The selectivity of protein kinase inhibitors: a further update - PubMed (original) (raw)
The selectivity of protein kinase inhibitors: a further update
Jenny Bain et al. Biochem J. 2007.
Abstract
The specificities of 65 compounds reported to be relatively specific inhibitors of protein kinases have been profiled against a panel of 70-80 protein kinases. On the basis of this information, the effects of compounds that we have studied in cells and other data in the literature, we recommend the use of the following small-molecule inhibitors: SB 203580/SB202190 and BIRB 0796 to be used in parallel to assess the physiological roles of p38 MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) isoforms, PI-103 and wortmannin to be used in parallel to inhibit phosphatidylinositol (phosphoinositide) 3-kinases, PP1 or PP2 to be used in parallel with Src-I1 (Src inhibitor-1) to inhibit Src family members; PD 184352 or PD 0325901 to inhibit MKK1 (MAPK kinase-1) or MKK1 plus MKK5, Akt-I-1/2 to inhibit the activation of PKB (protein kinase B/Akt), rapamycin to inhibit TORC1 [mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin)-raptor (regulatory associated protein of mTOR) complex], CT 99021 to inhibit GSK3 (glycogen synthase kinase 3), BI-D1870 and SL0101 or FMK (fluoromethylketone) to be used in parallel to inhibit RSK (ribosomal S6 kinase), D4476 to inhibit CK1 (casein kinase 1), VX680 to inhibit Aurora kinases, and roscovitine as a pan-CDK (cyclin-dependent kinase) inhibitor. We have also identified harmine as a potent and specific inhibitor of DYRK1A (dual-specificity tyrosine-phosphorylated and -regulated kinase 1A) in vitro. The results have further emphasized the need for considerable caution in using small-molecule inhibitors of protein kinases to assess the physiological roles of these enzymes. Despite being used widely, many of the compounds that we analysed were too non-specific for useful conclusions to be made, other than to exclude the involvement of particular protein kinases in cellular processes.
Figures
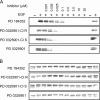
Figure 1. Effect of MKK1/MKK5 inhibitors on the activation of ERK1/ERK2 and ERK5
HeLa cells were serum-starved for 16 h and incubated for a further 1 h in the presence (+) or absence (−) of PD184352, PD 0325901-Cl [(R) steroisomer], PD 0325901 [(S) steroisomer] or PD 0325901 at the concentrations indicated. The cells were then stimulated for 10 min with 100 ng/ml EGF, lysed, and 30 μg of the extract protein was denatured in SDS, subjected to SDS/PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose membranes and immunoblotted with an antibody recognizing phosphorylated ERK1 and ERK2 in (A) and immunoblotted with an antibody that recognizes all forms of ERK5 equally well in (B).
Figure 2. Effect of PI 103 on the activities of PI3K superfamily members in HEK-293 cells
(A) HEK-293 (human embryonic kidney-293) cells were incubated for 1 h with (+) or without (−) 0.5 μM PI 103, then stimulated for 30 min with IGF-1 (50 ng/ml) and lysed. Cell extracts (60 μg of protein) were denatured in SDS, subjected to SDS/PAGE and, after transfer to PVDF membranes, immunoblotted with a phosphospecific antibody that recognizes PKB phosphorylated at Ser473 [pPKB (S473)]. (B) HEK-293 cells were incubated for 1 h with (+) or without (−) 0.5 μM PI 103, then treated for 2 h with the DNA-alkylating agent MMS (2 mM) and lysed. Cell extracts (60 μg of protein) were denatured in SDS, subjected to SDS/PAGE and, after transfer to PVDF membranes, immunoblotted with phosphospecific antibodies that recognize CHK1 phosphorylated at Ser345 [pChk1 (S345)]and CHK2 phosphorylated at Thr68 [pChk2 (T68)].
Similar articles
- The specificities of protein kinase inhibitors: an update.
Bain J, McLauchlan H, Elliott M, Cohen P. Bain J, et al. Biochem J. 2003 Apr 1;371(Pt 1):199-204. doi: 10.1042/BJ20021535. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 12534346 Free PMC article. - BI-D1870 is a specific inhibitor of the p90 RSK (ribosomal S6 kinase) isoforms in vitro and in vivo.
Sapkota GP, Cummings L, Newell FS, Armstrong C, Bain J, Frodin M, Grauert M, Hoffmann M, Schnapp G, Steegmaier M, Cohen P, Alessi DR. Sapkota GP, et al. Biochem J. 2007 Jan 1;401(1):29-38. doi: 10.1042/BJ20061088. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17040210 Free PMC article. - Two widely used RSK inhibitors, BI-D1870 and SL0101, alter mTORC1 signaling in a RSK-independent manner.
Roffé M, Lupinacci FC, Soares LC, Hajj GN, Martins VR. Roffé M, et al. Cell Signal. 2015 Aug;27(8):1630-42. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2015.04.004. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Cell Signal. 2015. PMID: 25889895 - New inhibitors of the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway: insights into mTOR signaling from a new generation of Tor Kinase Domain Inhibitors (TORKinibs).
Feldman ME, Shokat KM. Feldman ME, et al. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010;347:241-62. doi: 10.1007/82_2010_64. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20549474 Review.
Cited by
- Serum/glucocorticoid regulated kinase 1 (SGK1) in neurological disorders: pain or gain.
Howard PG, Zou P, Zhang Y, Huang F, Tesic V, Wu CY, Lee RH. Howard PG, et al. Exp Neurol. 2024 Dec;382:114973. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.114973. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Exp Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39326820 Review. - The proteomic landscape and temporal dynamics of mammalian gastruloid development.
Garge RK, Lynch V, Fields R, Casadei S, Best S, Stone J, Snyder M, McGann CD, Shendure J, Starita LM, Hamazaki N, Schweppe DK. Garge RK, et al. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 7:2024.09.05.609098. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.05.609098. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39282277 Free PMC article. Preprint. - CaMKK2: bridging the gap between Ca2+ signaling and energy-sensing.
McAloon LM, Muller AG, Nay K, Lu EL, Smeuninx B, Means AR, Febbraio MA, Scott JW. McAloon LM, et al. Essays Biochem. 2024 Nov 18;68(3):309-320. doi: 10.1042/EBC20240011. Essays Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39268917 Free PMC article. Review. - Reduction in mitochondrial ATP synthesis mimics the effect of low glucose in depolarizing neurons from the subpostremal nucleus of the solitary tract of rats.
Zarpellon PS, Murat C, Leão RM. Zarpellon PS, et al. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2024 Oct;56(5):483-493. doi: 10.1007/s10863-024-10037-8. Epub 2024 Sep 13. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2024. PMID: 39266925 - One-pot synthesis of tetrahydropyrimidinecarboxamides enabling in vitro anticancer activity: a combinative study with clinically relevant brain-penetrant drugs.
Upadhyay DB, Nogales J, Mokariya JA, Vala RM, Tandon V, Banerjee S, Patel HM. Upadhyay DB, et al. RSC Adv. 2024 Aug 27;14(37):27174-27186. doi: 10.1039/d4ra04171b. eCollection 2024 Aug 22. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39193280 Free PMC article.
References
- Regan J., Breitfelder S., Cirillo P., Gilmore T., Graham A. G., Hickey E., Klaus B., Madwed J., Moriak M., Moss N., et al. Pyrazole urea-based inhibitors of p38 MAP kinase: from lead compound to clinical candidate. J. Med. Chem. 2002;45:2994–3008. - PubMed
- Shpiro N. A., Marquez R. PD-184352. Synth. Commun. 2005;35:2265–2270.
- Barrett S. D., Biwersi C., Kaufman M., Tecle H., Warmus J. S. Preparation of oxygenated esters of 4-iodophenylaminobenzhydroxyamic acids as MEK inhibitors. World Pat. WO/2002/006213. 2002.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MC_U127015387/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U127081014/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U127084348/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous