Modulation of Neutrophil Apoptosis and the Resolution of Inflammation through β2 Integrins - PubMed (original) (raw)
Modulation of Neutrophil Apoptosis and the Resolution of Inflammation through β2 Integrins
Driss El Kebir et al. Front Immunol. 2013.
Abstract
Precise control of the neutrophil death program provides a balance between their defense functions and safe clearance, whereas impaired regulation of neutrophil death is thought to contribute to a wide range of inflammatory pathologies. Apoptosis is essential for neutrophil functional shutdown, removal of emigrated neutrophils, and timely resolution of inflammation. Neutrophils receive survival and pro-apoptosis cues from the inflammatory microenvironment and integrate these signals through surface receptors and common downstream mechanisms. Among these receptors are the leukocyte-specific membrane receptors β2 integrins that are best known for regulating adhesion and phagocytosis. Accumulating evidence indicate that outside-in signaling through the β2 integrin Mac-1 can generate contrasting cues in neutrophils, leading to promotion of their survival or apoptosis. Binding of Mac-1 to its ligands ICAM-1, fibrinogen, or the azurophilic granule enzyme myeloperoxidase suppresses apoptosis, whereas Mac-1-mediated phagocytosis of bacteria evokes apoptotic cell death. Mac-1 signaling is also target for the anti-inflammatory, pro-resolving mediators, including lipoxin A4, aspirin-triggered lipoxin A4, and resolvin E1. This review focuses on molecular mechanisms underlying Mac-1 regulation of neutrophil apoptosis and highlights recent advances how hierarchy of survival and pro-apoptosis signals can be harnessed to facilitate neutrophil apoptosis and the resolution of inflammation.
Keywords: Mac-1; apoptosis; lipoxins; myeloperoxidase; neutrophils; phagocytosis; resolution of inflammation; resolvins.
Figures
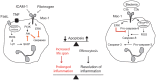
Figure 1
Contrasting outside-in signals through Mac-1 modulates survival and death decision in neutrophils. Aging neutrophils undergo constitutive apoptosis triggered by collapse of mitochondrial function. Engagement of Mac-1 with its ligands ICAM-1, fibrinogen, or MPO delays apoptosis by generating survival cues through activation of the PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK pathways. Additional stimulation of death receptors with TNF or FasL evokes release of ROS, which through activation of lyn and SHIP leads to inhibition of Akt. Mac-1-mediated phagocytosis of opsonized bacteria evokes ROS production by NADPH oxidase, leading to ROS-mediated activation of caspase-8 and inhibition of ERK, and acceleration of the cell death program. Apoptotic neutrophils are recognized and phagocytosed by macrophages (efferocytosis), thus contributing to inflammatory resolution. Extended neutrophil longevity contributes to aggravation and prolongation of the inflammatory response.
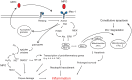
Figure 2
Myeloperoxidase (MPO)-Mac-1 self-amplifying circuit promotes neutrophils survival and inflammation. MPO binding to Mac-1 results in p38 MAPK-mediated NADPH oxidase, and PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK-mediated preservation of the anti-apoptotic protein Mcl-1, leading to suppression of apoptosis. MPO also triggers MPO release from the azurophilic granules, and upregulates Mac-1 expression, thereby forming an autocrine/paracrine self-amplifying circuit. MPO catalyzed formation of HOCl, activation of NF-κB-regulated transcription of pro-inflammatory genes, recruitment of neutrophils, and prolongation of neutrophil longevity contribute to tissue damage and inflammation.
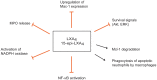
Figure 3
Multipronged actions of lipoxins to inhibit the myeloperoxidase (MPO)-Mac-1 circuit. Lipoxin A4 (LXA4) and aspirin-triggered 15-epi-LXA4 predominantly through FPR2/ALX attenuate MPO-stimulated degranulation, upregulation of surface expression of Mac-1, and superoxide formation, thus effectively interrupting this loop. LXA4 and15-epi-LXA4 redirect neutrophils to apoptosis by overriding the powerful survival signals from MPO through inducing loss of expression of Mcl-1 and aggravating mitochondrial dysfunction. Lipoxins also enhance phagocytosis of apoptotic neutrophils by macrophages.
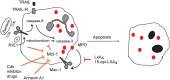
Figure 4
Therapeutic induction of neutrophil apoptosis with demonstrated pro-resolution actions in vivo. Treatment of experimental animals with CDK inhibitor drugs (e.g., R-roscovitine), 15-epi-LXA4, RvE1, rTRAIL, or annexin A1 enhance the resolution of inflammation by promoting apoptosis of neutrophils that have emigrated into tissues in various models of inflammation. Roscovitine through yet unidentified mechanisms, 15-epi-LXA4 through attenuating MPO-triggered Mac-1-mediated survival signaling and annexin A1 through dampening intracellular survival signaling down-regulate expression of the key survival protein Mcl-1. RvE1 enhances phagocytosis-induced apoptosis, leading to activation of caspase-8 and suppression of Mcl-1.rTRAIL activates caspase-8.
Similar articles
- Neutrophil beta2 integrins: moderators of life or death decisions.
Mayadas TN, Cullere X. Mayadas TN, et al. Trends Immunol. 2005 Jul;26(7):388-95. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2005.05.002. Trends Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15922663 Review. - β2 Integrin Regulation of Neutrophil Functional Plasticity and Fate in the Resolution of Inflammation.
Sekheri M, Othman A, Filep JG. Sekheri M, et al. Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 30;12:660760. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.660760. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33859651 Free PMC article. Review. - Neutrophil apoptosis: a target for enhancing the resolution of inflammation.
Filep JG, El Kebir D. Filep JG, et al. J Cell Biochem. 2009 Dec 1;108(5):1039-46. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22351. J Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19760640 Review. - 15-epi-lipoxin A4 inhibits myeloperoxidase signaling and enhances resolution of acute lung injury.
El Kebir D, József L, Pan W, Wang L, Petasis NA, Serhan CN, Filep JG. El Kebir D, et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009 Aug 15;180(4):311-9. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200810-1601OC. Epub 2009 May 29. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009. PMID: 19483113 Free PMC article. - 15-Epi-LXA4 and 17-epi-RvD1 restore TLR9-mediated impaired neutrophil phagocytosis and accelerate resolution of lung inflammation.
Sekheri M, El Kebir D, Edner N, Filep JG. Sekheri M, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Apr 7;117(14):7971-7980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1920193117. Epub 2020 Mar 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32205444 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- The diverse roles of neutrophils from protection to pathogenesis.
Herro R, Grimes HL. Herro R, et al. Nat Immunol. 2024 Dec;25(12):2209-2219. doi: 10.1038/s41590-024-02006-5. Epub 2024 Nov 20. Nat Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39567761 Review. - Circulating Neutrophil Profiles Undergo a Dynamic Shift during Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH) Progression.
Maretti-Mira AC, Salomon MP, Chopra S, Yuan L, Golden-Mason L. Maretti-Mira AC, et al. Biomedicines. 2024 May 16;12(5):1105. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12051105. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38791066 Free PMC article. - Lipoxygenases at the Intersection of Infection and Carcinogenesis.
Amoah AS, Pestov NB, Korneenko TV, Prokhorenko IA, Kurakin GF, Barlev NA. Amoah AS, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 2;25(7):3961. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073961. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612771 Free PMC article. Review. - NMDAR activation attenuates the protective effect of BM-MSCs on bleomycin-induced ALI via the COX-2/PGE2 pathway.
Li XH, Huang P, Cheng HP, Zhou Y, Feng DD, Yue SJ, Han Y, Luo ZQ. Li XH, et al. Heliyon. 2023 Dec 19;10(1):e23723. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23723. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38205313 Free PMC article. - Perturbational phenotyping of human blood cells reveals genetically determined latent traits associated with subsets of common diseases.
Homilius M, Zhu W, Eddy SS, Thompson PC, Zheng H, Warren CN, Evans CG, Kim DD, Xuan LL, Nsubuga C, Strecker Z, Pettit CJ, Cho J, Howie MN, Thaler AS, Wilson E, Wollison B, Smith C, Nascimben JB, Nascimben DN, Lunati GM, Folks HC, Cupelo M, Sridaran S, Rheinstein C, McClennen T, Goto S, Truslow JG, Vandenwijngaert S, MacRae CA, Deo RC. Homilius M, et al. Nat Genet. 2024 Jan;56(1):37-50. doi: 10.1038/s41588-023-01600-x. Epub 2023 Dec 4. Nat Genet. 2024. PMID: 38049662 Free PMC article.
References
- Allen L., Dockrell D. H., Pattery T., Lee D. G., Cornelis P., Hellewell P. G., et al. (2005). Pyocyanin production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa induces neutrophil apoptosis and impairs neutrophil-mediated host defenses in vivo. J. Immunol. 174, 3643–3649 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous