoform [24]. Hydroxylation of specific prolyl residues (proline 402 and proline 564 for human HIF-1α) regulates oxygen-dependent degradation of HIF-1α. Under conditions of hypoxia or by direct inhibition of the PHD enzymes, HIF-1α escapes hydroxylation and becomes stabilised [25, 26]. Furthermore, the asparaginyl hydroxylase factor-inhibiting hypoxia inducible factor (FIH)-1 is a Fe(II)-dependent and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase, like the PHD family members and plays a role in regulating HIF transcriptional activity. FIH-1 was identified as being the oxygenase catalysing hydroxylation of asparagine 803 in HIF-1α, thus preventing interaction with the p300 CH1 domain and preventing HIF transactivation [27, 28].
Figure 1
Hypoxia activates NFκB signalling via inhibitor of κB kinase. Under conditions of hypoxia, the hydroxylase-mediated repression of inhibitor of κB kinase (IKK) beta is suppressed – leading to enhanced IKKβ activity, enhanced IκBα phosphorylation and degradation as well as increased p65 NFκB activity. Factor-inhibiting hypoxia inducible factor inhibition by hypoxia or pharmacological inhibition reduces IκBα asparaginyl hydroxylation but does not appear to affect IκBα degradation. COX-2, cyclooxygenase 2; ICAM-1, intracellular adhesion molecule 1; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; RANTES, regulated upon activation normal T-cell expressed and secreted; PHD-1, prolyl hydroxylase 1; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1.
Other FIH substrates have been identified recently, and include members of the NFκB [29] and Notch [30, 31] signalling pathways. Cockman and colleagues discovered that both p105 (the precursor of the p50 component of NFκB) and IκBα are hydroxylated by FIH-1 at specific residues in their ankyrin-repeat domains (ARDs) [29]. Treatment of the cells with hypoxia or DMOG resulted in the repression of hydroxylation. The inhibitory action of IκB on NFκB DNA binding was unaffected by ARD hydroxylation, however, and the function of ARD hydroxylation is unknown to date. Given that some ARDs bind FIH-1 with higher affinity than the ARD of HIF-1α, ARDs may compete with HIF-1α for FIH-1, thus restricting the action of FIH-1 on HIF [30, 31]. The consequences of such competition would probably be extremely complex given the high number of ARDs in the proteome and the probable identification of new hydroxylase substrates.
NFκB and hypoxia inducible factor cross-talk
The hypoxic response is predominantly regulated by HIF-1, the α subunit of which is stabilised under low oxygen conditions leading to the induction of genes to restore blood supply and nutrients to the cell as well as allowing resumption of energy production. Upregulation of HIF by bacterial and viral compounds in cells of the immune system prepares the cells for migration to the hypoxic environment of inflamed and injured tissues. Furthermore, HIF-1α is essential for myeloid cell-mediated inflammation. Myeloid cells lacking HIF-1α had a lower glycolytic capacity, resulting in impairments in myeloid cell aggregation, motility, invasiveness and bacterial killing [32]. Elevated levels of HIF-1α have been found in the inflamed joints of patients suffering from rheumatoid arthritis (RA) [33]. HIF therefore appears to have an important role in the coordination of cellular responses under conditions of inflammation.
A molecular link between NFκB and HIF-1α was proposed initially in a study examining erythropoietin expression [34]. This article was followed by a number of studies from Jung and colleagues examining the cross-talk between NFκB and HIF-1α [35–37]. Their work reported that the inflammatory cytokine IL-1β upregulated HIF-1α protein via an inflammatory signalling pathway involving NFκB and cyclooxygenase 2. This upregulation occurred under normoxic conditions but provided the basis for future observations regarding links between NFκB and HIF [13, 38–44].
On the other hand, a positive role for HIF and NFκB interaction in inflammatory signalling under conditions of hypoxia was described by Walmsley and colleagues, who investigated hypoxia-induced neutrophil survival [45]. Neutrophils are the key effectors of the innate immune system, and hypoxia has been shown to inhibit neutrophil apoptosis. Investigation of this phenomenon led to the discovery that HIF-1α-dependent upregulation of NFκB p65 and IKKα occurred in neutrophils, and this led to the conclusion that HIF-1α-dependent NFκB signalling is of critical importance in the hypoxic response in neutrophils [45].
The presence of an NFκB site within the HIF-1α promoter -197/-188 base pairs upstream of the transcriptional start site provides further evidence of the link between these two crucially important transcription factors [39]. When this site was mutated, induction of HIF-1α by hypoxia was lost. Binding of NFκB p50 and p65 to the HIF-1α promoter in response to hypoxia gave evidence that NFκB regulates HIF-1α via a transcriptional mechanism [38].
Compelling in vivo evidence for cross-talk between NFκB and HIF-1α comes from a recent paper by Rius and colleagues [13]. This work directly linked NFκB, innate immunity and the hypoxic response through studies involving the depletion of a component of the NFκB signalling pathway. Using mice lacking IKKβ (the key catalytic subunit in inflammatory signalling) in a variety of cell types, NFκB was shown to be a critical transcriptional activator of HIF-1α [13]. This evidence provides support for the concept of NFκB and HIF-1α engaging in a positive enhancement loop under conditions of hypoxia and inflammation. Significantly, basal NFκB activity is required for the accumulation of HIF-1α in cultured cells under conditions of hypoxia as well as in the liver and brain of hypoxic animals. IKKβ links the hypoxic response and innate immunity since a deficiency in IKKβ leads to ineffective induction of HIF-1α target genes, meaning that resolution of inflammation in the injured cell is likely to be impaired. Furthermore, defects in HIF-1α expression are observed in mice exposed to hypoxia and to macrophages experiencing a bacterial infection in the absence of IKKβ [13]. A single component part of the NFκB signalling cascade has therefore been shown to play a crucial role in the cross-talk between the two pathways.
In another recent study, van Uden and colleagues suggest that both catalytic subunits of the IKK complex, IKKα and IKKβ, must be depleted for hypoxia-induced HIF-1α stabilisation to be impaired in mouse embryonic fibroblasts [44]. The different cell types used by the groups of van Uden and of Rius may account for the contrasting results observed. Rius and colleagues used bone-marrow-derived macrophages from IKKβ-/- mice while van Uden and colleagues used mouse embryonic fibroblasts to inform their conclusions [13]. Interestingly, van Uden and colleagues showed that the individual NFκB members have differential effects on HIF-1α mRNA levels [44], illustrating another level of complexity in this relationship. Several NFκB subunits (RelA, RelB, c-Rel, p50, p52) were found at the HIF-1α promoter using chromatin immunoprecipitation, indicating that the basal level of HIF-1α mRNA is directly modulated by NFκB [44].
The signalling subtleties with respect to the individual NFκB family proteins bound to the HIF-1α promoter have yet to be fully elucidated. Specific reviews on the cross-talk between HIF and NFκB at inflammatory hypoxic loci have recently been published [46, 47] and provide interesting interpretations of the recent published data. While the evidence to date does not lead to an unequivocal thesis, what is clear is that there is significant cross-talk between HIF-1α and NFκB transcriptional repertoires – with each being able to influence expression of the other's members in some cells. This is an important consideration with respect to designing intervention strategies in inflammatory disease. See Figure 2 for a schematic of NFκB and HIF-1α cross-talk.
Figure 2
NFκB and hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha cross-talk. Hypoxia acts as a stimulus for the activation of the inhibitor of κB kinase (IKK) complex as shown in Figure 1. Basal IKKβ-dependent NFκB activity is required for transcriptionally active dimer complexes to translocate to the nucleus and bind to a region -197/188 base pairs upstream of the hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-1α promoter. This results in an increase in HIF-1α mRNA and protein levels. Several NFκB proteins have been detected at the HIF-1α promoter region by chromatin immunoprecipitation. Increased levels of HIF-1α are observed in chronically inflamed tissue such as the rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovium and in the dermal glands of psoriatic skin. FIH, factor-inhibiting hypoxia inducible factor.
Hypoxia and inflammation
Hypoxia is a feature of sites of chronic inflammation, for example in the RA synovium, in atherosclerotic plaques, in sites of bacterial infection and at growing tumours [48]. This occurs when the cellular demand for oxygen, in order to meet the metabolic needs of the tissue to produce ATP, exceeds the vascular supply. While angiogenesis is a feature of hypoxic inflammation as well as being an adaptive response to decreased oxygen availability, the microvascular architecture is dysregulated in chronic inflammatory disease. Therefore, while there are more capillaries to deliver oxygen to a site of inflammation, the efficiency is poor. Furthermore, what limited oxygen is delivered to an inflammatory locus can be depleted further by oxygen consumption by highly metabolically active resident and infiltrating cells [49].
Rheumatoid arthritis
RA is a systemic autoimmune disorder that is characterised by persistent inflammation of a hyperplastic synovium, which consists of various cell types including synovial fibroblasts, B cells, T cells and macrophages. Cartilage and bone are invaded by the hyperplastic synovium, resulting in the progressive destruction of these joints [50]. An hypoxic environment has been shown to exist in RA synovium [51, 52] as well as an increase in the level of hypoxic metabolites compared with normal synovium [53].
A number of growth factors and cytokines capable of activating HIF-1α are known to be upregulated in RA; for example, the NFκB target genes TNFα and IL-1β. In addition, incubation of cultured synovial fibroblasts with IL-1β results in stabilisation of HIF-1 [54]. Studies have shown increased levels of HIF-1α protein in rheumatoid synovial tissues [33, 55], which has led to the hypothesis that tissue hypoxia together with HIF-1α-mediated expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is essential for the progression of RA through promotion of angiogenesis [56]. Angiogenesis provides the necessary vasculature so that migration of cells into the joints can occur [48]. HIF also promotes arthritis through the induction of the transcription factor Ets-1 [57]. Ets-1 is responsible for the induction of matrix metalloproteins, which are involved in cartilage and bone destruction [58].
To date, no strong links have been demonstrated between hypoxia-induced NFκB and RA. Hitchon and El-Gabalawy, however, suggest that cycles of hypoxia and reoxygenation in the arthritic joint lead to reactive oxygen species production, which would serve as a stimulus for NFκB activation [59].
Psoriasis
Angiogenesis induced by VEGF also appears to play a crucial role in the formation of psoriatic plaques. VEGF mRNA and mRNA for its receptor Flt-1 are increased in psoriatic skin compared with normal human skin [60]. Rosenberger and colleagues present the hypothesis that physiologic regional hypoxia occurring in the dermal glands triggers a cycle involving HIF, VEGF and Akt activation [61]. They showed that HIF-1α mRNA is elevated in the epidermis of psoriatic skin and that HIFs are strongly activated in cell types that express pivotal angiogenic factors. This led to the theory that more severe skin hypoxia in psoriasis could lead to keratinocyte and HIF-mediated angiogenesis through upregulation of VEGF and Flt-1. Phospho-Akt in the dermal capillaries is thought likely to provide positive feedback to the HIF-VEGF system [61].
Inflammatory bowel disease
Links between hypoxia, HIF-1 and NFκB signalling have been demonstrated for chronic inflammation in murine models of colitis. In cells of the gastrointestinal tract, the effects of hypoxia on transepithelial permeability have been implicated in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which consists of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis [21]. Both the HIF-1 and NFκB pathways have been demonstrated to have protective roles in intestinal epithelial cells through the use of intestinal epithelial cell conditional knockout mice for HIF-1α and IKKβ [62–64]. Karhausen and colleagues showed that mice constitutively expressing HIF-1α in the colon were protected from hypoxia-induced permeability changes, as well as from trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid (TNBS) colitis [64]. Conversely, conditional knockout of HIF-1α in the gut resulted in more severe symptoms of colitis. Meanwhile, Greten and colleagues demonstrated that conditional knockdown of IKK-β in enterocytes resulted in increased apoptotic damage in a murine model of dextran sulphate sodium-induced colitis [63].
DMOG is a pan hydroxylase inhibitor that has been shown to activate both HIF-1α-dependent [65] and NFκB-dependent [11] gene expression in vitro, most probably through the inhibition of hydroxylation-dependent repression of both signalling pathways. In a recent study we demonstrated that DMOG is profoundly protective in a murine model of dextran sulphate sodium colitis [66]. We hypothesised this to be via induction of both HIF-1α and NFκB pathways, and proposed that its occurrence was at least in part due to the development of an anti-apoptotic phenotype. Inhibition of apoptosis by DMOG is hypothesised to be important in the maintenance of epithelial barrier function in murine colitis and to prevent mixing of luminal antigens with the submucosa that houses the mucosal immune system. Previous studies have suggested that the regulation of intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis is crucial in the development of inflammation in the gut [67, 68]. Further support for the above data is provided by Robinson and colleagues [69] who demonstrated in a TNBS-induced murine model of colitis that induction of HIF-1α by FG-4497 (a novel PHD inhibitor) results in beneficial outcomes. This effect is likely due to a barrier-protective function.
Conversely, Shah and colleagues have suggested that HIF in fact augments experimental colitis through macrophage migration inhibitory factor-dependent signalling [70]. Their data show that a chronic increase in HIF signalling in colon epithelial cells results in increased expression of proinflammatory mediators, the levels of which were decreased by inhibition of the HIF target gene migration inhibitory factor. The perceived conflict between the above studies and this one may at least in part be explained by the fact that the proinflammatory phenotype of the VhlΔIE mouse model used by Shah and colleagues [70] was HIF-2α mediated, while the protection observed by Karhausen and colleagues [64] was HIF-1α mediated. This difference suggests that HIF-1α and HIF-2α may have distinct and separate roles in colon homeostasis. Other differences between the studies that may have contributed to the disparity in findings include (i) the specific promoter used to drive the intestinal epithelial cell knockout – Karhausen and colleagues [64] used mice expressing Cre-recombinase under the transcriptional control of a fatty acid binding protein promoter, while Shah and colleagues [70] used mice expressing Cre-recombinase under the control of the villin promoter – and (ii) the model of colitis employed – Karhausen and colleagues [64] used TNBS-induced colitis, while Shah and colleagues [70] used an irritant-based model of colitis.
Prolyl-hydroxylase inhibitors in inflammatory disease
The use and development of prolyl-hydroxylase inhibitors (PHDIs) in the treatment of disease is an area of intense research. Several recent studies have reported the potential for using PHDIs in animal models of ischaemia affecting the whole animal [71], the brain [72], the heart [73] and the kidney [74–76] as well as in IBD [66, 69].
The difficulty in developing specific PHDIs suitable for use in the clinic centres on the current lack of specificity of PHDIs as well as isoform-specific roles for the different PHDs. Most available PHDIs act at the substrate binding interface and interfere with the PHD interaction with essential co-factors (2-oxoglutarate, Fe2+, ascorbate). Structural mimetics of 2-oxoglutarate are amongst the most commonly used but other nonspecific compounds such as desferrioxamine and cobalt interfere with the iron/ascorbate balance. 2-Oxoglutarate analogues are essentially pan-hydroxylase inhibitors and inhibit prolyl and asparaginyl hydroxylases alike. Evidence from PHD3-/- mice suggests a neuronal role for PHD3 in sympathoadrenal development [77]. Evidence from PHD1-/-mice suggests a role for PHD1 in the regulation of basal metabolism [78]. PHD2-/- mice are embryonic lethal [79]. Against this background, systemic administration of pan-hydroxylase inhibitors may be undesirable given the diverse functions of the individual PHD isoforms. Development of specific PHDIs will probably advance their potential as therapies in the future.
Development of specific PHDIs may be of particular use in the treatment of inflammatory disease, where recent studies using the PHDIs DMOG and FG-4497 resulted in profound protection from experimentally induced colitis in mice. In a study using dextran sulphate sodium-induced colitis, intra-peritoneal injection of DMOG significantly reduced the development of colitis [66]. Using the PHDI FG-4497, Robinson and colleagues demonstrated similar protection in their model of TNBS-induced colitis [69]. Future work is needed to determine the specific hydroxylase isoform target of the drugs in vivo or, indeed, whether the protective effect from colitis is only evident against a background of pan-hydroxylase inhibition. Similarly, the downstream effectors of hydroxylase inhibition that occasion the protection from colitis need to be fully elucidated. Studying the development of experimental colitis in isoform-specific PHD null mice will greatly enhance our understanding of the role of hydroxylases as possible therapeutic targets in inflammatory disease.
The colon is ideally suited to avail of the benefits of PHDI in inflammatory disease. HIF-1α activation under conditions of hypoxia is known to activate a number of epithelial barrier-protective genes [49]. Maintenance of intestinal epithelial barrier integrity is of paramount importance in IBD such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. An intact epithelial barrier will prevent luminal antigenic material mixing inappropriately with the submucosa and will prevent inflammation. Targeted delivery of a PHDI that can activate NFκB and HIF at the beginning of an IBD episode may therefore prove beneficial through maintenance of barrier integrity via IKKβ-mediated suppression of enterocyte apoptosis [63] and HIF-1α-mediated barrier protection [64]. The use of PHDIs in inflammatory conditions, however, should be approached with caution. Activating NFκB via PHD inhibition – whilst potentially beneficial in the suppression of apoptosis and maintenance of epithelial barrier protection – could lead to inappropriate survival of cancer cells. Similarly, the addition of an NFκB-activating PHDI in an inflammatory setting may seem counterintuitive given the body of evidence for NFκB target genes contributing to inflammatory signalling [80, 81]. The targeted delivery of a PHDI in the appropriate inflammatory condition will therefore be of paramount importance.
Activation of HIF in inflammatory disease via PHDIs also comes with caveats. While one subset of HIF target genes actively maintains the epithelial barrier as discussed previously, another subset of HIF-1-dependent proangiogenic genes may also be activated. This could potentially contribute to localised angiogenesis and may increase the risk of inflammation-associated cancer.
As a consequence, PHDIs may not be indicated in RA because of the central contribution of angiogenesis in the pathogenesis and invasiveness of that particular inflammatory condition. Similarly, the contribution of angiogenesis to the development of psoriatic plaques may preclude the use of PHDIs. The use of PHDIs in IBD does, however, show some promise. The profound protection from experimentally induced colitis seen with DMOG [66] and with FG-4497 [69], coupled with the pre-eminent role of the intestinal epithelial cell in preventing inflammation, makes the use of PHDIs an attractive potential therapeutic strategy in IBD.
Conclusion
Identification of the co-regulation of NFκB and HIF pathways by hydroxylase family members has enhanced our understanding of the mechanism of hypoxia-induced NFκB activity. The fact that the inhibitory action of hydroxylases is at the level of the IKK complex through suppression of catalytic activity means that microenvironmental hypoxia has the potential to modulate NFκB signalling elicited through a range of stimuli such as TNFα. The implication of such NFκB-inducing stimuli in the initiation of HIF-1α transcription highlights the importance of hypoxia and NFκB together and in isolation in the inflammatory response. The complicated cross-talk between these two signalling pathways means that even specific inhibitors of NFκB and HIF are likely to influence the other pathway. Notwithstanding this, exciting new evidence is emerging for the potential therapeutic application of hydroxylase inhibitors in a range of ischaemic conditions affecting the whole animal [71], the brain [72], the heart [73] and the kidney [74–76], and also in models of hypoxic inflammation such as IBD [66, 69].
Authors' information
Owing to space restrictions, it was not possible in the present article to reference every publication relevant to the role of hydroxylases in NFκB signalling.
Abbreviations
ARD:
ankyrin-repeat domain
DMOG:
dimethyloxallylglycine
FIH:
factor-inhibiting hypoxia inducible factor
HIF:
hypoxia inducible factor
IBD:
inflammatory bowel disease
IKK:
inhibitor of κB kinase
IL:
interleukin
NF:
nuclear factor
PHD:
prolyl hydroxylase
PHDI:
prolyl-hydroxylase inhibitor
RA:
rheumatoid arthritis
TNBS:
trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid
TNF:
tumour necrosis factor
VEGF:
vascular endothelial growth factor.
References
- Chen LF, Greene WC: Shaping the nuclear action of NF-κB. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004, 5: 392-401. 10.1038/nrm1368.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Hayden MS, Ghosh S: Shared principles in NF-κB signaling. Cell. 2008, 132: 344-362. 10.1016/j.cell.2008.01.020.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Karin M: The IκB kinase – a bridge between inflammation and cancer. Cell Res. 2008, 18: 334-342. 10.1038/cr.2008.30.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Ryseck RP, Bull P, Takamiya M, Bours V, Siebenlist U, Dobrzanski P, Bravo R: RelB, a new Rel family transcription activator that can interact with p50-NF-κB. Mol Cell Biol. 1992, 12: 674-684.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Chen YQ, Sengchanthalangsy LL, Hackett A, Ghosh G: NF-κB p65 (RelA) homodimer uses distinct mechanisms to recognize DNA targets. Structure. 2000, 8: 419-428. 10.1016/S0969-2126(00)00123-4.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Van Waes C, Yu M, Nottingham L, Karin M: Inhibitor-κB kinase in tumor promotion and suppression during progression of squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2007, 13: 4956-4959. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1287.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Chen ZJ, Parent L, Maniatis T: Site-specific phosphorylation of IκBα by a novel ubiquitination-dependent protein kinase activity. Cell. 1996, 84: 853-862. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81064-8.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Chen FE, Huang DB, Chen YQ, Ghosh G: Crystal structure of p50/p65 heterodimer of transcription factor NF-κB bound to DNA. Nature. 1998, 391: 410-413. 10.1038/34356.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Pahl HL: Activators and target genes of Rel/NF-κB transcription factors. Oncogene. 1999, 18: 6853-6866. 10.1038/sj.onc.1203239.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Moynagh PN: The NF-κB pathway. J Cell Sci. 2005, 118 (Pt 20): 4589-4592. 10.1242/jcs.02579.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Cummins EP, Berra E, Comerford KM, Fitzgerald KT, Seeballuck F, Godson C, Nielsen JE, Moynagh P, Pouyssegur J, Taylor CT: Prolyl hydroxylase-1 negatively regulates IkB kinase-β giving insight into hypoxia-induced NFkB activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006, 103: 18154-18159. 10.1073/pnas.0602235103.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Koong AC, Chen EY, Giaccia AJ: Hypoxia causes the activation of nuclear factor κB through the phosphorylation of IκBα on tyrosine residues. Cancer Res. 1994, 54: 1425-1430.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Rius J, Guma M, Schachtrup C, Akassoglou K, Zinkernagel AS, Nizet V, Johnson RS, Haddad GG, Karin M: NF-κB links innate immunity to the hypoxic response through transcriptional regulation of HIF-1α. Nature. 2008, 453: 807-811. 10.1038/nature06905.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Li N, Karin M: Ionizing radiation and short wavelength UV activate NF-κB through two distinct mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998, 95: 13012-13017. 10.1073/pnas.95.22.13012.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - O'Dea EL, Kearns JD, Hoffmann A: UV as an amplifier rather than inducer of NF-κB activity. Mol Cell. 2008, 30: 632-641. 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.03.017.
Article PubMed Central PubMed Google Scholar - Schmidt KN, Amstad P, Cerutti P, Baeuerle PA: The roles of hydrogen peroxide and superoxide as messengers in the activation of transcription factor NF-κB. Chem Biol. 1995, 2: 13-22. 10.1016/1074-5521(95)90076-4.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Khachigian LM, Resnick N, Gimbrone MA, Collins T: Nuclear factor-κB interacts functionally with the platelet-derived growth factor B-chain shear-stress response element in vascular endothelial cells exposed to fluid shear stress. J Clin Invest. 1995, 96: 1169-1175. 10.1172/JCI118106.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Leeper-Woodford SK, Detmer K: Acute hypoxia increases alveolar macrophage tumor necrosis factor activity and alters NF-κB expression. Am J Physiol. 1999, 276 (6 Pt 1): L909-L916.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Chandel NS, Trzyna WC, McClintock DS, Schumacker PT: Role of oxidants in NF-κB activation and TNF-α gene transcription induced by hypoxia and endotoxin. J Immunol. 2000, 165: 1013-1021.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Schmedtje JF, Ji YS, Liu WL, DuBois RN, Runge MS: Hypoxia induces cyclooxygenase-2 via the NF-κB p65 transcription factor in human vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1997, 272: 601-608. 10.1074/jbc.272.1.601.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Taylor CT, Dzus AL, Colgan SP: Autocrine regulation of epithelial permeability by hypoxia: role for polarized release of tumor necrosis factor α. Gastroenterology. 1998, 114: 657-668. 10.1016/S0016-5085(98)70579-7.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Matsui H, Ihara Y, Fujio Y, Kunisada K, Akira S, Kishimoto T, Yamauchi-Takihara K: Induction of interleukin (IL)-6 by hypoxia is mediated by nuclear factor (NF)-κB and NF-IL6 in cardiac myocytes. Cardiovasc Res. 1999, 42: 104-112. 10.1016/S0008-6363(98)00285-5.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Zampetaki A, Mitsialis SA, Pfeilschifter J, Kourembanas S: Hypoxia induces macrophage inflammatory protein-2 (MIP-2) gene expression in murine macrophages via NF-κB: the prominent role of p42/p44 and PI3 kinase pathways. FASEB J. 2004, 18: 1090-1092.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Berra E, Benizri E, Ginouves A, Volmat V, Roux D, Pouyssegur J: HIF prolyl-hydroxylase 2 is the key oxygen sensor setting low steady-state levels of HIF-1α in normoxia. EMBO J. 2003, 22: 4082-4090. 10.1093/emboj/cdg392.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Ivan M, Kondo K, Yang H, Kim W, Valiando J, Ohh M, Salic A, Asara JM, Lane WS, Kaelin WG: HIFα targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation: implications for O2 sensing. Science. 2001, 292: 464-468. 10.1126/science.1059817.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Jaakkola P, Mole DR, Tian YM, Wilson MI, Gielbert J, Gaskell SJ, Kriegsheim A, Hebestreit HF, Mukherji M, Schofield CJ, Maxwell PH, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ: Targeting of HIF-α to the von Hippel–Lindau ubiquitylation complex by. Science. 2001, 292: 468-472. 10.1126/science.1059796.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Hewitson KS, McNeill LA, Riordan MV, Tian YM, Bullock AN, Welford RW, Elkins JM, Oldham NJ, Bhattacharya S, Gleadle JM, Ratcliffe PJ, Pugh CW, Schofield CJ: Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) asparagine hydroxylase is identical to factor inhibiting HIF (FIH) and is related to the cupin structural family. J Biol Chem. 2002, 277: 26351-26355. 10.1074/jbc.C200273200.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Lando D, Peet DJ, Gorman JJ, Whelan DA, Whitelaw ML, Bruick RK: FIH-1 is an asparaginyl hydroxylase enzyme that regulates the transcriptional activity of hypoxia-inducible factor. Genes Dev. 2002, 16: 1466-1471. 10.1101/gad.991402.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Cockman ME, Lancaster DE, Stolze IP, Hewitson KS, McDonough MA, Coleman ML, Coles CH, Yu X, Hay RT, Ley SC, Pugh CW, Oldham NJ, Masson N, Schofield CJ, Ratcliffe PJ: Post-translational hydroxylation of ankyrin repeats in IκB proteins by the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) asparaginyl hydroxylase, factor inhibiting HIF (FIH). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006, 103: 14767-14772. 10.1073/pnas.0606877103.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Coleman ML, McDonough MA, Hewitson KS, Coles C, Mecinovic J, Edelmann M, Cook KM, Cockman ME, Lancaster DE, Kessler BM, Oldham NJ, Ratcliffe PJ, Schofield CJ: Asparaginyl hydroxylation of the Notch ankyrin repeat domain by factor inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor. J Biol Chem. 2007, 282: 24027-24038. 10.1074/jbc.M704102200.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Zheng X, Linke S, Dias JM, Zheng X, Gradin K, Wallis TP, Hamilton BR, Gustafsson M, Ruas JL, Wilkins S, Bilton RL, Brismar K, Whitelaw ML, Pereira T, Gorman JJ, Ericson J, Peet DJ, Lendahl U, Poellinger L: Interaction with factor inhibiting HIF-1 defines an additional mode of cross-coupling between the Notch and hypoxia signaling pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008, 105: 3368-3373. 10.1073/pnas.0711591105.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Cramer T, Yamanishi Y, Clausen BE, Forster I, Pawlinski R, Mackman N, Haase VH, Jaenisch R, Corr M, Nizet V, Firestein GS, Gerber HP, Ferrara N, Johnson RS: HIF-1α is essential for myeloid cell-mediated inflammation. Cell. 2003, 112: 645-657. 10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00154-5.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Hollander AP, Corke KP, Freemont AJ, Lewis CE: Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α by macrophages in the rheumatoid synovium: implications for targeting of therapeutic genes to the inflamed joint. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44: 1540-1544. 10.1002/1529-0131(200107)44:7<1540::AID-ART277>3.0.CO;2-7.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Figueroa YG, Chan AK, Ibrahim R, Tang Y, Burow ME, Alam J, Scandurro AB, Beckman BS: NF-κB plays a key role in hypoxia-inducible factor-1-regulated erythropoietin gene expression. Exp Hematol. 2002, 30: 1419-1427. 10.1016/S0301-472X(02)00934-7.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Jung Y, Isaacs JS, Lee S, Trepel J, Liu ZG, Neckers L: Hypoxia-inducible factor induction by tumour necrosis factor in nor-moxic cells requires receptor-interacting protein-dependent nuclear factor κB activation. Biochem J. 2003, 370 (Pt 3): 1011-1017. 10.1042/BJ20021279.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Jung YJ, Isaacs JS, Lee S, Trepel J, Neckers L: IL-1β-mediated up-regulation of HIF-1α via an NFκB/COX-2 pathway identifies HIF-1 as a critical link between inflammation and oncogenesis. FASEB J. 2003, 17: 2115-2117.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Jung YJ, Isaacs JS, Lee S, Trepel J, Neckers L: Microtubule disruption utilizes an NFκB-dependent pathway to stabilize HIF-1α protein. J Biol Chem. 2003, 278: 7445-7452. 10.1074/jbc.M209804200.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Belaiba RS, Bonello S, Zahringer C, Schmidt S, Hess J, Kietzmann T, Gorlach A: Hypoxia up-regulates hypoxia-inducible factor-1α transcription by involving phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and nuclear factor κB in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2007, 18: 4691-4697. 10.1091/mbc.E07-04-0391.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Bonello S, Zahringer C, BelAiba RS, Djordjevic T, Hess J, Michiels C, Kietzmann T, Gorlach A: Reactive oxygen species activate the HIF-1α promoter via a functional NFκB site. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007, 27: 755-761. 10.1161/01.ATV.0000258979.92828.bc.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Frede S, Stockmann C, Freitag P, Fandrey J: Bacterial lipo-polysaccharide induces HIF-1 activation in human monocytes via p44/42 MAPK and NF-κB. Biochem J. 2006, 396: 517-527. 10.1042/BJ20051839.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Kim J, Shao Y, Kim SY, Kim S, Song HK, Jeon JH, Suh HW, Chung JW, Yoon SR, Kim YS, Choi I: Hypoxia-induced IL-18 increases hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression through a Rac1-dependent NF-κB pathway. Mol Biol Cell. 2008, 19: 433-444. 10.1091/mbc.E07-02-0182.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Sun HL, Liu YN, Huang YT, Pan SL, Huang DY, Guh JH, Lee FY, Kuo SC, Teng CM: YC-1 inhibits HIF-1 expression in prostate cancer cells: contribution of Akt/NF-κB signaling to HIF-1α accumulation during hypoxia. Oncogene. 2007, 26: 3941-3951. 10.1038/sj.onc.1210169.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Tacchini L, De Ponti C, Matteucci E, Follis R, Desiderio MA: Hepatocyte growth factor-activated NF-κB regulates HIF-1 activity and ODC expression, implicated in survival, differently in different carcinoma cell lines. Carcinogenesis. 2004, 25: 2089-2100. 10.1093/carcin/bgh227.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - van Uden P, Kenneth NS, Rocha S: Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α by NF-κB. Biochem J. 2008, 412: 477-484. 10.1042/BJ20080476.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Walmsley SR, Print C, Farahi N, Peyssonnaux C, Johnson RS, Cramer T, Sobolewski A, Condliffe AM, Cowburn AS, Johnson N, Chilvers ER: Hypoxia-induced neutrophil survival is mediated by HIF-1α-dependent NF-κB activity. J Exp Med. 2005, 201: 105-115. 10.1084/jem.20040624.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Taylor CT: Interdependent roles for hypoxia inducible factor and nuclear factor-κB in hypoxic inflammation. J Physiol. 2008, 586 (Pt 17): 4055-4059. 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.157669.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Gorlach A, Bonello S: The cross-talk between NF-κB and HIF-1: further evidence for a significant liaison. Biochem J. 2008, 412: e17-e19.
Article PubMed Google Scholar - Murdoch C, Muthana M, Lewis CE: Hypoxia regulates macrophage functions in inflammation. J Immunol. 2005, 175: 6257-6263.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Taylor CT, Colgan SP: Hypoxia and gastrointestinal disease. J Mol Med. 2007, 85: 1295-1300. 10.1007/s00109-007-0277-z.
Article PubMed Google Scholar - Distler O, Muller-Ladner U, Scholmerich J, Gay RE, Gay S: Rheumatoid arthritis: new molecular and cellular aspects. Med Klin (Munich). 1999, 94: 673-680.
Article CAS Google Scholar - FitzGerald O, Soden M, Yanni G, Robinson R, Bresnihan B: Morphometric analysis of blood vessels in synovial membranes obtained from clinically affected and unaffected knee joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1991, 50: 792-796. 10.1136/ard.50.11.792.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Paleolog EM: Angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. 2002, 4 (Suppl 3): S81-S90. 10.1186/ar575.
Article PubMed Central PubMed Google Scholar - Bodamyali T, Stevens CR, Billingham ME, Ohta S, Blake DR: Influence of hypoxia in inflammatory synovitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1998, 57: 703-710. 10.1136/ard.57.12.703.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Thornton RD, Lane P, Borghaei RC, Pease EA, Caro J, Mochan E: Interleukin 1 induces hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in human gingival and synovial fibroblasts. Biochem J. 2000, 350 (Pt 1): 307-312. 10.1042/0264-6021:3500307.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Makino Y, Nakamura H, Ikeda E, Ohnuma K, Yamauchi K, Yabe Y, Poellinger L, Okada Y, Morimoto C, Tanaka H: Hypoxia-inducible factor regulates survival of antigen receptor-driven T cells. J Immunol. 2003, 171: 6534-6540.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Ikeda E: Cellular response to tissue hypoxia and its involvement in disease progression. Pathol Int. 2005, 55: 603-610. 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2005.01877.x.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Oikawa M, Abe M, Kurosawa H, Hida W, Shirato K, Sato Y: Hypoxia induces transcription factor ETS-1 via the activity of hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001, 289: 39-43. 10.1006/bbrc.2001.5927.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Wernert N, Gilles F, Fafeur V, Bouali F, Raes MB, Pyke C, Dupressoir T, Seitz G, Vandenbunder B, Stehelin D: Stromal expression of c-Ets1 transcription factor correlates with tumor invasion. Cancer Res. 1994, 54: 5683-5688.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Hitchon CA, El-Gabalawy HS: Oxidation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2004, 6: 265-278. 10.1186/ar1447.
Article PubMed Central PubMed Google Scholar - Detmar M, Brown LF, Claffey KP, Yeo KT, Kocher O, Jackman RW, Berse B, Dvorak HF: Overexpression of vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in psoriasis. J Exp Med. 1994, 180: 1141-1146. 10.1084/jem.180.3.1141.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Rosenberger C, Solovan C, Rosenberger AD, Jinping L, Treudler R, Frei U, Eckardt KU, Brown LF: Upregulation of hypoxia-inducible factors in normal and psoriatic skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2007, 127: 2445-2452. 10.1038/sj.jid.5700874.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Chen LW, Egan L, Li ZW, Greten FR, Kagnoff MF, Karin M: The two faces of IKK and NF-κB inhibition: prevention of systemic inflammation but increased local injury following intestinal ischemia-reperfusion. Nat Med. 2003, 9: 575-581. 10.1038/nm849.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Greten FR, Eckmann L, Greten TF, Park JM, Li ZW, Egan LJ, Kagnoff MF, Karin M: IKKβ links inflammation and tumorigenesis in a mouse model of colitis-associated cancer. Cell. 2004, 118: 285-296. 10.1016/j.cell.2004.07.013.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Karhausen J, Furuta GT, Tomaszewski JE, Johnson RS, Colgan SP, Haase VH: Epithelial hypoxia-inducible factor-1 is protective in murine experimental colitis. J Clin Invest. 2004, 114: 1098-1106.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Elvidge GP, Glenny L, Appelhoff RJ, Ratcliffe PJ, Ragoussis J, Gleadle JM: Concordant regulation of gene expression by hypoxia and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase inhibition: the role of HIF-1α, HIF-2α, and other pathways. J Biol Chem. 2006, 281: 15215-15226. 10.1074/jbc.M511408200.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Cummins EP, Seeballuck F, Keely SJ, Mangan NE, Callanan JJ, Fallon PG, Taylor CT: The hydroxylase inhibitor dimethyloxalyl-glycine is protective in a murine model of colitis. Gastroenterology. 2008, 134: 156-165. 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.10.012.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Assi K, Pillai R, Gomez-Munoz A, Owen D, Salh B: The specific JNK inhibitor SP600125 targets tumour necrosis factor-α production and epithelial cell apoptosis in acute murine colitis. Immunology. 2006, 118: 112-121. 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2006.02349.x.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Lugering A, Lebiedz P, Koch S, Kucharzik T: Apoptosis as a therapeutic tool in IBD?. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006, 1072: 62-77. 10.1196/annals.1326.013.
Article PubMed Google Scholar - Robinson A, Keely S, Karhausen J, Gerich ME, Furuta GT, Colgan SP: Mucosal protection by hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibition. Gastroenterology. 2008, 134: 145-155. 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.09.033.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Shah YM, Ito S, Morimura K, Chen C, Yim SH, Haase VH, Gonzalez FJ: Hypoxia-inducible factor augments experimental colitis through an MIF-dependent inflammatory signaling cascade. Gastroenterology. 2008, 134: 2036-2048. 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.009.
Article PubMed Central PubMed Google Scholar - Kasiganesan H, Sridharan V, Wright G: Prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor treatment confers whole-animal hypoxia tolerance. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2007, 190: 163-169. 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2007.01676.x.
Article CAS Google Scholar - Nangaku M, Izuhara Y, Takizawa S, Yamashita T, Fujii-Kuriyama Y, Ohneda O, Yamamoto M, van Ypersele de Strihou C, Hirayama N, Miyata T: A novel class of prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors induces angiogenesis and exerts organ protection against ischemia. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007, 27: 2548-2554. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.148551.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Natarajan R, Salloum FN, Fisher BJ, Ownby ED, Kukreja RC, Fowler AA: Activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 via prolyl-4 hydoxylase-2 gene silencing attenuates acute inflammatory responses in postischemic myocardium. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007, 293: H1571-H1580. 10.1152/ajpheart.00291.2007.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Bernhardt WM, Campean V, Kany S, Jurgensen JS, Weidemann A, Warnecke C, Arend M, Klaus S, Gunzler V, Amann K, Willam C, Wiesener MS, Eckardt KU: Preconditional activation of hypoxia-inducible factors ameliorates ischemic acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006, 17: 1970-1978. 10.1681/ASN.2005121302.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Hill P, Shukla D, Tran MG, Aragones J, Cook HT, Carmeliet P, Maxwell PH: Inhibition of hypoxia inducible factor hydroxylases protects against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008, 19: 39-46. 10.1681/ASN.2006090998.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Rosenberger C, Rosen S, Shina A, Frei U, Eckardt KU, Flippin LA, Arend M, Klaus SJ, Heyman SN: Activation of hypoxia inducible factors (HIF) ameliorates hypoxic distal tubular injury in the isolated perfused rat kidney. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008, 28: 831-839.
Google Scholar - Bishop T, Gallagher D, Pascual A, Lygate CA, de Bono JP, Nicholls LG, Ortega-Saenz P, Oster H, Wijeyekoon B, Sutherland AI, Grosfeld A, Aragones J, Schneider M, van Geyte K, Teixeira D, Diez-Juan A, Lopez-Barneo J, Channon KM, Maxwell PH, Pugh CW, Davies AM, Carmeliet P, Ratcliffe PJ: Abnormal sympathoadrenal development and systemic hypotension in PHD3-/- mice. Mol Cell Biol. 2008, 28: 3386-3400. 10.1128/MCB.02041-07.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Aragones J, Schneider M, Van Geyte K, Fraisl P, Dresselaers T, Mazzone M, Dirkx R, Zacchigna S, Lemieux H, Jeoung NH, Lambrechts D, Bishop T, Lafuste P, Diez-Juan A, Harten SK, Van Noten P, De Bock K, Willam C, Tjwa M, Grosfeld A, Navet R, Moons L, Vandendriessche T, Deroose C, Wijeyekoon B, Nuyts J, Jordan B, Silasi-Mansat R, Lupu F, Dewerchin M, Pugh C, Salmon P, Mortelmans L, Gallez B, Gorus F, Buyse J, Sluse F, Harris RA, Gnaiger E, Hespel P, Van Hecke P, Schuit F, Van Veldhoven P, Ratcliffe P, Baes M, Maxwell P, Carmeliet P: Deficiency or inhibition of oxygen sensor Phd1 induces hypoxia tolerance by reprogramming basal metabolism. Nat Genet. 2008, 40: 170-180. 10.1038/ng.2007.62.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Takeda K, Ho VC, Takeda H, Duan LJ, Nagy A, Fong GH: Placental but not heart defects are associated with elevated hypoxia-inducible factor α levels in mice lacking prolyl hydroxylase domain protein 2. Mol Cell Biol. 2006, 26: 8336-8346. 10.1128/MCB.00425-06.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Holtmann MH, Neurath MF: Differential TNF-signaling in chronic inflammatory disorders. Curr Mol Med. 2004, 4: 439-444. 10.2174/1566524043360636.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Pallone F, Monteleone G: Mechanisms of tissue damage in inflammatory bowel disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2001, 17: 307-312. 10.1097/00001574-200107000-00002.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Acknowledgements
The authors are funded by the Science Foundation Ireland (CTT and EPC) and by the Health Research Board (Ireland) (KMO)
Note
This review is part of a series on Hypoxia edited by Ewa Paleolog. Other articles in this series can be found at http://arthritis-research.com/series/ar_Hypoxia
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- School of Medicine and Medical Science, Conway Institute, University College Dublin, Belfield, Dublin 4, Ireland
Kathryn M Oliver, Cormac T Taylor & Eoin P Cummins
Authors
- Kathryn M Oliver
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Cormac T Taylor
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Eoin P Cummins
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence toEoin P Cummins.
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oliver, K.M., Taylor, C.T. & Cummins, E.P. Hypoxia. Regulation of NFκB signalling during inflammation: the role of hydroxylases.Arthritis Res Ther 11, 215 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1186/ar2575
- Published: 23 February 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/ar2575