arviz.plot_trace — ArviZ dev documentation (original) (raw)
arviz.plot_trace(data, var_names=None, filter_vars=None, transform=None, coords=None, divergences='auto', kind='trace', figsize=None, rug=False, lines=None, circ_var_names=None, circ_var_units='radians', compact=True, compact_prop=None, combined=False, chain_prop=None, legend=False, plot_kwargs=None, fill_kwargs=None, rug_kwargs=None, hist_kwargs=None, trace_kwargs=None, rank_kwargs=None, labeller=None, axes=None, backend=None, backend_config=None, backend_kwargs=None, show=None)[source]#
Plot distribution (histogram or kernel density estimates) and sampled values or rank plot.
If divergences data is available in sample_stats, will plot the location of divergences as dashed vertical lines.
Parameters:
data: obj
Any object that can be converted to an arviz.InferenceData object Refer to documentation of arviz.convert_to_dataset() for details
var_names: str or list of str, optional
One or more variables to be plotted. Prefix the variables by ~ when you want to exclude them from the plot.
filter_vars: {None, “like”, “regex”}, optional, default=None
If None (default), interpret var_names as the real variables names. If “like”, interpret var_names as substrings of the real variables names. If “regex”, interpret var_names as regular expressions on the real variables names. A lapandas.filter.
coords: dict of {str: slice or array_like}, optional
Coordinates of var_names to be plotted. Passed to xarray.Dataset.sel()
divergences: {“bottom”, “top”, None}, optional
Plot location of divergences on the traceplots.
kind: {“trace”, “rank_bars”, “rank_vlines”}, optional
Choose between plotting sampled values per iteration and rank plots.
transform: callable, optional
Function to transform data (defaults to None i.e.the identity function)
figsize: tuple of (float, float), optional
If None, size is (12, variables * 2)
rug: bool, optional
If True adds a rugplot of samples. Defaults to False. Ignored for 2D KDE. Only affects continuous variables.
lines: list of tuple of (str, dict, array_like), optional
List of (var_name, {‘coord’: selection}, [line, positions]) to be overplotted as vertical lines on the density and horizontal lines on the trace.
circ_var_namesstr or list of str, optional
List of circular variables to account for when plotting KDE.
circ_var_unitsstr
Whether the variables in circ_var_names are in “degrees” or “radians”.
compact: bool, optional
Plot multidimensional variables in a single plot.
compact_prop: str or dict {str: array_like}, optional
Defines the property name and the property values to distinguish different
dimensions with compact=True. When compact=True it defaults to color, it is ignored otherwise.
combined: bool, optional
Flag for combining multiple chains into a single line. If False (default), chains will be plotted separately.
chain_prop: str or dict {str: array_like}, optional
Defines the property name and the property values to distinguish different chains. If compact=True it defaults to linestyle, otherwise it uses the color to distinguish different chains.
legend: bool, optional
Add a legend to the figure with the chain color code.
plot_kwargs, fill_kwargs, rug_kwargs, hist_kwargs: dict, optional
Extra keyword arguments passed to arviz.plot_dist(). Only affects continuous variables.
trace_kwargs: dict, optional
Extra keyword arguments passed to matplotlib.axes.Axes.plot()
labellerlabeller instance, optional
Class providing the method make_label_vert to generate the labels in the plot titles. Read the Label guide for more details and usage examples.
rank_kwargsdict, optional
Extra keyword arguments passed to arviz.plot_rank()
axes: axes, optional
Matplotlib axes or bokeh figures.
backend: {“matplotlib”, “bokeh”}, optional
Select plotting backend.
backend_config: dict, optional
Currently specifies the bounds to use for bokeh axes. Defaults to value set in rcParams.
backend_kwargs: dict, optional
These are kwargs specific to the backend being used, passed tomatplotlib.pyplot.subplots() orbokeh.plotting.figure().
show: bool, optional
Call backend show function.
Returns:
axes: matplotlib axes or bokeh figures
See also
Plot rank order statistics of chains.
Examples
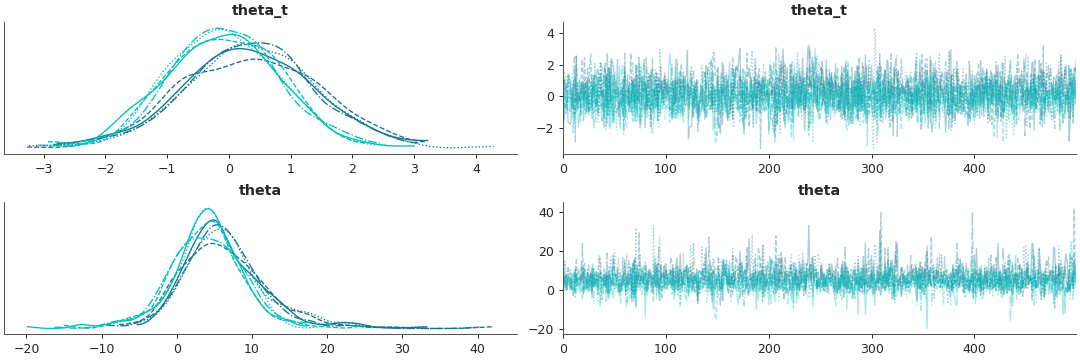
Plot a subset variables and select them with partial naming
import arviz as az data = az.load_arviz_data('non_centered_eight') coords = {'school': ['Choate', 'Lawrenceville']} az.plot_trace(data, var_names=('theta'), filter_vars="like", coords=coords)
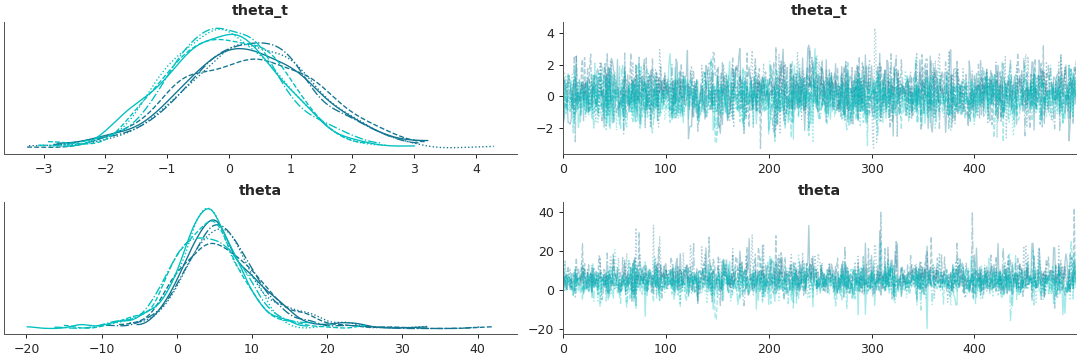
Show all dimensions of multidimensional variables in the same plot
az.plot_trace(data, compact=True)
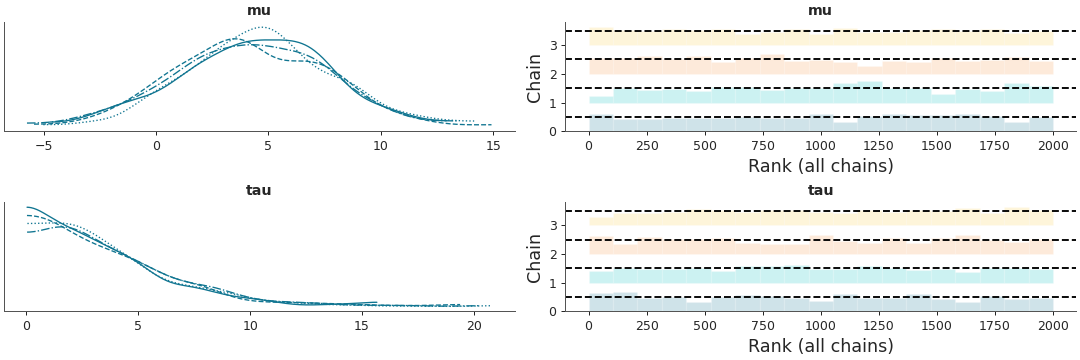
Display a rank plot instead of trace
az.plot_trace(data, var_names=["mu", "tau"], kind="rank_bars")
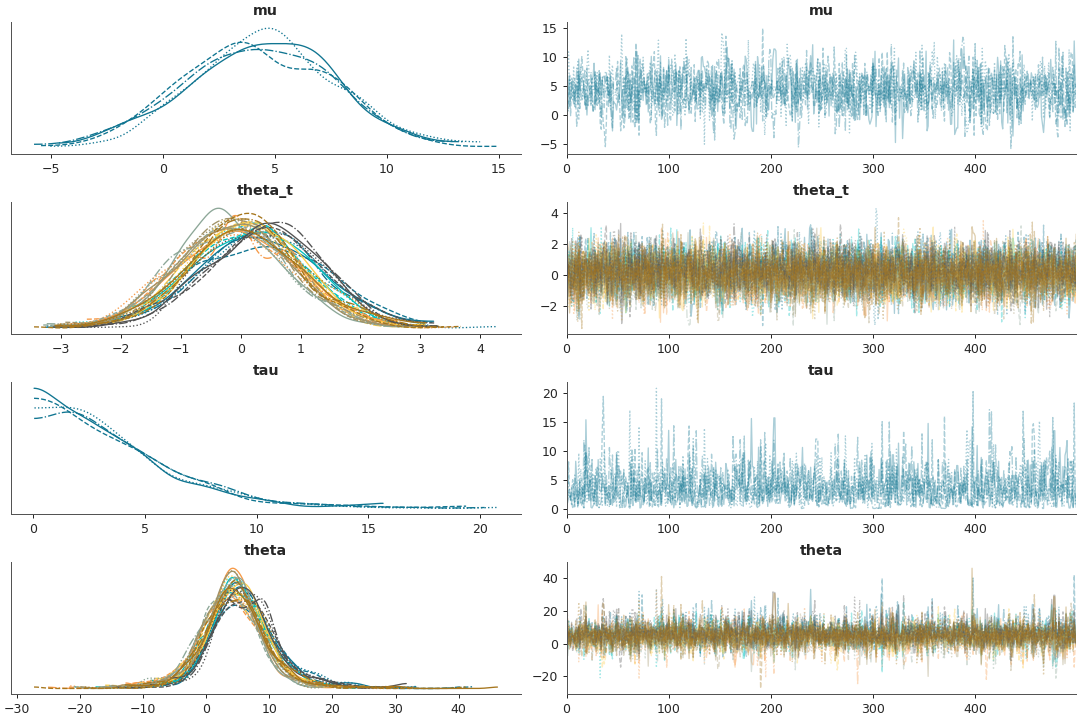
Combine all chains into one distribution and select variables with regular expressions
az.plot_trace( data, var_names=('^theta'), filter_vars="regex", coords=coords, combined=True )
Plot reference lines against distribution and trace
lines = (('theta_t',{'school': "Choate"}, [-1]),) az.plot_trace(data, var_names=('theta_t', 'theta'), coords=coords, lines=lines)