TiledChartLayout - Tiled chart layout appearance and behavior - MATLAB (original) (raw)
TiledChartLayout Properties
Tiled chart layout appearance and behavior
A tiled chart layout is a container for displaying a tiling of plots in a figure. Each tile can contain an axes object for displaying a plot. By changing property values, you can modify certain aspects of the layout.
t = tiledlayout(2,2); t.TileSpacing = 'compact';
Grid size, specified as a vector of the form [m n], wherem is the number of rows and n is the number of columns. You can set this property only when all the tiles in the layout are empty. When you set this property, MATLAB® sets the TileArrangement property to'fixed'.
The value of this property might change automatically for layouts that have theTileArrangement property set to 'flow'. For example, if the parent container resizes or the number of axes in the layout changes, the grid size updates to accommodate those changes.
This property is read-only.
Tile arrangement, returned as one of these values:
"fixed"— The layout is a grid with a fixed number of rows and columns as determined by theGridSizeproperty. Anm-by-nlayout with this tile arrangement can display up tom*nplots."flow"— The layout is a grid with a variable number of rows and columns. Each time you callnexttile, the layout reflows as needed to accommodate the new axes while maintaining an aspect ratio of roughly 4:3 for all the tiles."vertical"— The layout holds a vertical stack of axes. Each time you callnexttile, a new axes object is added to the bottom of the stack. (since R2023a)"horizontal"— The layout holds a horizontal stack of axes. Each time you callnexttile, a new axes object is added to the right side of the stack. (since R2023a)
MATLAB sets the value of this property to "fixed" if you manually set the GridSize property.
To set the tile arrangement, specify the arrangement argument when you call the tiledlayout function.
Tile spacing, specified as "loose", "compact","tight" or "none". Use this property to control the spacing between the tiles.
This table shows how each value affects the appearance of a 2-by-2 layout.
| Value | Appearance |
|---|---|
| "loose" | 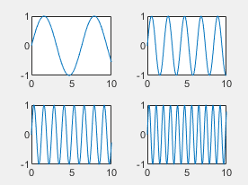 |
| "compact" | 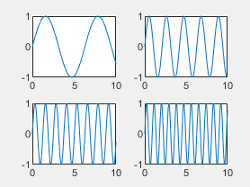 |
| "tight" | 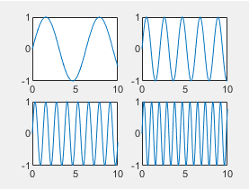 |
| "none" | 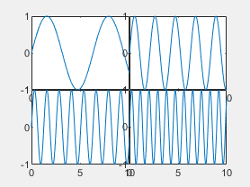 |
Padding around the perimeter of the layout, specified as "loose","compact", or "tight". The layout provides space for all decorations, such as axis labels, regardless of the value of this property.
This table shows how each value affects the appearance of a 2-by-2 layout.
| Value | Appearance |
|---|---|
| "loose" |  |
| "compact" |  |
| "tight" |  |
Tile indexing scheme, specified as a value from the table. Thenexttile function populates tiles according to this indexing scheme. If you change the tile indexing scheme of a populated layout, the tile positions change to match the new scheme. The indexing scheme also affects which axes object MATLAB returns when you call nexttile to get the axes object in a specific tile.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| 'rowmajor' | The tile numbers increase across the rows, from left to right. For example, this picture shows the row major tile indices for a 2-by-2 layout.  |
| 'columnmajor' | The tile numbers increase down the columns. For example, this picture shows the column major tile indices for a 2-by-2 layout.  |
Labels
Text object for a shared title. To add a shared title, set theString property of the Text object. To change the title appearance, such as the font style or color, set other properties. For example, create a shared title for a 2-by-2 layout that has a bold font weight.
t = tiledlayout(2,2); t.Title.String = 'My Title'; t.Title.FontWeight = 'bold';
Alternatively, pass the TiledChartLayout object to the title function.
title(t,'My Title','FontWeight','normal')
For a complete list of properties that you can specify, see Text Properties.
Note
The Text object is not contained in theChildren property of the layout, so it cannot be returned by thefindobj function.
Text object for the shared subtitle. To add a subtitle, set theString property of the text object. To change its appearance, such as the font angle, set other properties. For a complete list, see Text Properties.
t = tiledlayout(2,2); t.Subtitle.String = 'An Insightful Subtitle'; t.Subtitle.FontAngle = 'italic';
Alternatively, the subtitle function to add a subtitle and control the appearance.
subtitle('An Insightful Subtitle','FontAngle','italic')
Or use the title function, and specify two character vector input arguments and two output arguments. Then set properties on the second text object returned by the function.
[tt,s] = title(t,'Clever Title','An Insightful Subtitle'); s.FontAngle = 'italic';
Note
This text object is not contained in the axes Children property, cannot be returned by findobj, and does not use default values defined for text objects.
Text object for a shared _x_-axis label. To add a shared _x_-axis label, set the String property of the text object. To change the label appearance, such as the font size, set other properties. For example, create a shared _x_-axis label with a 14-point font for a 2-by-2 layout.
t = tiledlayout(2,2); t.XLabel.String = 'My x-Axis Label'; t.XLabel.FontSize = 14;
Alternatively, pass the TiledChartLayout object to the xlabel function.
xlabel(t,'My x-Axis Label','FontSize',14)
For a complete list of properties you can specify, see Text Properties.
Note
The Text object is not contained in the axesChildren property, so it cannot be returned by findobj.
Text object for a shared _y_-axis label. To add a shared _y_-axis label, set the String property of the text object. To change the label appearance, such as the font size, set other properties. For example, create a shared _y_-axis label with a 14-point font for a 2-by-2 layout.
t = tiledlayout(2,2); t.YLabel.String = 'My y-Axis Label'; t.YLabel.FontSize = 14;
Alternatively, pass the TiledChartLayout object to the ylabel function.
ylabel(t,'My y-Axis Label','FontSize',14)
For a complete list of properties you can specify, see Text Properties.
Note
The Text object is not contained in the axesChildren property, so it cannot be returned by findobj.
Position
Outer size and location, including the margins for decorations such titles and axis labels, specified as a four-element vector of the form [left bottom width height]. The values in the vector are in the units specified by theUnits property. The default value of [0 0 1 1] includes the whole interior of the container.
- The
leftandbottomelements define the distance from the lower left corner of the container (typically a figure, panel, or tab) to the lower left corner of the outer position boundary. - The
widthandheightelements are the outer position boundary dimensions.
In the following layout, the blue rectangle represents theOuterPosition property, and the red rectangle represents theInnerPosition and Position properties (which have the same value).

Note
Setting this property has no effect when the parent container is aTiledChartLayout object.
Inner size and location, excluding the margins for decorations such titles and axis labels, specified as a four-element vector of the form [left bottom width height]. This property is equivalent to the Position property.
Note
Setting this property has no effect when the parent container is aTiledChartLayout object.
Inner size and location, excluding the margins for decorations such titles and axis labels, specified as a four-element vector of the form [left bottom width height]. The values in the vector are in the units specified by theUnits property.
- The
leftandbottomelements define the distance from the lower left corner of the container (typically a figure, panel, or tab) to the lower left corner of the position boundary. - The
widthandheightelements are the position boundary dimensions. For axes in a 3-D view, thePositionproperty is the smallest rectangle that encloses the axes.
In the following layout, the blue rectangle represents theOuterPosition property, and the red rectangle represents theInnerPosition and Position properties (which have the same value).

Note
Setting this property has no effect when the parent container is aTiledChartLayout object.
Position property to hold constant when adding, removing, or changing decorations, specified as one of the following values:
"outerposition"— TheOuterPositionproperty remains constant when you add, remove, or change decorations such as a title or an axis label. If any positional adjustments are needed, MATLAB adjusts theInnerPositionproperty."innerposition"— TheInnerPositionproperty remains constant when you add, remove, or change decorations such as a title or an axis label. If any positional adjustments are needed, MATLAB adjusts theOuterPositionproperty.
Note
Setting this property has no effect when the parent container is aTiledChartLayout object.
Layout options, specified as a TiledChartLayoutOptions object. Use this property to position a nested layout within its parent layout. For instance, to position a layout within another tiled chart layout, set the Tile and TileSpan properties on theTiledChartLayoutOptions object.
For example, this code positions layout2 into the third tile oflayout1.
layout1 = tiledlayout(2,2); layout2 = tiledlayout(layout1,1,3); layout2.Layout.Tile = 3;
To make the nested layout span multiple tiles, specify theTileSpan property as a two-element vector. For example, this code spans layout2 across one row and two columns of tiles.
layout2.Layout.TileSpan = [1 2];
If you fill all the tiles in both layouts, the composite layout looks like this:

If the layout is not a child of another layout (for example, if it is a child of a figure or panel), then this property is empty and has no effect.
Interactivity
Shared data exploration toolbar, specified as an AxesToolbar object returned by the axtoolbar function. The toolbar appears in the top-right corner of the layout when you hover over it.
By default, there is no shared toolbar, and each of the individual axes objects has its own toolbar. When you create a shared toolbar, the toolbars on the individual axes objects become hidden. If you do not want any toolbars in the layout, leave this property empty and set the set the Visible property of theAxesToolbar object to 'off' for each axes.
t = tiledlayout(2,1); ax = nexttile; ax.Toolbar.Visible = 'off';
Callbacks
Since R2022b
Grid size changed callback, specified as one of these values:
- A function handle.
- A cell array in which the first element is a function handle. Subsequent elements in the cell array are the arguments to pass to the callback function.
- A string scalar or character vector containing a valid MATLAB expression (not recommended for apps). MATLAB evaluates this expression in the base workspace.
Note that a layout with the TileArrangement property set to"fixed" cannot change the grid size unless the layout is empty. This callback executes after the GridSize property has changed. The grid size typically changes when the TileArrangement property is set to "flow", and then you add or remove tiles or resize the figure.
The GridSizeChangedFcn callback function can access specific information about the grid size. MATLAB passes this information in a GridSizeChanged object as the second argument to your callback function. If you are developing an app in App Designer, the argument is calledevent. You can query the object properties using dot notation. For example, event.NewGridSize returns the new grid size. The GridSizeChanged object is not available to callback functions specified as strings or character vectors.
This table lists the properties of the GridSizeChanged object.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| NewGridSize | Two-element vector containing the new grid size |
| OldGridSize | Two-element vector containing the previous grid size |
| Source | TiledChartLayout object that executes the callback |
| EventName | 'GridSizeChanged' |
For an example of a GridSizeChangedFcn callback, see Colorbar That Adjusts as Tiles Reflow. For more information about writing callbacks in apps, see Callbacks in App Designer.
Callback Execution Control
This property is read-only.
Parent/Child
Parent container, specified as a Figure, Panel,Tab, or TiledChartLayout object.
Identifiers
This property is read-only.
Type of graphics object returned as 'tiledlayout'.
Object identifier, specified as a character vector or string scalar. You can specify a unique Tag value to serve as an identifier for an object. When you need access to the object elsewhere in your code, you can use the findobj function to search for the object based on the Tag value.
Version History
Introduced in R2019b
When you query the TileArrangement property, two new possible values are "horizontal" and "vertical". A value of"horizontal" corresponds to a horizontal stack of tiles, and"vertical" corresponds to a vertical stack.
To set the tile arrangement, specify the arrangement argument when you call the tiledlayout function.
Define the GridSizeChangedFcn callback function on a tiled chart layout. The callback function executes when the GridSize property of the layout changes. This callback is primarily useful for layouts that use the"flow" tile arrangement. For example, you can define a callback that displays the _x_-axis tick labels only in the bottom row of axes.
When you create a tiled chart layout, some of the TileSpacing and Padding properties provide a different result or have new names.
The new TileSpacing options are "loose","compact", "tight", and "none". The new Padding options are "loose","compact", and "tight". The following tables describe how the previous options relate to the new options.
TileSpacing Changes
| Previous TileSpacing Option | R2021a TileSpacing Option | How to Update Your Code |
|---|---|---|
"normal"  |
"loose"  |
Consider changing instances of "normal" to"loose".The"normal" option is no longer recommended, but it continues to work, and there are no plans to remove it. |
"compact"  |
"compact"  |
No changes needed. |
| Not Applicable | "tight"  |
"tight" is a new option. It provides the same result as"none" does in previous releases. |
"none"  |
"none"  |
The "none" option removes all the space between adjacent plot boxes, and the tick labels overlap with neighboring plot boxes.To preserve the spacing between the plot boxes, change instances of "none" to"tight". |
Padding Changes
| Previous Padding Option | R2021a Padding Option | How to Update Your Code |
|---|---|---|
"normal"  |
"loose"  |
Consider changing instances of "normal" to"loose".The"normal" option is no longer recommended, but it continues to work, and there are no plans to remove it. |
"compact"  |
"compact"  |
No changes needed. |
"none"  |
"tight"  |
Consider changing instances of "none" to"tight".The"none" option is no longer recommended, but it continues to work, and there are no plans to remove it. |