p21-activated kinase has substrate specificity similar to Acanthamoeba myosin I heavy chain kinase and activates Acanthamoeba myosin I - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
p21-activated kinase has substrate specificity similar to Acanthamoeba myosin I heavy chain kinase and activates Acanthamoeba myosin I
H Brzeska et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997.
Abstract
Acanthamoeba class I myosins are unconventional, single-headed myosins that express actin-activated Mg2+-ATPase and in vitro motility activities only when a single serine or threonine in the heavy chain is phosphorylated by myosin I heavy chain kinase (MIHCK). Some other, but not most, class I myosins have the same consensus phosphorylation site sequence, and the two known class VI myosins have a phosphorylatable residue in the homologous position, where most myosins have an aspartate or glutamate residue. Recently, we found that the catalytic domain of Acanthamoeba MIHCK has extensive sequence similarity to the p21-activated kinase (PAK)/STE20 family of kinases from mammals and yeast, which are activated by small GTP-binding proteins. The physiological substrates of the PAK/STE20 kinases are not well characterized. In this paper we show that PAK1 has similar substrate specificity as MIHCK when assayed against synthetic substrates and that PAK1 phosphorylates the heavy chain (1 mol of P(i) per mol) and activates Acanthamoeba myosin I as MIHCK does. These results, together with the known involvement of Acanthamoeba myosin I, yeast myosin I, STE20, PAK, and small GTP-binding proteins in membrane- and cytoskeleton-associated morphogenetic transformations and activities, suggest that myosins may be physiological substrates for the PAK/STE20 family and thus mediators of these events.
Figures
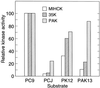
Figure 1
Substrate specificities of Acanthamoeba MIHCK, 35K, and PAK1. Kinase activities were determined as described with the synthetic peptides described in Table 1 as substrates. MIHCK was fully activated by autophosphorylation (11) before its assay; expressed 35K is fully active without autophosphorylation (17). His-PAK1 is constitutively active (U.G.K., unpublished observations). To compare their relative substrate specificities, the activities were normalized to their activities with PC9 as substrate as 100; the actual specific activities with PC9 were: MIHCK, 26 μmol·min−1·mg−1; 35K, 27 μmol·min−1·mg−1; and His-PAK1, 0.37 μmol·min−1·mg−1.
Figure 2
Autoradiography of the heavy chain of Acanthamoeba myosin IC after phosphorylation with expressed 35K and PAK1. Myosin IC was incubated with [γ-32P]ATP and either 35K (Left) or His-PAK1 (Right) as described for the indicated times. The reactions were stopped by addition of SDS sample buffer and the samples separated by PAGE. The autoradiogram of the myosin IC heavy chains is shown. The level of phosphorylation was ≈1 mol of Pi per mol in all samples except the 5-min 35K sample, which was ≈0.8 mol of Pi per mol.
Similar articles
- Myosin I heavy chain kinase: cloning of the full-length gene and acidic lipid-dependent activation by Rac and Cdc42.
Brzeska H, Young R, Knaus U, Korn ED. Brzeska H, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Jan 19;96(2):394-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.2.394. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 9892644 Free PMC article. - Calmodulin-binding and autoinhibitory domains of Acanthamoeba myosin I heavy chain kinase, a p21-activated kinase (PAK).
Brzeska H, Young R, Tan C, Szczepanowska J, Korn ED. Brzeska H, et al. J Biol Chem. 2001 Dec 14;276(50):47468-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M108957200. Epub 2001 Sep 28. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11579107 - The catalytic domain of acanthamoeba myosin I heavy chain kinase. II. Expression of active catalytic domain and sequence homology to p21-activated kinase (PAK).
Brzeska H, Szczepanowska J, Hoey J, Korn ED. Brzeska H, et al. J Biol Chem. 1996 Oct 25;271(43):27056-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.43.27056. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8900196 - Regulation of Dictyostelium myosin I and II.
de la Roche MA, Côté GP. de la Roche MA, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001 Mar 15;1525(3):245-61. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(01)00110-6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001. PMID: 11257438 Review. - Structure-function studies on Acanthamoeba myosins IA, IB, and II.
Korn ED, Atkinson MA, Brzeska H, Hammer JA 3rd, Jung G, Lynch TJ. Korn ED, et al. J Cell Biochem. 1988 Jan;36(1):37-50. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240360105. J Cell Biochem. 1988. PMID: 3277984 Review.
Cited by
- Identification by mass spectrometry of the phosphorylated residue responsible for activation of the catalytic domain of myosin I heavy chain kinase, a member of the PAK/STE20 family.
Szczepanowska J, Zhang X, Herring CJ, Qin J, Korn ED, Brzeska H. Szczepanowska J, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Aug 5;94(16):8503-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.16.8503. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. PMID: 9238006 Free PMC article. - How are the cellular functions of myosin VI regulated within the cell?
Buss F, Kendrick-Jones J. Buss F, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008 Apr 25;369(1):165-75. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.11.150. Epub 2007 Dec 7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008. PMID: 18068125 Free PMC article. Review. - p21-activated kinase 1 (Pak1) regulates cell motility in mammalian fibroblasts.
Sells MA, Boyd JT, Chernoff J. Sells MA, et al. J Cell Biol. 1999 May 17;145(4):837-49. doi: 10.1083/jcb.145.4.837. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10330410 Free PMC article. - Endocytic myosin-1 is a force-insensitive, power-generating motor.
Pedersen RTA, Snoberger A, Pyrpassopoulos S, Safer D, Drubin DG, Ostap EM. Pedersen RTA, et al. J Cell Biol. 2023 Oct 2;222(10):e202303095. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202303095. Epub 2023 Aug 7. J Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37549220 Free PMC article. - Analysis of the regulatory phosphorylation site in Acanthamoeba myosin IC by using site-directed mutagenesis.
Wang ZY, Wang F, Sellers JR, Korn ED, Hammer JA 3rd. Wang ZY, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Dec 22;95(26):15200-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.26.15200. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9860946 Free PMC article.
References
- Sellers J R, Goodson H V, Wang F. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1996;17:67–75. - PubMed
- Korn E D. Curr Top Membr Transp. 1991;38:13–30.
- Wolenski J A. Trends Cell Biol. 1995;5:310–317. - PubMed
- Brzeska H, Lynch T J, Korn E D. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:427–435. - PubMed
- Jung J, Hammer J A., III FEBS Lett. 1994;342:197–202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous