| Carolingian Kings of the Eastern Franks (East Francia / Kings of Germany) AD 840 - 911 & 961 The eastern half of the Frankish empire eventually evolved into modern Germany, but Frankish Carolingian rule was relatively brief before a High-German-speaking Teutonic ruling class was established. The empire had been established by Charlemagne through a series of campaigns, mostly between 771-800. He fought the Angrivarii, Avars, [ Bavarians](GermanyBavarians.htm#Bavarian Confederation), Lombards, Pomeranians, and Saxons to secure territory far to the east of the initial Frankish lands By the Act of Thionville in 806, he announced the division of his vast empire between his three sons. By 814, of the three only Louis 'the Pious' still survived to be crowned sole Frankish emperor at Aix-la-Chapelle. In 840, Louis left his empire to his own sons, but tried to ensure that the eldest gained the biggest share in order to avoid the fragmentation of territory which so weakened the Merovingians. Lothar received Middle Francia (the Rhine corridor including the kingdom of [Burgundy](FranceBurgundy.htm#Frankish Kingdom of Burgundy), and Italy), Charles 'the Bald' received [Western Francia](FranceFranks.htm#Western Franks) (France and the duchy of Burgundy), and Louis the German received Eastern Francia (Germany, including Alemannia,[Bavaria](GermanyBavarians.htm#Bavarian Confederation), [ Khorushka](EasternCarinthia.htm#Principality of Khorushka), and Saxony (against the wishes of the ruling Hattonids there), plus regions that were already emerging as Franconia and Thuringia). However, Lothar initially claimed overlordship over all three regions and Louis and Charles had to go to war to convince him to relent, which he did in 843. The Treaty of Verdun confirmed the official division of the empire between the three kings, with rule over the empire as a whole being nominal. (Information by Peter Kessler, with additional information from Hungarians and Europe in the Early Middle Ages: An Introduction to Early Hungarian History, András Róna-Tas (Central European University Press, 1999), from The Annals of Fulda (Manchester Medieval Series, Ninth-Century Histories, Volume II) Timothy Reuter (Trans) 1992, from Vita Karoli Magni (Life of Charles the Great), Einhard, from the Royal Frankish Annals (author unknown), from Sword, Miter, and Cloister: Nobility and the Church in Burgundy, 980-1198, Constance Brittain Bouchard (New York 1987), and from External Links: The Latin Library, and the Foundation for Medieval Genealogy.) |
|
|
| 840 - 876 |
Louis II the German |
Son ofCarolingian Louis I. Duke of Alemannia (& Breton March). |
| 840 - 843 |
Before his death, Louis 'the Pious', who is also duke of Alemannia, promulgates the Ordinatio Imperii in 817, proclaiming, despite the ancient Frankish custom of dividing territory between surviving sons, that his eldest son, Lothar, will be sole beneficiary of the imperial dignity and sole inheritor of the empire. The new idea proves too much, provoking rebellions and rivalries between all four of Louis' sons which last until after the king's death. (One of the sons, Pepin I of Aquitaine, has already predeceased his father.) 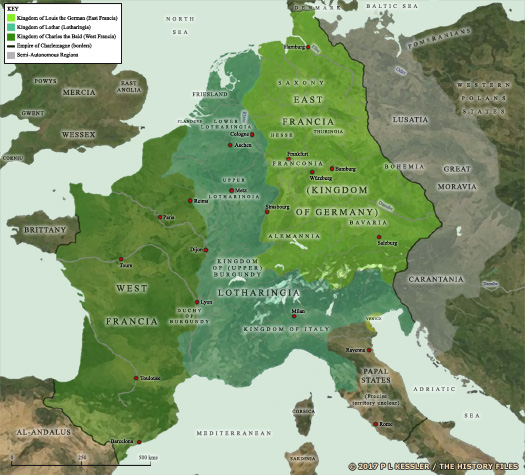 King Louis 'the Pious' of the Frankish empire attempted to leave the empire intact for his eldest son, Lothar, but the others rebelled at the idea. The treaty of Verdun in AD 843 confirmed the official division of the empire between Charlemagne's three surviving grandsons (click or tap on map to view full sized) King Louis 'the Pious' of the Frankish empire attempted to leave the empire intact for his eldest son, Lothar, but the others rebelled at the idea. The treaty of Verdun in AD 843 confirmed the official division of the empire between Charlemagne's three surviving grandsons (click or tap on map to view full sized) |
|
| Lothar initially claims overlordship over all three regions and Louis and Charles have to go to war to convince him to relent. The counties of the Spanish March all take sides during this period, with the powerful Bernard of Septimania, count of Barcelona (along with a large number of other marches and counties, including Agde, Béziers, Girona, Melgueil, Narbonne, Nîmes, Septimania, and Toulouse, capital of Aquitaine) siding with Pepin II of Aquitaine. Opposing them in favour of Charles are Sunifred, count of Urgel (andAndorra) and Cerdanya, his brother Sunyer I, count of Empúries, their sons (who collectively are sometimes referred to as the Bellonid dynasty or the Bellonids), Ricwin, count of Nantes (killed in battle in 841), and Lambert II, also later count of Nantes. Lothar does relent in 843, and the Treaty of Verdun confirms the official division of the empire between Charlemagne's surviving three grandsons, with rule over the empire as a whole being nominal. Lothar receives Middle Francia (the Rhine corridor, the kingdom of [ Burgundy](FranceBurgundy.htm#Frankish Kingdom of Burgundy), and Italy); Charles 'the Bald' receives [Western Francia](FranceFranks.htm#Western Franks) (France and the duchy of Burgundy), as well as holding onto Aquitaine; and Louis the German receives Eastern Francia (Germany, including Alemannia (Swabia),[Bavaria](GermanyBavarians.htm#Bavarian Confederation), [ Khorushka](EasternCarinthia.htm#Principality of Khorushka), and Saxony, plus regions that are already emerging asFranconia andThuringia). |
|
|
| 846 |
Prince Pribina, a Slav noble and adventurer who had been chased out of [Great Moravia](EasternBohemia.htm#Great Moravia) by Mojmir I, is granted the eastern section of Avar territory - in Lower Pannonia - as the principality of Balaton, with his headquarters near Lake Balaton on the River Zala (close to the modern village of Zalavár, in Zala County in Hungary, surrounded by forests and a swamp). As dux of the eastern march and prince of Balaton, Pribina's main duty is to hem the territorial ambitions both of Great Moravia and Bulgaria. Having himself been a victim of Moravia's ambitions, Pribina is only too happy to play a large role in Louis the German's campaigns against that state. |
|
| 855 |
With tensions increasing along the[Frankish](FranceFranks.htm#Western Franks)-Slavic border, Boris of Bulgaria is persuaded by Rastislav of[Great Moravia](EasternBohemia.htm#Great Moravia) to attack the Eastern Franks in support of him. The campaign is a complete failure, with subsequent retribution involving Louis 'the German' invading Bulgaria at the same time as it is attacked by previously-peacefulCroats (possibly a diversionary tactic organised by Louis). Peace is soon agreed, without necessarily harming Boris' standing at home. |
|
| 870 |
A province of East Francia (a province is termed a 'gau') is first mentioned in the Treaty of Meerssen in this year. Known as Hattuarian Gau, it is on the west bank of the Rhine. This may well be a surviving relic of the former Germanic tribe of the Chattuarii.  The treaty arises due to the death of Lothar II of Lotharingia. His territory is subsequently divided fairly by his uncles under the terms of the treaty, those uncles being Louis the German and Charles 'the Bald' of the [Western Franks](FranceFranks.htm#Western Franks). One territory which is affected by this arrangement is the diocese of Liège (see feature link). The treaty arises due to the death of Lothar II of Lotharingia. His territory is subsequently divided fairly by his uncles under the terms of the treaty, those uncles being Louis the German and Charles 'the Bald' of the [Western Franks](FranceFranks.htm#Western Franks). One territory which is affected by this arrangement is the diocese of Liège (see feature link).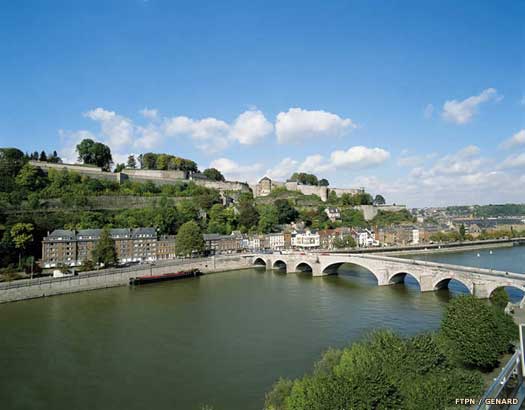  The Meuse valley, shown here at the citadel of Namur, formed the western border for the Chattuarii following their crossing of the Rhine, taking territory from the fading Roman administration The Meuse valley, shown here at the citadel of Namur, formed the western border for the Chattuarii following their crossing of the Rhine, taking territory from the fading Roman administration |
|
| 876 |
The death of Louis the German results in his territory being divided between his three sons. This is something that he had already foreseen, and portions of territory had been appointed to each of them in 865. Now in a peaceful succession, Carloman inherits [Bavaria](GermanyBavarians.htm#Bavarian Confederation) and the Ostmark (plus Lower Pannonia of the former Avar lands), Louis the Younger gains Franconia (which includes the Hessi lands), Saxony, and Thuringia, while Charles 'the Fat' succeeds to Rhaetia and Alemannia (Swabia). As the oldest son, Carloman also retains de facto dominance over the Eastern Franks as a whole. |
|
| 876 - 880 |
Carloman of Bavaria / Charles |
of Germany. King of [Bavaria](GermanyBavarians.htm#Bavarian Confederation), Italy, & part of Lotharingia. |
| 876 - 882 |
Louis III the Younger |
III of Germany. Ruled Franconia, Lotharingia &Empire (901). |
| 876 - 887 |
Charles III 'the Fat' |
III of Germany. [France](FranceFranks.htm#Western Franks) (884), Italy (879). III of Empire (881). |
| 877 - 879 |
Charles 'the Bald' of the [Western Franks](FranceFranks.htm#Western Franks) and Italy dies while fending off Carloman (son of Louis the German, who himself had been beaten to the Italian throne by Charles 'the Bald'). Carloman gains Italy, but suffers a debilitating stroke just two years later. Unable to rule in anything but name and having no legitimate offspring, he divides his holdings between his brothers. Louis the Younger gains [Bavaria](GermanyBavarians.htm#Bavarian Confederation) while Charles 'the Fat' gains Italy. Carloman's illegitimate son, Arnulf, becomes duke of [Carinthia](EasternCarinthia.htm#Duchy of Carinthia). |
|
| 880 |
Lotharingia, which has been divided between the Eastern Franks and the [Western Franks](FranceFranks.htm#Western Franks) since 870, is incorporated into the Frankish Empire thanks to the Treaty of Ribemont. |
|
| 881 - 882 |
Charles 'the Fat' succeeds as titular head of the Frankish empire, holding the position as Emperor Charles III. He is crowned by Pope John VIII. In the following year, 882, Louis the Younger dies and Charles, as the last remaining of the three brothers, inherits his territories of [Bavaria](GermanyBavarians.htm#Bavarian Confederation),Franconia, Saxony, and Thuringia, thereby reuniting East Francia following its division in 876.  Charles 'the Fat' (not necessarily living up to his descriptive sobriquet) welcomes messengers into his tent as titular head of the Frankish empire, as depicted in the fourteenth century Grandes Chroniques de France Charles 'the Fat' (not necessarily living up to his descriptive sobriquet) welcomes messengers into his tent as titular head of the Frankish empire, as depicted in the fourteenth century Grandes Chroniques de France |
|
| 887 |
The first noble to exercise domination over the papacy in Rome is Prince Theophylact of the Theophylactii. He has served Louis III as judex in Italy, and is now elected Consul by Rome's nobility. He is also a senator and magister militum, and count of Tusculum (modern Tuscany). |
|
| 888 |
The rule of Germany falls to non-Frankish emperors when the weak Charles is deposed by the Germans at the Diet of Tribur (November 887). The Frankish empire is now officially divided between east and west. In time the western section becomes [France](FranceFranks.htm#Western Franks), the eastern section Germany, with the title of Roman Emperor also being held by Germans. Charles 'the Fat' takes refuge in the monastery of Reichenau in Alemannia (Swabia) where he dies the following year. |
|
| 887 - 899 |
Arnulf of Carinthia |
Son of Carloman. Duke of[Carinthia](EasternCarinthia.htm#Duchy of Carinthia).Roman Emperor (896). |
| 888 |
Berengar of Friuli defeats his chief rival in Italy, Guy of Spoleto, as the two vie for control of the eastern half of the former Frankish empire. Arnulf immediately forces Berengar to accept vassal status under him, but it seems that Berengar holds the Germanic imperial title. |
|
| 896 |
Berengar of Friuli agrees on the formal division of Italy with Lambert II of Spoleto but, following a defeat in battle, Berengar emerges as sole ruler of Italy. However, he is still a vassal of Arnulf, who is now also Germanic Roman emperor. Arnulf triggers a period of confusion in the western fringes of his imperial territory when he hands Lotharingia to his illegitimate son, Zwentibold of Lorraine. |
|
| 899 - 911 |
Louis IV 'the Child' |
Son. IV of Germany. LastCarolingian ruler. |
| 903 |
Count Gebhard of the Wetterau in the lands of the Hessi is confirmed as duke of Lotharingia by Louis the Child, king of Germany. Unfortunately he is killed in 910 in battle against the Magyars, somewhere in the region of Augsburg. |
|
| 905 |
With Central Europe suffering constantly at the hands of the marauding Magyars, the title ofGerman Roman emperor appears to lapse. Louis III of Lower Burgundy and Provence, and Louis IV of the German kingdom of East Francia (the nascent Holy Roman empire in its core form) remains in titular command of East Francia though. |
|
| 911 - 915 |
The [Frankish](FranceFranks.htm#Western Franks) empire effectively disintegrates in 911, upon the untimely death of the young Louis. East Francia is formally secured by elected native German rulers, with Conrad I 'the Younger', duke ofFranconia, being the first to be elected as king of Germany (East Francia). Now ruling what had formerly been the eastern section of the Carolingian empire, Conrad is the duke of Franconia and also the count of Oberlahngau in the lands of the Hessi, but he appears not to be recognised as Germanic Roman emperor, leaving that title vacant. A large-scale political reorganisation of south-western Germany now creates the stem duchy of [Swabia](GermanySwabia.htm#Dukes of Swabia) while also moving the bishopric of Liege into German Frankish hands. |
|
| 911 - 918 |
Conrad I the Younger |
Duke ofFranconia (906-911). |
| 915 |
In September 915, Count Palatine Erchanger is confirmed as the first duke of [Swabia](GermanySwabia.htm#Dukes of Swabia) by the nobility. After being defeated at the Battle of Wahlwies, the proclamation is not supported by King Conrad I of Germany, despite him being Erchanger's brother-in-law. Erchanger's rise and fall is swift, perhaps unsurprisingly.  The Battle of Wahlwies took place in the Hegau, an extinct volcanic region in southern Swabia (and modern Germany), with Wahlwies itself being a small satellite village of the town of Stockach, now in the modern district of Konstanz, southern Baden-Württemberg (Photo by External Link: sued7.de) The Battle of Wahlwies took place in the Hegau, an extinct volcanic region in southern Swabia (and modern Germany), with Wahlwies itself being a small satellite village of the town of Stockach, now in the modern district of Konstanz, southern Baden-Württemberg (Photo by External Link: sued7.de) |
|
| 919 - 936 |
Henry I the Fowler |
Duke ofSaxony (912-936). |
| 936 - 944 |
Upon the death of his ally, Henry the Fowler, Gilbert of Maasgau, duke of Lorraine, rebels against his successor, Otto I. Instead he swears allegiance to Louis IV d'Outremer of the [West Franks](FranceFranks.htm#Western Franks). Gilbert rules Lorraine almost as an independent state for the next three years. |
|
| 936 - 961 |
Otto I the Great |
Duke of Saxony (936-973). |
| 936 - 944 |
Upon the death of his ally, Henry the Fowler, Gilbert of Maasgau, duke of Lorraine, rebels against his successor, Otto I. Instead he swears allegiance to Louis IV d'Outremer of the [West Franks](FranceFranks.htm#Western Franks). Gilbert rules Lorraine almost as an independent state for the next three years. |
|
| 937 |
A massive invasion is conducted by theMagyars as they sweep around in a giant circle through central and Southern Europe. They begin from their base in Pannonia to enter into and ravage[ Bavaria](GermanyBavarians.htm#Duchy of Bavaria %28Welfs%29), [ Swabia](GermanySwabia.htm#Dukes of Swabia),Saxony,Franconia, andThuringia within the East Frankish kingdom. From the Aachen area, the Magyars advance deep into the [West Frankish](FranceFranks.htm#Western Franks) kingdom, the kingdom of Provence, and then the territory of theMiddle (Italian) Franks. They attack Tuscany and the Papal States as far south as Naples, before returning to their adopted Hungarian homeland. |
|
| 938 |
Another large-scale raid is attempted along the same route as in 933. This time theMagyars are stopped at Erfurt by Otto I and his subjects of theEast Frankish kingdom, the powerful duke of Saxony. |
|
| 953 |
Feeling that his position is threatened by the marriage of his father, Otto I, to Adelaide, heiress of Italy, Ludolph of [Swabia](GermanySwabia.htm#Dukes of Swabia) joins forces with his brother-in-law, Conrad the Red, duke of Lorraine, in revolt. Ludolph is supported by the Swabians, but Conrad fails to gain the same support from his own subjects. Otto and Henry I of [ Bavaria](GermanyBavarians.htm#Duchy of Bavaria %28Welfs%29) defeat the rebellion. 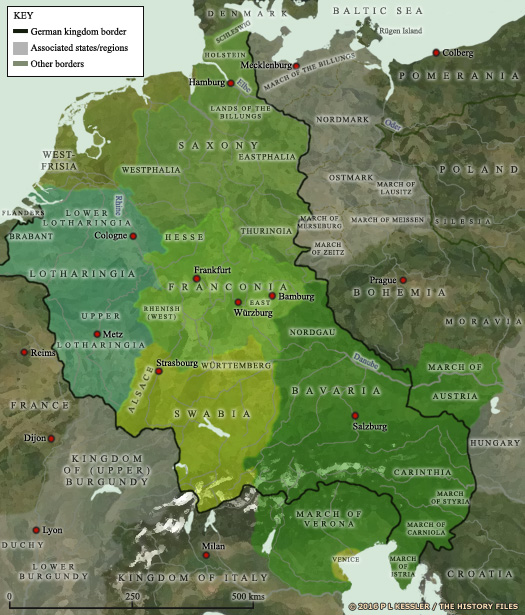 Germany in AD 962 may have had its new emperor to govern those territories which are shown within the dark black line, but it was still a patchwork of competing interests and power bases (click or tap on map to view full sized) Germany in AD 962 may have had its new emperor to govern those territories which are shown within the dark black line, but it was still a patchwork of competing interests and power bases (click or tap on map to view full sized) |
|
| 961 |
The Germanic emperors are overthrown by the Saxon king of Germany, Otto I. The two titles are effectively merged into one and the beginnings of the Holy Roman empire are born. In later years, the title 'King of the Germans' is viewed as the junior of the two, usually being granted to the heir to the imperial throne. Once an heir has been crowned king of the Germans, his route to becoming emperor upon the death of his father is usually unobstructed - at least in theory. |
|
 |
|
|
 King Louis 'the Pious' of the Frankish empire attempted to leave the empire intact for his eldest son, Lothar, but the others rebelled at the idea. The treaty of Verdun in AD 843 confirmed the official division of the empire between Charlemagne's three surviving grandsons (click or tap on map to view full sized)
King Louis 'the Pious' of the Frankish empire attempted to leave the empire intact for his eldest son, Lothar, but the others rebelled at the idea. The treaty of Verdun in AD 843 confirmed the official division of the empire between Charlemagne's three surviving grandsons (click or tap on map to view full sized) The treaty arises due to the death of Lothar II of Lotharingia. His territory is subsequently divided fairly by his uncles under the terms of the treaty, those uncles being Louis the German and Charles 'the Bald' of the [Western Franks](FranceFranks.htm#Western Franks). One territory which is affected by this arrangement is the diocese of Liège (see feature link).
The treaty arises due to the death of Lothar II of Lotharingia. His territory is subsequently divided fairly by his uncles under the terms of the treaty, those uncles being Louis the German and Charles 'the Bald' of the [Western Franks](FranceFranks.htm#Western Franks). One territory which is affected by this arrangement is the diocese of Liège (see feature link).  The Meuse valley, shown here at the citadel of Namur, formed the western border for the Chattuarii following their crossing of the Rhine, taking territory from the fading Roman administration
The Meuse valley, shown here at the citadel of Namur, formed the western border for the Chattuarii following their crossing of the Rhine, taking territory from the fading Roman administration Charles 'the Fat' (not necessarily living up to his descriptive sobriquet) welcomes messengers into his tent as titular head of the Frankish empire, as depicted in the fourteenth century Grandes Chroniques de France
Charles 'the Fat' (not necessarily living up to his descriptive sobriquet) welcomes messengers into his tent as titular head of the Frankish empire, as depicted in the fourteenth century Grandes Chroniques de France The Battle of Wahlwies took place in the Hegau, an extinct volcanic region in southern Swabia (and modern Germany), with Wahlwies itself being a small satellite village of the town of Stockach, now in the modern district of Konstanz, southern Baden-Württemberg (Photo by External Link: sued7.de)
The Battle of Wahlwies took place in the Hegau, an extinct volcanic region in southern Swabia (and modern Germany), with Wahlwies itself being a small satellite village of the town of Stockach, now in the modern district of Konstanz, southern Baden-Württemberg (Photo by External Link: sued7.de) Germany in AD 962 may have had its new emperor to govern those territories which are shown within the dark black line, but it was still a patchwork of competing interests and power bases (click or tap on map to view full sized)
Germany in AD 962 may have had its new emperor to govern those territories which are shown within the dark black line, but it was still a patchwork of competing interests and power bases (click or tap on map to view full sized)