Switch Case Action Subsystem - Subsystem whose execution is enabled by Switch Case block - Simulink (original) (raw)
Subsystem whose execution is enabled by Switch Case block
Libraries:
Simulink / Ports & Subsystems
Description
The Switch Case Action Subsystem block is a Subsystem block preconfigured as a starting point for creating a subsystem whose execution is controlled by a Switch Case block. The input port to aSwitch Case block selects a case defined using the Case conditions parameter. Depending on input value and case selected, an action signal is sent to execute a Switch Case Action Subsystem block. Execution of the subsystem is controlled by an Action Port block placed inside the subsystem.

Simulink® ignores a priority set on an Switch Case Action Subsystem block. Instead, set the priority on the Switch Case block that initiates execution of the subsystem.
All blocks in a Switch Case Action Subsystem block must run at the same rate as the driving Switch Case block. You can achieve this requirement by setting each block sample time parameter to be either inherited (-1) or the same value as the Switch Case block sample time.
Merge Signals from Switch Case Action Subsystem Blocks
The example model ex_switch_case_block shows how to create one signal from multiple subsystem output signals. For more information, see Select Subsystem Execution.
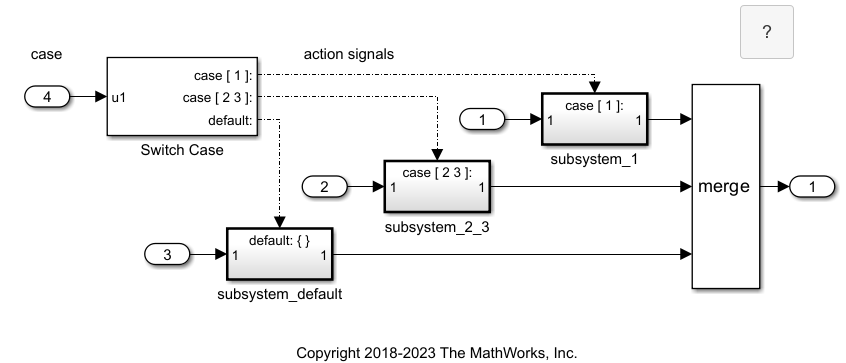
The Switch Case block selects the execution of one If Action Subsystem block from a set of subsystems. Regardless of which subsystem theSwitch Case block selects, you can create one resulting signal with aMerge block.
Examples
Ports
Input
Placing an Inport block in a subsystem adds an external input port to the Subsystem block. The port label matches the name of theInport block.
Use Inport blocks to get signals from the local environment.
Data Types: half | single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | Boolean | fixed point | enumerated | bus
The Action Port block inside a subsystem adds an external input port to the Subsystem block and changes the block to a Switch Case Action Subsystem block.
Note
The Action Port block is not available in the Simulink Library Browser. When using the Switch Case Action Subsystem block, you can access the Action Port block only from within the Switch Case Action Subsystem block.
Dot-dash lines from a Switch Case block to a Switch Case Action Subsystem block represent action signals. An action signal is a control signal connected to theAction port of a Switch Case Action Subsystem block. A message on the action signal initiates execution of the subsystem.
Data Types: action
Output
Placing an Outport block in a subsystem adds an output port from the Subsystem block. The port label on the subsystem block is the name of the Outport block.
Use Outport blocks to send signals to the local environment.
Data Types: half | single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | Boolean | fixed point | enumerated | bus
Parameters
To edit block parameters interactively, use theProperty Inspector. From the Simulink Toolstrip, on the Simulation tab, in thePrepare gallery, select Property Inspector.
Main
Select how to display port labels on the Subsystem block icon.
none— Do not display port labels.FromPortIcon— If the corresponding port icon displays a signal name, display the signal name on the Subsystem block. Otherwise, display the port block name or the port number if the block name is a default name.FromPortBlockName— Display the name of the corresponding port block on the Subsystem block.SignalName— If the signal connected to the port is named, display the name of the signal on the Subsystem block. Otherwise, display the name of the corresponding port block.
For port label editing on Subsystem blocks, see Edit Port Labels on Subsystem Blocks.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value programmatically, use the set_param function.
| Parameter: | ShowPortLabels | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Values: | 'FromPortIcon' (default) | 'FromPortBlockName' | 'SignalName' | 'none' |
Control user access to the contents of the subsystem.
ReadWrite— Enable opening and modification of subsystem contents.ReadOnly— Enable opening but not modification of the subsystem. If the subsystem resides in a block library, you can create and open links to the subsystem and can make and modify local copies of the subsystem but cannot change the permissions or modify the contents of the original library instance.NoReadOrWrite— Disable opening or modification of subsystem. If the subsystem resides in a library, you can create links to the subsystem in a model but cannot open, modify, change permissions, or create local copies of the subsystem.
You do not receive a response if you attempt to view the contents of a subsystem whose Read/Write permissions parameter is set to NoReadOrWrite. For example, when double-clicking such a subsystem, the software does not open the subsystem and does not display any messages.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value programmatically, use the set_param function.
| Parameter: | Permissions | |
|---|---|---|
| Values: | 'ReadWrite' (default) | 'ReadOnly' | 'NoReadOrWrite' |
Enter the name of a function to be called if an error occurs while the software executes the subsystem.
The software passes two arguments to the function: the handle of the subsystem and a character vector that specifies the error type. If no function is specified, the software displays a generic error message if executing the subsystem causes an error.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value programmatically, use the set_param function.
| Parameter: | ErrorFcn |
|---|---|
| Values: | '' (default) | function name in quotes |
| Data Types: | char | string |
Select whether to resolve names of workspace variables referenced by this subsystem.
For more information, see Symbol Resolution and Symbol Resolution Process.
All— Resolve all names of workspace variables used by this subsystem, including those used to specify block parameter values and Simulink data objects (for example, Simulink.Signal objects).ExplicitOnly— Resolve only names of workspace variables used to specify block parameter values, data store memory (where no block exists), signals, and states marked as “must resolve”.None— Do not resolve any workspace variable names.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value programmatically, use the set_param function.
| Parameter: | PermitHierarchicalResolution | |
|---|---|---|
| Values: | 'All' (default) | 'ExplicitOnly' | 'None' |
Select this parameter to display the reinitialize event ports. Clear this parameter to remove the ports.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, select Treat as atomic unit.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value programmatically, use the set_param function.
| Parameter: | ShowSubsystemReinitializePorts |
|---|---|
| Values: | 'off' (default) | 'on' |
Code Generation
Parameters on the Code Generation tab require a Simulink Coder™ or Embedded Coder® license.
Select the code format to be generated for an atomic (nonvirtual) subsystem.
Auto— The software chooses the optimal format for you based on the type and number of instances of the subsystem that exist in the model.Inline— The software inlines the subsystem unconditionally.Nonreusable function— If Filename options is set toAuto, the software packages separate functions in the model file. If File name options is set toUse subsystem name,Use function name, orUser specifiedusing different filenames, the software packages separate functions in separate files.
Subsystems with this setting generate functions that might have arguments depending on the Function interface parameter setting. You can name the generated function and file using parameters Function name and File name (no extension), respectively. These functions are not reentrant.Reusable function— The software generates a function with arguments that allows reuse of subsystem code when a model includes multiple instances of the subsystem.
This option also generates a function with arguments that allows subsystem code to be reused in the generated code of a model reference hierarchy that includes multiple instances of a subsystem across referenced models. In this case, the subsystem must be in a library.
For more information, see:
- Generate Code and Executables for Individual Subsystems (Simulink Coder)
- Generate Inlined Subsystem Code (Simulink Coder)
- Generate Subsystem Code as Separate Function and Files (Simulink Coder)
- Generate Reusable Code from Library Subsystems Shared Across Models (Simulink Coder)
The default value depends on the block configuration. For example, the default value for the Subsystem block is Auto. The default value for the CodeReuseSubsystem block isReusable function.
Tips
- When you want multiple instances of a subsystem to be represented as one reusable function, you can designate each one of them as
Autoor asReusable function. Using one or the other is best, as using both creates two reusable functions, one for each designation. The outcomes of these choices differ only when reuse is not possible. SelectingAutodoes not allow control of the function or filename for the subsystem code. - The
Reusable functionandAutooptions both try to determine if multiple instances of a subsystem exist and if the code can be reused. The difference between the behavior of each option is that when reuse is not possible:Autoyields inlined code, or if circumstances prohibit inlining, separate functions for each subsystem instance.Reusable functionyields a separate function with arguments for each subsystem instance in the model.
- If you select
Reusable functionwhile your generated code is under source control, set File name options toUse subsystem name,Use function name, orUser specified. Otherwise, the names of your code files change whenever you modify your model, which prevents source control on your files. - If you select an option other than
AutoorInlineand the model configuration parameterStates, the code generator produces separate output and update methods. The code generator does not take into account theCombine output and update methods for code generation and simulation specification.
Dependencies
- This parameter requires a Simulink Coder license for code generation.
- To enable this parameter, select Treat as atomic unit.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value programmatically, use the set_param function.
| Parameter: | RTWSystemCode | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Values: | 'Auto' | 'Inline' | 'Nonreusable function' | 'Reusable function' |
Select how the software names the function it generates for the subsystem.
If you have an Embedded Coder license, you can control function names with options on the Configuration Parameter > pane.
Auto— Assign a unique function name using the default naming convention,_`model`__ _`subsystem`_(), wheremodelis the name of the model and_subsystem_ is the name of the subsystem, or that of an identical one when code is being reused.
If you selectReusable functionfor theFunction packaging parameter and a model reference hierarchy contains multiple instances of the reusable subsystem, in order to generate reusable code for the subsystem, Function name options must be set toAuto.Use subsystem name— Use the subsystem name as the function name. By default, the function name uses the naming convention_`model`__ _`subsystem`_.
When a subsystem is in a library block and the subsystem parameter Function packaging is set toReusable function, if you set theUse subsystem nameoption, the code generator uses the name of the library block for the subsystem function name and filename.User specified— Enable the Function name field. Enter any legal C or C++ function name, which must be unique.
For more information, see Generate Subsystem Code as Separate Function and Files (Simulink Coder).
The default value depends on the block configuration. For example, the default value for the Subsystem block is Auto. The default value for the CodeReuseSubsystem block isUse subsystem name.
Dependencies
- This parameter requires a Simulink Coder license.
- To enable this parameter, set Function packaging to
Nonreusable functionorReusable function.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value programmatically, use the set_param function.
| Parameter: | RTWFcnNameOpts | |
|---|---|---|
| Values: | 'Auto' | 'Use subsystem name' | 'User specified' |
Specify a unique, valid C or C++ function name for subsystem code.
Use this parameter if you want to give the function a specific name instead of allowing the Simulink Coder code generator to assign its own autogenerated name or use the subsystem name. For more information, see Generate Subsystem Code as Separate Function and Files (Simulink Coder).
Dependencies
- This parameter requires a Simulink Coder license.
- To enable this parameter, set Function name options to
User specified.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value programmatically, use the set_param function.
| Parameter: | RTWFcnName |
|---|---|
| Values: | '' (default) | function name in quotes |
| Data Types: | char | string |
Select how the software names the separate file for the function it generates for the subsystem.
Auto— Depending on the configuration of the subsystem and how many instances are in the model,Autoyields different results.- If the code generator does not generate a separate file for the subsystem, the subsystem code is generated within the code module generated from the subsystem parent system. If the subsystem parent is the model itself, the subsystem code is generated within
_`model`_.cor_`model`_.cpp. - If you select
Reusable functionfor theFunction packaging parameter and your generated code is under source control, consider specifying a File name options value other thanAuto. This prevents the generated filename from changing due to unrelated model modifications, which is problematic for using source control to manage configurations. - If you select
Reusable functionfor theFunction packaging parameter and a model reference hierarchy contains multiple instances of the reusable subsystem, in order to generate reusable code for the subsystem, File name options must be set toAuto.
- If the code generator does not generate a separate file for the subsystem, the subsystem code is generated within the code module generated from the subsystem parent system. If the subsystem parent is the model itself, the subsystem code is generated within
Use subsystem name— The code generator generates a separate file, using the subsystem (or library block) name as the filename.
When File name options is set toUse subsystem name, the subsystem filename is mangled if the model containsModel blocks, or if a model reference target is being generated for the model. In these situations, the filename for the subsystem consists of the subsystem name prefixed by the model name.Use function name— The code generator uses the function name specified by Function name options as the filename.User specified— This option enables theFile name (no extension) text entry field. The code generator uses the name you enter as the filename. Enter any filename, but do not include the.cor.cpp(or any other) extension. This filename need not be unique.
While a subsystem source filename need not be unique, you must avoid giving nonunique names that result in cyclic dependencies. For example,sys_a.hincludessys_b.h,sys_b.hincludessys_c.h, andsys_c.hincludessys_a.h.
The default value depends on the block configuration. For example, the default value for the Subsystem block is Auto. The default value for the CodeReuseSubsystem block isUse function name.
Dependencies
- This parameter requires a Simulink Coder license.
- To enable this parameter, set Function packaging to
Nonreusable functionorReusable function.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value programmatically, use the set_param function.
| Parameter: | RTWFileNameOpts | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Values: | 'Auto' | 'Use subsystem name' | 'Use function name' | 'User specified' |
The filename that you specify does not have to be unique. However, avoid giving non-unique names that result in cyclic dependencies. For example,sys_a.h includes sys_b.h,sys_b.h includes sys_c.h, andsys_c.h includes sys_a.h.
For more information, see Generate Subsystem Code as Separate Function and Files (Simulink Coder).
Dependencies
- This parameter requires a Simulink Coder license.
- To enable this parameter, set File name options to
User specified.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value programmatically, use the set_param function.
| Parameter: | RTWFileName |
|---|---|
| Values: | '' (default) | filename in quotes |
| Data Types: | char | string |
Select how to use arguments with the generated function.
void_void— Generate a function without arguments and pass data as global variables. For example:
void subsystem_function(void)Allow arguments (Optimized)— Generate a function that uses arguments instead of passing data as global variables. This specification reduces global RAM. This option might reduce code size and improve execution speed and enable the code generator to apply additional optimizations. For example:
void subsystem_function(real_T rtu_In1, real_T rtu_In2,
real_T *rty_Out1)
In some cases, when generating optimized code, the code generator might not generate a function that has arguments.
Allow arguments (Match graphical interface)— Generate a function interface that uses arguments that match the Subsystem graphical block interface. The generated function interface is predictable and does not change. A predictable interface can be useful for debugging and testing your code and integrating with external applications. For example, if a model has twoInport blocks and two Outport blocks, then the generated function interface is:
void subsystem_function(real_T rtu_In1, real_T rtu_In2,
real_T *rty_Out1, real_T *rty_Out2)
For more information, see:
- Reduce Global Variables in Nonreusable Subsystem Functions (Embedded Coder)
- Generate Predictable Function Interface to Match Graphical Block Interface (Embedded Coder)
- Generate Modular Function Code for Nonvirtual Subsystems (Embedded Coder)
Dependencies
- This parameter requires an Embedded Coder license and an ERT-based system target file.
- To enable this parameter, set Function packaging to
Nonreusable function.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value programmatically, use the set_param function.
| Parameter: | FunctionInterfaceSpec | |
|---|---|---|
| Values: | 'void_void' (default) | 'Allow arguments (Optimized)' | 'Allow arguments (Match graphical interface)' |
Generate subsystem function code in which the internal data for an atomic subsystem is separated from its parent model and is owned by the subsystem.
off— Do not generate subsystem function code in which the internal data for an atomic subsystem is separated from its parent model and is owned by the subsystem.on— Generate subsystem function code in which the internal data for an atomic subsystem is separated from its parent model and is owned by the subsystem. The subsystem data structure is declared independently from the parent model data structures. A subsystem with separate data has its own block I/O andDWorkdata structure. As a result, the generated code for the subsystem is easier to trace and test. The data separation also tends to reduce the maximum size of global data structures throughout the model, because they are split into multiple data structures.
For details on how to generate modular function code for an atomic subsystem, seeGenerate Modular Function Code for Nonvirtual Subsystems (Embedded Coder).
For details on how to apply memory sections to atomic subsystems, see Override Default Memory Placement for Subsystem Functions and Data (Embedded Coder).
Dependencies
- This parameter requires an Embedded Coder license and an ERT-based system target file.
- To enable this parameter, set Function packaging to
Nonreusable function.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value programmatically, use the set_param function.
| Parameter: | FunctionWithSeparateData |
|---|---|
| Values: | 'off' (default) | 'on' |
Select how the software applies memory sections to the subsystem initialization and termination functions.
Inherit from model— Apply the root model memory sections to the subsystem function code.Default— Do not apply memory sections to the subsystem system code, overriding any model-level specification.- Apply one of the model memory sections to the subsystem.
Tips
- The possible values vary depending on what, if any, package of memory sections you have set for the model configuration. See Control Data and Function Placement in Memory by Inserting Pragmas (Embedded Coder) and Model Configuration Parameters: Code Generation (Simulink Coder).
- If you have not configured the model with a package,
Inherit from modelis the only available value. Otherwise, the list includesDefaultand all memory sections the model package contains. - These options can be useful for overriding the model memory section settings for the given subsystem. For details on how to apply memory sections to atomic subsystems, see Override Default Memory Placement for Subsystem Functions and Data (Embedded Coder).
Dependencies
- This parameter requires an Embedded Coder license and an ERT-based system target file.
- To enable this parameter, set Function packaging to
Nonreusable functionorReusable function.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value programmatically, use the set_param function.
| Parameter: | RTWMemSecFuncInitTerm | |
|---|---|---|
| Values: | 'Inherit from model' (default) | 'Default' | model memory section in quotes |
Select how Embedded Coder applies memory sections to the subsystem execution functions.
Inherit from model— Apply the root model memory sections to the subsystem function code.Default— Do not apply memory sections to the subsystem system code, overriding any model-level specification.- Apply one of the model memory sections to the subsystem.
Tips
- The possible values vary depending on what, if any, package of memory sections you have set for the model configuration. See Control Data and Function Placement in Memory by Inserting Pragmas (Embedded Coder) and Model Configuration Parameters: Code Generation (Simulink Coder).
- If you have not configured the model with a package,
Inherit from modelis the only available value. Otherwise, the list includesDefaultand all memory sections the model package contains. - These options can be useful for overriding the model memory section settings for the given subsystem. For details on how to apply memory sections to atomic subsystems, see Override Default Memory Placement for Subsystem Functions and Data (Embedded Coder).
Dependencies
- This parameter requires an Embedded Coder license and an ERT-based system target file.
- To enable this parameter, set Function packaging to
Nonreusable functionorReusable function.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value programmatically, use the set_param function.
| Parameter: | RTWMemSecFuncExecute | |
|---|---|---|
| Values: | 'Inherit from model' (default) | 'Default' | model memory section in quotes |
Select how the software applies memory sections to the subsystem constants.
Inherit from model— Apply the root model memory sections to the subsystem data.Default— Do not apply memory sections to the subsystem data, overriding any model-level specification.- Apply one of the model memory sections to the subsystem.
Tips
- The memory section that you specify applies to the corresponding global data structures in the generated code. For basic information about the global data structures generated for atomic subsystems, see Standard Data Structures (Simulink Coder).
- The possible values vary depending on what, if any, package of memory sections you have set for the model configuration. See Control Data and Function Placement in Memory by Inserting Pragmas (Embedded Coder).
- If you have not configured the model with a package,
Inherit from modelis the only available value. Otherwise, the list includesDefaultand all memory sections the model package contains. - These options can be useful for overriding the model memory section settings for the given subsystem. For details on how to apply memory sections to atomic subsystems, see Override Default Memory Placement for Subsystem Functions and Data (Embedded Coder).
Dependencies
- This parameter requires an Embedded Coder license and an ERT-based system target file.
- To enable this parameter, set Function packaging to
Nonreusable functionand select theFunction with separate data parameter.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value programmatically, use the set_param function.
| Parameter: | RTWMemSecDataConstants | |
|---|---|---|
| Values: | 'Inherit from model' (default) | 'Default' | model memory section in quotes |
Select how the software applies memory sections to the subsystem internal data.
Inherit from model— Apply the root model memory sections to the subsystem data.Default— Do not apply memory sections to the subsystem data, overriding any model-level specification.- Apply one of the model memory sections to the subsystem.
Tips
- The memory section that you specify applies to the corresponding global data structures in the generated code. For basic information about the global data structures generated for atomic subsystems, see Standard Data Structures (Simulink Coder).
- The possible values vary depending on what, if any, package of memory sections you have set for the model configuration. See Control Data and Function Placement in Memory by Inserting Pragmas (Embedded Coder).
- If you have not configured the model with a package,
Inherit from modelis the only available value. Otherwise, the list includesDefaultand all memory sections the model package contains. - These options can be useful for overriding the model memory section settings for the given subsystem. For details on how to apply memory sections to atomic subsystems, see Override Default Memory Placement for Subsystem Functions and Data (Embedded Coder).
Dependencies
- This parameter requires an Embedded Coder license and an ERT-based system target file.
- To enable this parameter, set Function packaging to
Nonreusable functionand select theFunction with separate data parameter.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value programmatically, use the set_param function.
| Parameter: | RTWMemSecDataInternal | |
|---|---|---|
| Values: | 'Inherit from model' (default) | 'Default' | model memory section in quotes |
Select how the software applies memory sections to the subsystem parameters.
Inherit from model— Apply the root model memory sections to the subsystem function code.Default— Do not apply memory sections to the subsystem system code, overriding any model-level specification.- Apply one of the model memory sections to the subsystem.
Tips
- The memory section that you specify applies to the corresponding global data structure in the generated code. For basic information about the global data structures generated for atomic subsystems, see Standard Data Structures (Simulink Coder).
- The possible values vary depending on what, if any, package of memory sections you have set for the model configuration. See Control Data and Function Placement in Memory by Inserting Pragmas (Embedded Coder).
- If you have not configured the model with a package,
Inherit from modelis the only available value. Otherwise, the list includesDefaultand all memory sections the model package contains. - These options can be useful for overriding the model memory section settings for the given subsystem. For details on how to apply memory sections to atomic subsystems, see Override Default Memory Placement for Subsystem Functions and Data (Embedded Coder).
Dependencies
- This parameter requires an Embedded Coder license and an ERT-based system target file.
- To enable this parameter, set Function packaging to
Nonreusable functionand select theFunction with separate data parameter.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value programmatically, use the set_param function.
| Parameter: | RTWMemSecDataParameters | |
|---|---|---|
| Values: | 'Inherit from model' (default) | 'Default' | model memory section in quotes |
Block Characteristics
| Data Types | Booleana | busa | doublea | enumerateda | fixed pointa | halfa | integera | singlea | stringa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Feedthrough | no | |||||||
| Multidimensional Signals | yesa | |||||||
| Variable-Size Signals | yesa | |||||||
| Zero-Crossing Detection | no | |||||||
| a Actual data type or capability support depends on block implementation. |
Extended Capabilities
Actual code generation support depends on block implementation.
HDL Coder™ provides additional configuration options that affect HDL implementation and synthesized logic.
HDL Architecture
| Architecture | Description |
|---|---|
| Module (default) | Generate code for the subsystem and the blocks within the subsystem. |
| BlackBox | Generate a black box interface. The generated HDL code includes only the input/output port definitions for the subsystem. Therefore, you can use a subsystem in your model to generate an interface to existing, manually written HDL code. The black-box interface generation for subsystems is similar to the Model block interface generation without the clock signals. |
| No HDL | Remove the subsystem from the generated code. You can use the subsystem in simulation, however, treat it as a “no-op” in the HDL code. |
HDL Block Properties
| General | |
|---|---|
| AdaptivePipelining | Automatic pipeline insertion based on the synthesis tool, target frequency, and multiplier word-lengths. The default is inherit. See alsoAdaptivePipelining (HDL Coder). |
| BalanceDelays | Detects introduction of new delays along one path and inserts matching delays on the other paths. The default is inherit. See also BalanceDelays (HDL Coder). |
| ClockRatePipelining | Insert pipeline registers at a faster clock rate instead of the slower data rate. The default is inherit. See also ClockRatePipelining (HDL Coder). |
| ConstrainedOutputPipeline | Number of registers to place at the outputs by moving existing delays within your design. Distributed pipelining does not redistribute these registers. The default is0. For more details, see ConstrainedOutputPipeline (HDL Coder). |
| DistributedPipelining | Pipeline register distribution, or register retiming. The default is inherit. See also DistributedPipelining (HDL Coder). |
| DSPStyle | Synthesis attributes for multiplier mapping. The default is none. See also DSPStyle (HDL Coder). |
| FlattenHierarchy | Remove subsystem hierarchy from generated HDL code. The default is inherit. See also FlattenHierarchy (HDL Coder). |
| InputPipeline | Number of input pipeline stages to insert in the generated code. Distributed pipelining and constrained output pipelining can move these registers. The default is0. For more details, see InputPipeline (HDL Coder). |
| OutputPipeline | Number of output pipeline stages to insert in the generated code. Distributed pipelining and constrained output pipelining can move these registers. The default is0. For more details, see OutputPipeline (HDL Coder). |
| SharingFactor | Number of functionally equivalent resources to map to a single shared resource. The default is 0. See also Resource Sharing (HDL Coder). |
| StreamingFactor | Number of parallel data paths, or vectors, that are time multiplexed to transform into serial, scalar data paths. The default is 0, which implements fully parallel data paths. See also Streaming (HDL Coder). |
Target Specification
This block cannot be the DUT, so the block property settings in the Target Specification tab are ignored.
Restrictions
If the output of the subsystem is a bus then Initial condition of the outport must be 0.
Actual data type support depends on block implementation.
Version History
Introduced before R2006a