How to secure data at rest, in use and in motion (original) (raw)
With internal and external cyber threats on the rise, check out these tips to best protect and secure data at rest, in use and in motion.
The easiest way to secure sensitive data is to not have any in the first place. Of course, that's not a realistic option for the vast majority of organizations.
In the face of escalating and evolving cyber threats, IT professionals must, therefore, devise a strategy based on best practices to secure data at rest, data in use and data in motion.
Why it's important to secure data at rest, in use and in motion
Information theft is the primary reason for organizations to pay attention to how they protect data. Stolen data can be used for identity fraud, for corporate or government espionage, and as a lure for ransomware.
Midsize and small organizations are attractive targets for information theft because they often don't have sophisticated data security policies and tools in place. Smaller organizations might also bristle at the cost of security tools or policy enforcement, but the risk of a major data loss to information theft should be justification for the resources -- both budget and staff -- to protect data.
While midsize and small organizations are attractive targets, that doesn't mean larger enterprises are immune. They too must ensure the proper budget and staff are allocated toward information security.
Additionally, whereas organizations used to spend a large amount of time identifying and mitigating external threats, internal threats now also require significant resources. Verizon's "2022 Data Breach Investigations Report" (DBIR) revealed nearly one in five data breaches are due to insider theft or negligence.
Once a company has committed to the necessary resources, its next step is to develop a strategy to monitor and secure data at rest, in use and in motion.
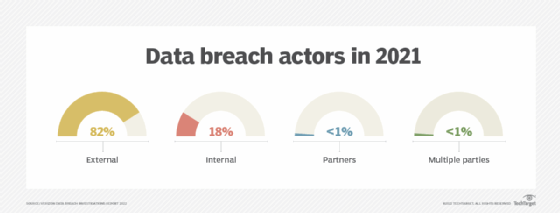
Threat actors: Who's behind the breach
How to secure sensitive data at rest
1. Identify and locate data
To best secure data at rest, organizations must know what data is sensitive -- such as personal information, business information and classified information -- and where that data resides. Companies need processes in place to limit the locations where sensitive data is stored, but that can't happen if they aren't able to properly identify the critical nature of their data.
2. Classify data
Data classification methods vary from one organization to the next. It is important, however, that various business department leaders assist in assessing and ranking which applications and data are considered most critical from a business continuation perspective. For example, if an application drives revenue or supports it in some way, it's likely vital to the livelihood of the business and should be considered critical.
Classification is a dynamic process that requires companies to constantly reevaluate sensitivity levels and readjust data protection levels accordingly. For instance, if data that was once labeled low risk or not sensitive for the organization is suddenly reassessed at a higher risk, if and how the data is encrypted should change. This not only includes the process of encryption, but also policy that helps manage encryption keys so they aren't accidently stolen or leaked.
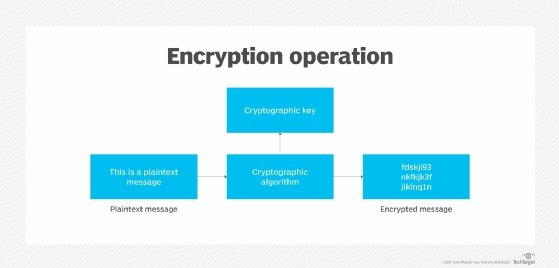
Algorithms and keys turn plaintext into ciphertext.
3. Embrace encryption
Some IT administrators may be concerned with encryption's potential performance degradation. This shouldn't prevent enterprises from reaping the security benefits encryption offers. Plus, there are plenty of ways to get around performance issues, such as the selective encryption of database fields, rows and columns versus encrypting all data regardless of sensitivity.
4. Secure the infrastructure
Remember, data at rest is only as secure as the infrastructure that supports it. The proper patching of servers, network hardware, OSes, and other on-premises and cloud software is also critical to keeping data secure. Continuously monitoring internal and external threats attempting to access data at rest is another great way to keep an eye on infrastructure.
5. Train users
Employees who have access to business-critical information need to understand the importance of securing data at rest to prevent data loss. Verizon's 2022 DBIR found 82% of breaches over the previous year involved a human element. Regular training can help mitigate the risk of human error.
How to secure sensitive data in use and in motion
Protecting data at rest is far easier than protecting data in use -- information that is being processed, accessed or read -- and data in motion -- information that is being transported between systems.
1. Control access to data
The best way to secure data in use is to restrict access by user role, limiting system access to only those who need it. Even better would be to get more granular and restrict access to the data itself.
This can be accomplished by enabling access to only specific data sets and fields or through the obfuscation of data not needed prior to analysis in other applications. The use of metadata, as opposed to raw data, can also help prevent sensitive information from leaking.
2. Encrypt data in use and in motion
Encryption plays a major role in protecting data in use or in motion. Data should always be encrypted when it's traversing any external or internal networks. This includes encrypting all data prior to transport or using protected tunnels, such as HTTPS or SSL/TLS. Encrypted tunnels, such as VPNs and Generic Routing Encapsulation, are also potential options.
3. Invest in visibility
One final tip to secure data in use or in motion is to provide proper visibility for breach detection purposes. Advancements in AI security tools that ingest network telemetry data and then analyze it to spot anomalies in data access behavior can identify threats, determine the extent of damage and provide actionable insights on how to stop further data loss. Modern AI and security analytics tools, such as network detection and response and AI for IT operations platforms, are great ways to gain the proper level of visibility without requiring large amounts of time from an administrative perspective.
Next Steps
4 enterprise database security best practices
Key factors to achieve data security in cloud computing
Symmetric vs. asymmetric encryption: What's the difference?
 An overview of storage encryption for enterprises
An overview of storage encryption for enterprises  By: Julia Borgini
By: Julia Borgini  cloud encryption By: Cameron Hashemi-Pour
cloud encryption By: Cameron Hashemi-Pour  storage security
storage security  By: Paul Kirvan
By: Paul Kirvan  Best practices for secure network automation workflows
Best practices for secure network automation workflows  By: Verlaine Muhungu
By: Verlaine Muhungu