Carbapenem-resistant strain of Klebsiella oxytoca harboring carbapenem-hydrolyzing beta-lactamase KPC-2 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Carbapenem-resistant strain of Klebsiella oxytoca harboring carbapenem-hydrolyzing beta-lactamase KPC-2
Hesna Yigit et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003 Dec.
Abstract
We investigated a Klebsiella oxytoca isolate demonstrating resistance to imipenem, meropenem, extended-spectrum cephalosporins, and aztreonam. The MICs of both imipenem and meropenem were 32 microg/ml. The beta-lactamase activity against imipenem and meropenem was inhibited in the presence of clavulanic acid. Isoelectric focusing studies demonstrated five beta-lactamases with pIs of 8.2 (SHV-46), 6.7 (KPC-2), 6.5 (unknown), 6.4 (probable OXY-2), and 5.4 (TEM-1). The presence of the bla(SHV) and bla(TEM) genes was confirmed by specific PCR assays and DNA sequence analysis. Transformation and conjugation studies with Escherichia coli showed that the beta-lactamase with a pI of 6.7, Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase-2 (KPC-2), was encoded on an approximately 70-kb conjugative plasmid that also carried SHV-46, TEM-1, and the beta-lactamase with a pI of 6.5. The bla(KPC-2) determinant was cloned in E. coli and conferred resistance to imipenem, meropenem, extended-spectrum cephalosporins, and aztreonam. The amino acid sequence of KPC-2 showed a single amino acid difference, S174G, when compared with KPC-1, another carbapenem-hydrolyzing beta-lactamase from K. pneumoniae 1534. Hydrolysis studies showed that purified KPC-2 hydrolyzed not only carbapenems but also penicillins, cephalosporins, and aztreonam. KPC-2 had the highest affinity for meropenem. The kinetic studies revealed that KPC-2 was inhibited by clavulanic acid and tazobactam. An examination of the outer membrane proteins of the parent K. oxytoca strain demonstrated that it expressed detectable levels of OmpK36 (the homolog of OmpC) and a higher-molecular-weight OmpK35 (the homolog of OmpF). Thus, carbapenem resistance in K. oxytoca 3127 is due to production of the Bush group 2f, class A, carbapenem-hydrolyzing beta-lactamase KPC-2. This beta-lactamase is likely located on a transposon that is part of a conjugative plasmid and thus has a very high potential for dissemination.
Figures
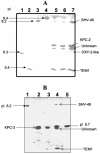
FIG. 1.
(A) Isoelectric focusing patterns of cell lysates from carbapenem-resistant strains. The gel was stained with nitrocefin. Lanes 1 to 4, cell lysates prepared from strains producing TEM-3 (pI 6.3), TEM-1 (pI 5.4), SHV-5 (pI 8.2), and MIR-1 (pI 8.4), respectively; lane 5, the imipenem-resistant E. coli HB101 transformant containing a 70-kb plasmid from 3127; lane 6, an imipenem-resistant E. coli HB101 transconjugant of 3127; lane 7, K. oxytoca 3127. (B) Isoelectric focusing patterns of cell lysates prepared from carbapenem-resistant clones of K. oxytoca 3127. Lane 1, strain producing SHV-46 (pI 8.2); lanes 2 to 3, clones of strain 3127; lane 4, an imipenem-resistant E. coli HB101 transconjugant of K. oxytoca 3127; lane 5, E. coli DH5α containing the _bla_KPC-1 clone. The pIs of the β-lactamases were calculated by using the known pIs of TEM-1 (5.4), TEM-3 (6. 3), SHV-5 (8.2), KPC-1 (6.7), and MIR-1 (8.4).
FIG. 2.
Alignment of the partial sequence of the protein encoded upstream of KPC-2 (GenBank accession number AAO53444.1) to IstB-like proteins (6); IS_21_ putative ATP-binding protein (GenBank accession number P15026), putative IS_100_ transposase from Y. pestis C092 (GenBank accession number NP_395401), putative transposase from Y. pestis (GenBank accession number AAC44982), and putative transposition helper protein from S. enterica subsp. enterica serotype Cubana (GenBank accession number AAM10642).
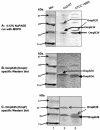
FIG. 3.
NuPAGE gel and Western blot analysis of OMPs of K. oxytoca 3127 and a carbapenem-susceptible control strain, K. pneumoniae ATCC 13883. (A) NuPAGE gel analysis of OMPs. Lane 1, molecular mass markers; lane 2, OMPs prepared from K. oxytoca 3127; lane 3, OMPs prepared from K. pneumoniae ATCC 13883. (B) Western blot analysis of OMPs performed with anti-OMPK36 antisera. (C) Western blot analysis of OMPs performed with anti-OMPK35 antisera. Molecular mass is indicated in gels to the left of each panel.
Similar articles
- Novel carbapenem-hydrolyzing beta-lactamase, KPC-1, from a carbapenem-resistant strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Yigit H, Queenan AM, Anderson GJ, Domenech-Sanchez A, Biddle JW, Steward CD, Alberti S, Bush K, Tenover FC. Yigit H, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001 Apr;45(4):1151-61. doi: 10.1128/AAC.45.4.1151-1161.2001. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001. PMID: 11257029 Free PMC article. - Emergence of Serratia marcescens, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Escherichia coli Isolates possessing the plasmid-mediated carbapenem-hydrolyzing beta-lactamase KPC-2 in intensive care units of a Chinese hospital.
Cai JC, Zhou HW, Zhang R, Chen GX. Cai JC, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008 Jun;52(6):2014-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01539-07. Epub 2008 Mar 10. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008. PMID: 18332176 Free PMC article. - Biochemical properties of a carbapenem-hydrolyzing beta-lactamase from Enterobacter cloacae and cloning of the gene into Escherichia coli.
Nordmann P, Mariotte S, Naas T, Labia R, Nicolas MH. Nordmann P, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 May;37(5):939-46. doi: 10.1128/AAC.37.5.939. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993. PMID: 8517720 Free PMC article. - Combination of IMP-4 metallo-beta-lactamase production and porin deficiency causes carbapenem resistance in a Klebsiella oxytoca clinical isolate.
Chen LR, Zhou HW, Cai JC, Zhang R, Chen GX. Chen LR, et al. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009 Oct;65(2):163-7. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2009.07.002. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 19748427 - Imipenem-Relebactam and Meropenem-Vaborbactam: Two Novel Carbapenem-β-Lactamase Inhibitor Combinations.
Zhanel GG, Lawrence CK, Adam H, Schweizer F, Zelenitsky S, Zhanel M, Lagacé-Wiens PRS, Walkty A, Denisuik A, Golden A, Gin AS, Hoban DJ, Lynch JP 3rd, Karlowsky JA. Zhanel GG, et al. Drugs. 2018 Jan;78(1):65-98. doi: 10.1007/s40265-017-0851-9. Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29230684 Review.
Cited by
- Polymyxins and Doripenem Combination Against KPC-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Lee GC, Burgess DS. Lee GC, et al. J Clin Med Res. 2013 Apr;5(2):97-100. doi: 10.4021/jocmr1220w. Epub 2013 Feb 25. J Clin Med Res. 2013. PMID: 23519391 Free PMC article. - "Stormy waters ahead": global emergence of carbapenemases.
Patel G, Bonomo RA. Patel G, et al. Front Microbiol. 2013 Mar 14;4:48. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00048. eCollection 2013. Front Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23504089 Free PMC article. - First identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates producing a KPC-type carbapenem-hydrolyzing beta-lactamase.
Villegas MV, Lolans K, Correa A, Kattan JN, Lopez JA, Quinn JP; Colombian Nosocomial Resistance Study Group. Villegas MV, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Apr;51(4):1553-5. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01405-06. Epub 2007 Jan 29. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17261621 Free PMC article. - Importance of position 170 in the inhibition of GES-type β-lactamases by clavulanic acid.
Frase H, Toth M, Champion MM, Antunes NT, Vakulenko SB. Frase H, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Apr;55(4):1556-62. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01292-10. Epub 2011 Jan 10. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21220532 Free PMC article.
References
- Archibald, L., L. Phillips, D. Monnet, J. E. McGowan, Jr., F. C. Tenover, and R. Gaynes. 1997. Antimicrobial resistance in isolates from inpatients and outpatients in the United States: increasing importance of the intensive care unit. Clin. Infect. Dis. 24:211-215. - PubMed
- Ardanuy, C., J. Linares, M. A. Dominguez, S. Hernandez-Alles, V. J. Benedi, and L. Martinez-Martinez. 1998. Outer membrane profiles of clonally related Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from clinical samples and activities of cephalosporins and carbapenems. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 42:1636-1640. - PMC - PubMed
- Bingen, E. H., P. Desjardins, G. Arlet, F. Bourgeois, P. Mariani-Kurkdjian, N. Y. Lambert-Zechovsky, E. Denamur, A. Philippon, and J. Elion. 1993. Molecular epidemiology of plasmid spread among extended broad-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in a pediatric hospital. J. Clin. Microbiol. 31:179-184. - PMC - PubMed
- Bradford, P. A., C. Urban, N. Mariano, S. J. Projan, J. J. Rahal, and K. Bush. 1997. Imipenem resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae is associated with the combination of ACT-1, a plasmid-mediated AmpC β-lactamase, and the loss of an outer membrane protein. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 41:563-569. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous