Mitigation of radiation-induced lung injury by genistein and EUK-207 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Mitigation of radiation-induced lung injury by genistein and EUK-207
Javed Mahmood et al. Int J Radiat Biol. 2011 Aug.
Abstract
Purpose: We examined the effects of genistein and/or Eukarion (EUK)-207 on radiation-induced lung damage and investigated whether treatment for 0-14 weeks (wks) post-irradiation (PI) would mitigate late lung injury.
Materials and methods: The lungs of female Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were irradiated with 10 Gy. EUK-207 was delivered by infusion and genistein was delivered as a dietary supplement starting immediately after irradiation (post irradiation [PI]) and continuing until 14 wks PI. Rats were sacrificed at 0, 4, 8, 14 and 28 wks PI. Breathing rate was monitored and lung fibrosis assessed by lung hydroxyproline content at 28 wks. DNA damage was assessed by micronucleus (MN) assay and 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) levels. The expression of the cytokines Interleukin (IL)-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1, and macrophage activation were analyzed by immunohistochemistry.
Results: Increases in breathing rate observed in the irradiated rats were significantly reduced by both drug treatments during the pneumonitis phase and the later fibrosis phase. The drug treatments decreased micronuclei (MN) formation from 4-14 wks but by 28 wks the MN levels had increased again. The 8-OHdG levels were lower in the drug treated animals at all time points. Hydroxyproline content and levels of activated macrophages were decreased at 28 wks in all drug treated rats. The treatments had limited effects on the expression of the cytokines.
Conclusion: Genistein and EUK-207 can provide partial mitigation of radiation-induced lung damage out to at least 28 wks PI even after cessation of treatment at 14 wks PI.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure Statement:
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Figures
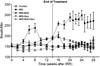
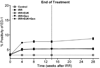
Figure 1
Breathing rate (mean breaths per minute) as a function of time after irradiation (10 Gy) for rats receiving no radiation or radiation only on the control diet, rats irradiated with 10 Gy lung irradiation with genistein, EUK-207 or combination treatment (G+E). All drug treatments started immediately after irradiation and finished at 14 wks. Each point represents the mean (±Standard Error of the Mean -SEM) for all rats available for analysis at the different times.
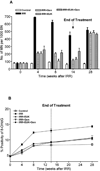
Figure 2
A) Micronucleus yield (MN/1000BN) in fibroblasts from rat lungs and B) percent positivity of 8-OHdG staining following lung irradiation (10 Gy) with Genistein, EUK-207 and combination (G+E) treatment. All drug treatments started immediately after irradiation and finished at 14 wks. The assays were performed at 0, 4, 8, 14 and 28 wks following irradiation. Percent positivity is the ratio of positive pixels/total number of positive and negative pixels in the tissue section (air spaces excluded). Each bar (A) or each point (B) represents the mean (±SEM).
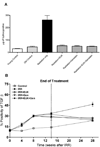
Figure 3
A) Hydroxyproline content (µg of hydroxyproline/100 mg of wet lung tissue) at 28 wks following lung irradiation (10 Gy) with Genistein, EUK-207 and combination (G+E) treatment. All drug treatments started immediately after irradiation and finished at 14 wks. Each bar represents the mean (±SEM). B) Protein expression of TGF-β at 0, 4, 8, 14 and 28 wks following lung irradiation (10 Gy) with Genistein, EUK-207 and combination (G+E) treatment. All drug treatments started immediately after irradiation and finished at 14 wks. Percent positivity is the ratio of positive pixels/total number of positive and negative pixels in the tissue section (air spaces excluded). Each point represents the mean (±SEM).
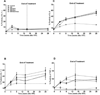
Figure 4
Protein expression of cytokines IL-1α (A), IL-1β (B), IL-6 (C), TNF-α (D) staining at 0, 4, 8, 14 and 28 wks following lung irradiation (10 Gy) with Genistein, EUK-207 and combination (G+E) treatment. All drug treatments started immediately after irradiation and finished at 14 wks. Percent positivity is the ratio of positive pixels/total number of positive and negative pixels in the tissue section (air spaces excluded). Each bar represents the mean (±SEM).
Figure 5
ED-1 staining for activated macrophages in the rat lung at 0, 4, 8, 14 and 28 wks following lung irradiation (10 Gy) with genistein, EUK-207 and combination (G+E) treatment. All drug treatments started immediately after irradiation and finished at 14 wks. Percent positivity is the ratio of positive pixels/total number of positive and negative pixels in the tissue section (air spaces excluded). Each bar represents the mean (±SEM).
Similar articles
- Targeting the Renin-angiotensin system combined with an antioxidant is highly effective in mitigating radiation-induced lung damage.
Mahmood J, Jelveh S, Zaidi A, Doctrow SR, Medhora M, Hill RP. Mahmood J, et al. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014 Jul 15;89(4):722-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.03.048. Epub 2014 May 24. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014. PMID: 24867538 Free PMC article. - Mitigation of radiation-induced lung injury with EUK-207 and genistein: effects in adolescent rats.
Mahmood J, Jelveh S, Zaidi A, Doctrow SR, Hill RP. Mahmood J, et al. Radiat Res. 2013 Feb;179(2):125-34. doi: 10.1667/RR2954.1. Epub 2012 Dec 13. Radiat Res. 2013. PMID: 23237541 Free PMC article. - Investigations into the role of inflammation in normal tissue response to irradiation.
Hill RP, Zaidi A, Mahmood J, Jelveh S. Hill RP, et al. Radiother Oncol. 2011 Oct;101(1):73-9. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2011.06.017. Epub 2011 Jul 2. Radiother Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21726914 Free PMC article. - Radiation induced lung injury: prediction, assessment and management.
Giridhar P, Mallick S, Rath GK, Julka PK. Giridhar P, et al. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(7):2613-7. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.7.2613. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015. PMID: 25854336 Review. - Salen Mn complexes mitigate radiation injury in normal tissues.
Rosenthal RA, Fish B, Hill RP, Huffman KD, Lazarova Z, Mahmood J, Medhora M, Molthen R, Moulder JE, Sonis ST, Tofilon PJ, Doctrow SR. Rosenthal RA, et al. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011 May 1;11(4):359-72. doi: 10.2174/187152011795677490. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21453241 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Pharmacology of natural radioprotectors.
Mun GI, Kim S, Choi E, Kim CS, Lee YS. Mun GI, et al. Arch Pharm Res. 2018 Nov;41(11):1033-1050. doi: 10.1007/s12272-018-1083-6. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Arch Pharm Res. 2018. PMID: 30361949 Free PMC article. Review. - Targeting the Renin-angiotensin system combined with an antioxidant is highly effective in mitigating radiation-induced lung damage.
Mahmood J, Jelveh S, Zaidi A, Doctrow SR, Medhora M, Hill RP. Mahmood J, et al. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014 Jul 15;89(4):722-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.03.048. Epub 2014 May 24. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014. PMID: 24867538 Free PMC article. - Treatment with the reactive oxygen species scavenger EUK-207 reduces lung damage and increases survival during 1918 influenza virus infection in mice.
Kash JC, Xiao Y, Davis AS, Walters KA, Chertow DS, Easterbrook JD, Dunfee RL, Sandouk A, Jagger BW, Schwartzman LM, Kuestner RE, Wehr NB, Huffman K, Rosenthal RA, Ozinsky A, Levine RL, Doctrow SR, Taubenberger JK. Kash JC, et al. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014 Feb;67:235-47. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.10.014. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014. PMID: 24140866 Free PMC article. - Mitigation of radiation-induced lung injury with EUK-207 and genistein: effects in adolescent rats.
Mahmood J, Jelveh S, Zaidi A, Doctrow SR, Hill RP. Mahmood J, et al. Radiat Res. 2013 Feb;179(2):125-34. doi: 10.1667/RR2954.1. Epub 2012 Dec 13. Radiat Res. 2013. PMID: 23237541 Free PMC article. - BIO 300, a nanosuspension of genistein, mitigates pneumonitis/fibrosis following high-dose radiation exposure in the C57L/J murine model.
Jackson IL, Zodda A, Gurung G, Pavlovic R, Kaytor MD, Kuskowski MA, Vujaskovic Z. Jackson IL, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Dec;174(24):4738-4750. doi: 10.1111/bph.14056. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28963717 Free PMC article.
References
- Abou-Seif MA, El-Naggar MM, El-Far M, Ramadan M, Salah N. Amelioration of radiation-induced oxidative stress and biochemical alteration by SOD model compounds in pre-treated gamma-irradiated rats. Clinica Chimica Acta. 2003;337:23–33. - PubMed
- Akiyama T, Ishida J, Nakagawa S, Ogawara H, Watanabe S, Itoh N, Shibuya M, Fukami Y. Genistein, a specific inhibitor of tyrosine-specific protein kinases. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1987;262:5592–5595. - PubMed
- Anscher MS, Thrasher B, Zgonjanin L, Rabbani ZN, Corbley MJ, Fu K, Sun L, Lee WC, Ling LE, Vujaskovic Z. Small molecular inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta protects against development of radiation-induced lung injury. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics. 2008;71:829–837. - PubMed
- Baxa DM, Yoshimura FK. Genistein reduces NF-kappa B in T lymphoma cells via a caspase-mediated cleavage of I kappa B alpha. Biochemical Pharmacology. 2003;66:1009–1018. - PubMed
- Bristow RG, Hill RP. Comparison between in vitro radiosensitivity and in vivo radioresponse of murine tumor cell lines. II: International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics. 1990;18:331–345. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous