Small silencing RNAs: an expanding universe (original) (raw)
. Author manuscript; available in PMC: 2009 Aug 11.
Published in final edited form as: Nat Rev Genet. 2009 Feb;10(2):94–108. doi: 10.1038/nrg2504
Abstract
Since the discovery in 1993 of the first small silencing RNA, a dizzying number of small RNA classes have been identified, including microRNAs (miRNAs), small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) and Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs). These classes differ in their biogenesis, modes of target regulation and in the biological pathways they regulate. There is a growing realization that, despite their differences, these distinct small RNA pathways are interconnected and that small RNA pathways compete and collaborate as they regulate genes and protect the genome from external and internal threats.
Introduction
The defining features of small silencing RNAs are their short length (~20–30 nt), and their association with members of the Argonaute (Ago) family of proteins, which they guide to their regulatory targets, typically resulting in reduced expression of target genes. Beyond these defining features, different small RNA classes guide diverse and complex schemes of gene regulation. Some small silencing RNAs, such as siRNAs, derive from double-stranded (ds) RNA, whereas others, such as piRNAs, do not. These different classes of regulatory RNAs also differ in the proteins required for their biogenesis, the constitution of the Argonaute-containing complexes that execute their regulatory functions, their modes of gene regulation, and the biological functions in which they participate. New small RNA classes and new examples of existing classes continue to be discovered, such as the recent identification of endo-siRNAs in flies and mammals. Here, we provide an overview of small silencing RNAs from plants and metazoan animals. For each class, we describe its biogenesis, function, and mode of target regulation, providing examples of the regulatory networks in which each participates (TABLE 1). Finally, we highlight several examples of unexpected, and often unexplained, complexity in the interactions between distinct small RNA pathways.
Table 1.
Types of small silencing RNAs.
| Name | Organism | Length(nt) | Proteins | Source of Trigger | Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miRNA | Plants, algae, animals, viruses, protists | 20–25 | Drosha (animals only) + Dicer | Pol II transcription (pri-miRNAs | Regulation of mRNA stability, translation | 92–94,199,200,225 |
| casiRNA | Plants | 24 | DCL3 | Transposons, repeats | Chromatin modification | 38,44,51,52,61–63 |
| tasiRNA | Plants | 21 | DCL4 | miRNA-cleaved TAS RNAs | Post transcriptional regulation | 64–68 |
| natsiRNA | Plants primarysecondary | 2421 | DCL2DCL1 | Bidirectional transcripts induced by stress | Regulate stress response genes | 71,72 |
| Exo-siRNA | Animals, fungi, protistsPlants | ~2121 & 24 | Dicer | Transgenic, viral or other exogenous dsRNA | Post transcriptional regulation, antiviral defense | 4,5,8,226 |
| EndosiRNA | Plants, algae, animals, fungi, protists, | ~21 | Dicer (Except secondary siRNAs in C. elegans, which are products of RdRP transcription, and are therefore not technically siRNAs.) | Structured loci, convergent and bidirectional transcription, mRNAs paired to antisense pseudogene transcripts | Post transcriptional regulation of transcripts and transposonsTranscriptional gene silencing | 75–79,82,83,86,87,199,200,227 |
| piRNA germ line | Drosophila melanogaster, mammals, zebrafish | 24–30 | Dicer-independent | Long, primary transcripts? | Transposon regulation, unknown functions | 156,162–168,176 |
| piRNA-like (soma | Drosophila melanogaster | 24–30 | Dicer-independen | In ago2 mutants in Drosophila | Unknown | 76 |
| 21U-RNA piRNAs | Caenorhabditis elegans | 21 | Dicer-independent | Individual transcription of each piRNA? | Transposon regulation ,unknown functions | 113,172–174 |
| 26G RNA | Caenorhabditis elegans | 26 | RdRP? | Enriched in sperm | Unknown | 113 |
The Discovery of RNAi
In 1998, Fire and Mello established dsRNA as the silencing trigger in C. elegans1. Their experiments overturned the contemporary view that antisense RNA induced silencing by base pairing to its mRNA counterpart, thereby preventing its translation into protein. In worms and other animals, siRNA-mediated silencing is known as RNA interference (RNAi). Remarkably, RNAi is systemic in both plants and nematodes, spreading from cell to cell2. In C. elegans, RNAi is also heritable: silencing can be transferred to the progeny of the worm originally injected with the trigger dsRNA3. Viral infection, inverted repeat transgenes, or aberrant transcription products, all lead to the production of dsRNA. dsRNA is converted to siRNAs that direct RNAi. siRNAs were discovered in plants4 and later shown in animal extracts to serve as guides that direct endonucleolytic cleavage of their target RNAs5,6. siRNAs can be classified according to the proteins involved in their biogenesis, their mode of regulation or their size. Here, we differentiate the major types of siRNAs according to the molecules that trigger their production, a classification scheme that best captures the biological distinctions among small silencing RNAs.
siRNAs derived from exogenous agents
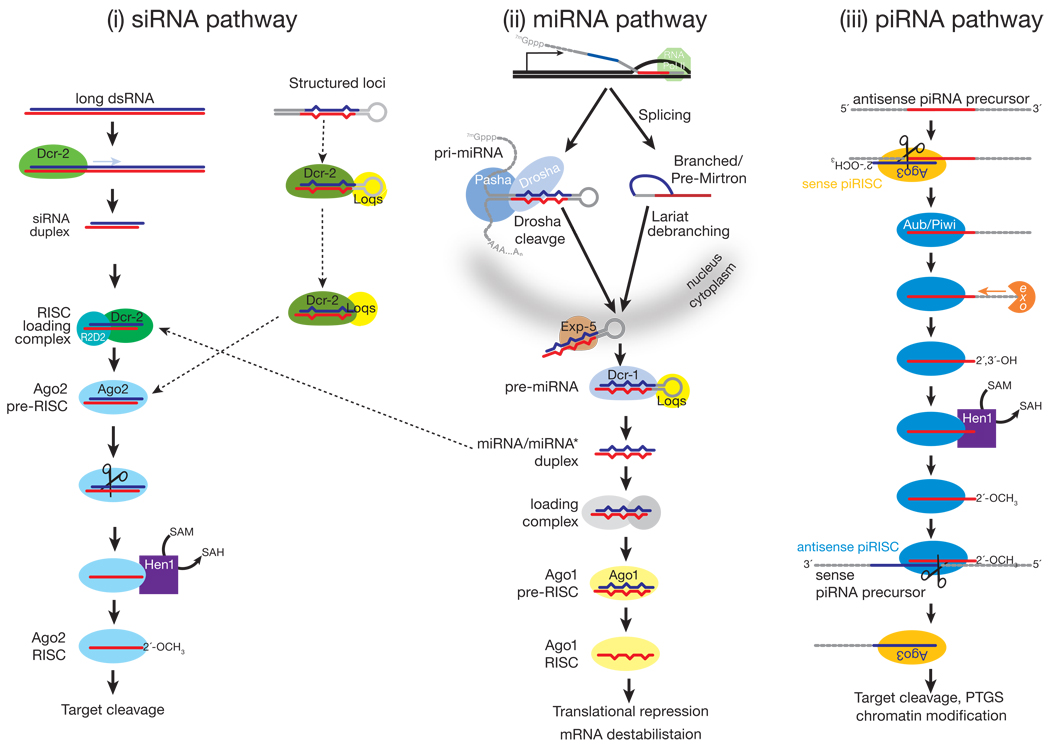
Early examples of RNAi were triggered by exogenous dsRNA. In these cases, long, exogenous dsRNA is cleaved into double-stranded siRNAs by Dicer (Dcr), a dsRNA-specific RNase III family ribonuclease7 (FIG. 1). siRNA duplexes produced by Dicer comprise two ~21 nt strands, each bearing a 5′ phosphate and 3′ hydroxyl group, paired so as to leave 3′, two-nucleotide overhangs5,8,9. The strand that directs silencing is called the guide, whereas the other strand, which is ultimately destroyed, is the passenger. Target regulation by siRNAs is mediated by the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), the generic name for an Argonaute-small RNA complex6. In addition to an Argonaute protein and a small RNA guide, RISC may also contain auxiliary proteins that extend or modify its function, for example, proteins that re-direct the target mRNA to a site of general mRNA degradation10.
Figure 1.
While mammals and C. elegans each have a single Dicer that makes both miRNAs and siRNAs11–14, Drosophila has two Dicers: Dcr-1 makes miRNAs, whereas Dcr-2 is specialized for siRNA production15. The fly RNAi pathway defends against viral infection, and Dicer specialization may reduce competition between pre-miRNAs and viral dsRNAs for Dicer. Alternatively, Dcr-2 and Ago2 specialization might reflect the evolutionary pressure on the siRNA pathway to counter rapidly evolving viral strategies to escape RNAi. In fact, dcr-2 and ago2 are among the most rapidly evolving Drosophila genes16. C. elegans may achieve similar specialization with a single Dicer by using the double-stranded RNA-binding protein, RDE-4, as the gatekeeper for entry into the RNAi pathway17. However, no natural virus infection has been documented in C. elegans18. In contrast, mammals may not use the RNAi pathway to respond to viral infection, having evolved an elaborate, protein-based immune system19–21.
The relative thermodynamic stabilities of the 5′ ends of the two siRNA strands in the duplex determines the identity of the guide and passenger strands22–24. In flies, this thermodynamic difference is sensed by the dsRNA-binding protein R2D2, the partner of Dcr-2 and a component of the RISC Loading Complex (RLC)25,26. The RLC recruits Argonaute2 (Ago2), to which it transfers the siRNA duplex. Ago2 can then cleave the passenger strand as if it were a target RNA27–31. (Ago2 always cleaves its RNA target at the phosphodiester bond that lies between the nucleotides paired to guide nucleotides 10 and 11 (Refs. 8,9). Release of the passenger strand after its cleavage converts pre-RISC to RISC: mature RISC contains only single-stranded guide RNA. In flies, the guide strand is 2′-_O_-methylated at its 3′ end by the _S_-adenosyl methionine-dependent methyltransferase, Hen1, completing RISC assembly32,33. In plants, both miRNAs and siRNAs are terminally methylated, which is crucial for their stability34–36.
Plants exhibit a surprising diversity of small RNA types and the proteins that generate them. The diversification of RNA silencing pathways in plants may reflect the need of a sessile organism to cope with biotic and abiotic stress. The number of RNA silencing proteins can vary enormously among animals, too, with C. elegans producing 27 distinct Argonaute proteins compared to five in flies. Phylogenetic data suggest that nearly all of these “extra” C. elegans Argonautes act in the secondary siRNA pathway, perhaps because endogenous, secondary siRNAs are so plentiful in worms37. Arabidopsis thaliana has four Dicer-like (DCL) proteins and 10 Argonautes, with both unique and redundant functions. In plants, inverted repeat transgenes or co-expressed sense and antisense transcripts produce two sizes of siRNAs, 21 nt and 24 nt38,39. The 21 nt siRNAs are produced by DCL4, but in the absence of DCL4, DCL2 can substitute, making 22 nt siRNAs40–44. The DCL4-produced 21-mers typically associate with AGO1 and guide mRNA cleavage. The 24-mers associate with AGO4 (major) and AGO6 (surrogate), and promote the formation of repressive chromatin45.
In plants, exogenous sources of siRNAs are not confined to dsRNAs. Single-stranded sense transcripts from tandemly repeated or highly expressed single-copy transgenes are converted to dsRNA by RDR6, a member of the RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase (RdRP) family, transcribe single-stranded RNA from an RNA template46 (Box 1). RDR6 and RDR1, also convert viral single-stranded RNA into dsRNA, initiating an anti-viral RNAi response47. The resulting dsRNA is cleaved by Dicer into siRNAs that are terminally 2′-_O_-methylated by HEN136. Why plants RNAs expressed from transgenes are converted by RDR6 into dsRNA, but abundant, endogenous mRNAs are not, is poorly understood. Recent evidence that some housekeeping exonucleases compete with plant RNA silencing pathways for aberrant RNAs suggests that substandard RNA transcripts—e.g. those lacking a 5′ cap or 3′ poly(A) tail—act as substrates for RdRPs. Highly expressed transgenes might overwhelm normal RNA quality control pathways, escape destruction, and be converted to dsRNA by RdRPs47–49.
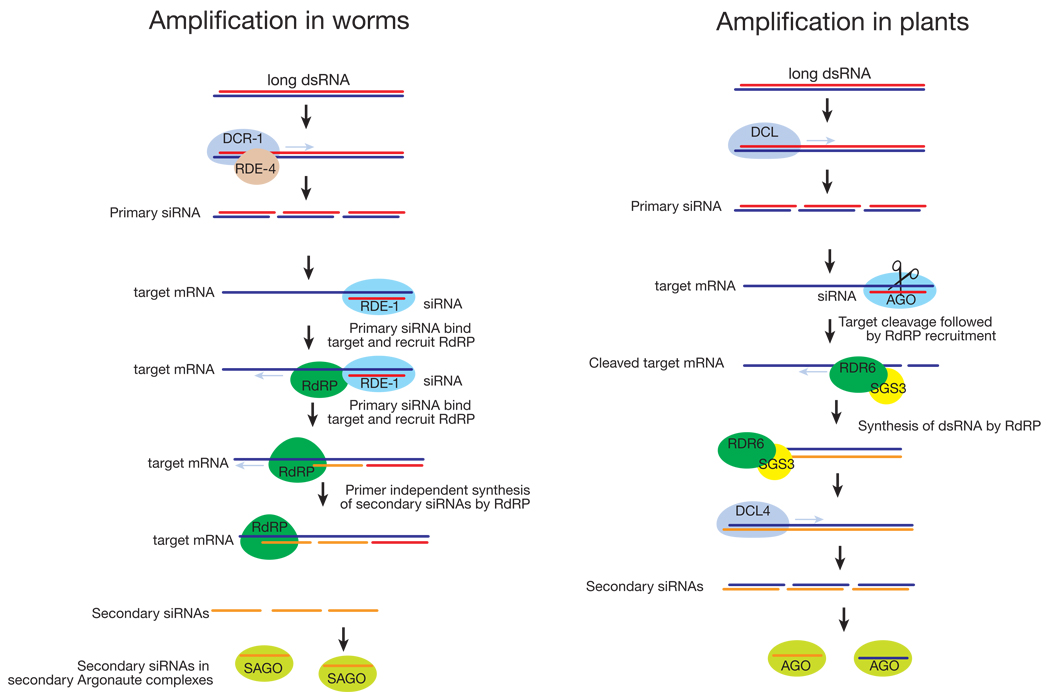
Box 1. Amplifying silencing
RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RdRPs) amplify the silencing response. Primary siRNAs derived from exogenous triggers by Dicer processing bind their mRNA targets and direct cleavage by AGO complexes203. In plants, RdRPs uses these cleaved transcript fragments as templates to synthesize long dsRNA; the dsRNA is then diced into secondary siRNAs41,42,44,46,204–206. Secondary siRNAs are formed both 5′ and 3′ of the primary targeted interval, suggesting that mRNA cleavage per se, rather than priming of RdRP by primary siRNAs is the signal for siRNA amplification. Other data suggest that production of secondary siRNAs in Arabidopsis may sometimes be primed207. RdRP amplification of siRNAs is especially important in defending plants against viral infection.
In C. elegans, primary siRNAs are amplified into secondary siRNAs by a different mechanism203. In worms, primary siRNAs are bound to RDE-1, a “primary Argonaute”208,209. The primary siRNAs guide RDE-1 to the target mRNA, to which it recruits RdRPs that synthesize secondary siRNAs210,211. Worm secondary siRNAs have a 5′ di- or triphosphate, indicating that they are produced by transcription rather than dicing208,209,212, and, at least in vitro, secondary siRNA production does not require Dicer211. How the length of siRNA transcription is controlled is perplexing, but in vitro, the Neurospora RdRP, QDE1, can directly transcribe short RNA oligomers ~22 nt long from a much longer template212. As a consequence of their production by an RdRP, secondary siRNAs in C. elegans are exclusively antisense to their mRNA targets208,213. Secondary siRNAs act bound to secondary Argonautes, such as CSR-1, which can cleave its mRNA targets just like fly and human Ago2 proteins211.
The presence of siRNA amplification in plants, worms, fungi, and according to some early reports, in flies, led to the speculation that RdRPs are a universal feature of RNAi. An amplification step in human RNAi could produce secondary siRNAs bearing homology to other genes, a significant impediment to the use of RNAi as a target discovery tool or as therapy for human diseases. However, the success of allele-specific RNAi in cultured human cells and in mice makes it unlikely that an RdRP-catalyzed amplification step occurs in mammals214–218. Similarly, extensive biochemical and genetic studies have demonstrated that the fly RNAi pathway does not use an RdRP enzyme5,39,219–222.
Endogenous siRNAs (endo-siRNAs)
The first endo-siRNAs were detected in plants and C. elegans38,50,51. Plants too produce a variety of endo-siRNAs, and, the recent discovery of endo-siRNAs in flies and mammals suggests that endo-siRNAs are ubiquitous among higher eukaryotes.
Plant endo-siRNAs
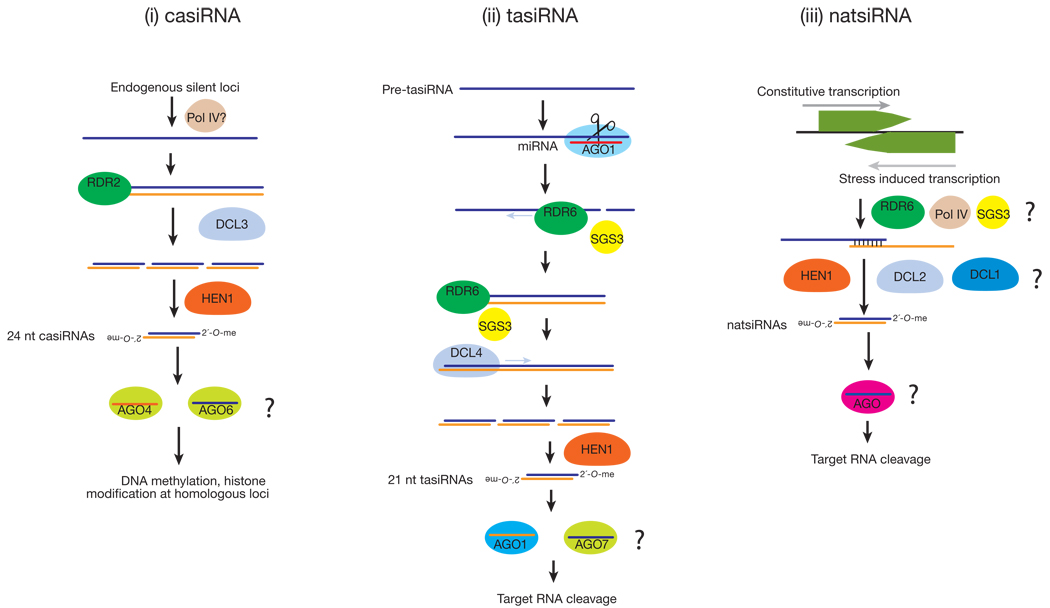
In plants, _cis_-acting siRNAs (casiRNAs) originate from transposons, repetitive elements, and tandem repeats such as 5S rRNA genes, and comprise the bulk of endo-siRNAs44 (FIG. 2). CasiRNAs are predominantly 24 nt long and methylated by HEN1. Their accumulation requires DCL3 and the RNA polymerases, RDR2 and POL IV, and either AGO6 (primarily) or AGO4, which act redundantly44,51–60. CasiRNAs promote heterochromatin formation by directing DNA methylation and histone modification of the loci from which they originate38,44,51,52,61–63.
Figure 2.
Another class of plant endo-siRNAs illustrates how distinct small RNA pathways interact. _Trans_-acting siRNAs (tasiRNAs) are endo-siRNAs generated by the convergence of the miRNA and siRNA pathways in plants64–68(FIG. 2). miRNA-directed cleavage of certain transcripts recruits the RdRP enzyme, RDR6. RDR6 then copies the cleaved transcript into dsRNA, which DCL4 dices into tasiRNAs that are phased. This phasing suggests that DCL4 begins dicing precisely at the miRNA cleavage site, making a tasiRNA every 21 nt68. The site of miRNA cleavage is critical, because in determining the entry point for Dicer, it establishes the target specificity of the tasiRNAs produced. One of the determinants that seems to predispose a transcript to produce tasiRNAs after its cleavage by a miRNA is the presence of a second miRNA or siRNA complementary site on the transcript. Of special mention is the TAS3 locus, whose RNA transcript has two binding sites for miR-390. Only one of these sites is efficiently cleaved by miR-390, but binding of the miRNA to both appears to be required to initiate conversion of the TAS3 transcript to dsRNA by RDR669,70.
Natural antisense transcript-derived siRNAs (natsiRNAs) are produced in response to stress in plants71,72(FIG. 2). They are generated from a pair of convergently transcribed RNAs: typically, one transcript is expressed constitutively, whereas the complementary RNA is transcribed only when the plant is subject to environmental stress, such as high salt. Production of 24 nt siRNAs from region of overlap of the two transcripts requires DCL2 and/or DCL1, RDR6, and SGS3 (SUPPRESSOR OF GENE SILENCING3, probably an RNA-binding protein)73 and Pol IV71,72. The 24 nt natsiRNAs then direct cleavage of one of the mRNAs of the pair, and in one such case, trigger the DCL1-dependent production of 21 nt secondary siRNAs72. In addition to natsiRNAs, “long” siRNAs (lsiRNAs) in Arabidopsis also originate from NAT pairs and are stress-induced. Unlike natsi-RNAs, lsiRNAs are 30–40 nts long and require DCL1, DCL4, AGO7, RDR6 and POL IV for their production74.
Animal endo-siRNAs
Plant and worm endo-siRNAs are typically produced through the action of RdRPs (Box 1). The genomes of flies and mammals seem not to encode such RdRP proteins, so the recent discovery of endo-siRNAs in flies and mice was unexpected.
The first mammalian endo-siRNAs to be reported corresponded to the LINE-1 retrotransposon and were detected in cultured human cells75. Full length LINE-1 (L1) contains both sense and antisense promoters in its 5′ untranslated region (UTR) that could, in principle, drive bi-directional transcription of L1, producing overlapping, complementary transcripts to be processed into siRNAs by Dicer, but the precise mechanism by which transposons trigger siRNA production in mammals remains unknown.
More recently, endogenous siRNAs have been detected in Drosophila somatic and germ cells and in mouse oocytes. High throughput sequencing of small RNAs from germ-line and somatic tissues of Drosophila and of Ago2 immunoprecipitates revealed a small RNA population that could readily be distinguished from miRNAs and piRNAs76–81. These small RNAs are nearly always exactly 21 nt long, are present in both sense and antisense orientations, have modified 3′ ends, and, unlike miRNAs and piRNAs, are not biased toward beginning with uracil. Production of the 21-mers requires Dcr-2, although in the absence of Dcr-2 a remnant of the endo-siRNA population inexplicably persists.
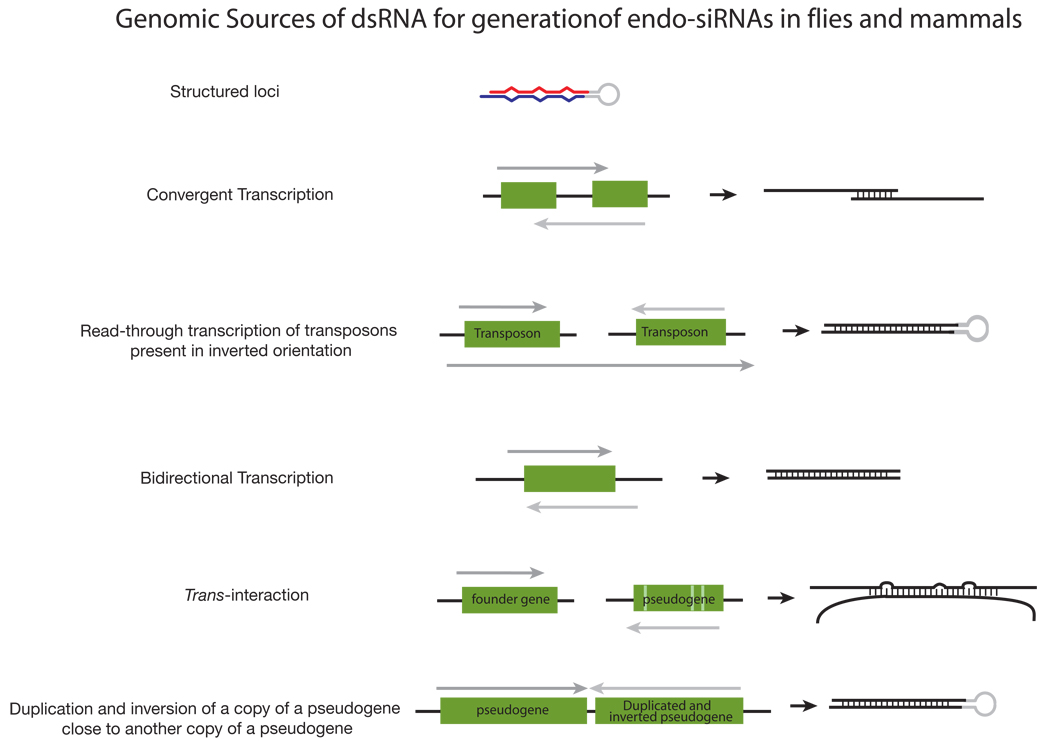
Fly endo-siRNAs derive from transposons, heterochromatic sequences, intergenic regions, long RNA transcripts with extensive structure, and, most interestingly, from mRNAs (FIG. 3). Expression of transposon mRNAs increases in both dcr-2 and ago2 mutants, implicating an endogenous RNAi pathway in the silencing of transposons in flies, as reported previously for C. elegans82,83. siRNAs derived from mRNAs are >10 times more likely to come from regions predicted to produce overlapping, convergent transcripts than expected by chance76, suggesting that endo-siRNAs originate from endogenous dsRNA formed when these complementary transcripts pair.
Figure 3.
A subset of fly endo-siRNAs derive from “structured loci” whose RNA transcripts can fold into long, intramolecularly paired hairpins77–79. Accumulation of these siRNAs requires Dcr-2 and the dsRNA-binding protein Loquacious (Loqs)—typically considered the partner of Dcr-1, the dicer that produces miRNA—rather than R2D284, the usual partner of Dcr-2 (FIG. 1). While surprising, a role for Loqs in the biogenesis of endo-siRNAs from structured loci was anticipated by the earlier finding that Loqs plays a role in the production of siRNAs from transgenes designed to produce long, intramolecularly paired inverted repeat transcripts so as to trigger RNAi in flies85.
Endo-siRNAs have also been identified in mouse oocytes86,87. As in flies, mouse endo-siRNAs are 21 nt long, Dicer-dependent, and derived from a variety of genomic sources (FIG. 3). The mouse endo-siRNAs were bound to Ago2, the sole mammalian Ago protein thought to mediate target cleavage, although it is not known if they also associate with any of the other three mouse Ago proteins. (Mammalian Ago2 is not, however, the ortholog of fly Ago2, whose sequence is considerably diverged from other Ago proteins.)
A subset of mouse oocyte endo-siRNAs maps to regions of protein-coding genes capable of pairing to their cognate pseudogenes and to regions of pseudogenes capable of forming inverted-repeat structures (FIG. 3). Pseudogenes can no longer encode proteins, yet they drift from their ancestral sequence more slowly than would be expected if they were simply junk. Perhaps some pseudogene sequences are under evolutionary selection to retain the ability to produce antisense transcripts that can pair with their cognate genes so as to produce endo-siRNAs88.
A key challenge for the future will be to understand the biological function of endo-siRNAs, especially those that can pair with protein-coding mRNAs. Do they regulate mRNA expression? Can endo-siRNAs act like miRNAs, tuning the expression of large numbers of genes?
miRNAs
The first microRNA, lin-4, was identified in a screen for genes required for post-embryonic development in C. elegans89,90. The lin-4 locus produces a 22 nt RNA that is partially complementary to sequences in the 3′ UTR of its regulatory target, the lin-14 mRNA89,91. miRNA binding to partially complementary sites in mRNA 3′ UTRs is now considered a hallmark of animal miRNA regulation. In 2001, tens of miRNAs were identified in humans, flies, and worms by small RNA cloning and sequencing, establishing miRNAs as a new class of small silencing RNAs92–94. miRBase (Release 12.0), the registry that coordinates miRNA naming, now lists 1,638 distinct miRNAs in plants and 6,930 in animals and their viruses95.
miRNA Biogenesis
miRNAs derive from precursor transcripts called pri-miRNAs, which are typically transcribed by Polymerase II96–99. Several miRNAs are present as clusters in the genome and likely derive from a common pri-miRNA transcript. Liberating a 20–24 nt miRNA from its pri-miRNA requires the sequential action of two RNase III endonucleases, assisted by their double-stranded RNA-binding domain (dsRBD) partner proteins (FIG. 1). First, the pri-miRNA is processed in the nucleus into a 60–70 nt long pre-miRNA by Drosha, acting with its dsRBD partner, called DGCR8 in mammals and Pasha in flies96,100–104. The resulting pre-miRNA has a hairpin structure: a loop flanked by base-paired arms that form a stem. Pre-miRNAs have a two nt overhang at their 3′ ends and a 5′ phosphate group, reflecting their production by an RNase III. The nuclear export protein, Exportin-5, carries the pre-miRNA to the cytoplasm bound to Ran GTP, a GTPase that moves RNA and proteins through the nuclear pore105–108.
In the cytoplasm, Dicer and its dsRBD partner protein, TRBP (mammals) or Loqs (flies), cleaves the pre-miRNA7,11–13,85,109–112. Drosha and Dicer differ in that Dicer—like Argonaute proteins, but unlike Drosha—contains a PAZ domain, presumably allowing it to bind the two-nucleotide, 3′ overhanging end left by Drosha. Dicer cleavage generates a duplex containing two strands, the miRNA and miRNA*, corresponding to the two sides of the base of the stem. These roughly correspond to the guide and passenger strands of an siRNA, and similar thermodynamic criteria influence the choice of miRNA versus miRNA*22,23. miRNAs can arise from either arm of the pre-miRNA stem, and some pre-miRNAs produce mature miRNAs from both arms, whereas others show such pronounced asymmetry that the miRNA* is rarely detected even in high throughput sequencing experiments113.
In flies, worms and mammals, a few pre-miRNAs are produced by the nuclear pre-mRNA splicing pathway instead of Drosha processing114–118. These pre-miRNA-like introns, “mirtrons,” are spliced out of mRNA precursors whose sequence suggests they encode proteins. The spliced introns first accumulate as lariat products that require 2′-5′ debranching by the lariat debranching enzyme. Debranching yields an authentic pre-miRNA, which can then enter the standard miRNA biogenesis pathway.
In plants, DCL1 fills the roles of both Drosha and Dicer, converting pri-miRNAs to miRNA/miRNA* duplexes44,119–121. DCL1, assisted by its dsRBD partner HYL1, converts pri-miRNAs to miRNA/miRNA* duplexes in the nucleus, after which the miRNA/miRNA* duplex is thought to be exported to the cytoplasm by HASTY, an Exportin-5 homolog (HASTY mutants develop precociously, hence their name)65,121–123. Unlike animal miRNAs, plant miRNAs are 2′-_O_-methylated at their 3′ ends by HEN134,119,124. HEN1 protects plant miRNAs from 3′ uridylation, thought to be a signal for degradation36. HEN1 likely acts before miRNAs are loaded into AGO1, because both miRNA* and miRNA strands are modified in plants34.
Target regulation by miRNAs
The mechanism by which a miRNA regulates its mRNA target reflects both the specific Argonaute protein into which the small RNA is loaded and the extent of complementarity between the miRNA and the mRNA125–127. A few miRNAs in flies and mammals are nearly fully complementary to their mRNA targets; these direct endonucleolytic cleavage of the mRNA128–132. Such extensive complementarity is considered the norm in plants, as target cleavage was thought to be the main mode of target regulation in plants39,62,133. However, in flies and mammals, most miRNAs pair with their targets through only a limited region of sequence at the 5′ end of the miRNA, the “seed”; these repress translation and direct degradation of their mRNA targets134–139. The “seed” region of all small silencing RNAs contributes most of the energy for target binding140,141. Thus, the seed is the primary specificity determinant for target selection. The small size of the seed means that a single miRNA can regulate many—even hundreds—of different genes142,143. Intriguingly, recent data suggests that the nuclear transcriptional history of an mRNA influences if a miRNA represses its translation at the initiation or the elongation step144.
Since plant miRNAs are highly complementary to their mRNA targets, they can direct mRNA target cleavage. Nonetheless, AGO1-loaded plant miRNAs can also block translation, suggesting a common mechanism between plant and animal miRNAs, despite the absence of specific miRNAs shared between the two kingdoms145.
Functions of miRNAs
Like transcription factors, miRNAs regulate diverse cellular pathways, and are widely believed to regulate most biological processes, in both plants and animals, ranging from housekeeping functions to responses to environmental stress. Covering this vast body of work is beyond the scope of this review; the cited reviews provide valuable insight146–148.
The study of miRNA pathway mutants provided early evidence for the influence of miRNAs on biological processes in both plants and animals. Loss of Dicer or miRNA-associated Argonaute proteins is nearly always lethal in animals, and such mutants show severe developmental defects in both plants and animals. In Drosophila, dcr-1 mutant germ-line stem cell clones divide slowly; in Arabidopsis, embryogenesis is abnormal in dcl1 mutants; in C. elegans, dcr-1 mutants display defects in germ-line development and embryonic morphogenesis; zebrafish lacking both maternal and zygotic Dicer are similarly defective in embryogenesis; and mice lacking Dicer die as early embryos, apparently devoid of stem cells14,119,149–152. Loss of Dicer in mouse embryonic fibroblasts causes increased DNA damage and consequently, the up-regulation of p19Arf and p53 signaling that induces premature senescence153.
Many miRNAs function in specific biological processes, in specific tissues, and at specific times154. The importance of small silencing RNAs goes far beyond the RNA silencing field: long-standing questions about the molecular basis of pluripotency, tumorogenesis, apoptosis, cell identity, etc. are finding answers in small RNAs146,155.
piRNAs: the longest small RNAs
piRNAs function in the germ line
Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) are the most recently discovered class of small RNAs, and, as their name suggests, they bind to the Piwi clade of Argonaute proteins. (Animal Argonaute proteins can be subdivided by sequence relatedness into Ago and Piwi sub-families.) The Piwi clade comprises Piwi, Aubergine (Aub) and Ago3 in flies, MILI, MIWI and MIWI2 in mice, and HILI, HIWI1, HIWI2 and HIWI3 in humans.
piRNAs were first proposed to ensure germ line stability by repressing transposons when Aravin and colleagues discovered in flies a class of longer small RNAs (~25–30 nt) associated with silencing of repetitive elements156. Later, these “repeat associated small interfering RNAs”—subsequently renamed piRNAs—were found to be distinct from siRNAs: they bind Piwi proteins and do not require Dcr-1 or Dcr-2 for their production, unlike miRNAs and siRNAs33,157,158. Moreover, they are 2′-_O_-methylated at their 3′ termini, unlike miRNAs, but like siRNAs in flies32,157,159–161.
High throughput sequencing of vertebrate piRNAs revealed a class of piRNAs unrelated to repetitive sequences, hence their name change87,162–168. Mammalian piRNAs can be divided into pre-pachytene and pachytene piRNAs, according to the stage of meiosis at which they are expressed in developing spermatocytes. Like piRNAs in flies, pre-pachytene piRNAs predominantly correspond to repetitive sequences and are implicated in silencing transposons, such as L1 and IAP165. In male mice, gametic methylation patterns are established when germ cells arrest their cell cycle 14.5 days postcoitum, resuming cell division 2–3 days after birth169,170. Both MILI and MIWI2 are expressed during this period, and miwi2 and mili deficient mice lose DNA methylation marks on transposons171. The pre-pachytene piRNAs, which bind MIWI2 and MILI, may serve as guides to direct DNA methylation of transposons. In contrast to pre-pachytene piRNAs, the pachytene piRNAs mainly arise from unannotated regions of the genome, not transposons, and their function remains unknown165.
Three recent studies report that the previously discovered germ-line “21U” RNAs in C. elegans are piRNAs113,172–174. These small RNAs were initially identified by high throughput sequencing113. They are precisely 21 nt long, begin with a uridine 5′-monophosphate, and are 3′ modified. They bind Piwi-Related Gene-1 (PRG-1), a C. elegans Piwi protein. Each 21U-RNA may be transcribed separately, as all are flanked by a common upstream motif. Like piRNAs in Drosophila, the 21U-RNAs are required for maintenance of the germ line and fertility, and like Drosophila Aub and other piRNA pathway components, PRG-1 is found in specialized granules, P granules, associated with germ-line function, in a cytoplasmic, perinuclear ring called “nuage.” Worm piRNAs resemble pachytene piRNAs in mammals: their targets and functions are largely unknown.
Biogenesis
piRNA sequences are stunningly diverse, with more than 1.5 million distinct piRNAs identified thus far in flies, but collectively they map to a few hundred genomic clusters77,79,81,158,175–177. The best studied cluster is the flamenco locus. flamenco was identified genetically as a repressor of the gypsy, ZAM and Idefix transposons33,178–182. Unlike siRNAs, flamenco piRNAs are mainly antisense, suggesting that piRNAs arise from long, single-stranded precursor RNAs. In fact, disruption of flamenco by insertion of a P-element near the 5′ end of the locus blocks the production of distal piRNAs up to 168 kbp away. Thus, an enormously long, single-stranded RNA transcript appears to be the source of those piRNAs that derive from the flamenco locus176.
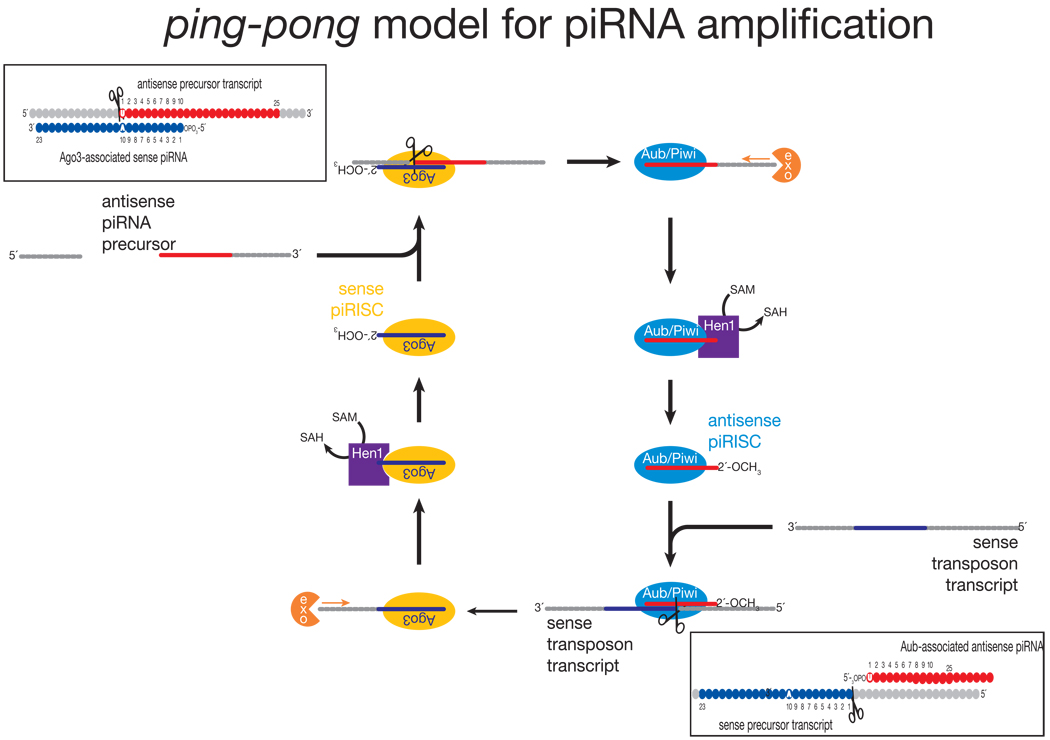
The current model for piRNA biogenesis was inferred from the sequences of piRNAs bound to Piwi, Aubergine and Ago3176,183. piRNAs bound to Piwi and Aubergine are typically antisense to transposon mRNAs, whereas Ago3 is loaded with piRNAs corresponding to the transposon mRNAs themselves (FIG. 1). Moreover, the first 10 nucleotides of antisense piRNAs are frequently complementary to the sense piRNAs found in Ago3. This unexpected sequence complementarity has been proposed to reflect a feed-forward amplification mechanism—”piRNA ping-pong”—that is activated only upon transposon mRNA transcription (FIG. 4)176,183. A similar amplification loop has been inferred from high throughput piRNA sequencing in vertebrates, implying its conservation through evolution162,171. Many aspects of the ping-pong model remain speculative. Why Ago3 appears to bind only sense piRNAs derived from transposon mRNAs is unknown. An untested idea is that different forms of RNA Pol II transcribe primary piRNA transcripts and transposon mRNAs and that the specialized RNA Pol II that transcribes the primary piRNA precursor recruits Piwi and Aub, but not Ago3. How the 3′ ends of piRNAs are made is also not known.
Figure 4.
piRNA Function and Regulation
Piwi family proteins are indispensable for germ-line development in many, perhaps all, animals; but they have thus far been most extensively studied in Drosophila. Piwi is restricted to the nucleoplasm of Drosophila germ cells and adjacent somatic cells. Piwi is required to maintain germ line stem cells and to promote their division; the protein is required in both the somatic niche cells that support germ-line stem cells and in the stem cells themselves184,185. In the male germ line, Aub is required for the silencing of the repetitive Stellate locus, which would otherwise cause male sterility. Expression of Stellate is controlled by the related, repetitive Suppressor of Stellate locus, the source of antisense piRNAs that act through Aub to repress Stellate156,157,186.
aub was originally identified because it is required for specification of the embryonic axes187. The loss of anterior-posterior and dorsal-ventral patterning in embryos from mothers lacking Aub is an indirect consequence of the double-stranded DNA breaks that occur in the oocyte in its absence188. The breaks appear to activate a DNA-damage checkpoint that disrupts patterning of the oocyte and, consequently, of the embryo. The defects in patterning, but not in silencing repetitive elements, are rescued by mutations that bypass the DNA damage signaling pathway, suggesting the breaks are caused by transposition. That activation of a DNA damage checkpoint should inappropriately reorganize embryonic polarity was most unexpected, but further underscores the vital role piRNAs play in germ line development.
piRNAs outside the germ line?
The role of piRNAs in the fly soma is hotly debated. Piwi and Aub are required to silence tandem arrays of white, a gene required to produce red eye pigment189. It is not understood if piRNAs are produced in the soma as well as in the germ line, or if piRNAs present during germ-line development deposit long-lived chromatin marks that exert their effects days later.
Both piRNAs and endo-siRNAs repress transposons in the germ line, where mutations caused by transposition, of course, would propagate to the next generation. siRNAs—that is, the RNAi pathway—likely provide a rapid response to the introduction of a new transposon into the germ line, a challenge not dissimilar to a viral infection. In contrast, the piRNA system appears to provide a more robust, permanent solution to the acquisition of a transposon. In the soma, however, endo-siRNAs are the predominant transposon-derived small RNA class, and their loss in dcr-2 and ago2 mutants increases transposon expression76,77,79,81. Somatic piRNA-like small RNAs have been observed in ago2 mutant flies76. Perhaps, in the absence of endo-siRNAs, piRNAs are produced somatically and resume transposon surveillance. Such a model implies significant cross-talk between the piRNA and endo-siRNA–generating machineries.
Intertwined pathways
The RNAi, miRNA and piRNA pathways were initially believed to be independent and distinct. However, the lines distinguishing them continue to fade. These pathways interact and rely on each other at several levels, competing for and sharing substrates, effector proteins and cross-regulating each other.
Competition for substrates during loading
Both the siRNA and miRNA pathways load dsRNA duplexes containing a 19 bp double-stranded core flanked by 2 nt 3′ overhangs. An siRNA duplex contains guide and passenger strands and is complementary throughout its core; a miRNA/miRNA* duplex contains mismatches, bulges and G:U wobble pairs. In Drosophila, biogenesis of small RNA duplexes is uncoupled from its loading into Ago1 or Ago2190,191. Instead, loading is governed by the structure of the duplex: duplexes bearing bulges and mismatches are sorted into the miRNA pathway and hence loaded into Ago1; duplexes with greater double-stranded character partition into Ago2, the Argonaute protein associated with RNAi.
The partitioning of small RNAs between Ago1 and Ago2 also has implications for target regulation. Ago1 primarily represses translation whereas Ago2 represses by target cleavage, reflecting the faster rate of target cleavage by Ago2 compared to Ago1191. Sorting creates competition between the two pathways for substrates190,191. In Drosophila loading of a small RNA duplex into one pathway decreases its association with other pathway.
Different double-stranded RNA precursors require distinct combinations of proteins to produce small silencing RNAs. For example, Drosophila endo-siRNAs derived from structured loci require Loqs, rather than R2D277–79. We presume that under some circumstances the endo-siRNA and miRNA pathways might therefore compete for Loqs. The endo-siRNA and RNAi pathways likely also compete for shared components.
In contrast to Drosophila, plants load small RNAs into Argonautes according to the identity of the 5′ nt of the small RNA69,192. AGO1 is the main effector Argonaute for miRNAs, and the majority of miRNAs begin with uracil; and AGO4 is the major effector of the heterochromatic pathway and is predominantly loaded with small RNAs beginning with an adenosine193. AGO2 and AGO5, however have no characterized function in plants193. Changing the 5 nt from A to U shifts the loading bias of a plant small RNA from AGO2 to AGO1, and vice versa. Similarly, Arabidopsis AGO4 binds small RNAs that begin with adenosine, while AGO5 prefers cytosine.
Aub- and Piwi-bound piRNAs typically begin with U, whereas those bound to Ago3 show no 5′ nucleotide bias. It remains to be determined if this reflects a 5′ nucleotide preference like the situation for the plant AGOs or some feature of an as-yet-discovered piRNA loading machinery that sorts piRNAs between Piwi proteins.
Cross talk
Small RNA pathways are often entangled. TasiRNA biogenesis in Arabidopsis is a classic example of such cross talk between pathways. miRNA-directed cleavage of tasiRNA-generating transcripts initiates tasiRNA production and subsequent regulation of tasiRNA targets64–68. In C. elegans, at least one piRNA has been implicated in initiating endo-siRNA production172,173, and in flies, the endo-siRNA pathway may repress expression of piRNAs in the soma76. Moreover, small RNA levels may be buffered by negative feedback loops in which small RNAs from one pathway alter the expression levels of RNA silencing proteins that act in the same or in other RNA silencing pathways.194–198.
Conclusions
Despite our growing understanding of the mechanism and function of small RNAs, their evolutionary origins remain obscure. siRNAs are present in all three eukaryotic kingdoms, plants, animals, and fungi, and provide anti-viral defense in at least plants and animals. Thus, the siRNA machinery was present in the last common ancestor of plants, animals and fungi. In contrast, miRNAs have only been found in land plants, the unicellular green alga, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, and metazoan animals, but not in unicellular choanoflagellates or fungi199–201. Deep sequencing experiments have found no miRNAs shared by plants and animals, suggesting that miRNA genes, unlike the miRNA protein machinery, arose independently at least twice in evolution. Finally, piRNAs appear to be the youngest major small RNA family, having been found only in metazoan animals201. While Dicer proteins have been identified only in eukaryotes, Argonaute proteins can also be found in eubacteria and archea, raising the prospect that small nucleic-acids may have served as guides for proteins at the very dawn of cellular life, and though the machinery might be ancient, the small RNA guides diversified over time to acquire specialized roles.
The history of small silencing RNAs makes predicting the future particularly daunting, as new discoveries have come at a breakneck pace, with each new small RNA mechanism or function forcing a re-evaluation of cherished models and “facts.” Several longstanding but unanswered questions, however, are worth highlighting. First, does RNAi—in the sense of an siRNA-guided defense against external nucleic acid threats such as viruses—exist in mammals? Second, how do miRNAs repress gene expression? Do several parallel mechanisms co-exist in vivo, or will the current, apparently contradictory, models for miRNA-directed translational repression and mRNA decay ultimately be unified in a larger mechanistic scheme? Third, can miRNA regulated genes ever be identified by computation alone, or will computational predictions ultimately give way to high-throughput experimental methods for associating individual miRNA species with their regulatory targets? Will network analysis uncover themes in miRNA-target relationships that reveal why miRNA-regulation is so widespread in animals? Fourth, how are piRNAs made? The feed-forward amplification “ping-pong” model is appealing, but likely underestimates the complexity of piRNA biogenesis mechanisms? We do not yet know how piRNA 3′ ends are generated. Nor do we have a coherent model for how long, antisense transcripts from piRNA clusters are fragmented into piRNAs. Finally, will the increasing number of examples of small RNAs carrying epigenetic information across generations3,202 ultimately force us to reexamine our Mendelian view of inheritance?
Box 2. High throughput sequencing and small RNA discovery
Much of the credit for the identification of small RNAs rests with advances in high throughput sequencing. Presently, there are three commercial “high depth” sequencing systems: Roche′s 454 GS FLX Genome Analyzer, Illumina′s Solexa Analyzer and, most recently, Applied Biosystem′s SOLiD System. Reference 223 describes how each method works. Whereas 454 has the advantage of sequencing >250 bp per read, compared to ~35–50 bp for Solexa and SOLiD, these two platforms provide 70- to 400-fold greater sequencing depth. All three platforms have been used successfully to identify novel small RNA species and to discover new small RNA classes in mutant plants and animals. Using less than 10 µg total RNA, high throughput sequencing, together with advances in small RNA library preparation, has revealed the length distribution, sequence identity, terminal structure, sequence and strand biases, isoform prevalence, genomic origins, and mode of biogenesis for millions of small RNAs. Initial small RNA sequencing experiments sought simply to identify novel small RNA species and classes. Increasingly, high throughput sequencing is being used to profile small RNA expression across the stages of development and in different tissues and disease states. Profiling by deep sequencing provides quantitative information about small RNA expression, like PCR- or microarray-based approaches, but can also precisely detect subtle changes in small RNA sequence or length.
Perhaps the most problematic step in small RNA sequencing is preparing the small RNA library. The most frequently employed cloning protocols require the small RNAs to have 5′ phosphate and a 3′ hydroxyl groups, the hallmarks of Dicer products. This approach identifies small RNAs with the expected termini, but alternative methods must be used to find small RNAs, such as C. elegans secondary siRNAs, with other terminal structures. Additionally, finding every possible small RNA in a cell using exhaustive deep sequencing is a game with diminishing returns. For example, while many miRNAs have been sequence 100,000′s or even a million times, the C. elegans miRNA lsy-6, which is apparently expressed in less than ten cells of the adult, has so far eluded high depth sequencing224.
Box 1.
Acknowledgments
We thank Hervé Seitz for bioinformatic assistance and Xuemei Chen, Ira Pekker and Stefan Ameres for helpful discussions. This work was supported, in part, by grants from the NIH to PDZ (GM065236 and GM062862).
References
- 1.Fire A, et al. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–811. doi: 10.1038/35888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Voinnet O. Non-cell autonomous RNA silencing. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:5858–5871. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.09.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Grishok A, Tabara H, Mello CC. Genetic requirements for inheritance of RNAi in C. elegans. Science. 2000;287:2494–2497. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5462.2494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hamilton AJ, Baulcombe DC. A species of small antisense RNA in posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science. 1999;286:950–952. doi: 10.1126/science.286.5441.950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zamore PD, Tuschl T, Sharp PA, Bartel DP. RNAi: double-stranded RNA directs the ATP-dependent cleavage of mRNA at 21 to 23 nucleotide intervals. Cell. 2000;101:25–33. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80620-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hammond SM, Bernstein E, Beach D, Hannon GJ. An RNA-directed nuclease mediates post-transcriptional gene silencing in Drosophila cells. Nature. 2000;404:293–296. doi: 10.1038/35005107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bernstein E, Caudy AA, Hammond SM, Hannon GJ. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature. 2001;409:363–366. doi: 10.1038/35053110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Elbashir SM, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T. RNA interference is mediated by 21-and 22-nucleotide RNAs. Genes Dev. 2001;15:188–200. doi: 10.1101/gad.862301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Elbashir SM, Martinez J, Patkaniowska A, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T. Functional anatomy of siRNAs for mediating efficient RNAi in Drosophila melanogaster embryo lysate. EMBO J. 2001;20:6877–6888. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.23.6877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Liu J, et al. A role for the P-body component GW182 in microRNA function. Nat Cell Biol. 2005;7:1161–1166. doi: 10.1038/ncb1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hutvágner G, et al. A cellular function for the RNA-interference enzyme Dicer in the maturation of the let-7 small temporal RNA. Science. 2001;293:834–838. doi: 10.1126/science.1062961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Grishok A, et al. Genes and Mechanisms Related to RNA Interference Regulate Expression of the Small Temporal RNAs that Control C. elegans Developmental Timing. Cell. 2001;106:23–34. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00431-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ketting RF, et al. Dicer functions in RNA interference and in synthesis of small RNA involved in developmental timing in C. elegans. Genes Dev. 2001;15:2654–2659. doi: 10.1101/gad.927801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Knight SW, Bass BL. A role for the RNase III enzyme DCR-1 in RNA interference and germ line development in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 2001;293:2269–2271. doi: 10.1126/science.1062039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lee YS, et al. Distinct roles for Drosophila Dicer-1 and Dicer-2 in the siRNA/miRNA silencing pathways. Cell. 2004;117:69–81. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00261-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Obbard DJ, Jiggins FM, Halligan DL, Little TJ. Natural selection drives extremely rapid evolution in antiviral RNAi genes. Curr Biol. 2006;16:580–585. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2006.01.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tabara H, Yigit E, Siomi H, Mello CC. The dsRNA Binding Protein RDE-4 Interacts with RDE-1, DCR-1, and a DexH-Box Helicase to Direct RNAi in C. elegans. Cell. 2002;109:861–871. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00793-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shaham S. Worming into the cell: viral reproduction in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:3955–3956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0600779103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Williams BR. PKR; a sentinel kinase for cellular stress. Oncogene. 1999;18:6112–6120. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kunzi MS, Pitha PM. Interferon research: a brief history. Methods Mol Med. 2005;116:25–35. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-939-7:025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Vilcek J. Fifty years of interferon research: aiming at a moving target. Immunity. 2006;25:343–348. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2006.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Schwarz DS, et al. Asymmetry in the assembly of the RNAi enzyme complex. Cell. 2003;115:199–208. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00759-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Khvorova A, Reynolds A, Jayasena SD. Functional siRNAs and miRNAs exhibit strand bias. Cell. 2003;115:209–216. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00801-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Aza-Blanc P, et al. Identification of modulators of TRAIL-induced apoptosis via RNAi-based phenotypic screening. Mol Cell. 2003;12:627–637. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00348-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Liu Q, et al. R2D2, a Bridge Between the Initiation and Effector Steps of the Drosophila RNAi Pathway. Science. 2003;301:1921–1925. doi: 10.1126/science.1088710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tomari Y, Matranga C, Haley B, Martinez N, Zamore PD. A protein sensor for siRNA asymmetry. Science. 2004;306:1377–1380. doi: 10.1126/science.1102755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Matranga C, Tomari Y, Shin C, Bartel DP, Zamore PD. Passenger-strand cleavage facilitates assembly of siRNA into Ago2-containing RNAi enzyme complexes. Cell. 2005;123:607–620. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kim K, Lee YS, Carthew RW. Conversion of pre-RISC to holo-RISC by Ago2 during assembly of RNAi complexes. RNA. 2006;13:22–29. doi: 10.1261/rna.283207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Leuschner PJ, Ameres SL, Kueng S, Martinez J. Cleavage of the siRNA passenger strand during RISC assembly in human cells. EMBO Rep. 2006;7:314–320. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Miyoshi K, Tsukumo H, Nagami T, Siomi H, Siomi MC. Slicer function of Drosophila Argonautes and its involvement in RISC formation. Genes Dev. 2005;19:2837–2848. doi: 10.1101/gad.1370605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rand TA, Petersen S, Du F, Wang X. Argonaute2 Cleaves the Anti-Guide Strand of siRNA during RISC Activation. Cell. 2005;123:621–629. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.10.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Horwich MD, et al. The Drosophila RNA methyltransferase, DmHen1, modifies germline piRNAs and single-stranded siRNAs in RISC. Curr Biol. 2007;17:1265–1272. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.06.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Pelisson A, Sarot E, Payen-Groschene G, Bucheton A. A novel repeat-associated small interfering RNA-mediated silencing pathway downregulates complementary sense gypsy transcripts in somatic cells of the Drosophila ovary. J Virol. 2007;81:1951–1960. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01980-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Yu B, et al. Methylation as a crucial step in plant microRNA biogenesis. Science. 2005;307:932–935. doi: 10.1126/science.1107130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ramachandran V, Chen X. Small RNA metabolism in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 2008;13:368–374. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2008.03.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Li J, Yang Z, Yu B, Liu J, Chen X. Methylation protects miRNAs and siRNAs from a 3’-end uridylation activity in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol. 2005;15:1501–1507. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.07.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tolia NH, Joshua-Tor L. Slicer and the Argonautes. Nat Chem Biol. 2007;3:36–43. doi: 10.1038/nchembio848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hamilton A, Voinnet O, Chappell L, Baulcombe D. Two classes of short interfering RNA in RNA silencing. EMBO J. 2002;21:4671–4679. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Tang G, Reinhart BJ, Bartel DP, Zamore PD. A biochemical framework for RNA silencing in plants. Genes Dev. 2003;17:49–63. doi: 10.1101/gad.1048103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dunoyer P, Himber C, Ruiz-Ferrer V, Alioua A, Voinnet O. Intra-and intercellular RNA interference in Arabidopsis thaliana requires components of the microRNA and heterochromatic silencing pathways. Nat Genet. 2007;39:848–856. doi: 10.1038/ng2081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Bouche N, Lauressergues D, Gasciolli V, Vaucheret H. An antagonistic function for Arabidopsis DCL2 in development and a new function for DCL4 in generating viral siRNAs. EMBO J. 2006;25:3347–3356. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Deleris A, et al. Hierarchical action and inhibition of plant Dicer-like proteins in antiviral defense. Science. 2006;313:68–71. doi: 10.1126/science.1128214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Gasciolli V, Mallory AC, Bartel DP, Vaucheret H. Partially redundant functions of Arabidopsis DICER-like enzymes and a role for DCL4 in producing trans-acting siRNAs. Curr Biol. 2005;15:1494–1500. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.07.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Xie Z, et al. Genetic and Functional Diversification of Small RNA Pathways in Plants. PLoS Biol. 2004;2:E104. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0020104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Chan SW. Inputs and outputs for chromatin-targeted RNAi. Trends Plant Sci. 2008;13:383–389. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2008.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Qu F, et al. RDR6 has a broad-spectrum but temperature-dependent antiviral defense role in Nicotiana benthamiana. J Virol. 2005;79:15209–15217. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.24.15209-15217.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Voinnet O. Use, tolerance and avoidance of amplified RNA silencing by plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2008;13:317–328. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2008.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Gazzani S, Lawrenson T, Woodward C, Headon D, Sablowski R. A link between mRNA turnover and RNA interference in Arabidopsis. Science. 2004;306:1046–1048. doi: 10.1126/science.1101092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Gy I, et al. Arabidopsis FIERY1, XRN2, and XRN3 are endogenous RNA silencing suppressors. Plant Cell. 2007;19:3451–3461. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.055319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ambros V, Lee RC, Lavanway A, Williams PT, Jewell D. MicroRNAs and other tiny endogenous RNAs in C. elegans. Curr Biol. 2003;13:807–818. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00287-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Zilberman D, Cao X, Jacobsen SE. ARGONAUTE4 control of locus-specific siRNA accumulation and DNA and histone methylation. Science. 2003;299:716–719. doi: 10.1126/science.1079695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Chan SW, et al. RNA silencing genes control de novo DNA methylation. Science. 2004;303:1336. doi: 10.1126/science.1095989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Zheng X, Zhu J, Kapoor A, Zhu JK. Role of Arabidopsis AGO6 in siRNA accumulation, DNA methylation and transcriptional gene silencing. EMBO J. 2007;26:1691–1701. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Boutet S, et al. Arabidopsis HEN1: a genetic link between endogenous miRNA controlling development and siRNA controlling transgene silencing and virus resistance. Curr Biol. 2003;13:843–848. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00293-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.El-Shami M, et al. Reiterated WG/GW motifs form functionally and evolutionarily conserved ARGONAUTE-binding platforms in RNAi-related components. Genes Dev. 2007;21:2539–2544. doi: 10.1101/gad.451207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Herr AJ, Jensen MB, Dalmay T, Baulcombe DC. RNA polymerase IV directs silencing of endogenous DNA. Science. 2005;308:118–120. doi: 10.1126/science.1106910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Kanoh J, Sadaie M, Urano T, Ishikawa F. Telomere binding protein Taz1 establishes Swi6 heterochromatin independently of RNAi at telomeres. Curr Biol. 2005;15:1808–1819. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.09.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Lee SK, et al. Lentiviral delivery of short hairpin RNAs protects CD4 T cells from multiple clades and primary isolates of HIV. Blood. 2005;106:818–826. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-10-3959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Onodera Y, et al. Plant nuclear RNA polymerase IV mediates siRNA and DNA methylation-dependent heterochromatin formation. Cell. 2005;120:613–622. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Pontier D, et al. Reinforcement of silencing at transposons and highly repeated sequences requires the concerted action of two distinct RNA polymerases IV in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev. 2005;19:2030–2040. doi: 10.1101/gad.348405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Tran RK, et al. DNA methylation profiling identifies CG methylation clusters in Arabidopsis genes. Curr Biol. 2005;15:154–159. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Llave C, Kasschau KD, Rector MA, Carrington JC. Endogenous and Silencing-Associated Small RNAs in Plants. Plant Cell. 2002;14:1605–1619. doi: 10.1105/tpc.003210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Mette MF, Aufsatz W, van der Winden J, Matzke MA, Matzke AJ. Transcriptional silencing and promoter methylation triggered by double-stranded RNA. EMBO J. 2000;19:5194–5201. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.19.5194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Vazquez F, et al. Endogenous trans-acting siRNAs regulate the accumulation of Arabidopsis mRNAs. Mol Cell. 2004;16:69–79. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.09.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Peragine A, Yoshikawa M, Wu G, Albrecht HL, Poethig RS. SGS3 and SGS2/SDE1/RDR6 are required for juvenile development and the production of trans-acting siRNAs in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev. 2004;18:2368–2379. doi: 10.1101/gad.1231804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Yoshikawa M, Peragine A, Park MY, Poethig RS. A pathway for the biogenesis of trans-acting siRNAs in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev. 2005;19:2164–2175. doi: 10.1101/gad.1352605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Williams L, Carles CC, Osmont KS, Fletcher JC. A database analysis method identifies an endogenous trans-acting short-interfering RNA that targets the Arabidopsis ARF2, ARF3, and ARF4 genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:9703–9708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504029102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Allen E, Xie Z, Gustafson AM, Carrington JC. microRNA-directed phasing during trans-acting siRNA biogenesis in plants. Cell. 2005;121:207–221. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Montgomery TA, et al. Specificity of ARGONAUTE7-miR390 interaction and dual functionality in TAS3 trans-acting siRNA formation. Cell. 2008;133:128–141. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.02.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Axtell MJ, Jan C, Rajagopalan R, Bartel DP. A two-hit trigger for siRNA biogenesis in plants. Cell. 2006;127:565–577. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Katiyar-Agarwal S, et al. A pathogen-inducible endogenous siRNA in plant immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:18002–18007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608258103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Borsani O, Zhu J, Verslues PE, Sunkar R, Zhu JK. Endogenous siRNAs derived from a pair of natural cis-antisense transcripts regulate salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Cell. 2005;123:1279–1291. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.11.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Zhang D, Trudeau VL. The XS domain of a plant specific SGS3 protein adopts a unique RNA recognition motif (RRM) fold. Cell Cycle. 2008;7:2268–2270. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.14.6306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Katiyar-Agarwal S, Gao S, Vivian-Smith A, Jin H. A novel class of bacteria-induced small RNAs in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev. 2007;21:3123–3134. doi: 10.1101/gad.1595107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Yang N, Kazazian HHJ. L1 retrotransposition is suppressed by endogenously encoded small interfering RNAs in human cultured cells. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006;13:763–771. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Ghildiyal M, et al. Endogenous siRNAs derived from transposons and mRNAs in Drosophila somatic cells. Science. 2008;320:1077–1081. doi: 10.1126/science.1157396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Czech B, et al. An endogenous small interfering RNA pathway in Drosophila. Nature. 2008;453:798–802. doi: 10.1038/nature07007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Okamura K, et al. The Drosophila hairpin RNA pathway generates endogenous short interfering RNAs. Nature. 2008;453:803–806. doi: 10.1038/nature07015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Kawamura Y, et al. Drosophila endogenous small RNAs bind to Argonaute 2 in somatic cells. Nature. 2008;453:793–797. doi: 10.1038/nature06938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Okamura K, Balla S, Martin R, Liu N, Lai EC. Two distinct mechanisms generate endogenous siRNAs from bidirectional transcription in Drosophila melanogaster. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008 doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Chung WJ, Okamura K, Martin R, Lai EC. Endogenous RNA Interference Provides a Somatic Defense against Drosophila Transposons. Curr Biol. 2008 doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.05.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Tabara H, et al. The rde-1 gene, RNA interference, and transposon silencing in C. elegans. Cell. 1999;99:123–132. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81644-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Ketting RF, Haverkamp TH, van Luenen HG, Plasterk RH. Mut-7 of C. elegans, required for transposon silencing and RNA interference, is a homolog of Werner syndrome helicase and RNaseD. Cell. 1999;99:133–141. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81645-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Zhou R, et al. Comparative analysis of argonaute-dependent small RNA pathways in Drosophila. Mol Cell. 2008;32:592–599. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.10.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Förstemann K, et al. Normal microRNA maturation and germ-line stem cell maintenance requires Loquacious, a double-stranded RNA-binding domain protein. PLoS Biol. 2005;3:e236. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Tam OH, et al. Pseudogene-derived small interfering RNAs regulate gene expression in mouse oocytes. Nature. 2008 doi: 10.1038/nature06904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Watanabe T, et al. Endogenous siRNAs from naturally formed dsRNAs regulate transcripts in mouse oocytes. Nature. 2008;453:539–543. doi: 10.1038/nature06908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Sasidharan R, Gerstein M. Genomics: protein fossils live on as RNA. Nature. 2008;453:729–731. doi: 10.1038/453729a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–854. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90529-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Neilson JR, Sharp PA. Small RNA regulators of gene expression. Cell. 2008;134:899–902. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Wightman B, Burglin TR, Gatto J, Arasu P, Ruvkun G. Negative regulatory sequences in the lin-14 3’-untranslated region are necessary to generate a temporal switch during Caenorhabditis elegans development. Genes Dev. 1991;5:1813–1824. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T. Identification of Novel Genes Coding for Small Expressed RNAs. Science. 2001;294:853–858. doi: 10.1126/science.1064921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Lee RC, Ambros V. An Extensive Class of Small RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 2001;294:862–864. doi: 10.1126/science.1065329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG, Bartel DP. An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 2001;294:858–862. doi: 10.1126/science.1065062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Griffiths-Jones S, Saini HK, van Dongen S, Enright AJ. miRBase: tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:D154–D158. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Lee Y, Jeon K, Lee JT, Kim S, Kim VN. MicroRNA maturation: stepwise processing and subcellular localization. EMBO J. 2002;21:4663–4670. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Lee Y, et al. MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II. EMBO J. 2004;23:4051–4060. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Cai X, Hagedorn CH, Cullen BR. Human microRNAs are processed from capped, polyadenylated transcripts that can also function as mRNAs. RNA. 2004;10:1957–1966. doi: 10.1261/rna.7135204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Birney E, et al. Identification and analysis of functional elements in 1% of the human genome by the ENCODE pilot project. Nature. 2007;447:799–816. doi: 10.1038/nature05874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Lee Y, et al. The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature. 2003;425:415–419. doi: 10.1038/nature01957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Denli AM, Tops BB, Plasterk RH, Ketting RF, Hannon GJ. Processing of primary microRNAs by the Microprocessor complex. Nature. 2004;432:231–235. doi: 10.1038/nature03049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Gregory RI, et al. The Microprocessor complex mediates the genesis of microRNAs. Nature. 2004;432:235–240. doi: 10.1038/nature03120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Han J, et al. The Drosha-DGCR8 complex in primary microRNA processing. Genes Dev. 2004;18:3016–3027. doi: 10.1101/gad.1262504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Landthaler M, Yalcin A, Tuschl T. The Human DiGeorge Syndrome Critical Region Gene 8 and Its D. melanogaster Homolog Are Required for miRNA Biogenesis. Curr Biol. 2004;14:2162–2167. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Yi R, Qin Y, Macara IG, Cullen BR. Exportin-5 mediates the nuclear export of pre-microRNAs and short hairpin RNAs. Genes Dev. 2003;17:3011–3016. doi: 10.1101/gad.1158803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Bohnsack MT, Czaplinski K, Gorlich D. Exportin 5 is a Ran GTP-dependent dsRNA-binding protein that mediates nuclear export of pre-miRNAs. RNA. 2004;10:185–191. doi: 10.1261/rna.5167604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Lund E, Guttinger S, Calado A, Dahlberg JE, Kutay U. Nuclear export of microRNA precursors. Science. 2004;303:95–98. doi: 10.1126/science.1090599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Zeng Y, Cullen BR. Structural requirements for pre-microRNA binding and nuclear export by Exportin 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:4776–4785. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Chendrimada TP, et al. TRBP recruits the Dicer complex to Ago2 for microRNA processing and gene silencing. Nature. 2005;436:740–744. doi: 10.1038/nature03868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Jiang F, et al. Dicer-1 and R3D1-L catalyze microRNA maturation in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 2005;19:1674–1679. doi: 10.1101/gad.1334005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Lee Y, et al. The role of PACT in the RNA silencing pathway. EMBO J. 2006;25:522–532. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Saito K, Ishizuka A, Siomi H, Siomi MC. Processing of pre-microRNAs by the Dicer-1-Loquacious complex in Drosophila cells. PLoS Biol. 2005;3:e235. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Ruby JG, et al. Large-scale sequencing reveals 21U-RNAs and additional microRNAs and endogenous siRNAs in C. elegans. Cell. 2006;127:1193–1207. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.10.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Okamura K, Hagen JW, Duan H, Tyler DM, Lai EC. The Mirtron Pathway Generates microRNA-Class Regulatory RNAs in Drosophila. Cell. 2007;130:89–100. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.06.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Ruby JG, Jan CH, Bartel DP. Intronic microRNA precursors that bypass Drosha processing. Nature. 2007 doi: 10.1038/nature05983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Glazov EA, et al. A microRNA catalog of the developing chicken embryo identified by a deep sequencing approach. Genome Res. 2008;18:957–964. doi: 10.1101/gr.074740.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Berezikov E, Chung WJ, Willis J, Cuppen E, Lai EC. Mammalian mirtron genes. Mol Cell. 2007;28:328–336. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.09.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Babiarz JE, Ruby JG, Wang Y, Bartel DP, Blelloch R. Mouse ES cells express endogenous shRNAs, siRNAs, and other Microprocessor-independent, Dicer-dependent small RNAs. Genes Dev. 2008;22:2773–2785. doi: 10.1101/gad.1705308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Park W, Li J, Song R, Messing J, Chen X. CARPEL FACTORY, a Dicer Homolog, and HEN1, a Novel Protein, Act in microRNA Metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana. Current Biology. 2002;12:1484–1495. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)01017-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Reinhart BJ, Weinstein EG, Rhoades MW, Bartel B, Bartel DP. MicroRNAs in plants. Genes Dev. 2002;16:1616–1626. doi: 10.1101/gad.1004402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Papp I, et al. Evidence for nuclear processing of plant micro RNA and short interfering RNA precursors. Plant Physiol. 2003;132:1382–1390. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.021980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Vazquez F, Gasciolli V, Crete P, Vaucheret H. The nuclear dsRNA binding protein HYL1 is required for microRNA accumulation and plant development, but not posttranscriptional transgene silencing. Curr Biol. 2004;14:346–351. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.01.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Park MY, Wu G, Gonzalez-Sulser A, Vaucheret H, Poethig RS. Nuclear processing and export of microRNAs in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:3691–3696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0405570102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Yang Z, Ebright YW, Yu B, Chen X. HEN1 recognizes 21–24 nt small RNA duplexes and deposits a methyl group onto the 2’ OH of the 3’ terminal nucleotide. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34:667–675. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Hutvágner G, Zamore PD. A microRNA in a Multiple-Turnover RNAi Enzyme Complex. Science. 2002;297:2056–2060. doi: 10.1126/science.1073827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Meister G, et al. Human Argonaute2 mediates RNA cleavage targeted by miRNAs and siRNAs. Mol Cell. 2004;15:185–197. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Liu J, et al. Argonaute2 is the catalytic engine of mammalian RNAi. Science. 2004;305:1437–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.1102513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Mansfield JH, et al. MicroRNA-responsive ‘sensor’ transgenes uncover Hox-like and other developmentally regulated patterns of vertebrate microRNA expression. Nat Genet. 2004;36:1079–1083. doi: 10.1038/ng1421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Pfeffer S, et al. Identification of virus-encoded microRNAs. Science. 2004;304:734–736. doi: 10.1126/science.1096781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Yekta S, Shih IH, Bartel DP. MicroRNA-directed cleavage of HOXB8 mRNA. Science. 2004;304:594–596. doi: 10.1126/science.1097434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Davis E, et al. RNAi-mediated allelic trans-interaction at the imprinted Rtl1/Peg11 locus. Curr Biol. 2005;15:743–749. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.02.060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Sullivan CS, Grundhoff AT, Tevethia S, Pipas JM, Ganem D. SV40-encoded microRNAs regulate viral gene expression and reduce susceptibility to cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 2005;435:682–686. doi: 10.1038/nature03576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Rhoades MW, et al. Prediction of plant microRNA targets. Cell. 2002;110:513–520. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00863-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Brennecke J, Stark A, Russell RB, Cohen SM. Principles of microRNA-target recognition. PLoS Biol. 2005;3:e85. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Burge CB. Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell. 2003;115:787–798. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)01018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 2005;120:15–20. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Stark A, Brennecke J, Bushati N, Russell RB, Cohen SM. Animal MicroRNAs confer robustness to gene expression and have a significant impact on 3’UTR evolution. Cell. 2005;123:1133–1146. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.11.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Xie X, et al. Systematic discovery of regulatory motifs in human promoters and 3’ UTRs by comparison of several mammals. Nature. 2005;434:338–345. doi: 10.1038/nature03441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Lai EC, et al. Predicting and validating microRNA targets. Genome Biol. 2004;5:115. doi: 10.1186/gb-2004-5-9-115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Ameres SL, Martinez J, Schroeder R. Molecular basis for target RNA recognition and cleavage by human RISC. Cell. 2007;130:101–112. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.04.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Haley B, Zamore PD. Kinetic analysis of the RNAi enzyme complex. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2004;11:599–606. doi: 10.1038/nsmb780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Baek D, et al. The impact of microRNAs on protein output. Nature. 2008;455:64–71. doi: 10.1038/nature07242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Selbach M, et al. Widespread changes in protein synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature. 2008;455:58–63. doi: 10.1038/nature07228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Kong YW, et al. The mechanism of micro-RNA-mediated translation repression is determined by the promoter of the target gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:8866–8871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0800650105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Brodersen P, et al. Widespread translational inhibition by plant miRNAs and siRNAs. Science. 2008;320:1185–1190. doi: 10.1126/science.1159151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Stefani G, Slack FJ. Small non-coding RNAs in animal development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:219–230. doi: 10.1038/nrm2347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Yekta S, Tabin CJ, Bartel DP. MicroRNAs in the Hox network: an apparent link to posterior prevalence. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:789–796. doi: 10.1038/nrg2400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Bartel DP, Chen CZ. Micromanagers of gene expression: the potentially widespread influence of metazoan microRNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:396–400. doi: 10.1038/nrg1328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Bernstein E, et al. Dicer is essential for mouse development. Nat Genet. 2003;35:215–217. doi: 10.1038/ng1253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Wienholds E et al. MicroRNA expression in zebrafish embryonic development. Science. 2005;309:310–311. doi: 10.1126/science.1114519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Giraldez AJ, et al. MicroRNAs regulate brain morphogenesis in zebrafish. Science. 2005;308:833–838. doi: 10.1126/science.1109020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Hatfield SD, et al. Stem cell division is regulated by the microRNA pathway. Nature. 2005;435:974–978. doi: 10.1038/nature03816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Mudhasani R, et al. Loss of miRNA biogenesis induces p19Arf-p53 signaling and senescence in primary cells. J Cell Biol. 2008;181:1055–1063. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200802105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Landgraf P, et al. A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell. 2007;129:1401–1414. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.04.040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Wienholds E, Plasterk RH. MicroRNA function in animal development. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:5911–5922. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.07.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Aravin AA, et al. Double-stranded RNA-mediated silencing of genomic tandem repeats transposable elements in the D. melanogaster germline. Curr Biol. 2001;11:1017–1027. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(01)00299-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Vagin VV, et al. A distinct small RNA pathway silences selfish genetic elements in the germline. Science. 2006;313:320–324. doi: 10.1126/science.1129333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Saito K, et al. Specific association of Piwi with rasiRNAs derived from retrotransposon and heterochromatic regions in the Drosophila genome. Genes Dev. 2006;20:2214–2222. doi: 10.1101/gad.1454806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Saito K, et al. Pimet, the Drosophila homolog of HEN1, mediates 2′-O-methylation of Piwi- interacting RNAs at their 3′ ends. Genes Dev. 2007;21:1603–1608. doi: 10.1101/gad.1563607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Kirino Y, Mourelatos Z. Mouse Piwi-interacting RNAs are 2′-O-methylated at their 3′ termini. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007;14:347–348. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Ohara T, et al. The 3′ termini of mouse Piwi-interacting RNAs are 2′-O-methylated. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007;14:349–350. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Houwing S, et al. A role for Piwi and piRNAs in germ cell maintenance and transposon silencing in Zebrafish. Cell. 2007;129:69–82. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.03.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Aravin A, et al. A novel class of small RNAs bind to MILI protein in mouse testes. Nature. 2006;442:203–207. doi: 10.1038/nature04916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Lau NC, et al. Characterization of the piRNA complex from rat testes. Science. 2006;313:363–367. doi: 10.1126/science.1130164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Aravin AA, Sachidanandam R, Girard A, Fejes-Toth K, Hannon GJ. Developmentally regulated piRNA clusters implicate MILI in transposon control. Science. 2007;316:744–747. doi: 10.1126/science.1142612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Girard A, Sachidanandam R, Hannon GJ, Carmell MA. A germline-specific class of small RNAs binds mammalian Piwi proteins. Nature. 2006;442:199–202. doi: 10.1038/nature04917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Grivna ST, Beyret E, Wang Z, Lin H. A novel class of small RNAs in mouse spermatogenic cells. Genes Dev. 2006;20:1709–1714. doi: 10.1101/gad.1434406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Grivna ST, Pyhtila B, Lin H. MIWI associates with translational machinery and PIWI-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) in regulating spermatogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:13415–13420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605506103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Kato Y, et al. Role of the Dnmt3 family in de novo methylation of imprinted and repetitive sequences during male germ cell development in the mouse. Hum Mol Genet. 2007;16:2272–2280. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Lees-Murdock DJ, De Felici M, Walsh CP. Methylation dynamics of repetitive DNA elements in the mouse germ cell lineage. Genomics. 2003;82:230–237. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(03)00105-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Aravin AA, et al. A piRNA pathway primed by individual transposons is linked to de novo DNA methylation in mice. Mol Cell. 2008;31:785–799. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.09.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Batista PJ, et al. PRG-1 and 21U-RNAs Interact to Form the piRNA Complex Required for Fertility in C. elegans. Mol Cell. 2008 doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.06.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Das PP, et al. Piwi and piRNAs Act Upstream of an Endogenous siRNA Pathway to Suppress Tc3 Transposon Mobility in the Caenorhabditis elegans Germline. Mol Cell. 2008 doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.06.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Wang G, Reinke V. A C. elegans Piwi, PRG-1, Regulates 21U-RNAs during Spermatogenesis. Curr Biol. 2008;18:861–867. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.05.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Ruby JG, et al. Evolution, biogenesis, expression, and target predictions of a substantially expanded set of Drosophila microRNAs. Genome Res. 2007;17:1850–1864. doi: 10.1101/gr.6597907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Brennecke J, et al. Discrete small RNA-generating loci as master regulators of transposon activity in Drosophila. Cell. 2007;128:1089–1103. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.01.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Nishida KM, et al. Gene silencing mechanisms mediated by Aubergine piRNA complexes in Drosophila male gonad. RNA. 2007;13:1911–1922. doi: 10.1261/rna.744307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Prud’homme N, Gans M, Masson M, Terzian C, Bucheton A. Flamenco, a gene controlling the gypsy retrovirus of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1995;139:697–711. doi: 10.1093/genetics/139.2.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Pelisson A, et al. Gypsy transposition correlates with the production of a retroviral envelope-like protein under the tissue-specific control of the Drosophila flamenco gene. EMBO J. 1994;13:4401–4411. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06760.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Desset S, Buchon N, Meignin C, Coiffet M, Vaury C. In Drosophila melanogaster the COM Locus Directs the Somatic Silencing of Two Retrotransposons through both Piwi-Dependent and -Independent Pathways. PLoS ONE. 2008;3:e1526. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Desset S, Meignin C, Dastugue B, Vaury C. COM, a heterochromatic locus governing the control of independent endogenous retroviruses from Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 2003;164:501–509. doi: 10.1093/genetics/164.2.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Mevel-Ninio MT, Pelisson A, Kinder J, Campos AR, Bucheton A. The flamenco locus controls the gypsy and ZAM retroviruses and is required for Drosophila oogenesis. Genetics. 2007 doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.068106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Gunawardane LS, et al. A Slicer-Mediated Mechanism for Repeat-Associated siRNA 5’ End Formation in Drosophila. Science. 2007;315:1587–1590. doi: 10.1126/science.1140494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Cox DN, et al. A novel class of evolutionarily conserved genes defined by piwi are essential for stem cell self-renewal. Genes & Development. 1998;12:3715–3727. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.23.3715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Cox DN, Chao A, Lin H. piwi encodes a nucleoplasmic factor whose activity modulates the number and division rate of germline stem cells. Development. 2000;127:503–514. doi: 10.1242/dev.127.3.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Aravin AA, et al. Dissection of a natural RNA silencing process in the Drosophila melanogaster germ line. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:6742–6750. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.15.6742-6750.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Schupbach T, Wieschaus E. Female sterile mutations on the second chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. II. Mutations blocking oogenesis or altering egg morphology. Genetics. 1991;129:1119–1136. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.4.1119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Klattenhoff C, et al. Drosophila rasiRNA pathway mutations disrupt embryonic axis specification through activation of an ATR/Chk2 DNA damage response. Dev Cell. 2007;12:45–55. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2006.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Pal-Bhadra M, et al. Heterochromatic silencing and HP1 localization in Drosophila are dependent on the RNAi machinery. Science. 2004;303:669–672. doi: 10.1126/science.1092653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Tomari Y, Du T, Zamore PD. Sorting of Drosophila small silencing RNAs. Cell. 2007;130:299–308. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Förstemann K, Horwich MD, Wee LM, Tomari Y, Zamore PD. Drosophila microRNAs are sorted into functionally distinct Argonaute protein complexes after their production by Dicer-1. Cell. 2007;130:287–297. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Mi S, et al. Sorting of small RNAs into Arabidopsis argonaute complexes is directed by the 5’ terminal nucleotide. Cell. 2008;133:116–127. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.02.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Vaucheret H. Plant ARGONAUTES. Trends Plant Sci. 2008;13:350–358. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2008.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Tokumaru S, Suzuki M, Yamada H, Nagino M, Takahashi T. let-7 regulates Dicer expression and constitutes a negative feedback loop. Carcinogenesis. 2008 doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgn187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Forman JJ, Legesse-Miller A, Coller HA. A search for conserved sequences in coding regions reveals that the let-7 microRNA targets Dicer within its coding sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:14879–14884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803230105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Xie Z, Kasschau KD, Carrington JC. Negative Feedback Regulation of Dicer-Like1 in Arabidopsis by microRNA-Guided mRNA Degradation. Curr Biol. 2003;13:784–789. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00281-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Vaucheret H, Vazquez F, Crete P, Bartel DP. The action of ARGONAUTE1 in the miRNA pathway and its regulation by the miRNA pathway are crucial for plant development. Genes Dev. 2004;18:1187–1197. doi: 10.1101/gad.1201404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Vaucheret H, Mallory AC, Bartel DP. AGO1 homeostasis entails coexpression of MIR168 and AGO1 and preferential stabilization of miR168 by AGO1. Mol Cell. 2006;22:129–136. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.03.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Zhao T, et al. A complex system of small RNAs in the unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Genes Dev. 2007;21:1190–1203. doi: 10.1101/gad.1543507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Molnar A, Schwach F, Studholme DJ, Thuenemann EC, Baulcombe DC. miRNAs control gene expression in the single-cell alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Nature. 2007;447:1126–1129. doi: 10.1038/nature05903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Grimson A, et al. Early origins and evolution of microRNAs and Piwi-interacting RNAs in animals. Nature. 2008;455:1193–1197. doi: 10.1038/nature07415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Brennecke J, et al. An epigenetic role for maternally inherited piRNAs in transposon silencing. Science. 2008;322:1387–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.1165171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Sijen T, et al. On the Role of RNA Amplification in dsRNA-Triggered Gene Silencing. Cell. 2001;107:465–476. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00576-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Voinnet O, Vain P, Angell S, Baulcombe DC. Systemic spread of sequence-specific transgene RNA degradation in plants is initiated by localized introduction of ectopic promoterless DNA. Cell. 1998;95:177–187. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81749-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Vaistij FE, Jones L, Baulcombe DC, et al. Spreading of RNA targeting and DNA methylation in RNA silencing requires transcription of the target gene and a putative RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Plant Cell. 2002;14:857–867. doi: 10.1105/tpc.010480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Fusaro AF, et al. RNA interference-inducing hairpin RNAs in plants act through the viral defence pathway. EMBO Rep. 2006;7:1168–1175. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Moissiard G, Parizotto EA, Himber C, Voinnet O. Transitivity in Arabidopsis can be primed, requires the redundant action of the antiviral Dicer-like 4 and Dicer-like 2, and is compromised by viral-encoded suppressor proteins. RNA. 2007;13:1268–1278. doi: 10.1261/rna.541307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Sijen T, Steiner FA, Thijssen KL, Plasterk RH. Secondary siRNAs result from unprimed RNA synthesis and form a distinct class. Science. 2007;315:244–247. doi: 10.1126/science.1136699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Pak J, Fire A. Distinct populations of primary and secondary effectors during RNAi in C. elegans. Science. 2007;315:241–244. doi: 10.1126/science.1132839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Smardon A, et al. EGO-1 is related to RNA-directed RNA polymerase and functions in germ-line development and RNA interference in C. elegans. Current Biology. 2000;10:169–178. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00323-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Aoki K, Moriguchi H, Yoshioka T, Okawa K, Tabara H. In vitro analyses of the production and activity of secondary small interfering RNAs in C. elegans. EMBO J. 2007 doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Makeyev EV, Bamford DH. Cellular RNA-dependent RNA polymerase involved in posttranscriptional gene silencing has two distinct activity modes. Mol Cell. 2002;10:1417–1427. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00780-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Tijsterman M, Ketting RF, Okihara KL, Sijen T, Plasterk RH. RNA helicase MUT-14-dependent gene silencing triggered in C. elegans by short antisense RNAs. Science. 2002;295:694–697. doi: 10.1126/science.1067534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Caplen NJ, et al. Rescue of polyglutamine-mediated cytotoxicity by double-stranded RNA-mediated RNA interference. Hum Mol Genet. 2002;11:175–184. doi: 10.1093/hmg/11.2.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.Xia H, Mao Q, Paulson HL, Davidson BL. siRNA-mediated gene silencing in vitro and in vivo. Nat Biotechnol. 2002;20:1006–1010. doi: 10.1038/nbt739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 216.Ding H, et al. Selective silencing by RNAi of a dominant allele that causes amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Aging Cell. 2003;2:209–217. doi: 10.1046/j.1474-9728.2003.00054.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217.Miller VM, et al. Allele-specific silencing of dominant disease genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:7195–7200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1231012100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218.Martinez LA, et al. Synthetic small inhibiting RNAs: efficient tools to inactivate oncogenic mutations and restore p53 pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:14849–14854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.222406899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Schwarz DS, Hutvagner G, Haley B, Zamore PD. Evidence that siRNAs function as guides, not primers, in the Drosophila and human RNAi pathways. Mol Cell. 2002;10:537–548. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00651-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220.Nykanen A, Haley B, Zamore PD. ATP requirements and small interfering RNA structure in the RNA interference pathway. Cell. 2001;107:309–321. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00547-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 221.Martinez J, Patkaniowska A, H HU, Lührmann R, Tuschl T. Single stranded antisense siRNA guide target RNA cleavage in RNAi. Cell. 2002;110:563–574. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00908-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 222.Roignant JY, et al. Absence of transitive and systemic pathways allows cell-specific and isoform-specific RNAi in Drosophila. RNA. 2003;9:299–308. doi: 10.1261/rna.2154103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 223.Rusk N, Kiermer V. Primer: Sequencing--the next generation. Nat Methods. 2008;5:15. doi: 10.1038/nmeth1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 224.Johnston RJ, Hobert O. A microRNA controlling left/right neuronal asymmetry in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 2003;426:845–849. doi: 10.1038/nature02255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225.Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP. Computational identification of plant microRNAs and their targets, including a stress-induced miRNA. Mol Cell. 2004;14:787–799. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.05.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 226.Elbashir SM, et al. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature. 2001;411:494–498. doi: 10.1038/35078107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227.Sijen T, Plasterk RH. Transposon silencing in the Caenorhabditis elegans germ line by natural RNAi. Nature. 2003;426:310–314. doi: 10.1038/nature02107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]