Copy number and targeted mutational analysis reveals novel somatic events in metastatic prostate tumors - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.1101/gr.107961.110. Epub 2010 Dec 8.
Waibov A Tembe, Angela Baker, Shripad Sinari, Tracy Y Moses, Stephen Beckstrom-Sternberg, James Beckstrom-Sternberg, Michael Barrett, James Long, Arul Chinnaiyan, James Lowey, Edward Suh, John V Pearson, David W Craig, David B Agus, Kenneth J Pienta, John D Carpten
Affiliations
- PMID: 21147910
- PMCID: PMC3012925
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.107961.110
Copy number and targeted mutational analysis reveals novel somatic events in metastatic prostate tumors
Christiane M Robbins et al. Genome Res. 2011 Jan.
Abstract
Advanced prostate cancer can progress to systemic metastatic tumors, which are generally androgen insensitive and ultimately lethal. Here, we report a comprehensive genomic survey for somatic events in systemic metastatic prostate tumors using both high-resolution copy number analysis and targeted mutational survey of 3508 exons from 577 cancer-related genes using next generation sequencing. Focal homozygous deletions were detected at 8p22, 10q23.31, 13q13.1, 13q14.11, and 13q14.12. Key genes mapping within these deleted regions include PTEN, BRCA2, C13ORF15, and SIAH3. Focal high-level amplifications were detected at 5p13.2-p12, 14q21.1, 7q22.1, and Xq12. Key amplified genes mapping within these regions include SKP2, FOXA1, and AR. Furthermore, targeted mutational analysis of normal-tumor pairs has identified somatic mutations in genes known to be associated with prostate cancer including AR and TP53, but has also revealed novel somatic point mutations in genes including MTOR, BRCA2, ARHGEF12, and CHD5. Finally, in one patient where multiple independent metastatic tumors were available, we show common and divergent somatic alterations that occur at both the copy number and point mutation level, supporting a model for a common clonal progenitor with metastatic tumor-specific divergence. Our study represents a deep genomic analysis of advanced metastatic prostate tumors and has revealed candidate somatic alterations, possibly contributing to lethal prostate cancer.
Figures
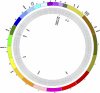
Figure 1.
Circos plot illustrating copy number alterations and genes affected by somatic mutation. Regions affected by focal copy number events are plotted within the gray inner circle with deleted regions deviating below copy neutrality (toward center) and amplified regions deviating above copy neutrality. Key genes mapping within copy number alterations are annotated within the innermost portion of the plot. Genes affected by somatic nonsysnonymous mutation are shown at their proper map positions on the outermost area of the Circos plot.
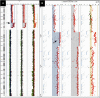
Figure 2.
Illustration of high-level amplification at 5p13.2 in tumors from patient RA45. (A) Chromosome view in Agilent DNA Analytics software showing log2 ratios for probes mapping along chromosome 5 for RA45M (left), RA45RM (middle), and RA45AT (right). Amplicon at 5p13.2 is depicted by the arrow. (B) Gene view in DNA Analytics showing log2 ratios for probes mapping to 5p13.2 for RA45M (left), RA45RM (middle), and RA45AT (right). Arrow points to map position of the SKP2 gene locus.
Similar articles
- Interfocal heterogeneity of PTEN/MMAC1 gene alterations in multiple metastatic prostate cancer tissues.
Suzuki H, Freije D, Nusskern DR, Okami K, Cairns P, Sidransky D, Isaacs WB, Bova GS. Suzuki H, et al. Cancer Res. 1998 Jan 15;58(2):204-9. Cancer Res. 1998. PMID: 9443392 - DNA copy number alterations in prostate cancers: a combined analysis of published CGH studies.
Sun J, Liu W, Adams TS, Sun J, Li X, Turner AR, Chang B, Kim JW, Zheng SL, Isaacs WB, Xu J. Sun J, et al. Prostate. 2007 May 15;67(7):692-700. doi: 10.1002/pros.20543. Prostate. 2007. PMID: 17342750 - Bone metastasis in prostate cancer: Recurring mitochondrial DNA mutation reveals selective pressure exerted by the bone microenvironment.
Arnold RS, Fedewa SA, Goodman M, Osunkoya AO, Kissick HT, Morrissey C, True LD, Petros JA. Arnold RS, et al. Bone. 2015 Sep;78:81-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2015.04.046. Epub 2015 May 5. Bone. 2015. PMID: 25952970 Free PMC article. - Recent advances in prostate cancer research: large-scale genomic analyses reveal novel driver mutations and DNA repair defects.
Frank S, Nelson P, Vasioukhin V. Frank S, et al. F1000Res. 2018 Aug 2;7:F1000 Faculty Rev-1173. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.14499.1. eCollection 2018. F1000Res. 2018. PMID: 30135717 Free PMC article. Review. - Involvement of the multiple tumor suppressor genes and 12-lipoxygenase in human prostate cancer. Therapeutic implications.
Gao X, Porter AT, Honn KV. Gao X, et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1997;407:41-53. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-1813-0_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1997. PMID: 9321930 Review.
Cited by
- The stromal genome heterogeneity between breast and prostate tumors revealed by a comparative transcriptomic analysis.
He K, Lv W, Zheng D, Cheng F, Zhou T, Ye S, Ban Q, Ying Q, Huang B, Chen L, Wu G, Liu D. He K, et al. Oncotarget. 2015 Apr 20;6(11):8687-97. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3478. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25826086 Free PMC article. - Multivalent recognition of histone tails by the PHD fingers of CHD5.
Oliver SS, Musselman CA, Srinivasan R, Svaren JP, Kutateladze TG, Denu JM. Oliver SS, et al. Biochemistry. 2012 Aug 21;51(33):6534-44. doi: 10.1021/bi3006972. Epub 2012 Aug 8. Biochemistry. 2012. PMID: 22834704 Free PMC article. - The 16p13.3 (PDPK1) Genomic Gain in Prostate Cancer: A Potential Role in Disease Progression.
Choucair KA, Guérard KP, Ejdelman J, Chevalier S, Yoshimoto M, Scarlata E, Fazli L, Sircar K, Squire JA, Brimo F, Cunha IW, Aprikian A, Gleave M, Lapointe J. Choucair KA, et al. Transl Oncol. 2012 Dec;5(6):453-60. doi: 10.1593/tlo.12286. Epub 2012 Dec 1. Transl Oncol. 2012. PMID: 23401739 Free PMC article. - Genome-wide investigation of multifocal and unifocal prostate cancer-are they genetically different?
Ibeawuchi C, Schmidt H, Voss R, Titze U, Abbas M, Neumann J, Eltze E, Hoogland AM, Jenster G, Brandt B, Semjonow A. Ibeawuchi C, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Jun 3;14(6):11816-29. doi: 10.3390/ijms140611816. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23736690 Free PMC article. - The emerging role of histone lysine demethylases in prostate cancer.
Crea F, Sun L, Mai A, Chiang YT, Farrar WL, Danesi R, Helgason CD. Crea F, et al. Mol Cancer. 2012 Aug 6;11:52. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-11-52. Mol Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22867098 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Agell L, Hernandez S, de Muga S, Lorente JA, Juanpere N, Esgueva R, Serrano S, Gelabert A, Lloreta J 2008. KLF6 and TP53 mutations are a rare event in prostate cancer: Distinguishing between Taq polymerase artifacts and true mutations. Mod Pathol 21: 1470–1478 - PubMed
- Bagchi A, Papazoglu C, Wu Y, Capurso D, Brodt M, Francis D, Bredel M, Vogel H, Mills AA 2007. CHD5 is a tumor suppressor at human 1p36. Cell 128: 459–475 - PubMed
- Bai C, Sen P, Hofmann K, Ma L, Goebl M, Harper JW, Elledge SJ 1996. SKP1 connects cell cycle regulators to the ubiquitin proteolysis machinery through a novel motif, the F-box. Cell 86: 263–274 - PubMed
- Dong JT 2006. Prevalent mutations in prostate cancer. J Cell Biochem 97: 433–447 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 1S10RR025056-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046592/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA143907/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- P50 CA69568/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA093900/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA46592/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR025056/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA069568/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA093900/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous