Role of astrocytic glutamate transporter in alcohol use disorder (original) (raw)
Abstract
Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is one of the most widespread neuropsychiatric conditions, having a significant health and socioeconomic impact. According to the 2014 World Health Organization global status report on alcohol and health, the harmful use of alcohol is responsible for 5.9% of all deaths worldwide. Additionally, 5.1% of the global burden of disease and injury is ascribed to alcohol (measured in disability adjusted life years, or disability adjusted life years). Although the neurobiological basis of AUD is highly complex, the corticostriatal circuit contributes significantly to the development of addictive behaviors. In-depth investigation into the changes of the neurotransmitters in this circuit, dopamine, gamma-aminobutyricacid, and glutamate, and their corresponding neuronal receptors in AUD and other addictions enable us to understand the molecular basis of AUD. However, these discoveries have also revealed a dearth of knowledge regarding contributions from non-neuronal sources. Astrocytes, though intimately involved in synaptic function, had until recently been noticeably overlooked in their potential role in AUD. One major function of the astrocyte is protecting neurons from excitotoxicity by removing glutamate from the synapse via excitatory amino acid transporter type 2. The importance of this key transporter in addiction, as well as ethanol withdrawal, has recently become evident, though its regulation is still under investigation. Historically, pharmacotherapy for AUD has been focused on altering the activity of neuronal glutamate receptors. However, recent clinical evidence has supported the animal-based findings, showing that regulating glutamate homeostasis contributes to successful management of recovery from AUD.
Keywords: Alcohol, Addiction, Glutamate, Astrocyte, Excitatory amino acid transporter type 2, Glia, Striatum
Core tip: Review of astroglial involvement in alcohol use disorder and potential for astrocyte-specific glutamate transporter excitatory amino acid transporter type 2 (EAAT2, Slc1a2)/GLT-1 in pharmacological treatment, including alcohol withdrawal symptoms.
INTRODUCTION
Substance abuse and addiction is a pervasive problem at all socioeconomic levels worldwide. Alcohol, though one of the most common addictive substances, is recreationally used by many people without incident. Alcohol use disorder (AUD) or alcohol addiction often results in one of the most lethal sets of withdrawal symptoms, including seizures, hallucinations, and delirium tremens, termed alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS). As with most addictive substances, craving and relapse rates are high, and predictability, and even recognition, of addiction is difficult to ascertain. This makes alleviation of withdrawal symptoms the primary focus on treating AUD.
Like other neuropsychiatric conditions, AUD involves dysfunction of normal signaling pathways. Importantly, neurons are not the only cells involved in neural signaling. The majority of cells in the central nervous system (CNS) are of the glial lineage[1]. Two of the major glial cell types, oligodendrocytes and microglia, have been well characterized, as they are relatively monofunctional: Oligodendrocytes myelinate neurons, and microglia regulate the CNS immune response[2]. Ironically, the most abundant glia, the astrocyte, is not as well understood. Its diverse role in maintaining vascular integrity and metabolic homeostasis, and regulating synaptogenesis and immune response[1,3], means that its morphology and gene expression vary greatly depending on its location, local contacts, and microenvironment[4,5].
AWS is attributed to elevated extracellular glutamate levels in certain brain regions, such as the striatum and hippocampus[6-8]. These regions are part of the mesocorticolimbic circuit, which is highly implicated in addiction disorders[9,10]. Astrocytes provide critical regulation of synaptic glutamate concentrations in these regions through bi- and uni-directional transporters. Glutamate, the most important excitatory neurotransmitter in the CNS, serves to stimulate action potentials by activating its cognate ionotropic receptors on the postsynaptic neurons, and modulate synaptic connectivity through its cognate metabotropic receptors. Astrocytes are responsible for removing glutamate from the extracellular space, thereby limiting its effects. Within the astrocyte, glutamate is converted to glutamine via glutamine synthetase, and released back out to the extracellular environment for uptake by presynaptic neurons, which convert it back to glutamate to be packaged into vesicles for synaptic release. In AWS, this glutamatergic tone is dysregulated, resulting in a hyperglutamatergic state that can lead to neuronal excitotoxicity. Clinically, benzodiazepines are often used to alleviate withdrawal symptoms, but patients can become physically dependent on these, as well[11].
Animal models have been extremely useful in studying addiction. The rodent corticolimbic circuitry is very similar to human, and thus provides an effective method for studying various aspects of the addiction and withdrawal processes. Certain species are useful for studying behaviors of different points and aspects of the addiction process, including consumption, preference, learning, tolerance, and withdrawal[12]. Additionally, through genetic manipulation of specific components of glutamatergic signaling, we have come to understand ethanol’s effects on involved neuronal glutamate receptors, such as NMDA and AMPA receptors[13-17]. This review will focus on the role of glia in neuronal function, both normal and pathological, and illuminate the importance of understanding astrocyte function in neuropsychiatric disorders, like AUD.
GLIAL FUNCTION IN NEUROPSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS
Glial cells are mostly known for their contributions to physiological processes and pathological involvement. There are many more glial cells than neurons (glia to neuron ratio = 4:1), and they are generally smaller[18]. Three subtypes have been identified in the CNS: Astrocytes, microglia and oligodendrocytes. The major function of glial cells is to maintain homeostasis in the CNS, including supporting blood vessels, providing nutrition and oxygen to neurons, regulating neurotransmitter metabolism and modulating the immune response. Therefore, balance disruption derived from any of these cell types could be associated with multiple kinds of psychiatric disorders.
Oligodendrocytes are one of the more numerous than the types of glial cells. Their primary role is to myelinate axons, which increases the resistance and reduces the effective capacitance of axonal membranes, accelerating the transmission of electrical signals. They arise from a large population of oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPCs), a source of replacement cells for damaged oligodendrocytes after injury or in disease. There are multiple trophic and growth factors that maintain oligodendrocyte survival and myelination[19]. One therapeutic option is to increase and amplify this OPC pool once the pathologically activated signaling pathways are identified[20]. Moreover, mounting evidence shows that oligodendrocytes may also play a critical role in neuropsychiatric disorders[21].
Astrocytes represent highly heterogeneous mediators that interact directly with neurons, which is crucial for maintaining brain function. Astrocytes play an essential role in neurogenesis and the development of the CNS, energy metabolism, synaptic signaling, immune defense, amino acid neurotransmitter clearance, neurotrophin production and ionic homeostasis[22]. More recently, many studies have suggested that astrocyte dysregulation is associated with neuropsychiatric disorders, such as Wernicke’s encephalopathy[23] and Korsakoff psychosis[24], schizophrenia[25], depression and addiction[26].
Microglia originates from hematopoietic progenitors and have been considered the resident immune cells in CNS. However, recent evidence has provided a notion that microglia are not only activated by inflammatory challenge or neuronal damage, but that they extend an array of physiological functions through synaptic maturation[27], maintenance of CNS homeostasis, memory processes and neurogenesis[28]. Additionally, disturbance of microglia responding to minor pathological intrusion is implicated in multiple neuropathological and neuropsychiatric disorders.
Pathological potential of neuroglia in AUD
Astrocytes play critical roles in CNS abnormalities associated with ethanol-induced neurotoxicity. Chronic ethanol exposure profoundly affects the expression of GFAP, an astroglial stress fiber, as well as the function of astrocytes. One interesting study found that by increasing astrocyte number by injecting purified astrocytes into rat forebrain learning and memory abilities associated with cholinergic signal recovery were improved[29]. It is well known that alcohol and its metabolite acetaldehyde show direct neurotoxicity by disturbing thiamine-related enzymes, resulting in thiamine deficiency and damage to astrocytes[30]. Our laboratory demonstrated the importance of adenosine signaling in regulating alcohol-related behaviors. Mice lacking type 1 equilibrative nucleoside transporter (ENT1), the glial transporter responsible for maintaining adenosine tone in the synapse, consume more ethanol in two bottle choice experiments when compared to wild-type littermates[31]. In addition, antagonists and agonists acting on the adenosine A2A receptor (A2AR) modulate ethanol preference and withdrawal symptoms. Moreover, inhibition of A2AR in the dorsomedial striatum promoted goal-directed behavior and increased sucrose or ethanol drinking[32]. We revealed that deletion of ENT1 decreased the expression of astrocytic glutamate transporter GLT-1, the protein responsible for regulating extracellular glutamate concentration in the striatum. Adenosine-mediated glutamate signaling in neuroglial interaction in ethanol intoxication and preference has been thoroughly described elsewhere[33,34].
Microglia are the resident macrophages and are distributed ubiquitously throughout the CNS. Alterations in microglia have even been noted in AUD models. After intensive chronic ethanol intoxication in rats, there were structural lesions in the CNS, including infiltration of mononuclear cells and lymphocytic-microglial nodules[35]. Changes in immune-related genes have been found in human alcoholic brain, including chemokines (Ccl2, Ccl3) and chemokine receptors (Ccr5, Ccr1 motif)[36]. Consumption and preference of ethanol decreased in mice after deleting either chemokines (Ccl2 or Ccl3) or chemokine receptors (Ccr2). Particularly the proinflammatory cytokine, CCL2, was extensively higher in alcoholics[37]. Also, consecutive 10-d injection of ethanol increased pro-inflammatory cytokine TNFα in the brain. Meanwhile, ethanol enhanced LPS-induced increases in TNFα, MCP-1, and IL-1β in brain[38]. Previous studies indicated that TLR4 response might be a vital mechanism of chronic ethanol-induced neuro-inflammation. The signaling pathways related to IL-1RI/TLR4 receptors were facilitated by chronic ethanol treatment[39], while the deletion of TLR4 prevented ethanol-induced glial activation and production of inflammatory mediators[40].
Regarding oligodendrocytes, alcohol appears to have different effects, but much of the evidence points toward reduced oligodendrocyte function. Prenatal alcohol exposure decreased the level of myelin basic protein (MBP) expression[41], consequently leading to a reduction in brain myelination that may contribute to the development of fetal alcohol syndrome[42]. Protein kinase C was activated after ethanol exposure, which delays MBP expression in differentiating CG-4 oligodendrocytes. Oligodendrocyte myelin glycoprotein was significantly decreased in rat hippocampus by chronic ethanol exposure[43]. This deficit may explain the demyelination observed in human alcoholics[44]. Recent studies showed that premyelinate oligodendrocytes and myelin-associated protein were decreased in medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) during chronic intermittent ethanol vapor exposure (CIE). However, protracted abstinence increased MBP levels in the mPFC, possibly a compensatory effect after CIE[45]. In contrast, the activity of enzyme 2’, 3’-cyclic nucleotide 3’-phosphodiesterase, a maker for oligodendrocytes, was increased in ethanol-treated cultures[46].
Neuroglia pathology in other psychiatric conditions
Glial pathology is also implicated in other neuropsychiatric conditions, like schizophrenia and bipolar disorder (BD). One study demonstrated decreased astrocytic gene expression in the deep layers of the anterior cingulate gyrus, including excitatory amino acid transporter 2 (EAAT2)[47]. In this regard, animal models have been somewhat helpful in investigating structural changes, glycogen metabolism and glutamate signaling[48].
BD, like AUD, involves the corticostriatal circuit. Morphometric postmortem and neuroimaging studies found decreased glial cell density in the mPFC of patients with BD[49]. Recent studies indicate that chronic treatment with anti-bipolar drugs could inhibit astroglial glutamate release[50]. Additionally, S100β, a neurotrophic factor mainly released by astrocytes, was increased after chronic lithium treatment, although astrocytes or interaction between neurons and astrocytes were unaffected[51].
Regarding microglia, studies in schizophrenia patients have yielded more consistent results. Microglia are activated along with increased cell population in the postmortem brains of schizophrenic patients[52]. Consistently, the level of cytokines, IL-1β, IL-6, and TGF-β, were elevated in schizophrenia. Interestingly, these alterations were reversed by antipsychotic treatment[53]. The dysfunction of microglia is associated with impairment of nervous system development, synaptic formation and pruning[27,54], processes that may also affect neural circuitry in AUD.
Neuroinflammation has also been linked to BD. The level of IL-1β was increased in cerebrospinal fluid of euthymic BD patients when compared with normal controls, and even higher in those who had recently experienced one or more manic/hypomanic episodes[55]. In addition, microglia activation induced higher levels of IL-1β, which was associated with increased suicide behavior in BD patients[56]. Moreover, concentrations of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are associated with increased activation of MAPK and NF-κB pathways in BD patients, were higher, as well. These results suggest that microglia play a potentially crucial role in BD. Interestingly, there is an increased incidence of BD in patients with the autoimmune disorder, multiple sclerosis, where oligodendrocytes are targeted by the immune system. And, oligodendrocytic markers are down regulated in patients with BD[57].
Multiple studies have confirmed oligodendrocytes and myelination are impaired in schizophrenia[58-60]. Oligodendrocytic and myelination abnormalities damage saltatory conduction and information transfer between neurons in schizophrenia[61]. White matter anomalies were found in schizophrenia patients from maternal and early postnatal immune challenge[62], perinatal hypoxia[63], and during childhood and adolescence[58,64], suggesting that damage to axonal integrity and conduction velocity may play a causal role in schizophrenia.
Taken together, studying glial cells is warranted for understanding neuropsychiatric disorders in regards to glutamatergic abnormalities.
SYNAPTIC, PERISYNAPTIC AND EXTRASYNAPTIC ASTROCYTIC PROCESSES IN REGULATING GLUTAMATE SIGNALING
Neurons connect to each other with a kind of chemical junction called a synapse, which consists of the pre-synapse, post-synapse, and synaptic cleft as a key information communication relay and central functional element of the nervous system[65,66]. Each neuron can receive a number of synaptic inputs and these synapses have diverse properties, including the type of neurotransmitter and the number of postsynaptic receptors. Neurotransmitter vesicles accumulate in the presynaptic terminal, while the neurotransmitter receptors located in the postsynaptic neurons are recruited to the postsynaptic.
Synaptic astrocytic processes
Astrocytes were widely thought to provide only metabolic and physical support for neurons, but now they are demonstrated to directly participate in neuronal signaling, even locally at synapses[67,68]. Many investigations have shown that astrocytes exhibit unique biophysical and functional electrical properties, are sensitive to neuronal activity and are actually involved in the control of synaptic transmission. Astrocytes are indeed equipped to sense and integrate neuronal information through ionic channels, neurotransmitter receptors and transporters, and intracellular signaling pathways[69]. Astrocytes are also known to influence synaptic activity via synthesizing and recycling glutamate[70] and responding to synaptic release of neurotransmitters[68,71,72]. Glutamate, as a major neurotransmitter in the brain, exerts a critical role in mediating synaptic activity and also causing a response in astrocytes[73,74]. Importantly, the involvement of astrocytes in glutamatergic regulation is very widespread, as most glutamate is taken up by transporters expressed on astrocytic membranes when it is released into the extracellular space between neurons[75,76], and it is estimated that only 20% of synaptic glutamate is taken up by transporters on the postsynaptic neurons[77]. Astrocytes can synchronize with neuronal activity, and subsequently regulate glutamate transmission between neurons[78]. Astrocyte-to-neuron glutamate signaling may mediate activity-dependent modulation of inhibitory synapses in the hippocampus, with glial glutamate release taking place at some distance from the synapse[79]. The increases in calcium (Ca2+) evoked by neuronal activity results in a release of glutamate from astrocytes[80,81]. This release of glutamate process is known to be a Ca2+-dependent exocytic pathway[82]. In addition, during synaptic activity neurons or astrocytes release ATP, which cause an increase in intracellular (Ca2+), mediated by the P2Y1 type purinergic receptors (P2Y1Rs) in hippocampal astrocytes[83]. As a G protein coupled receptor, P2Y1R signaling in astrocytes is coupled to Ca2+-dependent glutamate exocytosis[84,85].
Glutamate is able to induce a wide range of effects in astrocytes via metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR), NMDA receptors, and AMPA receptors[86]. Hippocampal astrocytes express functional AMPA receptors[87], the properties of which can be changed by astrocytes during postnatal development. It has been reported that immature astrocytes had a prolonged activation of the AMPA receptors, while glutamate responses were greatly increased as astrocytes matured. In addition, the presynaptic NMDA receptors are activated and the excitatory communication between neurons is increased once astrocytic glutamate is released[85]. Additionally, astrocytes also use the mGluRs to modulate neuronal activity. However, previous results suggest developmental changes in the expression of mGluRs in astrocytes[88], predicting its important role in development. Reports reveal that synaptic glutamate stimulates astrocytic mGluRs and subsequently triggers glutamate release from astrocytes[80,89].
Perisynaptic astrocytic processes
It has recently been recognized that astrocytes act as a third partner in synaptic processes, leading to the description of a “tripartite synapse[90]”, with the astrocytic processes in close apposition to the synaptic cleft[91]. Perisynaptic astrocytic processes (PAPs), assumed to mediate this communication, may detect glutamate spillover and other substances from active synapses[76,92]. Glutamate can also cause structural alterations of astrocytes, driving them to extend and modify their own processes[73,93] (Figure 1). It is thought that PAPs position next to the synaptic cleft, as the effectors of glia-neuronal crosstalk at the synapse, to exert their roles in ion buffering and transmitter uptake, thus keeping a low diffusion distance[94]. Glutamine synthetase is mainly expressed in the PAPs around identified glutamatergic synapses[95].
Figure 1.
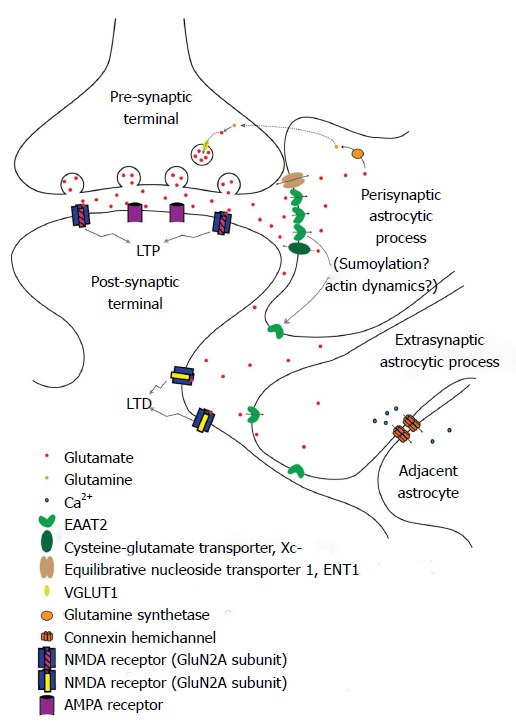
Fine regulation of glutamate levels and excitatory amino acid transporter 2 localization in neuron-glial interaction. The perisynaptic astrocytic process contains a higher concentration of EAAT2 immediately adjacent to the synapse. The EAP also contains EAAT2, but in lower concentrations. Glutamate spillover results in activation of GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors (increasing LTD response in the post-synaptic neuron), increased EAAT2 surface expression on and migration of EAPs, and activation of adjacent astrocytes via calcium waves propagated through connexin channels. LTP: Long term potentiation; LTD: Long term depression; EAAT2: Excitatory amino acid transporter 2; Xc-: Cysteine-glutamate transporter; ENT1: Equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1; VGLUT1: Vesicular glutamate transporter 1; NMDA: N-Nitrosodimethylamine; AMPA: α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid; EAP: Extrasynaptic astrocytic process.
There have been a few approaches that described peripheral astrocyte processes related to synapses using direct or indirect observations. Glial gamma-aminobutyricacid (GABA) receptor channels could be of functional importance in buffering extracellular Cl- in the perisynaptic microenvironment using patch-clamp techniques, and might relate to mechanisms not present in the peripheral processes[96]. Electrically stimulated parallel fibers increased intracellular calcium concentration in peripheral processes of Bergmann glia, astrocytic cells located in the cerebellum[97]. The transmitter release is affected by reduction in glutamate clearance through modulation of presynaptic mGluR. Therefore, astrocytic wrapping of neurons may contribute to the regulation of synaptic efficacy in the CNS[98]. Glia-synaptic interactions can be attributed to the astrocytic peripheral processes in the perisynaptic microenvironment. As the functions of PAPs displayed might not be representative of the astrocyte as a whole, they could be recognized as a specialized astroglial compartment[94].
Extrasynaptic astrocytic processes
In some instances, glutamate may escape from the synaptic cleft, generating extrasynaptic glutamate dynamics[99,100]. The kinetic simulations of extrasynaptic glutamate uptake show that glutamate can bind to several subtypes of receptors, but transporters rapidly reduce the free concentration of transmitter[101]. Extrasynaptic glutamate dynamics is believed to regulate a variety of important neural and glial functions including synaptic transmission[102], synaptic plasticity[103], synaptic crosstalk[104,105], nonsynaptic neurotransmission[106], neuronal survival[107], and gliotransmitter release[108].
Synaptic “spillover”, or extracellular diffusion of transmitters and modulators after extrasynaptic release in the local circuit regions, is an important short distance form of volume neurotransmission. The neurotransmitters bind to extrasynaptic neuronal and glial receptors and then activate related signaling pathways in the neuroglial networks of the brain (Figure 1). G protein-coupled receptor heteromers play a major role in the integrative processes of extrasynaptic signaling on glutamatergic synapses. The balance of activity in the different types of projection neurons is determined by the diverse distributions of high affinity receptors on the neurons and glia, where both neuronal extrasynaptic and long distance volume transmission signaling can be involved[109]. Temporal resolution at axon terminals of fast-spiking neurons might be due to rapid glutamate receptor desensitization. Transmitter diffusion is partly responsible for transmitter clearance from the synaptic cleft[76]. The glutamate transient duration seen at a distance from the release site can be greatly increased if interactions between glutamate and extrasynaptic binding sites reduce the effective diffusion constant, resulting in a greater probability of NMDA receptor activation[110]. Relatively small amounts of glutamate are likely to activate extrasynaptic receptors, especially if the diffusion coefficient in the extracellular medium is low[101]. Extrasynaptic glutamate spillover implies significant cross-talk between neighboring synapses, which could have major repercussions for information processing[111].
GLUTAMATE TRANSPORTERS IN AUD
Glutamate is arguably the most important neuroexcitatory amino acid in the CNS. As such, its concentration, both intra- and extra-cellularly, is tightly regulated by membrane transporters. Within neurons, the vesicular glutamate transporters, of which there are three known subtypes[112], pack glutamate from the cytosol into presynaptic vesicles utilizing the proton electrochemical gradient[113]. In glia, the cysteine-glutamate transporter (Xc-) is the major transporter responsible for releasing glutamate into the extracellular space, while a family of sodium-dependent transporters, called excitatory amino acid transporters (EAAT), removes glutamate from the extracellular environment. The function of these latter transporters is critical, as excessive synaptic glutamate can lead to neuronal excitoxicity and/or death. There are five mammalian EAAT subtypes (EAAT1-EAAT5) that have been identified to date. EAAT1 and EAAT2 (in rodents, designated glutamate and aspartate transporter, GLAST, and glutamate transporter 1, GLT-1, respectively) are the primary subtypes responsible for extracellular glutamate clearance throughout the CNS during neurotransmission, and are predominantly expressed in astrocytes[114,115]. EAAT1 is most abundantly expressed in the cerebellum, while EAAT2 has a more ubiquitous expression pattern, which is strongest in the forebrain[116]. EAAT3 (EAAC1 in rodents) is the most widely distributed, expressed in peripheral tissues, as well as in both neurons and astrocytes[117]. EAAT4 is most strongly expressed in cerebellar Purkinje cells[118], and EAAT5 is almost exclusively expressed in the retina[119].
In recent years, EAAT2 has received increasing attention in addiction research, as it is the primary EAAT subtype expressed in the striatum, a component of the basal ganglia that has been implicated in addiction and other psychiatric disorders, and is responsible for clearance of at least 90% of extracellular glutamate. Conceptually, alterations in EAAT2 surface expression should impact neurotransmission, and indeed, this has been demonstrated[120,121].
Structure, function and localization
Structurally, EAATs contain eight transmembrane segments. The N-terminal structures are involved in intersubunit contacts, while the C-terminal half is implicated in substrate transport[122]. EAATs appear to be oligomeric, and EAAT2 tends to form homotrimers and heterotrimers with its other isoforms[123,124], generating a bowl-shaped complex with the aqueous, concave side facing the extracellular space and the pointed side facing the cytoplasm. Interestingly, between the subunits on the hydrophobic transmembrane sides are distinct crevices that allow lipids to interact with key functional domains of the transporter[122], suggesting a role for lipid modulation of EAAT2 activity.
EAATs are capable of transporting both glutamate and aspartate. With one molecule of glutamate, they co-transport three sodium ions and one proton in exchange for one potassium ion[122]. Mouse EAAT2 (GLT-1) shares 97% sequence homology with humans and 99% with rats[125]. The Km of EAAT2 is fairly small (for D-aspartate, 17 ± 5 μmol/L for mouse[126], 54 ± 9 μmol/L for human[127]). Synaptic levels of glutamate can be as high as 1 mmol/L[128], so transport of glutamate out of the synapse occurs very rapidly. In this way, EAAT2 maintains low extracellular glutamate concentrations, preventing it from reaching excitotoxic levels.
In the striatum, EAAT2 is primarily located on the membrane surface of astrocytes, but can also be found on the outer mitochondrial membrane, on rough endoplasmic reticulum, and on polyribosomes[129]. EAAT2 tends to concentrate at cellular processes adjacent to glutamatergic synapses (PAPs; Figure 1) and in astrocytic endfeet near capillaries in the neurovascular unit[1]. It is tightly associated with cholesterol-rich lipid rafts[130,131], and it has been suggested that it may be part of a macromolecular complex that also contains Kir4.1 and AQP4 at capillary endfeet, implying a combined effort for glutamate and potassium ion homeostasis[132].
Glutamate transporter regulation
EAAT2, like most proteins, can be regulated by multiple methods. It is subject to transcriptional regulation by transcription factors and differential splicing, epigenetically by histone modifications and DNA methylation, post-translationally by various residue modifications, and functionally by certain toxins, membrane lipid composition, and cytoskeletal rearrangements[115,131,133-137] (Table 1 provides a more complete list of modulators).
Table 1.
Modulators of excitatory amino acid transporter 2 expression and/or function
| Compound | Demonstrated effect on EAAT2 | Process/pathway | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 17β-estradiol | Increased expression | Activation of both NF-κB and CREB | Lee et al[142] |
| cAMP/bromo-cAMP/dB-cAMP | Increased expression | PKA pathway, PI-3K and NF-κB | Su et al[115] |
| Ceftriaxone | Increased expression | Conventional NF-κB activation | Lee et al[146]; Rothestein et al[143] |
| EGF | Increased expression | Non-canonical NF-κB activation | Zelenaia et al[144] |
| PACAP | Increased expression | PKA and PKC activation | Figiel et al[139] |
| Parawixin1 | Increased transport speed | Allosteric enhancement of receptor function | Fontana et al[133] |
| Raloxifene | Increased expression | Activation of both NF-κB and CREB | Karki et al[135] |
| Riluzole | Increased expression and activity | Multiple pathways, mediated by estrogen receptors and HSF1 | Karki et al[135]; Liu et al[137] |
| Tamoxifen | Increased expression | Activation of both NF-κB and CREB | Karki et al[141] |
| TGF-α | Increased expression | Tyrosine Kinase activation | Lee et al[136]; Su et al[115] |
| TNFα | Decreased expression | Co-activation of NF-κB and N-myc | Sitcheran et al[145] |
The EAAT2 promoter contains several transcription factor binding sites, including CREB, KBBP, NF-κB, N-myc, Sp1 and Yin Yang 1[115,134,138]. The most studied of these, NF-κB, has been shown to be an effective regulator of EAAT2 expression, though by different mechanisms depending on the initiation factor[139-145]. For example, EGF-receptor stimulation induces increased EAAT2 transcription, but not via IκB degradation[115], whereas Ceftriaxone, a β-lactam antibiotic, does appear to activate EAAT2 through the canonical NF-κB pathway[146]. However, NF-κB has also been shown to reduce EAAT2 transcription through co-activation of the TNFα-mediated NF-κB activation and N-myc activation, converting NF-κB to a repressor[145] (Table 1). One intriguing method of EAAT2 up regulation is through an as yet unknown mechanism driven by the presence of neurons or neuronal supernatant in cultured astrocytes, involving NF-κB and the kappa B-motif binding phosphoprotein (KBBP)[147]. Interestingly, in cultured astrocytes, transcription factor Ying Yang 1 appears to act as a repressor by recruiting histone deacetylases, coordinating an epigenetic method of silencing the gene[134]. Hypermethylation of EAAT2 promoter DNA is another epigenetic mechanism for EAAT2 down regulation that has been suggested[147,148].
Several post-translation modifications have been suggested to control EAAT2 levels and cellular localization. EAAT2 is internalized and degraded through Nedd-2 dependent ubiquitination at its C-terminus[149]. Sumoylation may also be involved, as non-sumoylated EAAT2 is primarily localized to the plasma membrane while only sumoylated EAAT2 is found in intracellular compartments[150] (Figure 1).
Functionally, EAAT2 has been show to exhibit reduced glutamate uptake when membrane cholesterol levels are reduced[130], as suggested by the inter-subunit crevices revealed by its structure. Additionally, certain exon-skipping EAAT2 splice variants appear to have an effect on EAAT2 function and surface localization[123].
In neuropathology, EAAT1 and EAAT2 have been shown to be reduced in several neurodegenerative disorders, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, and Huntington’s disease, where it was causally related to excitotoxic neuronal cell death[151]. In AUD, one genetic variant of human EAAT2, G603A, has been associated with antisocial[152] and cirrhotic alcoholics[153]. Rodent models, however, have provided an excellent tool for studying EAAT2 in AUD. The mouse EAAT2 gene (slc1a2) is located near a quantitative trait loci on chromosome 2 (E2)[125] that modulates seizure frequency and neuro-excitability in mouse models of epilepsy and alcohol withdrawal[154]. Many mouse studies have supported the involvement of EAAT2 in both the acute and chronic effects of ethanol, as well as the symptoms of withdrawal. Mulholland et al[155] showed disruption of NMDA and EAAT2 dependent Kv2.1 potassium channels by acute ethanol in the hippocampus. Several studies have demonstrated increased glutamatergic tone in regions of the cortico-striatal circuit[156], but there are only a handful of publications providing strong support for a correlating decrease in EAAT2. Increased EAAT2 expression and/or function alleviates withdrawal symptoms and reduces ethanol consumption[157,158], highlighting the importance of EAAT2 in regulating synaptic glutamate signaling.
CONCLUSION
According to the DSM-5® (diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders), alcohol use becomes a disorder when at least two of eleven specific criteria are met, including uncontrolled consumption, alcohol craving, or a development of tolerance. Addiction is a chronic, relapsing disorder characterized by the progression from occasional, controlled use to uncontrolled use and behavior over seeking and consumption, to chronic relapse after protracted abstinence. This process involves neuroplastic changes, primarily in the mesolimbic dopamine system, going from impulsive, positively reinforced behaviors (euphoria, social aspects) to compulsive, negatively reinforced behaviors (removing withdrawal symptoms)[10,159].
Understandably, early research in the field of addiction was focused on the ascending monoamine pathways of the dopaminergic reward system (mesocorticolimbic and extended amygdala), including the involvement of GABA and serotonin, all of which are important in the early stages of addiction. In the past two decades, increased focus has shifted to glutamatergic signalling, as glutamate receptors in this system are greatly altered, and highly implicated in all stages of addiction, especially the later stages of dependence and withdrawal. The effects of alcohol on all types of glutamate receptors are under intense investigation, and much has been learned to date on how the dysregulated synaptic glutamate alters synaptic plasticity[66,67,86,121] (Figure 1). This shift in focus coincides with the success of clinical pharmacotherapies that alter the glutamatergic system. Acamprosate, a homo-taurine derivative similar in structure to GABA, especially when used with naltrexone, an opioid antagonist, has been one of the most effective drugs in preventing relapse in AUD[160]. However, the mechanistic understanding of these drugs is still not well understood. But, because of these relative successes, we are increasing our efforts in understanding synaptic glutamate modulation. For example, ceftriaxone, a beta-lactam antibiotic, has been shown not only to increase EAAT2 transcript levels, but also to attenuate ethanol consumption and withdrawal symptoms[157,158,161].
Regulation of EAAT2 and glutamate is complex, and understanding how to effectively control astrocytic EAAT2 function and/or expression could be the key to successfully treating AUD. By maintaining stable synaptic glutamatergic tone to ease withdrawal symptoms and allow re-establishment of non-pathological connections in the mesocorticolimbic circuit, recovery from addiction could be greatly ameliorated. In conclusion, a medication targeting an astrocytic glutamate transporter, especially EAAT2, will be an appropriate treatment option for AUD patients with pathologically increased glutamate levels.
Footnotes
Supported by Mayo Graduate School, NIAAA, No. AA018779; SC Johnson Genomics of Addiction Program, Ulm Family Foundation, Center for Individualized Medicine at Mayo; and David Lehr Research Award from American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Conflict-of-interest statement: No potential conflicts of interest.
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article which was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Peer-review started: September 6, 2015
First decision: November 11, 2015
Article in press: January 11, 2016
P- Reviewer: Romani A, Zhang ZM S- Editor: Ji FF L- Editor: A E- Editor: Jiao XK
References
- 1.Kandel ER, Schwarz MJ, Jessell TM. Principles of neural science. McGraw-Hill, 2000 [Google Scholar]
- 2.Volterra A, Meldolesi J. Astrocytes, from brain glue to communication elements: the revolution continues. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:626–640. doi: 10.1038/nrn1722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Barnett SC, Linington C. Myelination: do astrocytes play a role? Neuroscientist. 2013;19:442–450. doi: 10.1177/1073858412465655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Pannasch U, Rouach N. Emerging role for astroglial networks in information processing: from synapse to behavior. Trends Neurosci. 2013;36:405–417. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2013.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Heller JP, Rusakov DA. Morphological plasticity of astroglia: Understanding synaptic microenvironment. Glia. 2015;63:2133–2151. doi: 10.1002/glia.22821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rossetti ZL, Carboni S. Ethanol withdrawal is associated with increased extracellular glutamate in the rat striatum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995;283:177–183. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(95)00344-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Dahchour A, De Witte P. Effect of repeated ethanol withdrawal on glutamate microdialysate in the hippocampus. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1999;23:1698–1703. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1999.tb04063.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Saellstroem Baum S, Huebner A, Krimphove M, Morgenstern R, Badawy AA, Spies CD. Nicotine stimulation on extracellular glutamate levels in the nucleus accumbens of ethanol-withdrawn rats in vivo. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2006;30:1414–1421. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2006.00169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Everitt BJ, Robbins TW. Neural systems of reinforcement for drug addiction: from actions to habits to compulsion. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:1481–1489. doi: 10.1038/nn1579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Koob GF, Volkow ND. Neurocircuitry of addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010;35:217–238. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Amato L, Minozzi S, Davoli M. Efficacy and safety of pharmacological interventions for the treatment of the Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;(6):CD008537. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008537.pub2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ripley TL, Stephens DN. Critical thoughts on current rodent models for evaluating potential treatments of alcohol addiction and withdrawal. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;164:1335–1356. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01406.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Szumlinski KK, Lominac KD, Oleson EB, Walker JK, Mason A, Dehoff MH, Klugmann M, Cagle S, Welt K, During M, et al. Homer2 is necessary for EtOH-induced neuroplasticity. J Neurosci. 2005;25:7054–7061. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1529-05.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cowen MS, Schroff KC, Gass P, Sprengel R, Spanagel R. Neurobehavioral effects of alcohol in AMPA receptor subunit (GluR1) deficient mice. Neuropharmacology. 2003;45:325–333. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(03)00174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Boyce-Rustay JM, Holmes A. Functional roles of NMDA receptor NR2A and NR2B subunits in the acute intoxicating effects of ethanol in mice. Synapse. 2005;56:222–225. doi: 10.1002/syn.20143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gordey M, Mekmanee L, Mody I. Altered effects of ethanol in NR2A(DeltaC/DeltaC) mice expressing C-terminally truncated NR2A subunit of NMDA receptor. Neuroscience. 2001;105:987–997. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(01)00234-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kiefer F, Jahn H, Koester A, Montkowski A, Reinscheid RK, Wiedemann K. Involvement of NMDA receptors in alcohol-mediated behavior: mice with reduced affinity of the NMDA R1 glycine binding site display an attenuated sensitivity to ethanol. Biol Psychiatry. 2003;53:345–351. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(02)01486-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Yamamuro K, Kimoto S, Rosen KM, Kishimoto T, Makinodan M. Potential primary roles of glial cells in the mechanisms of psychiatric disorders. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015;9:154. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Casaccia-Bonnefil P. Cell death in the oligodendrocyte lineage: a molecular perspective of life/death decisions in development and disease. Glia. 2000;29:124–135. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1098-1136(20000115)29:2<124::aid-glia5>3.0.co;2-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gallo V, Deneen B. Glial development: the crossroads of regeneration and repair in the CNS. Neuron. 2014;83:283–308. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.06.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Nave KA. Myelination and support of axonal integrity by glia. Nature. 2010;468:244–252. doi: 10.1038/nature09614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ransom BR, Ransom CB. Astrocytes: multitalented stars of the central nervous system. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;814:3–7. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-452-0_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Burda JE, Sofroniew MV. Reactive gliosis and the multicellular response to CNS damage and disease. Neuron. 2014;81:229–248. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.12.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bernstein HG, Steiner J, Guest PC, Dobrowolny H, Bogerts B. Glial cells as key players in schizophrenia pathology: recent insights and concepts of therapy. Schizophr Res. 2015;161:4–18. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2014.03.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Barley K, Dracheva S, Byne W. Subcortical oligodendrocyte- and astrocyte-associated gene expression in subjects with schizophrenia, major depression and bipolar disorder. Schizophr Res. 2009;112:54–64. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2009.04.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Armstrong V, Reichel CM, Doti JF, Crawford CA, McDougall SA. Repeated amphetamine treatment causes a persistent elevation of glial fibrillary acidic protein in the caudate-putamen. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004;488:111–115. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Paolicelli RC, Bolasco G, Pagani F, Maggi L, Scianni M, Panzanelli P, Giustetto M, Ferreira TA, Guiducci E, Dumas L, et al. Synaptic pruning by microglia is necessary for normal brain development. Science. 2011;333:1456–1458. doi: 10.1126/science.1202529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sierra A, Encinas JM, Deudero JJ, Chancey JH, Enikolopov G, Overstreet-Wadiche LS, Tsirka SE, Maletic-Savatic M. Microglia shape adult hippocampal neurogenesis through apoptosis-coupled phagocytosis. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;7:483–495. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2010.08.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Arendt T. Impairment in memory function and neurodegenerative changes in the cholinergic basal forebrain system induced by chronic intake of ethanol. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1994;44:173–187. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-9350-1_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Butterworth RF. Pathophysiology of alcoholic brain damage: synergistic effects of ethanol, thiamine deficiency and alcoholic liver disease. Metab Brain Dis. 1995;10:1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF01991777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Choi DS, Cascini MG, Mailliard W, Young H, Paredes P, McMahon T, Diamond I, Bonci A, Messing RO. The type 1 equilibrative nucleoside transporter regulates ethanol intoxication and preference. Nat Neurosci. 2004;7:855–861. doi: 10.1038/nn1288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Nam HW, Hinton DJ, Kang NY, Kim T, Lee MR, Oliveros A, Adams C, Ruby CL, Choi DS. Adenosine transporter ENT1 regulates the acquisition of goal-directed behavior and ethanol drinking through A2A receptor in the dorsomedial striatum. J Neurosci. 2013;33:4329–4338. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3094-12.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ruby CL, Adams CA, Knight EJ, Nam HW, Choi DS. An essential role for adenosine signaling in alcohol abuse. Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2010;3:163–174. doi: 10.2174/1874473711003030163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sari Y, Sreemantula SN, Lee MR, Choi DS. Ceftriaxone treatment affects the levels of GLT1 and ENT1 as well as ethanol intake in alcohol-preferring rats. J Mol Neurosci. 2013;51:779–787. doi: 10.1007/s12031-013-0064-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jedrzejewska A, Staff-Zielińska E, Wierzba-Bobrowicz T, Poszwińska Z, Olejniczak P. [Histology of the central nervous system in rats after intensive chronic ethanol intoxication] Neuropatol Pol. 1990;28:93–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lewohl JM, Wang L, Miles MF, Zhang L, Dodd PR, Harris RA. Gene expression in human alcoholism: microarray analysis of frontal cortex. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2000;24:1873–1882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Blednov YA, Bergeson SE, Walker D, Ferreira VM, Kuziel WA, Harris RA. Perturbation of chemokine networks by gene deletion alters the reinforcing actions of ethanol. Behav Brain Res. 2005;165:110–125. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2005.06.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Qin L, He J, Hanes RN, Pluzarev O, Hong JS, Crews FT. Increased systemic and brain cytokine production and neuroinflammation by endotoxin following ethanol treatment. J Neuroinflammation. 2008;5:10. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-5-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Blanco AM, Guerri C. Ethanol intake enhances inflammatory mediators in brain: role of glial cells and TLR4/IL-1RI receptors. Front Biosci. 2007;12:2616–2630. doi: 10.2741/2259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Alfonso-Loeches S, Pascual-Lucas M, Blanco AM, Sanchez-Vera I, Guerri C. Pivotal role of TLR4 receptors in alcohol-induced neuroinflammation and brain damage. J Neurosci. 2010;30:8285–8295. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0976-10.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ozer E, Sarioglu S, Güre A. Effects of prenatal ethanol exposure on neuronal migration, neuronogenesis and brain myelination in the mice brain. Clin Neuropathol. 2000;19:21–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Bichenkov E, Ellingson JS. Ethanol exerts different effects on myelin basic protein and 2’,3’-cyclic nucleotide 3’-phosphodiesterase expression in differentiating CG-4 oligodendrocytes. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2001;128:9–16. doi: 10.1016/s0165-3806(01)00142-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Bichenkov E, Ellingson JS. Protein kinase C inhibitors counteract the ethanol effects on myelin basic protein expression in differentiating CG-4 oligodendrocytes. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2002;139:29–38. doi: 10.1016/s0165-3806(02)00512-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Okamoto H, Miki T, Lee KY, Yokoyama T, Kuma H, Wang ZY, Gu H, Li HP, Matsumoto Y, Irawan S, et al. Oligodendrocyte myelin glycoprotein (OMgp) in rat hippocampus is depleted by chronic ethanol consumption. Neurosci Lett. 2006;406:76–80. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2006.07.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Navarro AI, Mandyam CD. Protracted abstinence from chronic ethanol exposure alters the structure of neurons and expression of oligodendrocytes and myelin in the medial prefrontal cortex. Neuroscience. 2015;293:35–44. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.02.043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Aspberg A, Tottmar O. Ethanol-induced increase in catalase activity in reaggregation cultures of rat brain cells is due to increased oligodendrocyte differentiation. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1994;18:620–624. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1994.tb00920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Katsel P, Byne W, Roussos P, Tan W, Siever L, Haroutunian V. Astrocyte and glutamate markers in the superficial, deep, and white matter layers of the anterior cingulate gyrus in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011;36:1171–1177. doi: 10.1038/npp.2010.252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Xia M, Abazyan S, Jouroukhin Y, Pletnikov M. Behavioral sequelae of astrocyte dysfunction: focus on animal models of schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2014:Epub ahead of print. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2014.10.044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Savitz JB, Price JL, Drevets WC. Neuropathological and neuromorphometric abnormalities in bipolar disorder: view from the medial prefrontal cortical network. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2014;42:132–147. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Liu Z, Song D, Yan E, Verkhratsky A, Peng L. Chronic treatment with anti-bipolar drugs suppresses glutamate release from astroglial cultures. Amino Acids. 2015;47:1045–1051. doi: 10.1007/s00726-015-1936-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Emamghoreishi M, Keshavarz M, Nekooeian AA. Chronic lithium treatment increased intracellular S100ß levels in rat primary neuronal culture. Acta Med Iran. 2015;53:89–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Radewicz K, Garey LJ, Gentleman SM, Reynolds R. Increase in HLA-DR immunoreactive microglia in frontal and temporal cortex of chronic schizophrenics. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2000;59:137–150. doi: 10.1093/jnen/59.2.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Miller BJ, Buckley P, Seabolt W, Mellor A, Kirkpatrick B. Meta-analysis of cytokine alterations in schizophrenia: clinical status and antipsychotic effects. Biol Psychiatry. 2011;70:663–671. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.04.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Schafer DP, Lehrman EK, Kautzman AG, Koyama R, Mardinly AR, Yamasaki R, Ransohoff RM, Greenberg ME, Barres BA, Stevens B. Microglia sculpt postnatal neural circuits in an activity and complement-dependent manner. Neuron. 2012;74:691–705. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.03.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Söderlund J, Olsson SK, Samuelsson M, Walther-Jallow L, Johansson C, Erhardt S, Landén M, Engberg G. Elevation of cerebrospinal fluid interleukin-1ß in bipolar disorder. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2011;36:114–118. doi: 10.1503/jpn.100080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Monfrim X, Gazal M, De Leon PB, Quevedo L, Souza LD, Jansen K, Oses JP, Pinheiro RT, Silva RA, Lara DR, et al. Immune dysfunction in bipolar disorder and suicide risk: is there an association between peripheral corticotropin-releasing hormone and interleukin-1β? Bipolar Disord. 2014;16:741–747. doi: 10.1111/bdi.12214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Konradi C, Sillivan SE, Clay HB. Mitochondria, oligodendrocytes and inflammation in bipolar disorder: evidence from transcriptome studies points to intriguing parallels with multiple sclerosis. Neurobiol Dis. 2012;45:37–47. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2011.01.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Chew LJ, Fusar-Poli P, Schmitz T. Oligodendroglial alterations and the role of microglia in white matter injury: relevance to schizophrenia. Dev Neurosci. 2013;35:102–129. doi: 10.1159/000346157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Dracheva S, Davis KL, Chin B, Woo DA, Schmeidler J, Haroutunian V. Myelin-associated mRNA and protein expression deficits in the anterior cingulate cortex and hippocampus in elderly schizophrenia patients. Neurobiol Dis. 2006;21:531–540. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2005.08.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Takahashi N, Sakurai T, Davis KL, Buxbaum JD. Linking oligodendrocyte and myelin dysfunction to neurocircuitry abnormalities in schizophrenia. Prog Neurobiol. 2011;93:13–24. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2010.09.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Nave KA. Myelination and the trophic support of long axons. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2010;11:275–283. doi: 10.1038/nrn2797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Paintlia MK, Paintlia AS, Contreras MA, Singh I, Singh AK. Lipopolysaccharide-induced peroxisomal dysfunction exacerbates cerebral white matter injury: attenuation by N-acetyl cysteine. Exp Neurol. 2008;210:560–576. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2007.12.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Oorschot DE, Voss L, Covey MV, Goddard L, Huang W, Birchall P, Bilkey DK, Kohe SE. Spectrum of short- and long-term brain pathology and long-term behavioral deficits in male repeated hypoxic rats closely resembling human extreme prematurity. J Neurosci. 2013;33:11863–11877. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0342-12.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Huang H, Gundapuneedi T, Rao U. White matter disruptions in adolescents exposed to childhood maltreatment and vulnerability to psychopathology. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012;37:2693–2701. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Choquet D, Triller A. The role of receptor diffusion in the organization of the postsynaptic membrane. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003;4:251–265. doi: 10.1038/nrn1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Faissner A, Pyka M, Geissler M, Sobik T, Frischknecht R, Gundelfinger ED, Seidenbecher C. Contributions of astrocytes to synapse formation and maturation - Potential functions of the perisynaptic extracellular matrix. Brain Res Rev. 2010;63:26–38. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2010.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Allen NJ, Barres BA. Signaling between glia and neurons: focus on synaptic plasticity. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2005;15:542–548. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2005.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Witcher MR, Kirov SA, Harris KM. Plasticity of perisynaptic astroglia during synaptogenesis in the mature rat hippocampus. Glia. 2007;55:13–23. doi: 10.1002/glia.20415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Dallérac G, Chever O, Rouach N. How do astrocytes shape synaptic transmission? Insights from electrophysiology. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013;7:159. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Hertz L, Zielke HR. Astrocytic control of glutamatergic activity: astrocytes as stars of the show. Trends Neurosci. 2004;27:735–743. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2004.10.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Pascual O, Casper KB, Kubera C, Zhang J, Revilla-Sanchez R, Sul JY, Takano H, Moss SJ, McCarthy K, Haydon PG. Astrocytic purinergic signaling coordinates synaptic networks. Science. 2005;310:113–116. doi: 10.1126/science.1116916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Schipke CG, Kettenmann H. Astrocyte responses to neuronal activity. Glia. 2004;47:226–232. doi: 10.1002/glia.20029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Cornell-Bell AH, Thomas PG, Smith SJ. The excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate causes filopodia formation in cultured hippocampal astrocytes. Glia. 1990;3:322–334. doi: 10.1002/glia.440030503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Glaum SR, Holzwarth JA, Miller RJ. Glutamate receptors activate Ca2+ mobilization and Ca2+ influx into astrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1990;87:3454–3458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Bergles DE, Jahr CE. Synaptic activation of glutamate transporters in hippocampal astrocytes. Neuron. 1997;19:1297–1308. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80420-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Rusakov DA, Zheng K, Henneberger C. Astrocytes as regulators of synaptic function: a quest for the Ca2+ master key. Neuroscientist. 2011;17:513–523. doi: 10.1177/1073858410387304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Swanson RA. Neuroglia. 2nd ed. New York, NY, USA: Oxford University Press; 2005. pp. 346–350. [Google Scholar]
- 78.Amiri M, Bahrami F, Janahmadi M. Functional contributions of astrocytes in synchronization of a neuronal network model. J Theor Biol. 2012;292:60–70. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2011.09.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Kang J, Jiang L, Goldman SA, Nedergaard M. Astrocyte-mediated potentiation of inhibitory synaptic transmission. Nat Neurosci. 1998;1:683–692. doi: 10.1038/3684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Bezzi P, Carmignoto G, Pasti L, Vesce S, Rossi D, Rizzini BL, Pozzan T, Volterra A. Prostaglandins stimulate calcium-dependent glutamate release in astrocytes. Nature. 1998;391:281–285. doi: 10.1038/34651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Parpura V, Basarsky TA, Liu F, Jeftinija K, Jeftinija S, Haydon PG. Glutamate-mediated astrocyte-neuron signalling. Nature. 1994;369:744–747. doi: 10.1038/369744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Mazzanti M, Sul JY, Haydon PG. Glutamate on demand: astrocytes as a ready source. Neuroscientist. 2001;7:396–405. doi: 10.1177/107385840100700509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Bowser DN, Khakh BS. ATP excites interneurons and astrocytes to increase synaptic inhibition in neuronal networks. J Neurosci. 2004;24:8606–8620. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2660-04.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Domercq M, Brambilla L, Pilati E, Marchaland J, Volterra A, Bezzi P. P2Y1 receptor-evoked glutamate exocytosis from astrocytes: control by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and prostaglandins. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:30684–30696. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M606429200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Jourdain P, Bergersen LH, Bhaukaurally K, Bezzi P, Santello M, Domercq M, Matute C, Tonello F, Gundersen V, Volterra A. Glutamate exocytosis from astrocytes controls synaptic strength. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:331–339. doi: 10.1038/nn1849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Ota Y, Zanetti AT, Hallock RM. The role of astrocytes in the regulation of synaptic plasticity and memory formation. Neural Plast. 2013;2013:185463. doi: 10.1155/2013/185463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Zhou M, Kimelberg HK. Freshly isolated hippocampal CA1 astrocytes comprise two populations differing in glutamate transporter and AMPA receptor expression. J Neurosci. 2001;21:7901–7908. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-20-07901.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Sun W, McConnell E, Pare JF, Xu Q, Chen M, Peng W, Lovatt D, Han X, Smith Y, Nedergaard M. Glutamate-dependent neuroglial calcium signaling differs between young and adult brain. Science. 2013;339:197–200. doi: 10.1126/science.1226740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Bezzi P, Gundersen V, Galbete JL, Seifert G, Steinhäuser C, Pilati E, Volterra A. Astrocytes contain a vesicular compartment that is competent for regulated exocytosis of glutamate. Nat Neurosci. 2004;7:613–620. doi: 10.1038/nn1246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Araque A, Parpura V, Sanzgiri RP, Haydon PG. Tripartite synapses: glia, the unacknowledged partner. Trends Neurosci. 1999;22:208–215. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(98)01349-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Peters , A , Palay SL, and Webster HD. The fine structure of the nervous system: neurons and their supporting cells. New York: Oxford University Press; 1991. [Google Scholar]
- 92.Diamond JS. Deriving the glutamate clearance time course from transporter currents in CA1 hippocampal astrocytes: transmitter uptake gets faster during development. J Neurosci. 2005;25:2906–2916. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5125-04.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Hirrlinger J, Hülsmann S, Kirchhoff F. Astroglial processes show spontaneous motility at active synaptic terminals in situ. Eur J Neurosci. 2004;20:2235–2239. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Derouiche A, Anlauf E, Aumann G, Mühlstädt B, Lavialle M. Anatomical aspects of glia-synapse interaction: the perisynaptic glial sheath consists of a specialized astrocyte compartment. J Physiol Paris. 2002;96:177–182. doi: 10.1016/s0928-4257(02)00004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Derouiche A, Frotscher M. Astroglial processes around identified glutamatergic synapses contain glutamine synthetase: evidence for transmitter degradation. Brain Res. 1991;552:346–350. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Bormann J, Kettenmann H. Patch-clamp study of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor Cl- channels in cultured astrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1988;85:9336–9340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Grosche J, Matyash V, Möller T, Verkhratsky A, Reichenbach A, Kettenmann H. Microdomains for neuron-glia interaction: parallel fiber signaling to Bergmann glial cells. Nat Neurosci. 1999;2:139–143. doi: 10.1038/5692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Oliet SH, Piet R, Poulain DA. Control of glutamate clearance and synaptic efficacy by glial coverage of neurons. Science. 2001;292:923–926. doi: 10.1126/science.1059162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Barbour B. An evaluation of synapse independence. J Neurosci. 2001;21:7969–7984. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-20-07969.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Kullmann DM, Erdemli G, Asztély F. LTP of AMPA and NMDA receptor-mediated signals: evidence for presynaptic expression and extrasynaptic glutamate spill-over. Neuron. 1996;17:461–474. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80178-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Rusakov DA, Kullmann DM. Extrasynaptic glutamate diffusion in the hippocampus: ultrastructural constraints, uptake, and receptor activation. J Neurosci. 1998;18:3158–3170. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-09-03158.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Scanziani M, Salin PA, Vogt KE, Malenka RC, Nicoll RA. Use-dependent increases in glutamate concentration activate presynaptic metabotropic glutamate receptors. Nature. 1997;385:630–634. doi: 10.1038/385630a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Humeau Y, Shaban H, Bissière S, Lüthi A. Presynaptic induction of heterosynaptic associative plasticity in the mammalian brain. Nature. 2003;426:841–845. doi: 10.1038/nature02194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Arnth-Jensen N, Jabaudon D, Scanziani M. Cooperation between independent hippocampal synapses is controlled by glutamate uptake. Nat Neurosci. 2002;5:325–331. doi: 10.1038/nn825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Marcaggi P, Attwell D. Endocannabinoid signaling depends on the spatial pattern of synapse activation. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:776–781. doi: 10.1038/nn1458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Szapiro G, Barbour B. Multiple climbing fibers signal to molecular layer interneurons exclusively via glutamate spillover. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:735–742. doi: 10.1038/nn1907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Hardingham GE, Fukunaga Y, Bading H. Extrasynaptic NMDARs oppose synaptic NMDARs by triggering CREB shut-off and cell death pathways. Nat Neurosci. 2002;5:405–414. doi: 10.1038/nn835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Zhang JM, Wang HK, Ye CQ, Ge W, Chen Y, Jiang ZL, Wu CP, Poo MM, Duan S. ATP released by astrocytes mediates glutamatergic activity-dependent heterosynaptic suppression. Neuron. 2003;40:971–982. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00717-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Fuxe K, Borroto-Escuela DO, Romero-Fernandez W, Diaz-Cabiale Z, Rivera A, Ferraro L, Tanganelli S, Tarakanov AO, Garriga P, Narváez JA, et al. Extrasynaptic neurotransmission in the modulation of brain function. Focus on the striatal neuronal-glial networks. Front Physiol. 2012;3:136. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2012.00136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Kullmann DM, Asztely F. Extrasynaptic glutamate spillover in the hippocampus: evidence and implications. Trends Neurosci. 1998;21:8–14. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(97)01150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Asztely F, Erdemli G, Kullmann DM. Extrasynaptic glutamate spillover in the hippocampus: dependence on temperature and the role of active glutamate uptake. Neuron. 1997;18:281–293. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80268-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Danbolt NC. Glutamate uptake. Prog Neurobiol. 2001;65:1–105. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0082(00)00067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Liguz-Lecznar M, Skangiel-Kramska J. Vesicular glutamate transporters (VGLUTs): the three musketeers of glutamatergic system. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 2007;67:207–218. doi: 10.55782/ane-2007-1649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Amara SG, Fontana AC. Excitatory amino acid transporters: keeping up with glutamate. Neurochem Int. 2002;41:313–318. doi: 10.1016/s0197-0186(02)00018-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Su ZZ, Leszczyniecka M, Kang DC, Sarkar D, Chao W, Volsky DJ, Fisher PB. Insights into glutamate transport regulation in human astrocytes: cloning of the promoter for excitatory amino acid transporter 2 (EAAT2) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:1955–1960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0136555100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Gegelashvili G, Schousboe A. High affinity glutamate transporters: regulation of expression and activity. Mol Pharmacol. 1997;52:6–15. doi: 10.1124/mol.52.1.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Kanai Y, Hediger MA. Primary structure and functional characterization of a high-affinity glutamate transporter. Nature. 1992;360:467–471. doi: 10.1038/360467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Fairman WA, Vandenberg RJ, Arriza JL, Kavanaugh MP, Amara SG. An excitatory amino-acid transporter with properties of a ligand-gated chloride channel. Nature. 1995;375:599–603. doi: 10.1038/375599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Arriza JL, Eliasof S, Kavanaugh MP, Amara SG. Excitatory amino acid transporter 5, a retinal glutamate transporter coupled to a chloride conductance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:4155–4160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.8.4155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Murphy-Royal C, Dupuis JP, Varela JA, Panatier A, Pinson B, Baufreton J, Groc L, Oliet SH. Surface diffusion of astrocytic glutamate transporters shapes synaptic transmission. Nat Neurosci. 2015;18:219–226. doi: 10.1038/nn.3901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Filosa A, Paixão S, Honsek SD, Carmona MA, Becker L, Feddersen B, Gaitanos L, Rudhard Y, Schoepfer R, Klopstock T, et al. Neuron-glia communication via EphA4/ephrin-A3 modulates LTP through glial glutamate transport. Nat Neurosci. 2009;12:1285–1292. doi: 10.1038/nn.2394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Yernool D, Boudker O, Jin Y, Gouaux E. Structure of a glutamate transporter homologue from Pyrococcus horikoshii. Nature. 2004;431:811–818. doi: 10.1038/nature03018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Gebhardt FM, Mitrovic AD, Gilbert DF, Vandenberg RJ, Lynch JW, Dodd PR. Exon-skipping splice variants of excitatory amino acid transporter-2 (EAAT2) form heteromeric complexes with full-length EAAT2. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:31313–31324. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.153494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Shigeri Y, Seal RP, Shimamoto K. Molecular pharmacology of glutamate transporters, EAATs and VGLUTs. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2004;45:250–265. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2004.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Kirschner MA, Copeland NG, Gilbert DJ, Jenkins NA, Amara SG. Mouse excitatory amino acid transporter EAAT2: isolation, characterization, and proximity to neuroexcitability loci on mouse chromosome 2. Genomics. 1994;24:218–224. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Sutherland ML, Delaney TA, Noebels JL. Molecular characterization of a high-affinity mouse glutamate transporter. Gene. 1995;162:271–274. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(95)00293-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Arriza JL, Fairman WA, Wadiche JI, Murdoch GH, Kavanaugh MP, Amara SG. Functional comparisons of three glutamate transporter subtypes cloned from human motor cortex. J Neurosci. 1994;14:5559–5569. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-09-05559.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Augustine JA, Fitzpatrick D, Hall WC, LaMantia A, McNamara JO, Mooney RD, Platt ML, Purves D, Simon SA, White LE, et al. Neuroscience. Fourth ed. Sunderland, MA, USA: Sinauer Associates, Inc; 2008. p. 129. [Google Scholar]
- 129.Roberts RC, Roche JK, McCullumsmith RE. Localization of excitatory amino acid transporters EAAT1 and EAAT2 in human postmortem cortex: a light and electron microscopic study. Neuroscience. 2014;277:522–540. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.07.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Butchbach ME, Tian G, Guo H, Lin CL. Association of excitatory amino acid transporters, especially EAAT2, with cholesterol-rich lipid raft microdomains: importance for excitatory amino acid transporter localization and function. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:34388–34396. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M403938200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Takahashi K, Foster JB, Lin CL. Glutamate transporter EAAT2: regulation, function, and potential as a therapeutic target for neurological and psychiatric disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015;72:3489–3506. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1937-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Hinson SR, Roemer SF, Lucchinetti CF, Fryer JP, Kryzer TJ, Chamberlain JL, Howe CL, Pittock SJ, Lennon VA. Aquaporin-4-binding autoantibodies in patients with neuromyelitis optica impair glutamate transport by down-regulating EAAT2. J Exp Med. 2008;205:2473–2481. doi: 10.1084/jem.20081241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Fontana AC, de Oliveira Beleboni R, Wojewodzic MW, Ferreira Dos Santos W, Coutinho-Netto J, Grutle NJ, Watts SD, Danbolt NC, Amara SG. Enhancing glutamate transport: mechanism of action of Parawixin1, a neuroprotective compound from Parawixia bistriata spider venom. Mol Pharmacol. 2007;72:1228–1237. doi: 10.1124/mol.107.037127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Karki P, Webb A, Smith K, Johnson J, Lee K, Son DS, Aschner M, Lee E. Yin Yang 1 is a repressor of glutamate transporter EAAT2, and it mediates manganese-induced decrease of EAAT2 expression in astrocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 2014;34:1280–1289. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01176-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Karki P, Webb A, Zerguine A, Choi J, Son DS, Lee E. Mechanism of raloxifene-induced upregulation of glutamate transporters in rat primary astrocytes. Glia. 2014;62:1270–1283. doi: 10.1002/glia.22679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Lee E, Sidoryk-Wegrzynowicz M, Yin Z, Webb A, Son DS, Aschner M. Transforming growth factor-α mediates estrogen-induced upregulation of glutamate transporter GLT-1 in rat primary astrocytes. Glia. 2012;60:1024–1036. doi: 10.1002/glia.22329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Liu AY, Mathur R, Mei N, Langhammer CG, Babiarz B, Firestein BL. Neuroprotective drug riluzole amplifies the heat shock factor 1 (HSF1)- and glutamate transporter 1 (GLT1)-dependent cytoprotective mechanisms for neuronal survival. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:2785–2794. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.158220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Yang Y, Gozen O, Watkins A, Lorenzini I, Lepore A, Gao Y, Vidensky S, Brennan J, Poulsen D, Won Park J, et al. Presynaptic regulation of astroglial excitatory neurotransmitter transporter GLT1. Neuron. 2009;61:880–894. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.02.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Figiel M, Engele J. Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP), a neuron-derived peptide regulating glial glutamate transport and metabolism. J Neurosci. 2000;20:3596–3605. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-10-03596.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Karki P, Smith K, Johnson J, Lee E. Astrocyte-derived growth factors and estrogen neuroprotection: role of transforming growth factor-α in estrogen-induced upregulation of glutamate transporters in astrocytes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014;389:58–64. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2014.01.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Karki P, Webb A, Smith K, Lee K, Son DS, Aschner M, Lee E. cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) and nuclear factor κB mediate the tamoxifen-induced up-regulation of glutamate transporter 1 (GLT-1) in rat astrocytes. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:28975–28986. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.483826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Lee E, Sidoryk-Wêgrzynowicz M, Wang N, Webb A, Son DS, Lee K, Aschner M. GPR30 regulates glutamate transporter GLT-1 expression in rat primary astrocytes. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:26817–26828. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.341867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Rothstein JD, Patel S, Regan MR, Haenggeli C, Huang YH, Bergles DE, Jin L, Dykes Hoberg M, Vidensky S, Chung DS, et al. Beta-lactam antibiotics offer neuroprotection by increasing glutamate transporter expression. Nature. 2005;433:73–77. doi: 10.1038/nature03180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Zelenaia O, Schlag BD, Gochenauer GE, Ganel R, Song W, Beesley JS, Grinspan JB, Rothstein JD, Robinson MB. Epidermal growth factor receptor agonists increase expression of glutamate transporter GLT-1 in astrocytes through pathways dependent on phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and transcription factor NF-kappaB. Mol Pharmacol. 2000;57:667–678. doi: 10.1124/mol.57.4.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Sitcheran R, Gupta P, Fisher PB, Baldwin AS. Positive and negative regulation of EAAT2 by NF-kappaB: a role for N-myc in TNFalpha-controlled repression. EMBO J. 2005;24:510–520. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Lee SG, Su ZZ, Emdad L, Gupta P, Sarkar D, Borjabad A, Volsky DJ, Fisher PB. Mechanism of ceftriaxone induction of excitatory amino acid transporter-2 expression and glutamate uptake in primary human astrocytes. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:13116–13123. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M707697200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Yang Y, Gozen O, Vidensky S, Robinson MB, Rothstein JD. Epigenetic regulation of neuron-dependent induction of astroglial synaptic protein GLT1. Glia. 2010;58:277–286. doi: 10.1002/glia.20922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Perisic T, Holsboer F, Rein T, Zschocke J. The CpG island shore of the GLT-1 gene acts as a methylation-sensitive enhancer. Glia. 2012;60:1345–1355. doi: 10.1002/glia.22353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.García-Tardón N, González-González IM, Martínez-Villarreal J, Fernández-Sánchez E, Giménez C, Zafra F. Protein kinase C (PKC)-promoted endocytosis of glutamate transporter GLT-1 requires ubiquitin ligase Nedd4-2-dependent ubiquitination but not phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:19177–19187. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.355909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Foran E, Rosenblum L, Bogush A, Pasinelli P, Trotti D. Sumoylation of the astroglial glutamate transporter EAAT2 governs its intracellular compartmentalization. Glia. 2014;62:1241–1253. doi: 10.1002/glia.22677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Lauriat TL, McInnes LA. EAAT2 regulation and splicing: relevance to psychiatric and neurological disorders. Mol Psychiatry. 2007;12:1065–1078. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4002065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Sander T, Ostapowicz A, Samochowiec J, Smolka M, Winterer G, Schmidt LG. Genetic variation of the glutamate transporter EAAT2 gene and vulnerability to alcohol dependence. Psychiatr Genet. 2000;10:103–107. doi: 10.1097/00041444-200010030-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Foley PF, Loh EW, Innes DJ, Williams SM, Tannenberg AE, Harper CG, Dodd PR. Association studies of neurotransmitter gene polymorphisms in alcoholic Caucasians. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004;1025:39–46. doi: 10.1196/annals.1316.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Crabbe JC, Belknap JK. Behavior genetic analyses of drug withdrawal. Alcohol Alcohol Suppl. 1993;2:477–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Mulholland PJ, Carpenter-Hyland EP, Woodward JJ, Chandler LJ. Ethanol disrupts NMDA receptor and astroglial EAAT2 modulation of Kv2.1 potassium channels in hippocampus. Alcohol. 2009;43:45–50. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2008.10.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Griffin WC, Haun HL, Hazelbaker CL, Ramachandra VS, Becker HC. Increased extracellular glutamate in the nucleus accumbens promotes excessive ethanol drinking in ethanol dependent mice. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014;39:707–717. doi: 10.1038/npp.2013.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Abulseoud OA, Camsari UM, Ruby CL, Kasasbeh A, Choi S, Choi DS. Attenuation of ethanol withdrawal by ceftriaxone-induced upregulation of glutamate transporter EAAT2. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014;39:1674–1684. doi: 10.1038/npp.2014.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Medrano MC, Mendiguren A, Pineda J. Effect of ceftriaxone and topiramate treatments on naltrexone-precipitated morphine withdrawal and glutamate receptor desensitization in the rat locus coeruleus. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2015;232:2795–2809. doi: 10.1007/s00213-015-3913-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Rao PS, Bell RL, Engleman EA, Sari Y. Targeting glutamate uptake to treat alcohol use disorders. Front Neurosci. 2015;9:144. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Feeney GF, Connor JP, Young RM, Tucker J, McPherson A. Combined acamprosate and naltrexone, with cognitive behavioural therapy is superior to either medication alone for alcohol abstinence: a single centres’ experience with pharmacotherapy. Alcohol Alcohol. 2006;41:321–327. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agl007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Sari Y, Sakai M, Weedman JM, Rebec GV, Bell RL. Ceftriaxone, a beta-lactam antibiotic, reduces ethanol consumption in alcohol-preferring rats. Alcohol Alcohol. 2011;46:239–246. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agr023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]