electro-optic Q-switches (original) (raw)
Definition: electro-optic devices used for Q-switching of lasers
- optical switches
- Q-switches
* acousto-optic Q-switches
* electro-optic Q-switches
- Q-switches
Related: Q-switchingQ-switched lasersPockels cellselectro-opticsoptical switches
Page views in 12 months: 111
DOI: 10.61835/iql Cite the article: BibTex BibLaTex plain textHTML Link to this page! LinkedIn
Content quality and neutrality are maintained according to our editorial policy.
📦 For purchasing electro-optic Q-switches, use the RP Photonics Buyer's Guide — an expert-curated directory for finding all relevant suppliers, which also offers advanced purchasing assistance.
Contents
What are Electro-optic Q-switches?
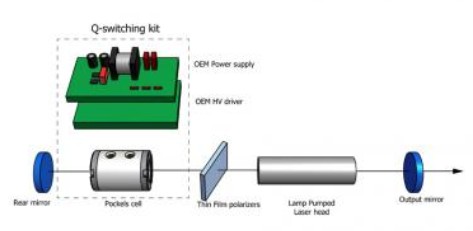
Electro-optic Q-switches are Q-switches based on Pockels cells, i.e., on an electro-optic device, and a polarizer. Used for pulse generation via Q-switching of various kinds of lasers, they can rapidly switch propagation losses between a rather high and a very low state.
Besides Q-switching, such devices are useful for other applications in laser technology:
- The characteristics are suitable for cavity dumping of lasers, where again one requires very fast switching — in this case, even in a time well below the laser resonator's round-trip time.
- Fast switching is also required for pulse pickers and as optical switches in regenerative amplifiers in ultrafast laser systems.
Operation Principle
Electro-optic switching relies on the following basic principles:
- A strong electric field applied to an electro-optic crystal via electrodes induces birefringence, which modifies the polarization of light.
- As a consequence, the power transmission through a polarizer is modified.
In a typical configuration, this works as follows:
- The crystal is not birefringent without an applied field, thus does not modify the light polarization, and the light can pass a polarizer without significant losses. This state is used during pulse generation.
- With the field applied, a quarter-wave phase retardation in the crystal is obtained, leading to a rotation of the polarization direction by 90°, so that the polarizer blocks the light. This state is used in the pumping phase before pulse generation, allowing one to accumulate substantial energy in the laser crystal.
The required driver voltages are substantial — often several kilovolts. Miniature devices often work with lower voltages, but can only switch lower powers.
Typical Requirements on Q-switches
The following requirements are typically essential for Q-switching of lasers:
- Hold-off losses: The device must achieve very high attenuation (via a 90° polarization change) to prevent premature lasing. High extinction ratios require uniform, precise polarization control across the beam profile.
- Insertion loss: The insertion loss in the non-blocking state should be as low as possible (ideally well below 1%) for laser applications, as losses can degrade laser performance and lead to heating. Good anti-reflection coatings are required.
- Switching speed: One usually requires quite fast switching from the blocked to the open state, since pulse build-up in such lasers is usually quite fast — particularly in high-gain lasers with short resonator round-trip time, as required for obtaining particularly short pulse durations.
- Note that although the switching time does not need to be similarly short as the pulse duration, it must be shorter than the time required for pulse build-up from noise. Q-switched lasers optimized for short pulses typically have a short round-trip time and/or high gain, thus fast pulse build-up.
- The switching speed is affected by the electric capacitance of the Pockels cell (and possibly by a cable) and by the peak current which the driver can deliver.
- Low ringing: Some electro-optic devices exhibit substantial “ringing”, meaning that after fast switching the polarization state exhibits some damped oscillations. This is related to mechanical vibrations through their piezoelectric properties, or possibly to non-ideal driver performance. (Find more details on ringing in the article on Pockels cells.) Ringing is undesirable, as it can deteriorate the Q-switching performance.
- Damage threshold: As the intracavity peak power and the pulse energy can be very high, a sufficiently high optical damage threshold is vital. For this to be achieved, one requires a resistant electro-optic material combined with a sufficiently large open aperture, allowing a large enough beam radius. For high-energy lasers, beam radii of several centimeters may be required.
- Thermal effects: As electro-optic materials have various thermal dependencies, it is desirable to minimize heat generation. In particular, absorption losses in the Pockels cell should be small for applications with high laser powers.
The usable wavelength range is usually determined by the anti-reflection coatings. Also note that the λ/4 voltage of the Pockels cell has some wavelength dependence; therefore, the switching voltage may need to be adjusted when moving to another wavelength.
Used Electro-optic Materials
Typically used electro-optic materials for Q-switches include:
- KD*P is a well-established material with low drive voltage and high damage threshold. Unfortunately, the tendency for ringing is particularly strong.
- RTP works with low drive voltage and offers high thermal stability. It also has much weaker ringing effects.
- BBO features a wide transparency range and high damage threshold, but requires higher drive voltages.
- LiNbO3 has a particularly high nonlinearity, allowing operation with relatively low voltages. However, its damage threshold is lower, and the tendency for ringing can be problematic.
After passing an electro-optic Q-switch, the laser light is linearly polarized. It can be problematic if that polarization state is changed before the light comes back to the Q-switch. This can happen under certain circumstances; some examples:
- Thermal effects in the laser crystal can lead to spatially varying depolarization. That causes depolarization loss when the light comes back to the Q-switch.
- When performing intracavity frequency doubling in a nonlinear crystal with type-II phase matching, the laser polarization is strongly affected. In such cases, an electro-optic Q-switch is generally not usable. However, frequency doubling is usually done outside the laser resonator, avoiding that problem.
Q-switch Drivers
Fast high-voltage drivers are essential to operate electro-optic Q-switches effectively. These specialized drivers are optimized for fast rise times and minimal ringing. Integration of driver electronics with the Q-switch module is common. When using a separate driver, the cable length must be kept short to avoid limiting the switching speed.
Comparison with Acousto-optic Q-switches
Electro-optic Q-switches are an alternative to the frequently used acousto-optic Q-switches, which is interesting due to several advantages:
- Electro-optic devices offer particularly high switching speed. This is required, for example, if the pulse duration is very short.
- Note that the switching speed of acousto-optic Q-switches is limited by the acoustic velocity and gets lower for large apertures.
- They also offer a higher hold-off loss — in principle, near 100% –, while acousto-optic devices have a limited diffraction efficiency.
- The low propagation losses are beneficial, particularly for high-power operation, where thermal lensing can be a problem.
Disadvantages of electro-optic Q-switches include:
- Price: Electro-optic devices together with their drivers are generally more expensive.
- The damage threshold of electro-optic crystals is typically lower. Larger apertures are then required, but large aperture electro-optic switches are still more costly, and it can also complicate the laser resonator design, which must accommodate a large beam radius.
- The high driver voltage is a disadvantage in terms of safety, and can make integration more difficult.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an electro-optic Q-switch?
An electro-optic Q-switch is a device for generating short, high-energy laser pulses. It consists of a Pockels cell and a polarizer, which work together to rapidly switch the optical losses inside a laser cavity from a high to a low state.
How does an electro-optic Q-switch work?
It applies a high voltage to an electro-optic crystal (Pockels cell), which induces birefringence. This alters the polarization of light, causing it to be blocked by a polarizer. Rapidly turning off the voltage eliminates this loss, allowing a powerful laser pulse to build up.
What are the main advantages of electro-optic Q-switches over acousto-optic ones?
Electro-optic Q-switches offer much faster switching speeds, essential for generating very short pulses. They also typically provide higher hold-off losses (better blocking of light) and lower insertion losses when in the transmissive state.
What is 'ringing' in an electro-optic Q-switch?
Ringing refers to damped oscillations of the polarization state after the device is switched. It is caused by mechanical vibrations in the crystal due to its piezoelectric properties and can degrade the Q-switching performance.
What materials are commonly used for electro-optic Q-switches?
Common materials include KD*P for its low drive voltage, RTP for its thermal stability, BBO for its high damage threshold, and LiNbO3 for its strong electro-optic effect, though it has a lower damage threshold.
Why do electro-optic Q-switches need high-voltage drivers?
A strong electric field, requiring a voltage of several kilovolts, is necessary to induce the required polarization rotation in the electro-optic crystal. A specialized driver is needed to apply and remove this high voltage very rapidly.
Suppliers
Sponsored content: The RP Photonics Buyer's Guide contains 15 suppliers for electro-optic Q-switches. Among them:
⚙ hardware
The GPC series Pockels Cells (PCs) are the core component for Q-switching and regenerative amplifiers. They come with a BBO crystal box and driver to apply high voltage to a BBO crystal for electro-optic modulation. The GPC series PCs provide parameter customization and offers optional λ/2 or λ/4 operating modes and adjustable operating frequencies tailored to the user requirements.
⚙ hardware
The G&H electro-optic Q-switch employs the highest optical quality lithium niobate available. The electro-optic effect of lithium niobate makes it extremely useful for Pockels cell Q-switching of several laser types including Nd:YAG, Nd:YALO, Nd:YLF and Er:YLF. Lithium niobate Q-switches are used in both military and commercial applications, including target designating, range finding, and ophthalmic surgery. Our crystals offer low loss, high contrast ratio, and low wavefront distortion, and are qualified for use at 300 MW/cm2. The temperature-stable (TS and XTS) versions of our electro-optic LN Q-switches allow operation over a wide range of temperatures while maintaining excellent contrast ratio.
⚙ hardware🧩 accessories and parts🧴 consumables🔧 maintenance, repair📏 metrology, calibration, testing💡 consulting🧰 development
Hangzhou Shalom EO offers standard and custom Pockels cells made of DKDP, BBO crystals, and LiNbO3 or MgO:LiNbO3 crystals.
Shalom EO’s DKDP Pockels cells feature high deuteration (>98%, or even 99% can be obtained), low capacitance and fast rise time, and high transmission, high extinction ratio, with a maximum aperture of 50 mm available. Recently, we have succeeded in developing a 3-pin connector DKDP Pockels cells for 755 nm alexandrite lasers manufactured using 1 pce of 99% deuteration DKDP crystal with 3 gold plating.
Shalom EO’s LiNbO3 and MgO:LiNbO3 Pockels cells are excellent choices for ultraviolet (UV) lasers to infrared lasers with long operating wavelengths up to 4 μm. LiNbO3 Pockels cells are especially preferable for Er:YAG, Ho:YAG and Tm:YAG lasers.
Our BBO Pockels cells have significant advantages in terms of high damage threshold, low insertion loss, high extinction ratio, minimal piezoelectric ringing, and competitive price. BBO Pockels cells with both single and double BBO crystal designs and low-voltage geometries are available upon request.
Hangzhou Shalom EO also offers polished and AR-coated DKDP, BBO, LiNbO3, and MgO:LiNbO3 crystals with Cr–Au electrodes, which can be used as central components of Pockels cells.
⚙ hardware
Artifex Engineering offers customised Pockels cells, available as DKDP (KD*P), MgO:LiNbO₃ and BBO. Our Pockels cells feature low insertion loss, high damage threshold. These are cost effective units at OEM prices. We also offer a range of standard Pockels cells with an aperture of 6 mm to 12 mm diameter. Visit our product page for more information. We look forward to your inquiry.
⚙ hardware
EKSMA Optics manufactures OEM type Q-switching kits for the laser cavities that include Pockels cells with DKDP, BBO, or RTP electro-optical crystals, high voltage Pockels cells drivers optimized for the specific laser operation parameters, and high voltage power supplies for Pockels cells drivers powering. The complete Q-switching components sets are tested and adjusted for the optimal operation before shipping to the customers.
⚙ hardware
RTP Q-switches are ideal for high-performance applications requiring superior damage threshold and temperature stability, such as military, aerospace and high-power scientific lasers. Key specifications:
- half-wave voltage 3.6 kV
- >35 dB extinction ratio
- up to 15 × 15 mm² aperture
- high damage threshold (>1 GW/cm²)
- wide temperature range (–50°C to 70°C)
- non-hygroscopic
- MHz repetition rates
Questions and Comments from Users
Here you can submit questions and comments. As far as they get accepted by the author, they will appear above this paragraph together with the author’s answer. The author will decide on acceptance based on certain criteria. Essentially, the issue must be of sufficiently broad interest.
Please do not enter personal data here. (See also our privacy declaration.) If you wish to receive personal feedback or consultancy from the author, please contact him, e.g. via e-mail.
By submitting the information, you give your consent to the potential publication of your inputs on our website according to our rules. (If you later retract your consent, we will delete those inputs.) As your inputs are first reviewed by the author, they may be published with some delay.
 photonic devices
photonic devices