opengl - (To be removed) Control OpenGL rendering - MATLAB (original) (raw)
(To be removed) Control OpenGL rendering
opengl will be removed in a future release. For more information, seeVersion History.
Syntax
Description
opengl [info](#bug2yed-1-info) prints information about the OpenGL® implementation currently in use by MATLAB®, such as the version, vendor, and graphics features that it supports. Using this command loads OpenGL. Starting in R2019a, this syntax is no longer recommended. For more information, see Version History.
`d` = opengl('data') returns the same data provided with opengl info, but stores it in a structure. Starting in R2019a, this syntax is no longer recommended.
opengl [software](#bug2yed-1-software) uses a software version of OpenGL to render subsequent graphics for the current MATLAB session. This command works only on Windows® systems.
opengl [hardware](#bug2yed-1-hardware) uses a hardware-accelerated version of OpenGL to render subsequent graphics. If your graphics hardware does not support hardware-accelerated OpenGL, then MATLAB uses a software version instead.
opengl [hardwarebasic](#bug2yed-1-hardwarebasic) uses a hardware-accelerated version of OpenGL, but disables some advanced graphics features that are unstable with certain graphics drivers. If your graphics hardware does not support hardware-accelerated OpenGL, then MATLAB uses a software version instead.
opengl('save',[pref](#bug2yed-1-pref)) sets your preferences so that future sessions of MATLAB on this computer use the preferred version of OpenGL. Specify pref as 'software','hardware', 'hardwarebasic', or'none'. This command does not affect the current session.
Examples
Determine Graphics Hardware
Using the opengl info command, determine your graphics hardware by checking the Vendor and Renderer fields.
Version: '3.3.0'
Vendor: 'NVIDIA Corporation'
Renderer: 'Quadro 400/PCIe/SSE2'
RendererDriverVersion: '9.18.13.3182'
RendererDriverReleaseDate: '11-Nov-2013'
MaxTextureSize: 8192
Visual: 'Visual 0x07, (RGBA 32 bits...'
Software: 'false'
HardwareSupportLevel: 'full'
SupportsGraphicsSmoothing: 1
SupportsDepthPeelTransparency: 1
SupportsAlignVertexCenters: 1
Extensions: {248x1 cell}
MaxFrameBufferSize: 8192Note
If the returned fields contain the line Software: 'true', then you are using software OpenGL and the name listed in the Vendor field is not your graphics hardware vendor. Instead, the Vendor field indicates the manufacturer of the software OpenGL implementation.
Determine Graphics Hardware When Using Software OpenGL (Windows)
Close all figures, switch to hardware OpenGL, and issue the opengl info command. Then, switch back to software OpenGL.
close all opengl hardware opengl info opengl software
Determine Graphics Hardware When Using Software OpenGL (Linux)
Start MATLAB with the -nosoftwareopengl flag. Then, issue the opengl info command.
Use Software OpenGL for Current Session
Switch to using software OpenGL to render graphics in the current session.
This command works only on Windows systems.
Use Software OpenGL for Future Sessions
Set your preferences so that MATLAB uses software OpenGL to render graphics in all future sessions. This command does not affect the current session.
opengl('save','software')
Input Arguments
info — Information about OpenGL implementation
info
Information about the OpenGL implementation currently in use by MATLAB, specified as info. The opengl info command returns the fields listed in this table.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Version | Version of the OpenGL implementation. |
| Vendor | Manufacturer of the OpenGL implementation. |
| RendererDriverVersion | Version of the OpenGL driver (Windows systems with hardware-accelerated OpenGL only). This field does not display on virtual machines. |
| RendererDriverReleaseDate | Release date of the OpenGL driver (Windows systems with hardware-accelerated OpenGL only). This field does not display on virtual machines. |
| Renderer | Description of the OpenGL renderer. If you are using hardware-accelerated OpenGL, this field is the graphics card model name. |
| MaxTextureSize | Maximum texture size supported by the OpenGL implementation. |
| Visual | Display properties of the OpenGL implementation. |
| Software | Software OpenGL enabled, returned as 'true' or 'false'. |
| HardwareSupportLevel | Hardware support level, returned as one of these values: 'full' — Hardware-accelerated OpenGL (all graphics features enabled)'basic' — Basic hardware-accelerated OpenGL (some graphics features disabled)'none' — Software OpenGLIf MATLAB detects an unsupported driver, this field also contains'known graphics driver issues'. |
| SupportsGraphicsSmoothing | Graphics smoothing feature support, returned as 1 if supported or 0 otherwise. |
| SupportsDepthPeelTransparency | Depth peel transparency feature support, returned as 1 if supported or 0 otherwise. |
| SupportsAlignVertexCenters | Align vertex centers feature support, returned as 1 if supported or 0 otherwise. |
| Extensions | Extended capabilities supported by the OpenGL implementation. |
| MaxFrameBufferSize | Maximum frame buffer size supported by the OpenGL implementation. |
For more information about the graphics smoothing, depth peel transparency, and align vertex centers features, see Advanced Graphics Features.
software — Software OpenGL
software
Software OpenGL, specified as software.
To switch to software OpenGL:
- On Windows systems, execute
opengl software. - On Linux® systems, start MATLAB with the
-softwareopenglflag. - Macintosh systems do not support software OpenGL.
Software OpenGL can be slower than hardware-accelerated OpenGL and does not support all graphics features. For a table of supported features, see Advanced Graphics Features.
hardware — Hardware-accelerated OpenGL
hardware
Hardware-accelerated OpenGL, specified as hardware. All systems support using the opengl hardware command to switch from basic hardware to hardware OpenGL. However, only Windows systems support using the opengl hardware command to switch from software to hardware OpenGL. To switch from software to hardware on Linux systems, start MATLAB with the -nosoftwareopengl flag.
If your system automatically switched to using software OpenGL, then forcing your system to use hardware OpenGL can cause instabilities.
hardwarebasic — Basic version of hardware-accelerated OpenGL
hardwarebasic
Basic version of hardware-accelerated OpenGL, specified as hardwarebasic. This version of hardware-accelerated OpenGL uses your graphics hardware, but disables graphics features that are unstable with some graphics drivers. The disabled features might change in future releases as graphics features change and graphics hardware evolves. For a table of disabled features, see Advanced Graphics Features.
pref — OpenGL version preference for future sessions
'software' | 'hardware' | 'hardwarebasic' | 'none'
OpenGL version preference for future sessions, specified as one of these options:
'software'— Software OpenGL. This option is not available on Macintosh systems.'hardware'— Hardware-accelerated OpenGL.'hardwarebasic'— Hardware-accelerated OpenGL with some advanced graphics features disabled. For more information, see Advanced Graphics Features.'none'— Default value for your system.
More About
Advanced Graphics Features
Advanced graphics features are features that require certain implementations of OpenGL. These features are graphics smoothing, depth peel transparency, align vertex centers, and hardware-accelerated markers. Support for these features depends on:
- Whether you are using hardware, basic hardware, or software OpenGL. To determine which implementation you are using, check the
HardwareSupportLevelfield returned byopengl info. - The version of the OpenGL implementation. To determine the version in use, check the
Versionfield returned byopengl info. To get the latest version available for your graphics hardware, upgrade your graphics drivers from your computer manufacturer website. For more information on upgrading graphics drivers, see System Requirements for Graphics.
This table lists the advanced graphics features and the circumstances under which they are supported.
| Graphics Feature | Hardware OpenGL | Basic Hardware OpenGL | Software OpenGL on Windows | Software OpenGL on Linux |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Graphics Smoothing | Supported for OpenGL 2.1 or higher | Supported for OpenGL 2.1 or higher | Not supported | Not supported |
| Depth Peel Transparency | Supported for OpenGL 2.1 or higher | Disabled | Not supported | Supported |
| Align Vertex Centers | Supported for OpenGL 2.1 or higher | Disabled | Not supported | Not supported |
| Hardware-accelerated markers | Supported for OpenGL 4.0 or higher | Disabled | Not supported | Not supported |
Graphics Smoothing
Graphics smoothing is a technique to improve the appearance of plots by reducing the appearance of jagged lines. By default, this feature is enabled if your system supports it.
This table shows the difference when the feature is enabled or disabled. To turn off this feature for a particular figure, set the GraphicsSmoothing property of the figure to 'off'.
| When Supported and Enabled | When Not Supported or Disabled |
|---|---|
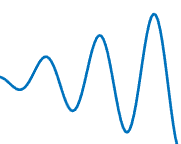 |
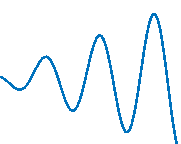 |
(Zoomed-in view) 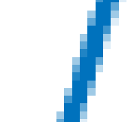 |
(Zoomed-in view) 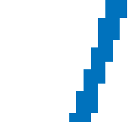 |
Depth Peel Transparency
Depth peel transparency is a feature for correctly drawing transparent 3-D objects or complex plots that contain intersecting transparent objects. In the table, the left image shows the result of using transparency on a sphere when the depth peel transparency feature is supported. The right image shows the same sphere with unexpected shaded areas that occur when the feature is not supported.
| When Supported | When Not Supported |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Align Vertex Centers
Align vertex centers is a feature for sharp vertical and horizontal lines. If graphics smoothing is enabled, it can cause horizontal and vertical lines to appear uneven in thickness or color. The align vertex centers feature eliminates the uneven appearance. By default, the align vertex centers feature is not enabled. However, if your system supports this feature, then you can turn it on for objects that have an AlignVertexCenters property by setting the property to 'on'.
This table shows the difference when the feature is enabled or disabled.
| When Supported and Enabled | When Not Supported or Disabled |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Hardware-Accelerated Markers
Hardware-accelerated markers take advantage of your graphics hardware for improved performance and quality. This table shows the difference when the feature is supported or not supported.
| When Supported | When Not Supported |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Tips
- Painters is an alternate rendering method for screen display and printing. For more information, see the figure’s Renderer property.
- By default, MATLAB uses hardware-accelerated OpenGL if your graphics hardware supports it. However, in some cases, MATLAB automatically switches to software OpenGL, for example, if it detects:
- You are using a graphics driver with known issues or graphics virtualization.
- A previous MATLAB session crashed due to a graphics issue. If the previous session was using software OpenGL and crashed, then subsequent sessions use a more stable version of software OpenGL that has fewer capabilities.
- You do not have graphics hardware or your graphics hardware does not support hardware OpenGL.
Version History
Introduced before R2006a
R2022a: To be removed in a future release
The opengl function will be removed in a future release.
- To query the renderer, use the rendererinfo function instead of the
openglfunction. - Changing the renderer with the
openglfunction will no longer be necessary when the function is removed.
R2019a: Querying the graphics renderer is not recommended
Using the opengl function to get information about the graphics renderer is not recommended. Specifically, these syntaxes are not recommended:
opengl infod = opengl('data')
There are no plans to remove support for these syntaxes at this time. Instead of calling opengl to get the renderer information, call the rendererinfo function instead:
Specifyax as any type of axes or a chart that can be a child of a figure (such as a heatmap). The output is a structure containing most of the same information as theopengl function provides.
| Fields in opengl Structure | Corresponding Fields in rendererinfo Structure |
|---|---|
| d.Version | info.Version |
| d.Vendor | info.Vendor |
| d.Renderer | info.RendererDevice |
| d.RendererDriverVersion | info.Details.RendererDriverVersion |
| d.RendererDriverReleaseDate | info.Details.RendererDriverReleaseDate |
| d.MaxTextureSize | info.Details.MaxTextureSize |
| d.Visual | No longer needed |
| d.Software | This information is stored in info.GraphicsRenderer, but to get the equivalent logical value, usestrcmp(info.GraphicsRenderer,'OpenGL Software') |
| d.HardwareSupportLevel | info.Details.HardwareSupportLevel |
| d.SupportsGraphicsSmoothing | info.Details.SupportsGraphicsSmoothing |
| d.SupportsDepthPeelTransparency | info.Details.SupportsDepthPeelTransparency |
| d.SupportsAlignVertexCenters | info.Details.SupportsAlignVertexCenters |
| d.Extensions | No longer needed |
| d.MaxFrameBufferSize | info.Details.MaxFrameBufferSize |