Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the oral, small-molecule mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in patients with advanced cancers - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
. 2008 May 1;26(13):2139-46.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.14.4956. Epub 2008 Apr 7.
Roger B Cohen, Wilbur Franklin, Clive Morris, David Wilson, Julian R Molina, Lorelei J Hanson, Lia Gore, Laura Chow, Stephen Leong, Lara Maloney, Gilad Gordon, Heidi Simmons, Allison Marlow, Kevin Litwiler, Suzy Brown, Gregory Poch, Katie Kane, Jerry Haney, S Gail Eckhardt
Affiliations
- PMID: 18390968
- PMCID: PMC2718422
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2007.14.4956
Clinical Trial
Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the oral, small-molecule mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in patients with advanced cancers
Alex A Adjei et al. J Clin Oncol. 2008.
Abstract
Purpose: To assess the tolerability, pharmacokinetics (PKs), and pharmacodynamics (PDs) of the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK) 1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in patients with advanced cancer.
Patients and methods: In part A, patients received escalating doses to determine the maximum-tolerated dose (MTD). In both parts, blood samples were collected to assess PK and PD parameters. In part B, patients were stratified by cancer type (melanoma v other) and randomly assigned to receive the MTD or 50% MTD. Biopsies were collected to determine inhibition of ERK phosphorylation, Ki-67 expression, and BRAF, KRAS, and NRAS mutations.
Results: Fifty-seven patients were enrolled. MTD in part A was 200 mg bid, but this dose was discontinued in part B because of toxicity. The 50% MTD (100 mg bid) was well tolerated. Rash was the most frequent and dose-limiting toxicity. Most other adverse events were grade 1 or 2. The PKs were less than dose proportional, with a median half-life of approximately 8 hours and inhibition of ERK phosphorylation in peripheral-blood mononuclear cells at all dose levels. Paired tumor biopsies demonstrated reduced ERK phosphorylation (geometric mean, 79%). Five of 20 patients demonstrated >or= 50% inhibition of Ki-67 expression, and RAF or RAS mutations were detected in 10 of 26 assessable tumor samples. Nine patients had stable disease (SD) for >or= 5 months, including two patients with SD for 19 (thyroid cancer) and 22 (uveal melanoma plus renal cancer) 28-day cycles.
Conclusion: AZD6244 was well tolerated with target inhibition demonstrated at the recommended phase II dose. PK analyses supported twice-daily dosing. Prolonged SD was seen in a variety of advanced cancers. Phase II studies are ongoing.
Conflict of interest statement
AUTHORS’ DISCLOSURES OF POTENTIAL CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
Although all authors completed the disclosure declaration, the following author(s) indicated a financial or other interest that is relevant to the subject matter under consideration in this article. Certain relationships marked with a “U” are those for which no compensation was received; those relationships marked with a “C” were compensated. For a detailed description of the disclosure categories, or for more information about ASCO’s conflict of interest policy, please refer to the Author Disclosure Declaration and the Disclosures of Potential Conflicts of Interest section in Information for Contributors.
Employment or Leadership Position: Clive Morris, AstraZeneca (C); David Wilson, AstraZeneca (C); Lara Maloney, Array BioPharma Inc (C); Heidi Simmons, Array BioPharma Inc (C); Allison Marlow, Array BioPharma Inc (C); Kevin Litwiler, Array BioPharma Inc (C); Suzy Brown, Array BioPharma Inc (C); Gregory Poch, Array BioPharma Inc (C); Katie Kane, Array BioPharma Inc (C) Consultant or Advisory Role: Alex A. Adjei, Array BioPharma Inc (C); Roger B. Cohen, Array BioPharma Inc (C); Gilad Gordon, Array BioPharma Inc (C); S. Gail Eckhardt, AstraZeneca (C), Array BioPharma Inc (C) Stock Ownership: Clive Morris, AstraZeneca; David Wilson, AstraZeneca; Lara Maloney, Array BioPharma Inc; Kevin Litwiler, Array BioPharma Inc; Gregory Poch, Array BioPharma Inc Honoraria: None Research Funding: Roger B. Cohen, Array BioPharma Inc, AstraZeneca; S. Gail Eckhardt, AstraZeneca Expert Testimony: None Other Remuneration: S. Gail Eckhardt, AstraZeneca, fellowship funding
Figures
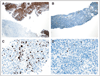
Fig 1
Immunostains of pre- and post-treatment melanoma specimens from the same patient. (A) Before dose, tumor cells are reactive to anti-pERK antibody (brown staining; magnification, ×100). (B) After dose, cells are unreactive to same anti-pERK antibody (magnification, ×100). (C) Before dose, variable nuclear Ki-67 labeling (approximately 30% positive nuclei; magnification, ×400). (D) After dose, marked reduction in nuclear Ki-67 labeling (< 1% positive nuclei; magnification, ×400)
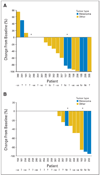
Fig 2
Percent change from baseline at day 15 (± 7 days) in (A) tumor cell nuclei H-score for pERK and (B) proportion of tumor cell nuclei staining for Ki-67. Patients received 100 mg bid or 200 mg bid (denoted by *).
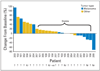
Fig 3
Best percent change from baseline in target lesion size for patients who have at least postbaseline efficacy assessment.
Similar articles
- The first-in-human study of the hydrogen sulfate (Hyd-sulfate) capsule of the MEK1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886): a phase I open-label multicenter trial in patients with advanced cancer.
Banerji U, Camidge DR, Verheul HM, Agarwal R, Sarker D, Kaye SB, Desar IM, Timmer-Bonte JN, Eckhardt SG, Lewis KD, Brown KH, Cantarini MV, Morris C, George SM, Smith PD, van Herpen CM. Banerji U, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Mar 1;16(5):1613-23. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2483. Epub 2010 Feb 23. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20179232 Clinical Trial. - Activity of the oral MEK inhibitor trametinib in patients with advanced melanoma: a phase 1 dose-escalation trial.
Falchook GS, Lewis KD, Infante JR, Gordon MS, Vogelzang NJ, DeMarini DJ, Sun P, Moy C, Szabo SA, Roadcap LT, Peddareddigari VG, Lebowitz PF, Le NT, Burris HA 3rd, Messersmith WA, O'Dwyer PJ, Kim KB, Flaherty K, Bendell JC, Gonzalez R, Kurzrock R, Fecher LA. Falchook GS, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2012 Aug;13(8):782-9. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70269-3. Epub 2012 Jul 16. Lancet Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22805292 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - A first-in-human phase I study to evaluate the MEK1/2 inhibitor, cobimetinib, administered daily in patients with advanced solid tumors.
Rosen LS, LoRusso P, Ma WW, Goldman JW, Weise A, Colevas AD, Adjei A, Yazji S, Shen A, Johnston S, Hsieh HJ, Chan IT, Sikic BI. Rosen LS, et al. Invest New Drugs. 2016 Oct;34(5):604-13. doi: 10.1007/s10637-016-0374-3. Epub 2016 Jul 16. Invest New Drugs. 2016. PMID: 27424159 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Selumetinib in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer.
Bernabé R, Patrao A, Carter L, Blackhall F, Dean E. Bernabé R, et al. Future Oncol. 2016 Nov;12(22):2545-2560. doi: 10.2217/fon-2016-0132. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Future Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27467210 Review. - Treating non-small cell lung cancer with selumetinib: an up-to-date drug evaluation.
Imyanitov EN, Levchenko EV, Kuligina ES, Orlov SV. Imyanitov EN, et al. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020 Nov;21(16):1943-1953. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2020.1798930. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32880495 Review.
Cited by
- Biomarker-driven phase 2 study of MK-2206 and selumetinib (AZD6244, ARRY-142886) in patients with colorectal cancer.
Do K, Speranza G, Bishop R, Khin S, Rubinstein L, Kinders RJ, Datiles M, Eugeni M, Lam MH, Doyle LA, Doroshow JH, Kummar S. Do K, et al. Invest New Drugs. 2015 Jun;33(3):720-8. doi: 10.1007/s10637-015-0212-z. Epub 2015 Feb 1. Invest New Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25637165 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - CInQ-03, a novel allosteric MEK inhibitor, suppresses cancer growth in vitro and in vivo.
Kim DJ, Lee MH, Reddy K, Li Y, Lim DY, Xie H, Lee SY, Yeom YI, Bode AM, Dong Z. Kim DJ, et al. Carcinogenesis. 2013 May;34(5):1134-43. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt015. Epub 2013 Jan 25. Carcinogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23354306 Free PMC article. - Opportunities and challenges provided by crosstalk between signalling pathways in cancer.
Prahallad A, Bernards R. Prahallad A, et al. Oncogene. 2016 Mar 3;35(9):1073-9. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.151. Epub 2015 May 18. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 25982281 Review. - The RAF inhibitor PLX4032 inhibits ERK signaling and tumor cell proliferation in a V600E BRAF-selective manner.
Joseph EW, Pratilas CA, Poulikakos PI, Tadi M, Wang W, Taylor BS, Halilovic E, Persaud Y, Xing F, Viale A, Tsai J, Chapman PB, Bollag G, Solit DB, Rosen N. Joseph EW, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Aug 17;107(33):14903-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1008990107. Epub 2010 Jul 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20668238 Free PMC article. - The serine protease inhibitor serpinE2 is a novel target of ERK signaling involved in human colorectal tumorigenesis.
Bergeron S, Lemieux E, Durand V, Cagnol S, Carrier JC, Lussier JG, Boucher MJ, Rivard N. Bergeron S, et al. Mol Cancer. 2010 Oct 13;9:271. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-271. Mol Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20942929 Free PMC article.
References
- Sebolt-Leopold JS, Dudley DT, Herrera R, et al. Blockade of the MAP kinase pathway suppresses growth of colon tumors in vivo. Nat Med. 1999;5:810–816. - PubMed
- Tecle H. The development of kinase inhibitors with unusual mechanism of action: CI-1040, a selective, non-ATP competitive MEK inhibitor in the clinic. Presented at the IBC 2nd International Conference of Protein Kinases: Target Validation, Drug Discovery and Clinical Development of Kinase Therapeutics; September 9–10, 2002; Boston, MA.
- Trachet E, Przybranowski S, Howard C. In vivo evaluation of MEK inhibitor, CI-1040 (PD 0184352), against a panel of human pancreatic tumor xenografts. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2002;43:2096. (abstr 5426)
- Yeh TC, Marsh V, Bernat BA, et al. Biological characterization of ARRY-142886 (AZD6244), a potent, highly selective mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:1576–1583. - PubMed
- Huynh H, Soo KC, Chow PK, et al. Targeted inhibition of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase pathway with AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6:138–146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K12 CA090628-08/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K12 CA090628/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046934/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 CA106349/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA006927/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA46934/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5P30CA006927/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous